 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1680171
潜水艇救援系统市场:全球2025-2035年Global Submarine Rescue Systems Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
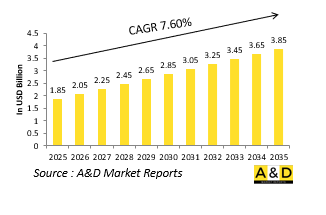
全球潜舰救援系统市场规模预计到2025年将成长至 18.5亿美元,到2035年将成长至 38.5亿美元,2025-2035年预测期内的年复合成长率(CAGR)为 7.60%。
全球潜舰救援系统市场是国防和海上安全产业的重要组成部分,确保在发生水下紧急情况时潜舰船员的生存。潜舰是世界各国海军的重要组成部分,承担着威慑、情报收集和作战等任务。然而,在深海环境中操作潜水艇会面临机械故障、船上火灾和碰撞等风险,这些风险可能导致潜水艇搁浅在海底。潜艇救援系统的发展是为了应对这些风险,为海军提供快速反应能力,从瘫痪或沉没的潜艇中营救船员。这些系统包括专用潜水器、逃生舱、遥控潜水器(ROV)以及配备减压室和医疗设施的水面支援船。由于安全威胁不断演变,人们对海军安全的关注度不断提高,加上潜舰部署不断增加,对先进的潜舰救援解决方案的需求也日益成长。
技术进步显着提高了潜舰救援系统的效率和效力,创新重点集中在深水作业能力、自动化和互通性。其中一项主要技术进步是整合深海潜水器,该潜水器可连接在遇险潜艇上并到达极深深度以安全撤离船员。这些潜水器配备了最先进的导航和通讯系统,可自主运作或远端控制执行精确的救援任务。材料科学的发展带动了高强度、轻量材料的研发,使得救援船更加耐用、耐压,确保在深海环境中的安全作业。
机器人和人工智慧(AI)的使用彻底改变了潜水艇救援行动。遥控潜水器可在载人救援行动之前部署,在评估搁浅潜艇状况、清除障碍物和提供即时态势感知方面发挥着非常重要的作用。人工智慧预测分析还提高了潜艇救援系统的维护和准备能力,使海军能够在设备故障发生之前发现潜在的故障。此外,还引进了模组化救援系统以提高操作灵活性,允许快速部署和整合到不同类型的潜艇上,无论其设计或原产国如何。这种对互通性的重视对于多国海军合作尤其重要,确保盟军救援资产能够在紧急情况下部署而不会出现相容性问题。
全球潜舰舰队的扩张是潜舰救援系统市场的主要驱动力。许多国家增强其潜艇能力,以加强海上安全、遏制潜在威胁并在争议水域中保持战略优势。随着潜舰的扩张,确保潜舰船员安全的责任也随之增加,对救援基础设施和设备的投资也随之增加。此外,随着濒海和深海战争战略的兴起,潜舰救援能力变得越来越重要。现代潜艇在更具挑战性的环境中运行,被缠结的风险也更高。下一代不依赖空气推进(AIP)和核潜艇的采用需要开发适合这些潜艇独特作战特性的先进救援解决方案。
国际合作和联合训练进一步推动了市场发展,各国海军优先考虑潜舰救援行动的合作。北约潜舰救援系统(NSRS)和国际潜水艇逃生和救援联络处(ISMERLO)等组织促进世界各国海军之间的协调,以确保在发生潜艇紧急情况时能够快速应对。这些措施促成了共享救援资产的采购、培训计划和救援协议的标准化,促进了全球一体化的潜艇安全方法。多国海上演习的增加增强了潜舰救援系统之间无缝互通性的必要性,并鼓励对可在不同海军舰队中运作的标准化设备进行投资。
本报告研究了全球潜舰救援系统市场,并提供了依细分市场的10年市场预测、技术趋势、机会分析、公司概况和国家资料 。
目录
潜舰救援系统市场报告定义
潜舰救援系统市场区隔
- 依类型
依最终用户
依地区
未来 10年潜舰救援系统市场分析
潜舰救援系统市场市场技术
全球潜舰救援系统市场预测
潜舰救援系统市场趋势及预测(依地区)
- 北美洲
- 驱动因素、限制因素与挑战
- PEST
- 市场预测与情境分析
- 大型公司
- 供应商层级结构
- 企业基准
- 欧洲
- 中东
- 亚太地区
- 南美洲
潜舰救援系统市场国家分析
- 美国
- 国防计划
- 最新消息
- 专利
- 目前该市场的技术成熟度
- 市场预测与情境分析
- 加拿大
- 义大利
- 法国
- 德国
- 荷兰
- 比利时
- 西班牙
- 瑞典
- 希腊
- 澳洲
- 南非
- 印度
- 中国
- 俄罗斯
- 韩国
- 日本
- 马来西亚
- 新加坡
- 巴西
潜舰救援系统市场机会矩阵
潜水艇救援系统市场报告专家意见
结论
关于航空和国防市场报告
The Global submarine rescue systems market is estimated at USD 1.85 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 3.85 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.60% over the forecast period 2025-2035.

Introduction to Submarine Rescue Systems Market
The global submarine rescue systems market is a critical segment of the defense and maritime security industry, ensuring the survivability of submarine crews in the event of an underwater emergency. Submarines are a vital component of naval forces worldwide, serving roles in deterrence, intelligence gathering, and combat operations. However, their operations in deep-sea environments expose them to risks such as mechanical failures, onboard fires, and collisions, which can lead to stranding at the ocean floor. Submarine rescue systems have been developed to address these risks, providing navies with rapid-response capabilities to save crew members from disabled or sunken submarines. These systems include specialized submersibles, escape pods, remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), and surface support ships equipped with decompression chambers and medical facilities. The growing emphasis on naval safety, along with increasing submarine deployments due to evolving security threats, has fueled demand for advanced submarine rescue solutions.
Technology Impact in Submarine Rescue Systems Market:
Technological advancements have significantly improved the efficiency and effectiveness of submarine rescue systems, with innovations focusing on deep-sea operation capabilities, automation, and interoperability. One of the key technological developments is the integration of deep-diving submersibles capable of reaching extreme depths to attach to distressed submarines and safely evacuate crews. These submersibles are equipped with state-of-the-art navigation and communication systems, allowing them to operate autonomously or be remotely piloted for precision rescues. Advances in materials science have led to the development of high-strength, lightweight materials that enhance the durability and pressure resistance of rescue vehicles, ensuring safe operations in deep-sea environments.
The use of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized submarine rescue operations. ROVs, which can be deployed ahead of human-piloted rescue missions, play a crucial role in assessing the condition of stranded submarines, clearing obstructions, and providing real-time situational awareness. AI-driven predictive analytics have also improved the maintenance and readiness of submarine rescue systems, allowing naval forces to identify potential equipment failures before they occur. Additionally, modular rescue systems have been introduced to enhance operational flexibility, allowing rapid deployment and integration with different types of submarines regardless of their design or country of origin. This focus on interoperability has been particularly important for multinational naval collaborations, ensuring that rescue assets from allied forces can be deployed in emergencies without compatibility issues.
Key Drivers in Submarine Rescue Systems Market:
The expansion of submarine fleets worldwide has been a key driver for the submarine rescue systems market. Many nations are increasing their submarine capabilities to enhance maritime security, deter potential threats, and maintain strategic dominance in contested waters. With this expansion comes the growing responsibility of ensuring the safety of submarine crews, leading to increased investments in rescue infrastructure and equipment. The rise of littoral and deep-sea warfare strategies has also heightened the importance of submarine rescue capabilities, as modern submarines are operating in more challenging environments with higher risks of entrapment. The adoption of next-generation air-independent propulsion (AIP) and nuclear-powered submarines has necessitated the development of advanced rescue solutions tailored to the unique operational profiles of these vessels.
International collaborations and joint training exercises have further propelled the market, with naval forces prioritizing cooperation in submarine rescue operations. Organizations such as the NATO Submarine Rescue System (NSRS) and the International Submarine Escape and Rescue Liaison Office (ISMERLO) facilitate coordination among global navies to ensure rapid-response capabilities in the event of a submarine emergency. These initiatives have led to the procurement of shared rescue assets, training programs, and standardization of rescue protocols, fostering a globally integrated approach to submarine safety. The increasing number of multinational maritime exercises has reinforced the need for seamless interoperability among submarine rescue systems, encouraging investment in standardized equipment that can operate across different naval fleets.
Regional Trends in Submarine Rescue Systems Market:
Regional trends in the submarine rescue systems market reflect varying strategic priorities, technological capabilities, and naval force structures. North America remains a dominant player in this market, with the United States Navy maintaining some of the most advanced submarine rescue assets. The U.S. Navy's Submarine Rescue Diving and Recompression System (SRDRS) is a key component of its submarine rescue strategy, offering rapid deployment capabilities and deep-sea operational effectiveness. The U.S. continues to invest in research and development to enhance the efficiency of its rescue systems, particularly in the areas of automation, rapid mobilization, and compatibility with next-generation submarines. Canada has also been expanding its maritime security initiatives, emphasizing cooperation with allied forces to ensure access to submarine rescue capabilities.
Europe has been at the forefront of multinational submarine rescue cooperation, with several countries investing in shared rescue systems. The NATO Submarine Rescue System (NSRS), developed by the United Kingdom, France, and Norway, represents a key example of regional collaboration aimed at enhancing submarine crew survivability. European defense firms, including those specializing in underwater technology and naval engineering, have been actively developing cutting-edge rescue solutions, incorporating advanced robotics, AI, and improved deep-sea navigation systems. The European market is also characterized by its emphasis on sustainability and cost efficiency, with naval forces seeking to optimize rescue system designs to maximize operational effectiveness while minimizing resource consumption.
The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing significant growth in the submarine rescue systems market, driven by rising naval modernization efforts and territorial disputes in strategic maritime zones. China, India, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in both submarine development and corresponding rescue capabilities. China's expanding submarine fleet has led to the acquisition of advanced submarine rescue vehicles (SRVs) and deployment of specialized rescue ships. India, which has been strengthening its naval capabilities under the Make in India initiative, has procured deep-sea rescue assets from international suppliers while also developing indigenous solutions. Japan and South Korea, both heavily reliant on maritime security, have prioritized investments in cutting-edge submarine rescue technology to support their growing underwater fleets. The region's focus on securing sea lanes and deterring potential threats has made submarine rescue preparedness a crucial aspect of national security strategies.
Key Submarine Rescue Systems Program:
JFD has been awarded a £193 million contract by the Indian Navy to provide and support its submarine rescue capabilities over the long term. The contract includes the design, construction, and supply of two complete submarine rescue systems, along with a 25-year comprehensive annual maintenance agreement. This deal strengthens JFD's global submarine rescue service presence, following the previous year's announcement of a £12.1 million contract awarded by the UK Ministry of Defence for operating the NATO Submarine Rescue System (NSRS). With this new contract, JFD will be providing submarine rescue services to six of the world's most advanced navies, further solidifying its leadership in this specialized field. JFD will deliver two fully equipped fly-away submarine rescue systems, which will include Deep Search and Rescue Vehicles (DSRV), Launch and Recovery Systems (LARS), Transfer Under Pressure (TUP) systems, and all necessary logistics and support equipment for operation. The equipment will be designed, manufactured, integrated, and tested by JFD before being shipped to India for final commissioning and trials.
The Ministry of Defence has revealed plans to award a £10 million contract for relocating the NATO Submarine Rescue System (NSRS) assets. This initiative aims to enhance the system's operational readiness by securing a new facility that meets all necessary requirements. The contract covers the identification, acquisition, and adaptation of a suitable building to house the NSRS, ensuring it complies with technical and logistical standards. The relocation will support the long-term sustainability and efficiency of the system, which plays a critical role in submarine rescue operations for NATO member nations. By investing in upgraded infrastructure, the Ministry of Defence seeks to strengthen the UK's commitment to international maritime safety and enhance global submarine rescue capabilities.
Table of Contents
Submarine Rescue Market Report Definition
Submarine Rescue Market Segmentation
By Type
By End Users
By Region
Submarine Rescue Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year submarine rescue market analysis would give a detailed overview of submarine rescue market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Submarine Rescue Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Submarine Rescue Market Forecast
The 10-year submarine rescue market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Submarine Rescue Market Trends & Forecast
The regional submarine rescue market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Submarine Rescue Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Submarine Rescue Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Submarine Rescue Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2025-2035
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Type, 2025-2035
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By End User, 2025-2035
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Type, 2025-2035
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By End User, 2025-2035
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Submarine Rescue Systems Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 2: Global Submarine Rescue Systems Market Forecast, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 3: Global Submarine Rescue Systems Market Forecast, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 4: Global Submarine Rescue Systems Market Forecast, By End User, 2025-2035
- Figure 5: North America, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 6: Europe, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 7: Middle East, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 8: APAC, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 9: South America, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 10: United States, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 11: United States, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 12: Canada, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 13: Canada, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 14: Italy, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 15: Italy, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 16: France, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 17: France, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 18: Germany, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 19: Germany, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 22: Belgium, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 23: Belgium, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 24: Spain, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 25: Spain, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 26: Sweden, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 27: Sweden, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 28: Brazil, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 29: Brazil, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 30: Australia, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 31: Australia, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 32: India, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 33: India, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 34: China, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 35: China, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 38: South Korea, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 39: South Korea, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 40: Japan, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 41: Japan, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 44: Singapore, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 45: Singapore, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By Region (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By Type (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By Type (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By End User (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By End User (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Cumulative Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Global Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By End User, 2025-2035
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, By End User, 2025-2035
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Submarine Rescue Systems Market, 2025-2035










