 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1706585
小型UAV的全球市场:2025年~2035年Global Small UAV Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
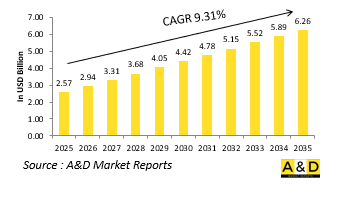
2025 年全球小型无人机市场规模估计为 25.7 亿美元,预计到 2035 年将增长到 62.6 亿美元,2025-2035 年预测期内的复合年增长率 (CAGR) 为 9.31%。
小型无人机市场简介:
小型无人机(UAV),通常被称为微型无人机或战术无人机,已成为世界各地现代军事行动的重要组成部分。这些平台通常被定义为翼展小于 3 公尺、重量小于 150 公斤的无人机,用于近距离侦察、监视、目标获取、通讯中继甚至轻型作战任务。与用于战略任务的大型无人机不同,小型军用无人机在速度、隐身性和易于部署至关重要的战术环境中表现出色。全球军事格局越来越依赖这些紧凑、多功能的平台来获取前线情报和快速态势感知。它价格低廉、操作简单、适应性强,是常规部队和特种作战部队的宝贵工具。小型无人机可以透过手动、弹射或垂直起飞发射,非常适合大型系统无法有效运作的任务,例如崎岖地形、人口密集的城市地区或偏远的战场。随着战争性质转向机动性、城市交战和多领域作战,小型无人机正成为陆、海、空部队的重要资产。
科技对小型无人机市场的影响:
技术进步大大提高了小型军用无人机的能力和实用性。最大的变化是感测器和有效载荷的小型化。电光和红外线摄影机、合成孔径雷达、电子战模组和化学感测器现在已经足够小,可以安装到小型无人机上而不会影响性能。这使得部队能够即时收集可操作的情报,而无需暴露其位置。自主性和人工智慧也正在重新定义小型无人机的使用方式。先进的导航演算法允许无 GPS 操作,这在电子对抗环境中至关重要。人工智慧物体辨识可协助无人机区分平民、车辆和武器系统,从而实现即时威胁识别。此外,正在开发的群体演算法允许小型无人机群独立或协同运行,以压倒敌人的防御并覆盖大面积区域,而无需集中控制。
改良的电池和推进系统增加了续航能力和作战范围。高密度锂硫电池、混合推进系统甚至太阳能辅助设计的使用,使飞行时间远远超出了以前的极限。这些技术进步使得无需频繁重新部署即可维持持续监控或支援长期任务。由于电子战风险日益增加,安全通讯和资料加密至关重要。许多最新的军用小型无人机现在都具有抗干扰和跳频功能,以确保在有争议的电磁环境中具有抵抗力。同时,机载资料处理减少了传输大量资料的需要,降低了被拦截的风险。最后,与平视显示器和战术指挥网路等士兵系统的整合将改善决策和反应时间。士兵将能够透过腕戴设备或扩增实境介面发射和控制无人机,为移动中的部队提供直接、即时的回馈,使这些无人机更像是战场上的队友而不是远程工具。
小型无人机市场的关键推动因素:
有几个关键因素推动了世界各地军事行动对小型无人机的需求和部署。其中最重要的是战争性质的变化,人们更重视快速机动、分散作战和不对称威胁。小型无人机在速度和隐身性至关重要的环境中,在检测隐藏威胁、绘製未知地形和引导精确打击方面具有战术优势。预算效率和成本效益也是强大的驱动力。与大型无人机和载人飞机相比,小型无人机的采购、维护和操作成本要低得多。这使得它不仅适合军事大国使用,也适合发展中国家和资源有限的部队使用。它的可重复使用性和低风险部署进一步增强了其在衝突区域和监视任务中的吸引力。
边境安全和反叛乱行动也会影响采用。应对走私、恐怖主义和跨境渗透的国家需要持续保持警惕,但不能升级衝突。小型无人机可以有效地发挥这一作用,提供即时监视能力,同时最大限度地降低人为风险。它们还可以配备声学设备和照明弹等非致命有效载荷,使其无需参与战斗即可发挥有效的威慑作用。另一个关键因素是增加对网路中心战能力的投资。小型无人机正在作为远端感测器和前沿瞭望台融入更广泛的作战系统。它能够将数据直接传输给炮兵部队、空袭协调员或网路战小组,使其成为即时数位战场上的关键节点。对陆、海、空、网路和太空等多领域作战的重视,加速了对能够适应和与各种指挥系统介接的灵活无人机平台的需求。竞争和近距无人机威胁的增加迫使军队至少提高其战术 ISR(情报、监视和侦察)能力。在争夺或失去空中优势的衝突中,小型无人机可以在不依赖传统空中支援或卫星资产的情况下提供关键的当地眼耳,为地面部队提供生存和获胜所需的态势感知。
小型无人机市场的区域趋势:
全球对军用小型无人机的采用因地区而异,并受到地缘政治优先事项、军事理论和技术能力的影响。北美,特别是美国,在小型军用无人机的研究、开发和作战使用方面处于领先地位。 RQ-11 "大渡鸦" 、 "美洲豹" 和 "黑黄蜂" 等平台在美国军队各兵种中广泛使用。透过与特种部队和常规部队的整合,这些系统已成为战术情报、监视和侦察(ISR)和任务支援的主要部分。美国也透过国防高级研究计划局 (DARPA) 和其他军事研究计画在群体技术和人工智慧无人机领域处于领先地位。
欧洲的采用率正在稳步增长,特别是寻求加强 ISR 能力和战场网络的北约盟国。英国、法国和德国等国家正在投资本土无人机项目,以减少对美国平台的依赖。法国的NX70和德国的Mikado系列是自主研发模组化、单兵便携式无人机的典范。此外,欧洲防务局非常重视无人机互通性标准,以支援联合任务。亚太地区呈现出高度活跃的景象。中国正在迅速扩大其小型无人机队,供国内使用和出口。大疆和中航工业等中国製造商正在向中国人民解放军提供各种无人机,包括用于前线部队的蜂群无人机和便携式背包式系统。印度国防研究与发展组织所发展的无人机也取得了长足进步,并正在增加小型无人机的采购,用于反叛乱和边境安全任务。韩国、日本和澳洲等国家已优先将无人机纳入其国防理论,以应对区域威胁并加强沿海防御。
主要国防小型无人机计画
无人机技术创新的全球领导者ideaForge Technology Limited 宣布,其 SWITCH MINI 无人机成为第一款也是唯一一款获得享有盛誉的 "适合印度军事用途" 认证的小型无人机。该认证认可了 SWITCH MINI 无人机的卓越性能、品质和可靠性,以及其符合印度武装部队严格的作战标准的能力。该认证经过印度品质保证总局(DGQA)的严格评估后颁发,标誌着印度无人机行业的一个重要里程碑。它还巩固了 Idea Forge 在国防和民用两用无人机技术领域的全球领先地位。
经过测试和评估后,美国陆军授予犹他州无人机製造商 Teal Drones 一份合同,为其提供数千架黑寡妇无人机。 Teal Drones 总部位于盐湖城,在当地生产无人机,是总部位于波多黎各的 Red Cat Holdings Inc. 的子公司。
本报告提供全球小型UAV市场相关调查,彙整10年的各分类市场预测,技术趋势,机会分析,企业简介,各国资料等资讯。
目录
小型UAV市场报告定义
小型UAV市场区隔
各地区
各类型
各用途
未来 10 年小型无人机市场分析
本章透过十年小型无人机市场分析,详细概述了小型无人机市场的成长、变化趋势、技术采用概述和市场吸引力。
小型无人机市场的市场技术
本部分涵盖预计将影响该市场的十大技术以及这些技术可能对整个市场产生的影响。
全球小型无人机市场预测
针对未来 10 年小型无人机市场的预测已详细涵盖上述各部分。
小型无人机市场趋势及各地区预测
本部分涵盖小型无人机市场的区域趋势、推动因素、阻碍因素、课题以及政治、经济、社会和技术方面。它还提供了详细的区域市场预测和情境分析。区域分析包括主要公司概况、供应商格局和公司基准测试。目前市场规模是根据正常业务情境估算的。
北美
促进因素,阻碍因素,课题
PEST
市场预测与情势分析
主要企业
供应商阶层的形势
企业基准
欧洲
中东
亚太地区
南美
小型UAV市场各国分析
本章重点介绍该市场的主要防御计划,并介绍该市场的最新新闻和专利。它还提供国家级的 10 年市场预测和情境分析。
美国
防卫计划
最新消息
专利
这个市场上目前技术成熟度
市场预测与情势分析
加拿大
义大利
法国
德国
荷兰
比利时
西班牙
瑞典
希腊
澳洲
南非
印度
中国
俄罗斯
韩国
日本
马来西亚
新加坡
巴西
小型UAV市场机会矩阵
小型UAV市场报告相关专家的意见
结论
关于航空·国防市场报告
The Global Small UAV market is estimated at USD 2.57 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 6.26 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.31% over the forecast period 2025-2035.

Introduction to Small UAV Market:
Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), often referred to as mini or tactical drones, have become integral to modern military operations across the globe. Defined typically as UAVs with a wingspan under 3 meters and weighing less than 150 kg, these platforms are designed for close-range reconnaissance, surveillance, target acquisition, communication relay, and even light combat roles. Unlike larger UAVs used for strategic missions, small military UAVs excel in tactical environments where speed, stealth, and ease of deployment are critical. The global military landscape is increasingly leaning on these compact, versatile platforms for frontline intelligence and rapid situational awareness. Their affordability, ease of operation, and adaptability make them valuable tools for both conventional forces and special operations units. Small UAVs can be launched by hand, catapult, or vertical take-off methods, making them ideal for missions in rugged terrain, dense urban zones, or remote battlefields where larger systems cannot operate efficiently. As the nature of warfare shifts toward mobility, urban engagement, and multi-domain operations, small UAVs are emerging as indispensable assets across land, sea, and air-based units.
Technology Impact in Small UAV Market:
Technological advancements have significantly elevated the capability and utility of small military UAVs. The most transformative impact has come from miniaturization of sensors and payloads. Electro-optical and infrared cameras, synthetic aperture radars, electronic warfare modules, and chemical sensors are now small enough to be carried by mini-UAVs without sacrificing performance. This allows troops to gather actionable intelligence in real time without revealing their position. Autonomy and artificial intelligence are also redefining how small UAVs are employed. Advanced navigation algorithms allow for GPS-denied operations, crucial in electronically contested environments. AI-enabled object recognition helps UAVs distinguish between civilians, vehicles, or weapons systems, enabling real-time threat identification. Furthermore, swarm algorithms are being developed to allow groups of small UAVs to coordinate independently, overwhelming enemy defenses and enabling large-area coverage without centralized control.
Battery and propulsion improvements are enhancing endurance and operational range. The adoption of high-density lithium-sulfur batteries, hybrid propulsion systems, and even solar-assisted designs have extended flight times well beyond earlier limits. These innovations make it possible to maintain persistent surveillance or support prolonged missions without frequent redeployment. Secure communications and data encryption have become critical due to the growing risk of electronic warfare. Many modern military small UAVs are now equipped with anti-jamming and frequency-hopping capabilities to ensure resilience in contested electromagnetic environments. In parallel, onboard data processing reduces the need to transmit large volumes of data, lowering the risk of interception. Finally, the integration with soldier systems-such as heads-up displays or tactical command networks-enhances decision-making and reaction speed. Troops can now launch and control UAVs from wrist-mounted devices or augmented reality interfaces, providing real-time feedback directly to units in motion, making these drones more like battlefield teammates than remote tools.
Key Drivers in Small UAV Market:
Several key factors are propelling the demand and deployment of small UAVs in military operations worldwide. Chief among them is the changing nature of warfare, which increasingly emphasizes rapid maneuvering, decentralized operations, and asymmetric threats. Small UAVs offer a tactical edge in detecting hidden threats, mapping unknown terrain, and guiding precision strikes in environments where speed and stealth are paramount. Budget efficiency and cost-effectiveness are strong drivers as well. Compared to larger UAVs or manned aircraft, small drones are significantly cheaper to procure, maintain, and operate. This makes them accessible not only to major military powers but also to developing countries or units with limited resources. Their reusability and low-risk deployment further strengthen their appeal in contested regions or surveillance missions.
Border security and counterinsurgency operations are also influencing adoption. Nations dealing with smuggling, terrorism, and cross-border incursions require persistent surveillance without escalating conflict. Small UAVs serve this role effectively, offering real-time monitoring capabilities while minimizing human risk. They can be equipped with non-lethal payloads, such as acoustic devices or illumination flares, making them useful for deterrence without engagement. Another crucial factor is increased investment in network-centric warfare capabilities. Small UAVs are being integrated into broader combat systems as remote sensors or forward observers. Their ability to transmit data directly to artillery units, airstrike coordinators, or cyber warfare teams makes them vital nodes in the real-time digital battlefield. The emphasis on multi-domain operations-from land and sea to cyber and space-is accelerating the need for flexible UAV platforms that can adapt and interface with various command systems. The rise of peer and near-peer threats is pushing militaries to improve their tactical ISR (intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance) capabilities at the lowest levels. In conflicts where air dominance is contested or denied, small UAVs provide critical local eyes and ears that do not rely on traditional air support or satellite assets, giving ground troops the situational awareness needed to survive and win.
Regional Trends in Small UAV Market:
The global adoption of small military UAVs varies by region, influenced by geopolitical priorities, military doctrine, and technological capacity. North America, particularly the United States, leads in the research, development, and operational use of military small UAVs. Platforms like the RQ-11 Raven, Puma, and Black Hornet are extensively used across various branches of the U.S. military. Integration with special forces and conventional units alike has made these systems a staple in tactical ISR and mission support. The U.S. is also at the forefront of swarm technology and AI-driven UAVs through DARPA and other military research initiatives.
Europe is witnessing steady growth in adoption, especially among NATO members seeking enhanced ISR capabilities and battlefield networking. Countries like the UK, France, and Germany are investing in indigenous UAV programs to reduce dependence on U.S. platforms. France's NX70 and Germany's Mikado series are examples of localized efforts to develop modular, soldier-portable UAVs. Additionally, the European Defence Agency has emphasized interoperability standards for drones to support joint missions. Asia-Pacific presents a highly dynamic landscape. China has rapidly expanded its small UAV fleet for both domestic use and export. Chinese manufacturers such as DJI and AVIC are supplying the People's Liberation Army with a wide variety of drones, including swarm-capable units and backpack-portable systems for frontline troops. India is also making significant progress with its DRDO-developed UAVs and increased procurement of small drones for counter-insurgency and border patrol roles. Countries like South Korea, Japan, and Australia are prioritizing drone integration into their defense doctrines to counter regional threats and bolster coastal defense.
Key Defense Small UAV Program:
ideaForge Technology Limited, a global leader in drone innovation, proudly announces that its SWITCH MINI UAV has become the first and only small unmanned aerial vehicle to receive the prestigious "Fit for Indian Military Use" certification. This recognition highlights the UAV's exceptional performance, quality, and reliability, as well as its ability to meet the stringent operational standards of the Indian armed forces. The certification, awarded following rigorous evaluations conducted by the Directorate General of Quality Assurance (DGQA), marks a significant milestone for the Indian drone industry. It also reinforces ideaForge's standing as a global frontrunner in dual-use drone technologies designed for both defense and civilian applications.
The U.S. Army has awarded a contract to Utah-based drone manufacturer Teal Drones to supply thousands of its Black Widow unmanned aerial vehicles, following a successful test and evaluation process. Teal Drones, headquartered in Salt Lake City, produces the UAVs locally and operates as a subsidiary of Red Cat Holdings Inc., which is based in Puerto Rico.
Table of Contents
Small UAV Market Report Definition
Small UAV Market Segmentation
By Region
By Type
By Application
Small UAV Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year small UAV market analysis would give a detailed overview of small UAV market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Small UAV Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Small UAV Market Forecast
The 10-year small UAV market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Small UAV Market Trends & Forecast
The regional small UAV market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Small UAV Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Small UAV Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Small UAV Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2025-2035
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Product Type, 2025-2035
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Application, 2025-2035
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Product Type, 2025-2035
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Application, 2025-2035
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Small UAV Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 2: Global Small UAV Market Forecast, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 3: Global Small UAV Market Forecast, By Product Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 4: Global Small UAV Market Forecast, By Application, 2025-2035
- Figure 5: North America, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 6: Europe, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 7: Middle East, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 8: APAC, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 9: South America, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 10: United States, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 11: United States, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 12: Canada, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 13: Canada, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 14: Italy, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 15: Italy, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 16: France, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 17: France, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 18: Germany, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 19: Germany, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 22: Belgium, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 23: Belgium, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 24: Spain, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 25: Spain, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 26: Sweden, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 27: Sweden, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 28: Brazil, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 29: Brazil, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 30: Australia, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 31: Australia, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 32: India, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 33: India, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 34: China, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 35: China, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 38: South Korea, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 39: South Korea, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 40: Japan, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 41: Japan, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 44: Singapore, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 45: Singapore, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Small UAV Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Small UAV Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Small UAV Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Small UAV Market, By Region (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Small UAV Market, By Product Type (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Small UAV Market, By Product Type (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Small UAV Market, By Application (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Small UAV Market, By Application (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Small UAV Market, Cumulative Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Small UAV Market, Global Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Small UAV Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Small UAV Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Small UAV Market, By Product Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Small UAV Market, By Application, 2025-2035
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Small UAV Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Small UAV Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Small UAV Market, By Product Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Small UAV Market, By Application, 2025-2035
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Small UAV Market, 2025-2035





