 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1706588
军事通讯的全球市场:2025年~2035年Global Military Communication Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
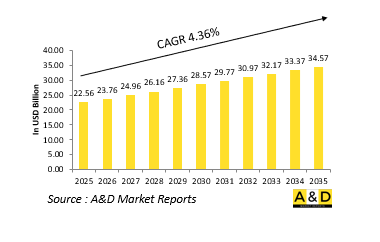
到 2025 年,全球军事通讯市场价值估计将达到 225.6 亿美元。预计到 2035 年,该市场将成长到 345.7 亿美元,复合年增长率为 4.36%。
军事通讯市场简介:
军事通讯系统是现代战场指挥与控制(C2)的命脉。这些系统能够在陆地、海洋、空中、太空和网路空间等多个领域的部队之间安全、快速、可靠地交换资料、语音、视讯和影像。从卫星上行链路和战术无线电到安全的网路协定和战场讯息平台,军事通讯是将决策者、战斗人员和支援部队联繫成一支有凝聚力的战斗力量的纽带。从历史上看,军事通讯已经从旗帜讯号和有线电报发展到高度加密的网路和数位传输系统。当今的策略环境强调跨多个平台和联盟伙伴的互通性、弹性和即时连接性。无论是协调空袭、导航无人系统或监控网路防御,通讯能力现在都与武器系统本身一样决定着作战的有效性。随着威胁变得更加分散和多维,对手的范围从近乎对等到不对称,军队越来越需要维护能够在整个电磁频谱和网路漏洞区域运作的强大、适应性强的通讯网路。网路中心战、联合部队理论和多领域作战的日益普及,正在将军事通讯从战术支援功能提升为国防战略的核心支柱。
科技对军事通讯市场的影响:
最近的技术进步已将军事通讯转变为一个高度灵活、智慧、以数据为中心的领域。最具颠覆性的变化之一是向软体定义无线电(SDR)的转变。这些无线电用可以动态切换频率、调製类型和加密协定的灵活软体取代了依赖硬体的通讯系统。即使使用不同的系统或在频段限制下操作,SDR 也能使各单位实现互连,从而增强任务适应性。
5G 和边缘运算正在成为实现低延迟、高频宽资料交换的关键技术。这些技术能够在密集环境中实现即时数据融合和传输,为从无人机即时馈送到扩增实境 (AR) 战斗覆盖和支援物联网的物流追踪的一切提供支援。 5G与边缘处理的结合将减少对集中指挥中心的依赖,使前线部队能够独立处理资料和行动。另一项突破性进展是低地球轨道 (LEO) 卫星星座的整合,这将重新定义安全的全球覆盖和冗余。与传统的地球静止卫星不同,Starlink 和 OneWeb 部署的低地球轨道 (LEO) 网路具有更低的延迟、更快的资料吞吐量以及更好的极地和偏远地区覆盖范围。各国军队正在快速探索低地球轨道 (LEO) 集成,以在点对点衝突场景中实现不间断的 C2。
人工智慧 (AI) 对军事通讯的影响怎么强调也不为过。现在,人工智慧系统正被用于优化频宽使用、侦测通讯模式中的异常,甚至跨语言和加密方法自动进行讯息翻译。智慧通讯路由确保资料以最快、最安全的路径传输,最大限度地减少漏洞。此外,量子通讯和后量子密码学正在探索不受传统网路窃听影响的超安全通讯管道。虽然这些尖端技术仍处于早期阶段,但国防官员正在投入巨资,为即将到来的量子运算威胁做好准备。同时,网路安全技术正直接融入通讯架构中。端对端加密、零信任框架和动态存取控制对于维护操作安全至关重要。随着军事网路面临来自国家和非国家行为者日益严重的网路威胁,安全通讯管道已成为关键技术领域。
军事通讯市场的关键推动因素:
多种战略和营运因素正在推动全球军事通讯系统的发展和扩张。其中最主要的是需要无缝多域操作。现代战争需要陆、海、空、天和网路部队之间的协调,通常是即时的。通讯网路必须支援这些领域的同步努力,以确保任务成功。联合作战和合成作战的兴起也是一个主要推动因素。大多数现代军事行动都涉及多国部队,并需要跨越不同系统和理论的互通性。为此,北约的联邦任务网络(FMN)等标准化协议已经开发出来,以支援盟军之间的资料共享和安全通讯。
另一个重要因素是战场资产日益复杂。无人系统、感测器和武器平台会产生大量数据,从而推动对能够在战术边缘移动、处理和解释资讯的快速、安全的数据管道的需求。这也推动了人们对网状网路和智慧频宽管理的兴趣。态势感知和快速决策的需求变得越来越大。指挥官现在需要来自多个感测器、部队追踪器和 ISR 平台的即时资讯来做出明智的决策。这迫使通讯系统优先考虑资料融合、即时分析和压力下的復原能力。
此外,电子战 (EW) 和网路攻击的威胁日益增加也影响着通讯策略。目前,对手利用干扰、欺骗和骇客技术来破坏或削弱军事网路的通讯。这就是为什么对抗干扰技术、频率捷变和网路强化传输协议的投资不断增加的原因。预算考虑也起着一定作用。许多国家都在平衡对尖端通讯系统的需求与降低生命週期成本和减少对专有平台的依赖的压力。这推动了开放标准、模组化升级和可用于军事加固的商用现货 (COTS) 组件的采用。
军事通讯市场的区域趋势:
全球军事通讯格局由地区防御优先事项、威胁认知和技术能力决定。
在北美,尤其是美国,人们非常重视透过统一、有弹性的通讯架构来实现全领域优势。联合全局指挥与控制(JADC2)等项目旨在透过人工智慧资料共享和安全通讯整合跨领域的力量。美国军方正大力投资低地球轨道卫星网路、频谱管理和人工智慧驱动的网路安全,以确保相对于当代竞争对手的战略优势。加拿大也在升级其通讯基础设施,以提高与美国和北约部队的互通性,特别是在北极和海上领域。欧洲致力于提高北约成员国之间的互通性并对遗留系统进行现代化改造。欧洲安全软体定义无线电(ESSOR)项目和泛欧军事卫星通讯能力的发展等措施反映了这一趋势。法国、德国和英国在战术通讯、战场网路和主权卫星能力的投资方面处于领先地位。此外,乌克兰衝突促使许多国家加速部署安全通讯系统,为电子战做好准备。在亚太地区,地区紧张局势和军事现代化计划正在刺激通讯技术的快速发展。为了确保作战的连续性,中国正在推行自己的网路弹性通讯系统,该系统整合了卫星、地面和高频(HF)频道。作为其现代化计画的一部分,印度正在投资网路中心战和基于卫星的指挥与控制系统,其中包括国防太空总署的努力。日本和韩国正在加强战场通讯基础设施,以遏制地区威胁并支持美国主导的联合行动。
主要军事通信项目:
2025 年 2 月 20 日,国防部与班加罗尔的印度电子有限公司 (BEL) 签署合同,为印度海岸防卫队采购 149 台软体定义无线电 (SDR)。价格为 12,212 千万卢比,属于采购(印度-IDDM)类别。这些先进的软体无线电旨在提供安全、高速的数据和语音通信,以增强资讯共享、营运协调和态势感知。这些整合将使印度海岸防卫队显着增强其在海上执法、搜救、渔业保护和海洋环境保护等关键任务领域的能力。该无线电也将增强联合行动期间与印度海军的互通性。该举措是提高海岸防卫队作战准备的战略举措,同时也透过加强海上安全来支持印度政府的蓝色经济目标。依照 "自力更生印度" 的愿景,该计画也将促进本土军用级通讯技术能力的发展,促进本土製造业,创造就业机会,促进国防部门的技能发展。
全球领先的卫星网路技术和服务供应商吉拉特卫星网路有限公司宣布,其国防部门赢得了一份价值 600 万美元的订单,为亚太地区的军事组织提供 SkyEdge II-c 平台。这种先进的卫星通讯解决方案将支援固定和移动操作,为关键的国防任务提供安全可靠的连接,同时增强空中介面层级的网路保护。
本报告提供全球军事通讯市场相关调查,彙整10年的各分类市场预测,技术趋势,机会分析,企业简介,各国资料等资讯。
目录
军事通讯市场报告定义
军事通讯市场区隔
各地区
各零件
各终端用户
未来 10 年军事通讯市场分析
本章对十多年来军事通讯市场的分析提供了军事通讯市场成长、变化趋势、技术采用概况和市场吸引力的详细概述。
军事通讯市场的市场技术
本部分涵盖预计将影响该市场的十大技术以及这些技术可能对整个市场产生的影响。
全球军事通讯市场预测
针对该市场未来 10 年的军事通讯市场预测,已详细列出上述各部分。
区域军事通讯市场趋势与预测
本部分涵盖区域军事通讯市场趋势、推动因素、阻碍因素、课题以及政治、经济、社会和技术方面。它还提供了详细的区域市场预测和情境分析。区域分析包括主要公司概况、供应商格局和公司基准测试。目前市场规模是根据正常业务情境估算的。
北美
促进因素,阻碍因素,课题
PEST
市场预测与情势分析
主要企业
供应商阶层的形势
企业基准
欧洲
中东
亚太地区
南美
军事通讯市场国家分析
本章重点介绍该市场的主要防御计划,并介绍该市场的最新新闻和专利。它还提供国家级的 10 年市场预测和情境分析。
美国
防卫计划
最新消息
专利
这个市场上目前技术成熟度
市场预测与情势分析
加拿大
义大利
法国
德国
荷兰
比利时
西班牙
瑞典
希腊
澳洲
南非
印度
中国
俄罗斯
韩国
日本
马来西亚
新加坡
巴西
军事通讯市场机会矩阵
军事通讯市场报告相关专家的意见
结论
关于航空·国防市场报告
The Global Military Communication market is estimated at USD 22.56 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 34.57 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.36% over the forecast period 2025-2035.

Introduction to Military Communication Market:
Military communication systems are the lifelines of command and control (C2) on the modern battlefield. These systems enable the secure, rapid, and reliable exchange of data, voice, video, and imagery between forces across different domains-land, sea, air, space, and cyberspace. From satellite uplinks and tactical radios to secure internet protocols and battlefield messaging platforms, military communication is the connective tissue that links decision-makers, combat units, and support elements into a cohesive fighting force. Historically, military communication evolved from flag signals and wire-based telegraphy to sophisticated encrypted networks and digital transmission systems. In the current strategic environment, the emphasis is on interoperability, resilience, and real-time connectivity across multiple platforms and coalition partners. Whether coordinating airstrikes, navigating unmanned systems, or monitoring cyber defense, communication capabilities now determine operational effectiveness as much as weapon systems themselves. As threats become more dispersed and multidimensional-from near-peer adversaries to asymmetric actors-military forces are under increasing pressure to maintain robust, adaptive communication networks that function across contested electromagnetic spectrums and cyber-compromised zones. The growing adoption of network-centric warfare, joint-force doctrines, and multi-domain operations has elevated military communication from a tactical support function to a core pillar of defense strategy.
Technology Impact in Military Communication Market:
Recent technological advancements have transformed military communication into a highly agile, intelligent, and data-centric domain. One of the most disruptive changes is the shift toward Software-Defined Radios (SDRs). These radios replace hardware-dependent communication systems with flexible software that can dynamically switch frequencies, modulation types, and encryption protocols. SDRs allow units to interconnect even when using different systems or operating under spectrum constraints, boosting mission adaptability.
5G and edge computing are emerging as significant enablers of low-latency, high-bandwidth data exchange. These technologies allow for real-time data fusion and transmission in dense environments, enabling everything from live drone feeds to augmented reality (AR) combat overlays and IoT-enabled logistics tracking. The combination of 5G and edge processing reduces reliance on centralized command centers and allows frontline units to process and act on data independently. Another game-changing development is the integration of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations, which are redefining secure global coverage and redundancy. Unlike traditional geostationary satellites, LEO networks-such as those deployed by Starlink and OneWeb-offer lower latency, faster data throughput, and improved coverage in polar and remote regions. Militaries are rapidly exploring LEO integration for uninterrupted C2 during peer conflict scenarios.
The impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in military communication cannot be overstated. AI-powered systems are now used to optimize bandwidth usage, detect anomalies in communication patterns, and even automate message translation across languages and encryption schemes. Intelligent communication routing ensures that data takes the fastest, most secure path, minimizing vulnerabilities. Additionally, Quantum communication and post-quantum encryption are being explored for ultra-secure channels immune to conventional cyber interception. These cutting-edge technologies are still in their nascent stages but are attracting significant investment as defense establishments prepare for the advent of quantum computing threats. Meanwhile, cybersecurity technologies are being built directly into communication architectures. End-to-end encryption, zero-trust frameworks, and dynamic access controls are vital for maintaining operational security. As military networks face increasing cyber threats from state and non-state actors, secure communication channels have become a critical area of technological focus.
Key Drivers in Military Communication Market:
Several strategic and operational factors are propelling the evolution and expansion of global military communication systems. Chief among them is the need for seamless multi-domain operations. Modern warfare demands coordination between land, sea, air, space, and cyber forces-often in real time. Communication networks must support synchronized efforts across these domains to ensure mission success. The rise of joint and coalition operations is another major driver. Most modern military engagements involve multi-national forces, requiring interoperability across disparate systems and doctrines. This has led to the development of standardized protocols like NATO's Federated Mission Networking (FMN), which supports data sharing and secure communications among allied forces.
Another important factor is the increasing complexity of battlefield assets. With unmanned systems, sensors, and weapon platforms generating vast amounts of data, there is a growing demand for high-speed, secure data pipelines that can move, process, and interpret information at the tactical edge. This has also driven interest in mesh networking and intelligent bandwidth management. Situational awareness and rapid decision-making are further amplifying demand. Commanders now require live feeds from multiple sensors, troop trackers, and ISR platforms to make informed decisions. This pushes communication systems to prioritize data fusion, real-time analytics, and resilience under pressure.
Moreover, the growing threat from electronic warfare (EW) and cyber-attacks is influencing communication strategies. Adversaries now target military networks with jamming, spoofing, and hacking techniques to disrupt or degrade communications. This has led to increased investment in anti-jamming technologies, frequency agility, and cyber-hardened transmission protocols. Budgetary considerations also play a role. Many nations are balancing the need for cutting-edge communication systems with pressure to reduce lifecycle costs and minimize dependence on proprietary platforms. This drives the adoption of open standards, modular upgrades, and commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components that can be ruggedized for military use.
Regional Trends in Military Communication Market:
The global military communication landscape is shaped by regional defense priorities, threat perceptions, and technological capabilities.
In North America, particularly the United States, the focus is on achieving full-spectrum dominance through resilient and unified communication architectures. Programs like the Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2) aim to integrate forces across domains via AI-powered data sharing and secure communications. The U.S. military is heavily investing in LEO satellite networks, spectrum management, and AI-driven cybersecurity to ensure strategic edge over peer rivals. Canada is similarly upgrading its communication infrastructure for interoperability with U.S. and NATO forces, especially in Arctic and maritime domains. Europe is concentrating on enhancing interoperability among NATO members and modernizing legacy systems. Initiatives like the European Secure Software Defined Radio (ESSOR) project and the development of pan-European military satcom capabilities reflect this trend. France, Germany, and the UK are leading the charge with investments in tactical communications, battlefield networking, and sovereign satellite capabilities. The war in Ukraine has also prompted many countries to accelerate secure communication deployments to guard against electronic warfare. In Asia-Pacific, regional tensions and military modernization programs are fueling rapid advances in communication technologies. China is pursuing indigenous, cyber-resilient communication systems with integrated satellite, terrestrial, and HF (high frequency) channels to ensure operational continuity. India is investing in network-centric warfare and satellite-based C2 systems as part of its modernization initiatives, including the Defense Space Agency's efforts. Japan and South Korea are enhancing their battlefield communication infrastructure to deter regional threats and support U.S.-led joint operations.
Key Military Communication Program:
On February 20, 2025, the Ministry of Defence signed a contract with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Bengaluru, for the procurement of 149 Software Defined Radios (SDRs) for the Indian Coast Guard. Valued at ₹1,220.12 crore, the acquisition falls under the Buy (Indian-IDDM) category. These advanced SDRs are designed to provide secure, high-speed data and voice communication, enhancing information sharing, operational coordination, and situational awareness. Their integration will significantly boost the Indian Coast Guard's capabilities in key mission areas such as maritime law enforcement, search and rescue, fisheries protection, and marine environmental safeguarding. The radios will also improve interoperability with the Indian Navy during joint operations. This initiative represents a strategic move to enhance the Coast Guard's operational readiness while supporting the Government of India's Blue Economy goals by strengthening maritime security. In line with the Atmanirbhar Bharat vision, the project will also contribute to the development of indigenous capabilities in military-grade communication technologies, promote local manufacturing, create employment opportunities, and foster skill development in the defense sector.
Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd, a global leader in satellite networking technologies and services, has announced that its Defense Division has secured a $6 million order to supply its SkyEdge II-c platform to a military organization in the Asia-Pacific region. The advanced satellite communications solution will support both stationary and mobile operations, delivering secure and reliable connectivity for critical defense missions, with enhanced cyber protection at the air interface level.
Table of Contents
Military Communication Market Report Definition
Military Communication Market Segmentation
By Region
By Component
By End-User
Military Communication Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year Military Communication Market analysis would give a detailed overview of Military Communication Market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Military Communication Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Military Communication Market Forecast
The 10-year Military Communication Market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Military Communication Market Trends & Forecast
The regional Military Communication Market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Military Communication Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Military Communication Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Military Communication Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2025-2035
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By End User, 2025-2035
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Type, 2025-2035
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By End User, 2025-2035
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Type, 2025-2035
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Military Communication Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 2: Global Military Communication Market Forecast, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 3: Global Military Communication Market Forecast, By End User, 2025-2035
- Figure 4: Global Military Communication Market Forecast, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 5: North America, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 6: Europe, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 7: Middle East, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 8: APAC, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 9: South America, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 10: United States, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 11: United States, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 12: Canada, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 13: Canada, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 14: Italy, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 15: Italy, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 16: France, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 17: France, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 18: Germany, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 19: Germany, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 22: Belgium, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 23: Belgium, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 24: Spain, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 25: Spain, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 26: Sweden, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 27: Sweden, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 28: Brazil, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 29: Brazil, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 30: Australia, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 31: Australia, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 32: India, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 33: India, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 34: China, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 35: China, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 38: South Korea, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 39: South Korea, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 40: Japan, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 41: Japan, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 44: Singapore, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 45: Singapore, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Military Communication Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Military Communication Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Military Communication Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Military Communication Market, By Region (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Military Communication Market, By End User (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Military Communication Market, By End User (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Military Communication Market, By Type (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Military Communication Market, By Type (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Military Communication Market, Cumulative Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Military Communication Market, Global Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Military Communication Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Military Communication Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Military Communication Market, By End User, 2025-2035
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Military Communication Market, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Military Communication Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Military Communication Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Military Communication Market, By End User, 2025-2035
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Military Communication Market, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Military Communication Market, 2025-2035












