 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1706590
以网路为中心的战斗的全球市场:2025年~2035年Global Network Centric Warfare Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
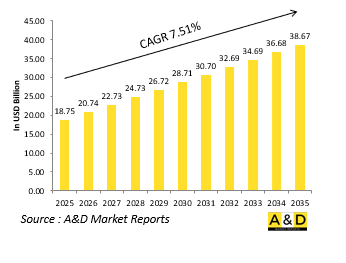
全球网路中心战市场规模预计在 2025 年为 187.5 亿美元,预计到 2035 年将成长到 386.7 亿美元,在 2025-2035 年预测期内的复合年增长率 (CAGR) 为 7.51%。
网路中心战市场介绍:
网路中心战 (NCW) 代表了军事理论的变革性转变,其核心是利用资讯优势来获得战术和战略优势。无缝整合感测器、通讯网路、指挥系统和作战力量,创造一个有凝聚力、反应迅速、即时的作战环境。 NCW 的核心是将资讯转化为战斗力——连接跨领域的射手、决策者和资讯资产,以增强态势感知、同步行动并加快决策週期。
传统的指挥和控制结构正在被数位互联繫统所取代,从而实现分散决策和协调回应。该框架将使军队能够以更大的灵活性、精确度和适应性开展行动,特别是在动态和复杂的作战区域。网路中心战将不仅限于空中和网路领域,还将扩展到陆地、海上、太空和联合部队环境,即时整合力量,重塑战场态势。在当今的多域衝突中,威胁混合、分散且技术复杂,NCW 对于获得资讯优势和实现力量倍增至关重要。从即时无人机馈送到卫星通讯中继,全球防御格局日益由盟军之间资讯共享的深度和速度决定。
科技对网路中心作战市场的影响:
支援 NCW 的技术环境正在快速发展,并从根本上改变现代军队计划和开展行动的方式。 NCW 的核心是宽频通讯基础设施,包括战术资料链路、卫星网路和 5G/6G 功能。这些确保了网路中所有节点之间的不间断连接,无论是地面部队、空中资产或指挥中心。人工智慧 (AI) 和机器学习 (ML) 将在提高 NCW 效率方面发挥关键作用。人工智慧演算法可以即时处理大量资料集,以识别威胁、提出战术回应或以最少的人为干预优化资产部署。预测分析还可以实现更好的任务规划和风险评估,使指挥官对其作战决策更有信心。
无人驾驶汽车、远端感测器和机器人辅助装置等自主系统的兴起进一步增加了我们对网路架构的依赖。这些资产通常半独立运行,但仍与指挥网络紧密整合,需要强大而安全的协议来保持同步和响应。网路安全和弹性也已成为网路中心战系统的重要组成部分。由于整个理论依赖于资料流和数位连接,因此保护通讯链路和防止资料外洩、干扰和网路破坏至关重要。这就是为什么量子加密、区块链安全通讯和多层身份验证机制正在积极开发和实施的原因。
另一个重要的技术进步是穿戴式战场网路与智慧士兵系统的整合。现代步兵装备现在配备了可穿戴电脑、平视显示器、生物感测器和战术无线电。这将创造一个数位化的战士,他们可以在与无人机、车辆和指挥中心即时互动的同时保持敏捷和杀伤力。
网路中心战市场的关键推动因素:
有几个核心推动因素正在推动 NCW 能力的全球采用和扩展:
日益增加的作战复杂性和多领域战争使得传统部队结构的效率降低。在现代衝突中,决策速度和跨陆地、海上、空中、网路和太空领域的协同能力至关重要。 NCW 可以实现这种整合的、快节奏的作战,相对于依赖速度较慢的遗留系统的对手,它具有不对称优势。
地缘政治不稳定和联盟变化也影响全球防御态势。由于各国面临不确定的安全环境,他们正在投资 NCW 以改善自身的防御态势和与盟军的互通能力。例如,北约高度重视联合作战能力和协同指挥体系,成员国采用网路中心战的进程正在加速。
随着技术融合——人工智慧、云端运算、边缘处理和物联网的融合——NCW 所需的基础设施变得越来越容易存取和可扩展。军队现在可以使用现成的技术与定制的军用级解决方案相结合来构建有弹性的模组化 NCW 框架,从而降低成本并缩短部署时间。
叛乱网路、网路攻击和无人机群等非对称和混合威胁进一步要求使用 NCW。与传统军队不同,这些威胁往往是分散的、机动的。应对这些问题需要快速传播威胁情报、灵活的部署策略和即时威胁可见性,这些都是 NCW 的标誌。
世界各地的国防现代化计划都专注于数位化和连通性。各国已开始围绕网路中心战采取举措,包括重组指挥结构、更新具有网路功能的平台以及训练部队在联网战场上作战。采购重点正在转向可以无缝 "插入" 这种数位架构的平台和系统。
最后,联盟和多国行动中的互通性要求正在推动 NCW 技术的标准化和采用。无论是联合演习还是作战任务,部队之间能够共享共同的作战影像都至关重要,而网路中心战为这种同步提供了支撑。
网路中心战市场的区域趋势:
美国是网路中心战能力的先驱和主导力量。透过 JADC2(联合全局指挥与控制)等项目,美国国防部正在将陆军、海军、空军、海军陆战队和太空部队等所有军种整合到由人工智慧和自主系统支援的统一指挥结构中,从而改变战争方式。加拿大也在推动数位指挥能力,以更好地协调联合行动并加强其北极防御态势。北约接受国家中心战作为集体防御的重要工具。欧洲国家正在投资跨成员国运作的安全、可互通的指挥平台。德国的 "数位化军队" 和英国的 "陆地环境战术通讯和资讯系统" (LE TacCIS)就是陆军数位化和创造即插即用指挥环境的典范。法国、瑞典和波兰也将NCW框架纳入其防空、边境监视和远征行动。
中国正在 "资讯化" 的旗号下大力推进其网路中心能力。中国人民解放军的目标是建立集太空、网路和动能作战于一体的统一指挥网络。日本和韩国正在对其 C4ISR(指挥、控制、通讯、电脑、情报、监视和侦察)基础设施进行现代化改造,以确保快速资料共享和即时威胁响应,尤其是在地区紧张局势下。作为其未来部队概念的一部分,澳洲正在投资综合战斗管理系统,旨在实现无缝联合作战。沙乌地阿拉伯、阿联酋和卡达等海湾国家正迅速采用网路中心战系统来加强其内部安全和力量投射。该地区的采购策略强调综合防空反导系统以及装甲和步兵部队的战场数位化。以色列继续在网路中心战部署方面处于领先地位,特别是在感测器融合、无人机协调和网路战场感知方面。
非洲的国家网路中心战实施仍处于起步阶段,但正在不断发展。南非、埃及和奈及利亚等国家已经采用了基本的网路中心组件来协调反叛乱和边境安全行动。非洲大陆面临的课题——从糟糕的连通基础设施到有限的预算——正在减缓采用该技术的步伐。然而,捐助国支持的现代化计画和区域安全倡议正在将 NCW 原则引入一些军事单位。
重大网路中心战计画
在印度,无人机和飞弹等先进系统的引进引起了媒体的关注。然而,在公众看来,印度仍然存在巨大的能力差距,包括印度空军中队实力下降、海军潜艇短缺以及陆军推迟引进先进追踪火炮系统(ATAGS)。仍然存在一个关键但不太明显的差距,那就是陆军 20 多年来对全面网路中心作战能力的长期需求。其中的核心是为陆军实施综合战场管理系统 (BMS),这项需求需要持续的关注和解决。
本报告提供全球以网路为中心的战斗市场相关调查,彙整10年的各分类市场预测,技术趋势,机会分析,企业简介,各国资料等资讯。
目录
防卫资产管理软体市场报告定义
防卫资产管理软体市场区隔
- 各终端用户
- 各地区
- 各平台
未来10年网路中心战分析
本章透过长达十年的网路中心战分析,详细概述了网路中心战的成长、变化趋势、技术采用概况以及整体市场吸引力。
网路中心作战市场技术
本部分涵盖预计将影响该市场的十大技术以及这些技术可能对整个市场产生的影响。
以网路为中心的世界战争预测
针对该市场未来 10 年的网路中心战预测已详细划分为上述几个部分。
区域网路中心战的趋势与预测
本部分涵盖该地区网路中心战的趋势、推动因素、阻碍因素、课题以及政治、经济、社会和技术层面。它还提供了详细的区域市场预测和情境分析。区域分析的最后阶段包括主要公司概况、供应商格局和公司基准测试。目前市场规模是根据正常业务情境估算的。
北美
促进因素,阻碍因素,课题
PEST
市场预测与情势分析
主要企业
供应商阶层的形势
企业基准
欧洲
中东
亚太地区
南美
各国网路中心战分析
本章重点介绍该市场的主要防御计划,并介绍该市场的最新新闻和专利。它还提供国家级的 10 年市场预测和情境分析。
美国
防卫计划
最新消息
专利
这个市场上目前技术成熟度
市场预测与情势分析
加拿大
义大利
法国
德国
荷兰
比利时
西班牙
瑞典
希腊
澳洲
南非
印度
中国
俄罗斯
韩国
日本
马来西亚
新加坡
巴西
以网路为中心的战斗的机会矩阵
以网路为中心的战斗相关专家的意见报告
结论
关于航空·国防市场报告
The Global Network Centric Warfare market is estimated at USD 18.75 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 38.67 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.51% over the forecast period 2025-2035.

Introduction to Network Centric Warfare Market:
Network Centric Warfare (NCW) represents a transformative shift in military doctrine, centered on leveraging information superiority to gain a tactical and strategic advantage. It involves the seamless integration of sensors, communication networks, command systems, and combat units into a cohesive, responsive, and real-time operational environment. At its core, NCW is about turning information into combat power-connecting shooters, decision-makers, and intelligence assets across domains to achieve enhanced situational awareness, synchronized operations, and faster decision cycles.
Traditional command-and-control structures are being replaced by digitally interconnected systems that enable distributed decision-making and coordinated responses. This framework allows militaries to operate with greater agility, precision, and adaptability, particularly in dynamic and complex combat theaters. Network centric operations are not confined to air or cyber realms-they extend across ground, sea, space, and joint-forces environments, unifying efforts in real-time and reshaping battlefield dynamics. In today's multi-domain conflicts-where threats are hybrid, dispersed, and technologically sophisticated-NCW is critical for gaining information dominance and enabling force multiplication. From real-time UAV feeds to satellite communication relays, the global defense landscape is increasingly defined by the depth and speed of information sharing among allied units.
Technology Impact in Network Centric Warfare Market:
The technology landscape underpinning NCW has advanced rapidly, fundamentally altering how modern militaries plan and execute operations. At the heart of NCW are high-bandwidth communication infrastructures, including tactical data links, satellite networks, and 5G/6G capabilities. These ensure uninterrupted connectivity between all nodes in the network, whether ground troops, air assets, or command centers. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) play a significant role in enhancing the efficiency of NCW. AI algorithms can process massive datasets in real time, identifying threats, suggesting tactical responses, or optimizing asset deployment with minimal human intervention. Predictive analytics also enables better mission planning and risk assessment, giving commanders more confidence in their operational decisions.
The rise of autonomous systems-such as unmanned vehicles, remote sensors, and robotic support units-has further intensified reliance on networked architecture. These assets often operate semi-independently but remain tightly integrated within the command network, requiring robust and secure protocols to maintain synchronization and responsiveness. Cybersecurity and resilience have also become integral aspects of NCW systems. Since the entire doctrine depends on data flow and digital connectivity, defending communication links and protecting against data breaches, jamming, and cyber sabotage are paramount. As such, quantum encryption, blockchain-secured communications, and multi-layered authentication mechanisms are being actively developed and deployed.
Another key technological advancement is the integration of wearable battlefield networks and smart soldier systems. Modern infantry kits now include body-worn computers, heads-up displays, biosensors, and tactical radios-all of which feed into and extract data from the broader network. This creates a digitized warfighter, capable of interacting with drones, vehicles, and headquarters in real-time while remaining mobile and lethal.
Key Drivers in Network Centric Warfare Market:
Several core drivers are propelling the adoption and expansion of NCW capabilities on a global scale.
Operational complexity and multi-domain warfare have made traditional force structures less effective. In modern conflicts, the speed of decision-making and the ability to coordinate across land, sea, air, cyber, and space domains are crucial. NCW enables that kind of integrated, fast-paced operation, offering an asymmetric advantage over adversaries relying on slower, legacy systems.
Geopolitical instability and shifting alliances are also influencing the global defense posture. As nations face uncertain security environments, they are investing in NCW to boost their defense readiness and interoperability with allied forces. For instance, NATO's emphasis on joint operability and coordinated command systems has accelerated NCW adoption among member states.
Technological convergence-the blending of AI, cloud computing, edge processing, and IoT-has made the infrastructure required for NCW more accessible and scalable. Militaries are now able to build resilient, modular NCW frameworks using off-the-shelf technologies integrated with custom military-grade solutions, reducing cost and deployment time.
Asymmetric and hybrid threats, such as insurgent networks, cyberattacks, and drone swarms, further necessitate the use of NCW. Unlike conventional armies, these threats are often decentralized and mobile. Countering them requires the rapid dissemination of intelligence, flexible deployment strategies, and real-time threat visualization-all hallmarks of NCW.
Defense modernization programs globally are heavily focused on digitization and connectivity. Countries are launching NCW-centric initiatives that restructure command chains, update platforms with networking capabilities, and train forces to operate in a connected battlefield. Procurement priorities are shifting toward platforms and systems that can "plug into" these digital architectures seamlessly.
Lastly, interoperability requirements in coalition and multinational operations are driving standardization and adoption of NCW technologies. Whether in joint exercises or real-world missions, being able to share a common operational picture across forces is essential-and NCW provides the backbone for such synchronization.
Regional Trends in Network Centric Warfare Market:
The United States is the pioneer and dominant force in NCW capabilities. Through programs like Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2), the U.S. Department of Defense is transforming how it fights wars by integrating all branches-Army, Navy, Air Force, Marines, and Space Force-into a unified command structure supported by AI and autonomous systems. Canada is similarly advancing its digital command capabilities to better coordinate joint operations and reinforce Arctic defense postures. NATO has embraced NCW as a critical enabler of collective defense. European nations are investing in secure, interoperable command platforms that can work across member states. Germany's "Digitale Krafte" and the UK's "Land Environment Tactical Communication and Information Systems" (LE TacCIS) are examples of efforts to digitize land forces and create plug-and-play command environments. France, Sweden, and Poland are also integrating NCW frameworks into air defense, border surveillance, and expeditionary operations.
China is aggressively advancing its network-centric capabilities under the banner of "informatization." The People's Liberation Army (PLA) aims to build integrated command networks that unify space, cyber, and kinetic operations. Japan and South Korea are modernizing their C4ISR (Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance) infrastructures to ensure rapid data sharing and real-time threat response, especially in the context of regional tensions. Australia is investing in integrated battle management systems as part of its future force initiatives, aiming for seamless joint-service operability. Gulf countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Qatar are rapidly adopting NCW systems to enhance both internal security and power projection. The region's procurement strategies emphasize integrated air and missile defense systems, as well as battlefield digitization for armored and infantry units. Israel remains a leader in NCW deployment, particularly in sensor fusion, drone coordination, and cyber-enabled battlefield awareness.
NCW implementation in Africa is still nascent but growing. Countries like South Africa, Egypt, and Nigeria are adopting basic network-centric components to coordinate counterinsurgency efforts and border patrol operations. The continent's challenges-ranging from low connectivity infrastructure to limited budget-slow down the pace of adoption. However, donor-backed modernization programs and regional security initiatives are introducing NCW principles into select military units.
Key Network Centric Warfare Program:
In India, media attention has increasingly centered on the induction of advanced systems such as drones and missiles. However, significant capability gaps remain in public perception-such as the Indian Air Force's declining squadron strength, the Navy's shortage of submarines, and the delayed induction of the Army's Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS). One critical yet less visible gap that persists is the Army's long-standing requirement-spanning over two decades-for comprehensive Network Centric Warfare capabilities. Central to this is the implementation of an Integrated Battlefield Management System (BMS) for land forces, a need that continues to demand focused attention and resolution
Table of Contents
Network centric warfare Report Definition
Network Centric Warfare Segmentation
By Region
By Type
By Platform
Network centric warfare Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year network centric warfare analysis would give a detailed overview of network centric warfare growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Network centric warfare
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Network centric warfare Forecast
The 10-year network centric warfare forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Network centric warfare Trends & Forecast
The regional network centric warfare trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Network centric warfare
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Network centric warfare
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Network centric warfare Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2025-2035
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Type, 2025-2035
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Type, 2025-2035
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 2: Global Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 3: Global Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Figure 4: Global Network Centric Warfare Market Forecast, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 5: North America, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 6: Europe, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 7: Middle East, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 8: APAC, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 9: South America, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 10: United States, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 11: United States, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 12: Canada, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 13: Canada, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 14: Italy, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 15: Italy, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 16: France, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 17: France, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 18: Germany, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 19: Germany, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 22: Belgium, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 23: Belgium, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 24: Spain, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 25: Spain, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 26: Sweden, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 27: Sweden, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 28: Brazil, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 29: Brazil, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 30: Australia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 31: Australia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 32: India, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 33: India, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 34: China, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 35: China, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 38: South Korea, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 39: South Korea, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 40: Japan, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 41: Japan, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 44: Singapore, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 45: Singapore, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Network Centric Warfare Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Network Centric Warfare Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, Cumulative Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Network Centric Warfare Market, Global Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Network Centric Warfare Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Network Centric Warfare Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Network Centric Warfare Market, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Network Centric Warfare Market, 2025-2035






