 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1927661
全球作战潜舰市场(2026-2036)Global Combat Submersible Vehicles Market 2026-2036 |
||||||
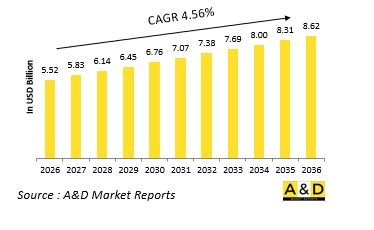
据估计,2026年全球作战潜舰市场规模为55.2亿美元,预计到2036年将达到86.2亿美元,2026年至2036年的复合年增长率(CAGR)为4.56%。
全球作战潜舰市场简介
作战潜舰是专门设计的水下平台,旨在支援各种军事行动,在海上作战环境中提供隐蔽性、机动性和多功能性。 这些舰艇能够隐藏部署人员、装备和侦察工具,使部队能够不被发现地执行特种作战、监视和情报蒐集任务。与传统潜舰不同,作战潜舰通常体积较小、机动性较强,针对在浅水或受限水域的快速部署和回收进行了最佳化。现代设计强调流体动力效率、降噪和运行可靠性,以确保在各种条件下有效作战。它们可以独立作战,也可以与大型舰艇协同作战,从而实现精确的部队部署、特种部队回收以及对水雷对抗和反潜作战的支援。其模组化设计使其能够携带专用有效载荷、感测器和无人系统,从而增强作战灵活性。在日益复杂的海上安全挑战(包括领土争端、非对称威胁以及对快速反应能力的需求)下,作战潜舰的战略价值日益凸显。对作战潜舰研发的投资反映了在保持隐蔽性和作战安全性的同时,扩大海军作战范围的更广泛趋势。这些平台正日益被认为是现代海战中不可或缺的资产,弥合了传统水面作战和先进水下作战之间的差距。
科技对世界作战潜舰的影响
技术进步正在显着改变作战潜舰的能力,提升其作战性能、隐密性和作战弹性。现代推进系统,包括电力推进和混合动力推进,能够降低声学特征,使其更难被侦测到。先进的导航系统结合了声吶测绘、惯性导引和GPS定位,能够在复杂的水下环境中进行精确机动。配备多光谱探测、成像声吶和环境监测功能的感测器能够提供即时态势感知,从而实现精确侦察和威胁评估。自动化和人工智慧技术有助于自适应航线规划、威胁规避和作战最佳化,从而减轻操作人员的工作负荷并提高任务成功率。模组化酬载设计能够根据作战需求整合无人水下航行器、监视设备或专用作战系统。先进材料,例如轻质复合材料和耐腐蚀合金,能够提高耐久性,并在极端压力和温度波动下增强性能。 安全的通讯网路确保潜舰与指挥中心之间可靠的资料交换,即使在电子战环境下也能如此。网路安全措施可保护舰艇控制系统免受骇客攻击和电子干扰。这些技术创新使作战潜艇能够以更高的效率、灵活性和生存能力运行,使其成为现代海军战略和特种作战中至关重要的资产。
作战潜舰的关键驱动因素
多种因素正在推动全球作战潜舰的研发和部署。对包括情报收集、侦察和特种部队作战在内的隐蔽海上行动的需求日益增长,催生了对隐蔽水下平台的需求。近岸和争议水域的地缘政治紧张局势和区域衝突迫使各国利用快速反应、低可观测性的装备来加强其海上能力。推进系统、感测器系统、材料和自动化技术的进步支持了更快、更安静、更通用的舰艇的研发。 现代海军战略强调多域作战,将潜舰与水面舰队、无人平台和空中侦察结合,从而促进协同作战。用于部队现代化和非对称作战能力的预算拨款正在推动对潜舰平台的投资。以往衝突的作战经验表明,这些潜舰在提高态势感知能力、执行精确作战以及支援广泛的海军目标方面卓有成效。伙伴关係、国防合作和国内製造计划加速了研发和生产,确保及时采购。日益严峻的海上安全挑战,例如海盗活动、领土侵犯和海底基础设施保护,进一步推动了对专用潜艇解决方案的需求。这些因素使得作战潜舰成为现代海军战略的关键组成部分,将技术创新与作战需求紧密连结。 本报告分析了全球作战潜艇市场,深入探讨了影响该市场的技术、未来十年的预测以及区域趋势。
目录
作战潜舰市场报告定义
作战潜舰市场区隔
按地区
按类型
按推进方式
未来十年作战潜舰市场分析
作战潜舰市场技术
全球作战潜舰市场预测
区域作战潜舰市场趋势及预测
北美
驱动因素、限制因素与挑战
PEST分析
市场预测及情境分析
主要公司
供应商层级状况
公司标竿分析
欧洲
中东
亚太地区
南美洲
作战潜舰市场国家分析
美国
国防项目
最新消息
专利
当前市场技术成熟度
市场预测及情境分析
加拿大
义大利
法国
德国
荷兰
比利时
西班牙
瑞典
希腊
澳洲
南非
印度
中国
俄罗斯
韩国
日本
马来西亚
新加坡
巴西
作战潜舰市场机会矩阵
专家对作战潜舰市场的看法
结论
关于航空和国防市场报告
The Global Combat Submersible vehicles market is estimated at USD 5.52 billion in 2026, projected to grow to USD 8.62 billion by 2036 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.56% over the forecast period 2026-2036.

Introduction to Global Combat Submersible Vehicles
Combat submersible vehicles are specialized underwater platforms designed to support a range of military operations, providing stealth, mobility, and versatility in contested maritime environments. These vehicles enable covert deployment of personnel, equipment, and reconnaissance tools, allowing forces to conduct special operations, surveillance, and intelligence-gathering missions undetected. Unlike traditional submarines, combat submersibles are often smaller, more maneuverable, and optimized for rapid deployment and retrieval in shallow or restricted waters. Modern designs focus on hydrodynamic efficiency, noise reduction, and operational reliability, ensuring effective navigation under diverse conditions. They can operate independently or in coordination with larger naval vessels, facilitating precision insertions, extraction of special forces, and support for mine countermeasure or anti-submarine operations. With modular configurations, these vehicles can carry specialized payloads, sensors, or unmanned systems, enhancing mission flexibility. The increasing complexity of maritime security challenges, including territorial disputes, asymmetric threats, and the need for rapid response capabilities, has elevated the strategic value of combat submersibles. Investment in their development reflects a broader trend toward enhancing naval operational reach while maintaining stealth and operational security. These platforms are increasingly recognized as indispensable assets in modern naval warfare, bridging the gap between conventional surface operations and advanced underwater missions.
Technology Impact in Global Combat Submersible Vehicles
Technological advancements have dramatically transformed the capabilities of combat submersible vehicles, enhancing their operational performance, stealth, and mission versatility. Modern propulsion systems, including electric and hybrid drives, reduce acoustic signatures, making detection by adversaries more difficult. Advanced navigation systems, combining sonar mapping, inertial guidance, and GPS integration, allow precise maneuvering in complex underwater environments. Sensors equipped with multi-spectral detection, imaging sonar, and environmental monitoring provide real-time situational awareness, enabling accurate reconnaissance and threat assessment. Automation and artificial intelligence facilitate adaptive route planning, threat avoidance, and mission optimization, reducing operator workload and increasing mission success rates. Modular payload designs allow integration of unmanned underwater vehicles, surveillance equipment, or specialized combat systems depending on operational requirements. Advanced materials, such as lightweight composites and corrosion-resistant alloys, improve durability and enhance performance under extreme pressure and temperature variations. Secure communication networks ensure reliable data exchange between submersibles and command centers, even in contested electronic environments. Cybersecurity measures protect vehicle control systems from hacking or electronic interference. These technological innovations collectively enable combat submersible vehicles to operate with higher efficiency, flexibility, and survivability, making them crucial assets for modern naval strategies and special operations missions.
Key Drivers in Combat Submersible Vehicles
Several key factors drive the development and deployment of combat submersible vehicles globally. The increasing need for covert maritime operations, such as intelligence gathering, reconnaissance, and special forces insertions, creates demand for stealthy underwater platforms. Geopolitical tensions and regional disputes in coastal and contested waters compel nations to strengthen maritime capabilities with rapid-response, low-visibility assets. Technological progress in propulsion, sensor systems, materials, and automation supports the creation of vehicles that are faster, quieter, and more versatile. Modern naval strategies emphasize multi-domain operations, integrating submersible vehicles with surface fleets, unmanned platforms, and aerial reconnaissance for coordinated missions. Budget allocations toward force modernization and asymmetric warfare capabilities encourage investment in submersible platforms. Operational experience from past conflicts has demonstrated the effectiveness of these vehicles in enhancing situational awareness, conducting precision operations, and supporting broader naval objectives. Partnerships, defense collaborations, and domestic manufacturing initiatives accelerate research and production, ensuring timely acquisition. Increasing maritime security challenges, such as piracy, territorial incursions, and undersea infrastructure protection, further amplify the need for specialized submersible solutions. Collectively, these drivers establish combat submersible vehicles as critical components of modern naval doctrine, bridging technological innovation with operational necessity.
Regional Trends in Combat Submersible Vehicles
Regional trends in the deployment and development of combat submersible vehicles vary according to strategic priorities, security environments, and naval capabilities. North America focuses on highly advanced, long-endurance submersibles designed for special operations, deep reconnaissance, and integration with multi-domain networks. European nations prioritize interoperability, collaborative development programs, and modular platforms to balance capabilities with cost-effectiveness. In the Asia-Pacific region, rising maritime territorial disputes and the need for rapid coastal defense drive investment in domestically produced, versatile submersibles capable of operating in shallow waters and congested maritime zones. Middle Eastern countries emphasize tactical submersibles for surveillance, coastal protection, and special forces operations, often acquiring technology through partnerships or imports. African and South American nations focus on cost-efficient, operationally flexible designs to enhance maritime security without extensive investment in large naval fleets. Across regions, integration with unmanned underwater vehicles, advanced sensors, and real-time command networks is increasingly common. Regional exercises and joint operations support operational readiness while influencing vehicle design and capability requirements. Variations in strategic priorities, threat perception, and technological infrastructure shape the development of combat submersible vehicles worldwide, reflecting diverse operational needs while advancing stealth, mobility, and multi-role effectiveness.
Key Combat Submersible vehicles Program:
Teledyne Technologies Incorporated announced that its Huntsville, Alabama-based subsidiary, Teledyne Brown Engineering, has been awarded a sole-source contract by the Naval Sea Systems Command for the follow-on production of MK11 Shallow Water Combat Submersible systems. Including all available options, the contract carries a total value of $178 million. The MK11 SWCS is a manned combat submersible designed to support the covert insertion and extraction of Special Operations Forces in high-threat environments. Under an earlier agreement with the U.S. Special Operations Command, Teledyne Brown Engineering successfully completed the design, manufacturing, testing, and delivery of the Engineering Development Model of the system. Following the successful completion of the EDM phase, USSOCOM exercised contract options authorizing the production and delivery of additional MK11 SWCS units.
Table of Contents
Combat Submersible Vehicles Market - Table of Contents
Combat Submersible Vehicles Market Report Definition
Combat Submersible Vehicles Market Segmentation
By Region
By Type
By Propulsion
Combat Submersible Vehicles Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year combat submersible vehicles market analysis would give a detailed overview of missile and smart kits guidance market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Combat Submersible Vehicles Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Combat Submersible Vehicles Market Forecast
The 10-year combat submersible vehicles market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Combat Submersible Vehicles Market Trends & Forecast
The regional combat submersible vehicles market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Combat Submersible Vehicles Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Combat Submersible Vehicles Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Combat Submersible Vehicles Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2026-2036
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2026-2036
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Type, 2026-2036
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Propulsion, 2026-2036
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2026-2036
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Type, 2026-2036
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Propulsion, 2026-2036
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Combat Submersible Vehicles Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 2: Global Combat Submersible Vehicles Market Forecast, By Region, 2026-2036
- Figure 3: Global Combat Submersible Vehicles Market Forecast, By Type, 2026-2036
- Figure 4: Global Combat Submersible Vehicles Market Forecast, By Propulsion, 2026-2036
- Figure 5: North America, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 6: Europe, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 7: Middle East, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 8: APAC, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 9: South America, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 10: United States, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 11: United States, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 12: Canada, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 13: Canada, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 14: Italy, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 15: Italy, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 16: France, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 17: France, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 18: Germany, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 19: Germany, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 22: Belgium, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 23: Belgium, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 24: Spain, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 25: Spain, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 26: Sweden, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 27: Sweden, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 28: Brazil, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 29: Brazil, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 30: Australia, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 31: Australia, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 32: India, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 33: India, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 34: China, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 35: China, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 38: South Korea, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 39: South Korea, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 40: Japan, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 41: Japan, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 44: Singapore, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 45: Singapore, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Technology Maturation, 2026-2036
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Market Forecast, 2026-2036
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2026-2036
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Region (CAGR), 2026-2036
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Type (Cumulative Market), 2026-2036
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Type (CAGR), 2026-2036
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Propulsion (Cumulative Market), 2026-2036
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Propulsion (CAGR), 2026-2036
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Cumulative Market, 2026-2036
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Global Market, 2026-2036
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Total Market, 2026-2036
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Region, 2026-2036
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Type, 2026-2036
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Propulsion, 2026-2036
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, Total Market, 2026-2036
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Region, 2026-2036
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Type, 2026-2036
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, By Propulsion, 2026-2036
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Combat Submersible Vehicles Market, 2026-2036


