 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1164297
中国铀资源进口分析(2023-2032年)Research Report on China's Uranium Resource Import 2023-2032 |
||||||
近年来,我国核电发展突飞猛进。 到2022年底,中国将有53座商业核电站投入运行,总装机容量5560万千瓦。 在建核电站23座,总装机容量2419万千瓦。 中国核电在建容量连续多年位居世界第一。 随着中国核电装机容量的增加,对中国铀资源的需求也在增加。 中国铀资源贫乏,总储量不足20万吨,开采成本高,每年必须进口大量铀资源。
示例视图
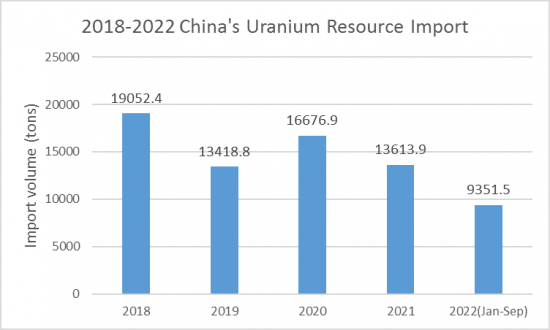
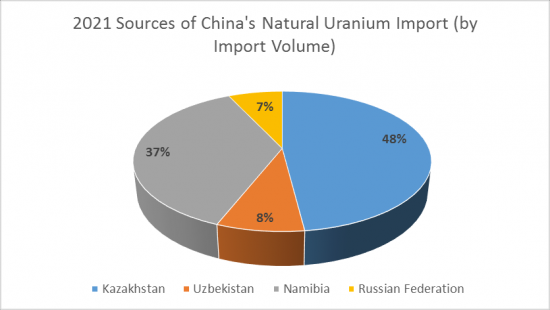
2021年我国将进口铀资源13613.9吨(同比下降18.4%),进口额13.1亿美元(同比下降22.6%)。 2022年前三季度,中国进口铀9351.5吨(同比增长5.2%),进口额13.6亿美元(同比增长48.5%)。
从 2018 年到 2022 年,铀的平均进口价格将保持波动。 2019年铀资源进口均价为125.2美元/公斤(同比上涨38.3%),但2019-2021年持续下降,2021年达到96.5美元/公斤。 2022年前三季度,铀的平均进口价格大幅上涨至145.6美元/公斤,比2021年同期上涨41.1%。
中国进口两类铀资源:天然铀和U235浓缩铀。 2021年中国将进口天然铀13535.8吨(占进口运费的99.4%),进口额12.1亿美元(占进口总额的92.4%)。 2021年中国从5个国家和地区进口天然铀资源。 按进口量计算,哈萨克斯坦是中国最大的天然铀进口来源国。 2021年,中国将从哈萨克斯坦进口价值5.5亿美元的铀资源6459.1吨(占进口总量的47.7%)。
随着中国核电厂数量的不断增加以及对铀资源的需求不断扩大,预计从 2023 年到 2032 年,中国的铀进口量将继续增加。
在本报告中,我们分析了中国铀资源进口市场,包括总体进口量和进口价值、主要进口来源地(2018-2022 年)、按类型分类的详细趋势、进口价格趋势,我们将汇总并发布主要市场信息驱动因素和製约因素、主要参与者的概况和战略,以及未来进口趋势的展望(2023-2032 年)。
内容
第一章中国铀进口分析(2018-2022)
- 中国铀资源进口规模
- 中国进口铀资源
- 中国铀资源进口值
- 中国铀进口价格
- 中国铀资源表观消费量
- 中国对进口铀资源的依赖
- 中国主要的铀资源进口国
- 进口量
- 进口价值
第2章中国天然铀进口分析(2018-2022)
- 进口量
- 进口价值
- 进口价格
- 依赖进口
- 按类型进行进口分析
- 进口量:按类型分类
- 导入值:按类型
- 进口价格:按类型
- 主要进口商
- 进口量
- 进口价值
第三章中国浓缩铀进口分析(2018-2022)
第四章中国铀资源主要进口来源地分析(2018-2022年)
- 哈萨克斯坦铀资源进口分析
- 从纳米比亚进口铀资源分析
- 从乌兹别克斯坦进口铀资源分析
- 从俄罗斯进口铀资源分析
- 从德国进口铀资源分析
- 从其他国家进口铀资源的分析
第5章中国铀进口展望(2023-2032)
- 影响中国铀资源进口的因素
- 有利因素
- 不利因素
- 中国铀进口预测 (2023-2032)
- 进口量预测
- 进口量预测:按主要进口来源
- 进口量预测:按主要类型
In recent years, China has seen rapid development of nuclear power. By the end of 2022, China had 53 commercial nuclear power units in operation, with a total installed capacity of 55.6 million kilowatts. There are 23 nuclear power units under construction, with a total installed capacity of 24.19 million kilowatts. China's installed capacity of nuclear power generation units under construction has remained the world's largest for many years. As China's installed nuclear power capacity rises, so does the country's demand for uranium resources. Since China's indigenous uranium resources are poor, with total reserves of no more than 200,000 tons and high mining costs, China needs to import large amounts of uranium resources every year.
SAMPLE VIEW


In 2021, China's imports of uranium resources reached 13,613.9 tons, down 18.4% year-on-year, and the import value of US$1.31 billion, down 22.6% year-on-year. In the first three quarters of 2022, China imported 9,351.5 tons of uranium, up 5.2% year-on-year, and US$1.36 billion in imports, up 48.5% year-on-year, according to CRI analysis.
The average import price of uranium is volatile in 2018-2022. In 2019, the average import price of uranium resources in China is US$125.2 per kg, an increase of 38.3% year-on-year. According to CRI's analysis, the average import price of uranium decreases continuously from 2019 to 2021, with the average import price of uranium decreasing to US$96.5 per kg in 2021. In the first three quarters of 2022, the average import price of uranium increases significantly to US$145.6 per kg, an increase of 41.1% compared to the same period in 2021.
China imports uranium resources mainly in two categories: natural uranium and U235 enriched uranium. In 2021, China imported 13,535.8 tons of natural uranium, accounting for 99.4% of total imports, and the import value of US$1.21 billion, accounting for 92.4% of total imports. In 2021, China imported natural uranium resources from five countries and regions. According to CRI's analysis, Kazakhstan is the largest source of natural uranium imports to China by import volume. In 2021, China imported 6,459.1 tons of natural uranium from Kazakhstan, accounting for 47.7% of total natural uranium imports, and US$550 million, or 45.6% of total natural uranium imports.
China lacks indigenous uranium resources and is highly dependent on imports. China's nuclear power generation accounts for approximately 5% of the country's total power generation, leaving much room for improvement, and CRI expects that China's uranium imports are expected to continue to rise from 2023-2032 as the country's installed nuclear power generation rises further and demand for uranium resources continues to grow.
Topics covered:
- China's Uranium Resource Import Status and Major Sources in 2018-2022
- What is the Impact of COVID-19 on China's Uranium Resource Import?
- Which Companies are the Major Players in China's Uranium Resource Import Market and What are their Competitive Benchmarks?
- Key Drivers and Market Opportunities in China's Uranium Resource Import
- What are the Key Drivers, Challenges, and Opportunities for China's Uranium Resource Import during 2023-2032?
- What is the Expected Revenue of China's Uranium Resource Import during 2023-2032?
- What are the Strategies Adopted by the Key Players in the Market to Increase Their Market Share in the Industry?
- What are the Competitive Advantages of the Major Players in China's Uranium Resource Import Market?
- Which Segment of China's Uranium Resource Import is Expected to Dominate the Market in 2032?
- What are the Major Adverse Factors Facing China's Uranium Resource Import?
Table of Contents
1. 2018-2022 China Uranium Resources Import Analysis
- 1.1. Import Scale of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.1.1. Import Volume of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.1.2. Import Value of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.1.3. Import Price of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.1.4. Apparent Consumption of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.1.5. Import Dependence of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.2 Major Import Sources of Uranium Resources in China
- 1.2.1. By Import Volume
- 1.2.2. By Import Value
2. China's Natural Uranium Import Analysis, 2018-2022
- 2.1 Natural Uranium Import Volume
- 2.2 Natural Uranium Import Volume
- 2.3. Natural Uranium Import Prices
- 2.4 Import Dependence of Natural Uranium
- 2.5 Import Analysis of Natural Uranium by Type
- 2.5.1 Natural Uranium Imports by Type
- 2.5.2 Import Value of Natural Uranium by Category
- 2.5.3. Import Prices of Natural Uranium by Category
- 2.6 Sources of Natural Uranium Imports
- 2.6.1. By Import Volume
- 2.6.2. By Import Value
3. 2018-2022 China Import Analysis of Enriched Uranium
- 3.1. Import Volume of Enriched Uranium
- 3.2. Import Value of Enriched Uranium
- 3.3. Import Price of Enriched Uranium
- 3.4 Import Dependence of Enriched Uranium
- 3.5 Analysis of Various Types of Enriched Uranium Imports
- 3.5.1 Enriched Uranium Imports by Type
- 3.5.2. Import Value of Enriched Uranium by Type
- 3.5.3. Import Prices of Various Types of Enriched Uranium
- 3.6 Import Sources of Enriched Uranium
- 3.6.1. By Import Volume
- 3.6.2. By Import Value
4. 2018-2022 Analysis of Major Import Sources of Uranium Resources in China
- 4.1 Analysis of Uranium Resources Imports from Kazakhstan
- 4.2. Analysis of Uranium Resources Imports from Namibia
- 4.3 Analysis of Uranium Resources Imports from Uzbekistan
- 4.4 Analysis of Uranium Resources Imports from the Russian Federation
- 4.5 Analysis of Uranium Imports into Germany
- 4.6 Analysis of Other Uranium Resources Imports
5. China's Uranium Resource Import Outlook 2023-2032
- 5.1 Factors Affecting China's Uranium Resource Imports
- 5.1.1 Favorable Factors
- 5.1.2 Disadvantageous Factors
- 5.2. China's Uranium Resource Import Forecast, 2023-2032
- 5.2.1 Import Volume Forecast
- 5.2.2. Forecast of Major Import Sources
- 5.2.3. Forecast of Major Imported Uranium Resources Types










