 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1740757
商业航太发射市场机会、成长动力、产业趋势分析及 2025 - 2034 年预测Commercial Space Launch Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
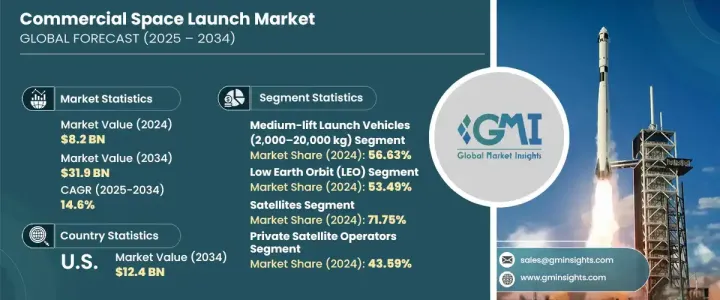
2024年,全球商业航太发射市场规模达82亿美元,预计2034年将以14.6%的复合年增长率成长,达到319亿美元。这一爆炸性增长的动力源于航太技术的快速进步、发射服务价格的日益亲民,以及对互联互通、地球观测和科学研究的需求日益增长。随着商业参与者变得更加活跃和具有影响力,全球航太经济正经历一场根本性的转变,将曾经由政府主导的领域转变为一个竞争激烈、创新驱动的产业。卫星的小型化和製造成本的降低,使得私人和机构客户更容易进入太空。
随着人们对低地球轨道卫星星座、气象监测、即时成像和下一代通讯的兴趣日益浓厚,商业航太发射领域已发展成为更广泛的航太生态系统的重要支柱。随着航太经济超越传统探索,走向多元化,资料服务、星间连结和天基基础设施领域的机会不断开拓新的领域。世界各国正大力投资发射基础设施、监管改革和研发,这使得商业航太发射市场成为吸引资本和人才的磁铁。
| 市场范围 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 预测年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 82亿美元 |
| 预测值 | 319亿美元 |
| 复合年增长率 | 14.6% |
随着部署紧凑型有效载荷的可行性不断提高,小型卫星的发射需求也随之飙升,这些载荷可用于通讯、地球成像、气候追踪和科学实验等多种用途。能够更频繁、更经济地发射小型卫星,对商业企业和政府机构来说都将带来翻天覆地的变化。发射成本的大幅降低以及经济高效的小型化技术的引入,加速了这一转变。
因此,企业现在可以更广泛地使用轨道平台,从而能够快速部署创新卫星服务。私营部门越来越多地参与发射运营,加上政府的支持性政策和简化的许可程序,正在重塑全球航太发射生态系统。越来越多的专用发射场和区域航太港正在建设中,以支援日益增加、种类繁多的商业任务。这种扩张吸引了更广泛的机构和商业客户群体,大幅提升了发射频率。
然而,地缘政治贸易紧张局势和国际政策波动加剧了该行业的成本结构。航太零件和推进系统的进口关税扰乱了供应链,并增加了生产成本。为了降低这些风险,企业正在转向在地化生产和国内采购材料。这项战略重心不仅符合国家航太政策,还能透过减少对国际供应商的依赖来增强营运稳定性。国内采购有助于更好地控製成本,缩短交货时间,并确保更好地遵守安全法规。
2024年,中型运载火箭占据了56.63%的市场份额,占据了市场主导地位。这些火箭将有效载荷容量和运行效率完美结合,使其成为各种发射任务的热门选择。其灵活性使其既能承载单一客户的有效载荷,也能承担共乘任务,这对商业营运商和政府机构都极具吸引力。中型运载火箭能够同时到达低地球轨道 (LEO) 和地球静止转移轨道 (GTO),因此仍然是发射行业的主力。
低地球轨道在轨道类型方面保持领先地位,2024 年占据了 53.49% 的市场。低地球轨道的普及源自于其低延迟、更快的资料传输速度和更低的部署成本等优势。这些因素对于宽频连线、监控和环境监测等应用至关重要。低地球轨道距离地球较近,因此可以以可扩展且经济高效的方式部署密集的卫星星座。致力于提供低延迟通讯服务和即时资料解决方案的公司越来越多地将目光瞄准低地球轨道,使其成为商业太空活动的策略热点。
预计到2034年,美国商业航太发射市场规模将达到124亿美元,这得益于强而有力的公私合作。精简的法规、创新激励措施以及对基础设施的投资,正推动美国成为全球航太领域的领导者。公共资金、与私人企业的合作以及研发计画正在加速可重复使用发射系统和模组化卫星有效载荷的突破。各机构正持续与商业参与者携手合作,以推动下一代发射能力的发展。
塑造全球市场格局的关键参与者包括SpaceX、联合发射联盟(United Launch Alliance)、美国火箭实验室(Rocket Lab USA)、蓝色起源(Blue Origin)和赛峰集团(Safran SA)。这些公司正在积极开发可重复使用的发射系统,以降低任务成本并提高发射频率。与国防组织和电信营运商的战略合作使他们能够获得长期合约。透过投资私人发射基础设施、垂直整合製造流程以及建立全球合作伙伴关係,这些公司正在增强供应链的韧性、提高营运灵活性并拓展其国际影响力。
目录
第一章:方法论与范围
第二章:执行摘要
第三章:行业洞察
- 产业生态系统分析
- 川普政府关税
- 对贸易的影响
- 贸易量中断
- 报復措施
- 对产业的影响
- 供给面影响(服务提供者)
- 关键服务价格波动
- 供应链重组
- 生产成本影响
- 需求面影响(定价)
- 价格传导至终端市场
- 市占率动态
- 消费者反应模式
- 供给面影响(服务提供者)
- 受影响的主要公司
- 策略产业反应
- 伺服器提供者重新配置
- 定价和服务策略
- 政策参与
- 展望与未来考虑
- 对贸易的影响
- 产业衝击力
- 成长动力
- 小型卫星发射需求成长
- 可重复使用运载火箭日益受到关注
- 私人发射提供者和太空港的出现
- 加强政府与私部门的合作
- 太空旅游和亚轨道飞行的扩展
- 产业陷阱与挑战
- 发射成本高且资本密集
- 监管和安全合规的复杂性
- 成长动力
- 成长潜力分析
- 监管格局
- 技术格局
- 未来市场趋势
- 差距分析
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL分析
第四章:竞争格局
- 介绍
- 公司市占率分析
- 主要市场参与者的竞争分析
- 竞争定位矩阵
- 策略仪表板
第五章:市场估计与预测:依酬载类型,2021-2034
- 主要趋势
- 卫星
- 货运与物流
- 载人航太
- 行星际任务
第六章:市场估计与预测:按运载火箭类型,2021-2034
- 主要趋势
- 小型运载火箭(< 2,000 公斤)
- 中型运载火箭(2,000-20,000公斤)
- 重型运载火箭(> 20,000 公斤)
第七章:市场估计与预测:依轨道类型,2021-2034
- 主要趋势
- 低地球轨道(LEO)
- 地球静止轨道(GEO)
- 中地球轨道(MEO)
- 极地和太阳同步轨道(SSO)
- 深空
第八章:市场估计与预测:依最终用途,2021-2034
- 私营卫星营运商
- 政商合作
- 太空旅游公司
- 研究与学术机构
- 国防与军事
第九章:市场估计与预测:按地区,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 西班牙
- 义大利
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳新银行
- 韩国
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 中东和非洲
- 阿联酋
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
第十章:公司简介
- Agnikul Cosmos
- Astra
- Blue Origin
- Firefly Aerospace
- GALACTIC ENERGY
- Isar Aerospace SE
- ispace
- LandSpace
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Northrop Grumman
- PLD Space
- Relativity Space
- Rocket Lab USA
- Safran SA
- SpaceX
- United Launch Alliance, LLC.
- Skyroot Aerospace
The Global Commercial Space Launch Market was valued at USD 8.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.6% to reach USD 31.9 billion by 2034. This explosive growth is fueled by rapid advancements in space technologies, increasing affordability of launch services, and rising demand for connectivity, Earth observation, and scientific research. The global space economy is undergoing a fundamental shift as commercial players become more active and influential, transforming what was once a government-dominated sector into a competitive, innovation-driven industry. Miniaturization of satellites and reduced manufacturing costs have made it easier for private and institutional customers to access space.

With growing interest in low Earth orbit satellite constellations, weather monitoring, real-time imaging, and next-generation communications, the commercial space launch sector has evolved into a key pillar of the broader aerospace ecosystem. As the space economy diversifies beyond traditional exploration, opportunities in data services, inter-satellite links, and space-based infrastructure continue to open new frontiers. Countries around the world are investing heavily in launch infrastructure, regulatory reform, and research and development, making the commercial space launch market a magnet for both capital and talent.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $8.2 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $31.9 Billion |
| CAGR | 14.6% |
Demand for small satellite launches has skyrocketed due to the rising feasibility of deploying compact payloads that serve a wide range of functions across communication, Earth imaging, climate tracking, and scientific experimentation. The ability to launch smaller satellites more frequently and affordably is a game-changer for both commercial enterprises and government agencies. This transformation has been accelerated by significant reductions in launch costs and the introduction of cost-effective miniaturization technologies.
As a result, companies now have greater access to orbital platforms, enabling the rapid deployment of innovative satellite services. Increased participation from the private sector in launch operations, combined with supportive government policies and streamlined licensing procedures, is reshaping the global space launch ecosystem. A growing number of dedicated launch sites and regional spaceports are being developed to support the increasing volume and variety of commercial missions. This expansion is drawing in a broader base of institutional and commercial clients, contributing to a sharp increase in launch frequency.
However, geopolitical trade tensions and fluctuating international policies have added complexity to the industry's cost structure. Import tariffs on aerospace components and propulsion systems have disrupted supply chains and increased production costs. To mitigate these risks, companies are moving toward localizing production and sourcing materials domestically. This strategic pivot not only aligns with national space policies but also enhances operational stability by reducing reliance on international suppliers. Domestic sourcing supports better cost control, improves delivery timelines, and ensures greater compliance with security regulations.
In 2024, medium-lift launch vehicles dominated the market with a 56.63% share. These rockets offer the ideal combination of payload capacity and operational efficiency, making them a popular choice for a broad spectrum of launch missions. Their flexibility allows them to accommodate both single-customer payloads and ride-share missions, which is highly attractive to commercial operators and government agencies alike. With capabilities to reach both low Earth orbit (LEO) and geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), medium-lift vehicles remain the workhorses of the launch industry.
Low Earth orbit maintained the lead by orbit type, capturing 53.49% of the market in 2024. Its popularity stems from advantages such as low latency, faster data transmission, and reduced deployment costs. These factors are critical for applications like broadband connectivity, surveillance, and environmental monitoring. LEO's proximity to Earth allows for the deployment of dense satellite constellations in a scalable, cost-efficient manner. Companies aiming to deliver low-latency communication services and real-time data solutions are increasingly targeting LEO, making it a strategic hotspot for commercial space activity.
The United States Commercial Space Launch Market is forecasted to reach USD 12.4 billion by 2034, underpinned by strong public-private collaboration. Streamlined regulations, innovation incentives, and investments in infrastructure are driving the U.S. forward as a global space leader. Public funding, partnerships with private firms, and R&D initiatives are fast-tracking breakthroughs in reusable launch systems and modular satellite payloads. Agencies continue to work hand-in-hand with commercial players to advance next-generation launch capabilities.
Key players shaping the global market landscape include SpaceX, United Launch Alliance, Rocket Lab USA, Blue Origin, and Safran S.A. These companies are actively developing reusable launch systems to lower mission costs and increase launch frequency. Strategic collaborations with defense organizations and telecom providers are enabling them to secure long-term contracts. By investing in private launch infrastructure, vertically integrating manufacturing processes, and entering global partnerships, these firms are strengthening supply chain resilience, increasing operational flexibility, and extending their international reach.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology and Scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definitions
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.3.1 Base year calculation
- 1.3.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.4 Forecast model
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.5.2 Data mining sources
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 360° synopsis
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.2 Trump administration tariffs
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.2.1.1 Trade volume disruptions
- 3.2.1.2 Retaliatory measures
- 3.2.2 Impact on the industry
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (service providers)
- 3.2.2.1.1 Price volatility in key services
- 3.2.2.1.2 Supply chain restructuring
- 3.2.2.1.3 Production cost implications
- 3.2.2.2 Demand-side impact (pricing)
- 3.2.2.2.1 Price transmission to end markets
- 3.2.2.2.2 Market share dynamics
- 3.2.2.2.3 Consumer response patterns
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (service providers)
- 3.2.3 Key companies impacted
- 3.2.4 Strategic industry responses
- 3.2.4.1 Server provider reconfiguration
- 3.2.4.2 Pricing and service strategies
- 3.2.4.3 Policy engagement
- 3.2.5 Outlook and future considerations
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.3 Industry impact forces
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3.1.1 Growth in small satellite launch demand
- 3.3.1.2 Rising focus on reusable launch vehicles
- 3.3.1.3 Emergence of private launch providers and spaceports
- 3.3.1.4 Increased government-private sector collaborations
- 3.3.1.5 Expansion of space tourism and suborbital flights
- 3.3.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.3.2.1 High launch costs and capital intensity
- 3.3.2.2 Regulatory and safety compliance complexities
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.4 Growth potential analysis
- 3.5 Regulatory landscape
- 3.6 Technology landscape
- 3.7 Future market trends
- 3.8 Gap analysis
- 3.9 Porter's analysis
- 3.10 PESTEL analysis
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategy dashboard
Chapter 5 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Payload Type, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Satellites
- 5.3 Cargo & logistics
- 5.4 Human spaceflight
- 5.5 Interplanetary missions
Chapter 6 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Launch Vehicle Type, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Small-lift launch vehicles (< 2,000 kg)
- 6.3 Medium-lift launch vehicles (2,000–20,000 kg)
- 6.4 Heavy-lift launch vehicles (> 20,000 kg)
Chapter 7 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Orbit Type, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Low earth orbit (LEO)
- 7.3 Geostationary orbit (GEO)
- 7.4 Medium earth orbit (MEO)
- 7.5 Polar & sun-synchronous orbit (SSO)
- 7.6 Deep space
Chapter 8 Market Estimates & Forecast, By End Use, 2021-2034 (USD Billion)
- 8.1 Private satellite operators
- 8.2 Government-commercial partnerships
- 8.3 Space tourism companies
- 8.4 Research & academic institutions
- 8.5 Defense & military
Chapter 9 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Region, 2021 – 2034 (USD Billion)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 North America
- 9.2.1 U.S.
- 9.2.2 Canada
- 9.3 Europe
- 9.3.1 Germany
- 9.3.2 UK
- 9.3.3 France
- 9.3.4 Spain
- 9.3.5 Italy
- 9.4 Asia Pacific
- 9.4.1 China
- 9.4.2 India
- 9.4.3 Japan
- 9.4.4 ANZ
- 9.4.5 South Korea
- 9.5 Latin America
- 9.5.1 Brazil
- 9.5.2 Mexico
- 9.6 Middle East and Africa
- 9.6.1 UAE
- 9.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 9.6.3 South Africa
Chapter 10 Company Profiles
- 10.1 Agnikul Cosmos
- 10.2 Astra
- 10.3 Blue Origin
- 10.4 Firefly Aerospace
- 10.5 GALACTIC ENERGY
- 10.6 Isar Aerospace SE
- 10.7 ispace
- 10.8 LandSpace
- 10.9 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- 10.10 Northrop Grumman
- 10.11 PLD Space
- 10.12 Relativity Space
- 10.13 Rocket Lab USA
- 10.14 Safran S.A.
- 10.15 SpaceX
- 10.16 United Launch Alliance, LLC.
- 10.17 Skyroot Aerospace










