 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1740954
运输燃料电池市场机会、成长动力、产业趋势分析及 2025 - 2034 年预测Transport Fuel Cell Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
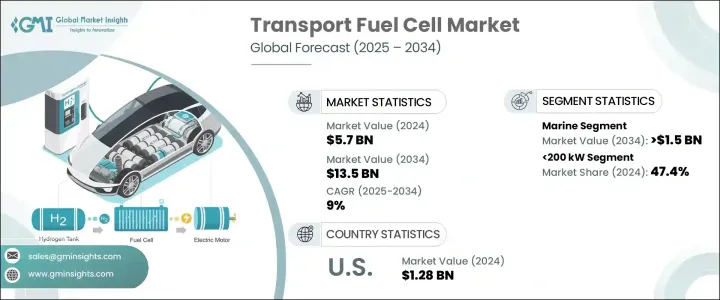
2024 年全球运输燃料电池市场价值为 57 亿美元,预计到 2034 年将以 9% 的复合年增长率增长,达到 135 亿美元,这得益于政府对清洁能源应用的支持力度加大以及持续努力发展加氢基础设施。随着各国加快实现运输脱碳目标并越来越多地接受公路、铁路、海运和空运等各种运输方式的氢动力出行,市场正获得强劲发展势头。 PEM 燃料电池技术的进步,加上对建构弹性氢生态系统的更大关注,正在重塑零排放运输的未来。随着绿色氢气生产规模的扩大和燃料电池电动车 (FCEV) 竞争力的增强,该产业有望经历变革性成长。航空和航运等领域对可靠、可扩展的氢能的需求激增,这为製造商创造了新的机会,并推动了对高需求环境的尖端燃料电池设计的投资。
然而,运输燃料电池市场并非一帆风顺。不断变化的国际贸易格局带来了巨大的阻力。美国政府对来自中国和墨西哥等主要製造业中心的进口产品征收新关税,扰乱了全球供应链。这些措施推高了燃料电池电动车(FCEV)所用关键零件(例如燃料电池电堆、电力电子设备和先进系统)的成本结构。随着生产和采购成本的上升,製造商面临艰难的抉择,这可能导致汽车价格上涨,使FCEV在价格敏感的市场中难以普及。这可能会推迟FCEV在尚未实现与内燃机(ICE)汽车成本平价的地区的普及。
| 市场范围 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 预测年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 57亿美元 |
| 预测值 | 135亿美元 |
| 复合年增长率 | 9% |
预计到2034年,运输燃料电池市场中的船舶部分将创造15亿美元的产值。这一成长主要源自于整个航运业持续进行的改装工作,例如渡轮、拖船和货船等船舶正在配备低排放推进系统。产业领导者正在设计专门的燃料电池解决方案,以满足海上严格的性能和耐用性标准。同时,世界各地的港口当局正在大力投资加氢基础设施,这体现了将氢能纳入清洁航运走廊和零排放港口策略的更广泛承诺。
预计到2034年,200千瓦至1兆瓦的燃料电池系统将以8%的复合年增长率成长。这些中高容量模组凭藉其模组化特性、系统冗余和车队营运的可扩展性,正迅速成为重型运输应用的首选。随着绿氢能的日益普及,中国和韩国等国正推出数千辆搭载200-300千瓦燃料电池堆的公车和物流卡车。
2024年,美国运输燃料电池市场产值达12.8亿美元,这得益于其强大的政策环境,包括为氢气生产、FCEV采购和基础设施建设提供激励措施和税收抵免。旨在减少排放和加速向清洁交通转型的联邦和州级项目正在显着推动市场成长。这种政策驱动的势头,加上公私合作对加氢枢纽和加氢站的投资,使美国成为全球向零排放出行转型的重要参与者。
运输燃料电池产业的主要参与者包括丰田汽车、Stellantis、PowerCell Sweden、Quantron、尼古拉公司、ElringKlinger、本田汽车、沃尔沃集团、通用汽车和 Hyzon Motors。各公司正在大力投资垂直整合、合资企业和区域扩张策略。许多公司正在提升研发能力,以开发耐用、经济高效的燃料电池堆,同时扩大产能,使其更贴近目标市场。与物流公司和公共交通机构的合作有助于获得长期合约并扩大氢能基础设施的规模。一些公司专注于为特定车辆类别(船舶、铁路或商用车队)提供客製化解决方案,根据特定的最终用途需求客製化燃油效率和系统性能。
目录
第一章:方法论与范围
第二章:执行摘要
第三章:行业洞察
- 产业生态系统
- 川普政府关税分析
- 对贸易的影响
- 贸易量中断
- 报復措施
- 对产业的影响
- 供应方影响(原料)
- 关键材料价格波动
- 供应链重组
- 生产成本影响
- 需求面影响(售价)
- 价格传导至终端市场
- 市占率动态
- 消费者反应模式
- 供应方影响(原料)
- 受影响的主要公司
- 策略产业反应
- 供应链重组
- 定价和产品策略
- 政策参与
- 展望与未来考虑
- 对贸易的影响
- 监管格局
- 产业衝击力
- 成长动力
- 产业陷阱与挑战
- 成长潜力分析
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL分析
第四章:竞争格局
- 介绍
- 战略仪表板
- 创新与技术格局
第五章:市场规模及预测:依产能,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- < 200 千瓦
- 200千瓦-1兆瓦
- ≥1兆瓦
第六章:市场规模及预测:依产品,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 质子交换膜燃料电池
- 直接甲醇燃料电池
- 固态氧化物燃料电池
- 平安金融中心及亚洲金融中心
- MCFC
第七章:市场规模及预测:依最终用途,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 海洋
- 铁路
- 燃料电池电动车
- 其他的
第八章:市场规模及预测:按地区,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 奥地利
- 亚太地区
- 日本
- 韩国
- 中国
- 印度
- 菲律宾
- 越南
- 中东和非洲
- 南非
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿联酋
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 秘鲁
- 墨西哥
第九章:公司简介
- Toyota Motors
- Honda Motors
- Nikola Corporation
- PowerCell Sweden
- ElringKlinger
- Volvo Group
- General Motors
- Stellantis
- Hyzon
- Quantron
The Global Transport Fuel Cell Market was valued at USD 5.7 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 9% to reach USD 13.5 billion by 2034, driven by rising government support for clean energy adoption and ongoing efforts to develop hydrogen refueling infrastructure. The market is gaining strong momentum as nations accelerate their transport decarbonization goals and increasingly accept hydrogen-powered mobility across a wide range of transportation modes, including road, rail, marine, and air. Advances in PEM fuel cell technologies, combined with a greater focus on building resilient hydrogen ecosystems, are reshaping the future of zero-emission transportation. As green hydrogen production scales up and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) become more competitive, the industry is positioned to experience transformative growth. Sectors like aviation and shipping are witnessing a surge in demand for reliable, scalable hydrogen power, creating new opportunities for manufacturers and fueling investment into cutting-edge fuel cell designs tailored for high-demand environments.

However, the transport fuel cell market is not without challenges. Evolving international trade dynamics are presenting major headwinds. The introduction of new tariffs by the U.S. government on imports from key manufacturing hubs such as China and Mexico is disrupting global supply chains. These measures are driving up the cost structure of critical components like fuel cell stacks, power electronics, and advanced systems used in FCEVs. With rising production and sourcing costs, manufacturers are facing tough decisions that could result in higher vehicle pricing, making FCEVs less accessible in price-sensitive markets. This could delay adoption in regions where cost parity with internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles has yet to be achieved.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $5.7 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $13.5 Billion |
| CAGR | 9% |
The marine segment within the transport fuel cell market is projected to generate USD 1.5 billion by 2034. Much of this growth comes from ongoing retrofitting efforts across the maritime sector, where vessels such as ferries, tugboats, and cargo ships are being outfitted with low-emission propulsion systems. Industry leaders are designing specialized fuel cell solutions that meet the rigorous performance and durability standards required at sea. At the same time, port authorities worldwide are heavily investing in hydrogen refueling infrastructure, reflecting a broader commitment to integrating hydrogen into clean shipping corridors and zero-emission port strategies.
Fuel cell systems ranging from 200 kW to 1 MW are expected to grow at a CAGR of 8% through 2034. These medium- to high-capacity modules are rapidly becoming the preferred choice for heavy-duty transport applications, thanks to their modular nature, system redundancy, and scalability for fleet operations. With green hydrogen becoming increasingly available, countries like China and South Korea are rolling out thousands of buses and logistics trucks powered by fuel cell stacks in the 200-300 kW range.
The United States transport fuel cell market generated USD 1.28 billion in 2024, supported by a robust policy environment that offers incentives and tax credits for hydrogen production, FCEV procurement, and infrastructure development. Federal and state programs aimed at cutting emissions and accelerating the transition to clean transportation are significantly driving market growth. This policy-driven momentum, combined with public-private investments in hydrogen hubs and refueling stations, positions the U.S. as a major player in the global shift toward zero-emission mobility.
Key players in the transport fuel cell industry include Toyota Motors, Stellantis, PowerCell Sweden, Quantron, Nikola Corporation, ElringKlinger, Honda Motors, Volvo Group, General Motors, and Hyzon Motors. Companies are investing heavily in vertical integration, joint ventures, and regional expansion strategies. Many are enhancing their R&D capabilities to develop durable, cost-efficient fuel cell stacks while expanding manufacturing capacity closer to target markets. Partnerships with logistics firms and public transit agencies are helping secure long-term contracts and scale hydrogen infrastructure. Several players are focusing on customized solutions for specific vehicle classes-marine, rail, or commercial fleets-tailoring fuel efficiency and system performance to specific end-use demands.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology & Scope
- 1.1 Research design
- 1.2 Base estimates & calculations
- 1.3 Forecast model
- 1.4 Primary research & validation
- 1.4.1 Primary sources
- 1.4.2 Data mining sources
- 1.5 Market definitions
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry synopsis, 2021 – 2034
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem
- 3.2 Trump administration tariff analysis
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.2.1.1 Trade volume disruptions
- 3.2.1.2 Retaliatory measures
- 3.2.2 Impact on the industry
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (raw materials)
- 3.2.2.1.1 Price volatility in key material
- 3.2.2.1.2 Supply chain restructuring
- 3.2.2.1.3 Production cost implications
- 3.2.2.2 Demand-side impact (selling price)
- 3.2.2.2.1 Price transmission to end markets
- 3.2.2.2.2 Market share dynamics
- 3.2.2.2.3 Consumer response patterns
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact (raw materials)
- 3.2.3 Key companies impacted
- 3.2.4 Strategic industry responses
- 3.2.4.1 Supply chain reconfiguration
- 3.2.4.2 Pricing and product strategies
- 3.2.4.3 Policy engagement
- 3.2.5 Outlook and future considerations
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.3 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4 Industry impact forces
- 3.4.1 Growth drivers
- 3.4.2 Industry pitfalls & challenges
- 3.5 Growth potential analysis
- 3.6 Porter's analysis
- 3.6.1 Bargaining power of suppliers
- 3.6.2 Bargaining power of buyers
- 3.6.3 Threat of new entrants
- 3.6.4 Threat of substitutes
- 3.7 PESTEL analysis
Chapter 4 Competitive landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Strategic dashboard
- 4.3 Innovation & technology landscape
Chapter 5 Market Size and Forecast, By Capacity, 2021 – 2034 (USD Million & MW)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 < 200 kW
- 5.3 200 kW - 1 MW
- 5.4 ≥ 1 MW
Chapter 6 Market Size and Forecast, By Product, 2021 – 2034 (USD Million & MW)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 PEMFC
- 6.3 DMFC
- 6.4 SOFC
- 6.5 PAFC & AFC
- 6.6 MCFC
Chapter 7 Market Size and Forecast, By End Use, 2021 – 2034 (USD Million & MW)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Marine
- 7.3 Railways
- 7.4 FCEVs
- 7.5 Others
Chapter 8 Market Size and Forecast, By Region, 2021 – 2034 (USD Million & MW)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 North America
- 8.2.1 U.S.
- 8.2.2 Canada
- 8.3 Europe
- 8.3.1 Germany
- 8.3.2 UK
- 8.3.3 France
- 8.3.4 Italy
- 8.3.5 Spain
- 8.3.6 Austria
- 8.4 Asia Pacific
- 8.4.1 Japan
- 8.4.2 South Korea
- 8.4.3 China
- 8.4.4 India
- 8.4.5 Philippines
- 8.4.6 Vietnam
- 8.5 Middle East & Africa
- 8.5.1 South Africa
- 8.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 8.5.3 UAE
- 8.6 Latin America
- 8.6.1 Brazil
- 8.6.2 Peru
- 8.6.3 Mexico
Chapter 9 Company Profiles
- 9.1 Toyota Motors
- 9.2 Honda Motors
- 9.3 Nikola Corporation
- 9.4 PowerCell Sweden
- 9.5 ElringKlinger
- 9.6 Volvo Group
- 9.7 General Motors
- 9.8 Stellantis
- 9.9 Hyzon
- 9.10 Quantron







