 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1750495
铜及铜合金废料及回收市场机会、成长动力、产业趋势分析及2025-2034年预测Copper And Copper Alloy Scrap and Recycling Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
2024年,全球铜及铜合金废料及回收市场规模达424亿美元,预计到2034年将以10.2%的复合年增长率增长,达到1196亿美元,这主要得益于工业活动的不断增长和全球对永续发展的推动。世界各国政府对循环经济的重视,导致对铜废料及其合金的需求不断增加。再生铜因其优异的导电性、可回收性和高应用价值,正日益成为从电气到建筑等各行各业的重要资源。
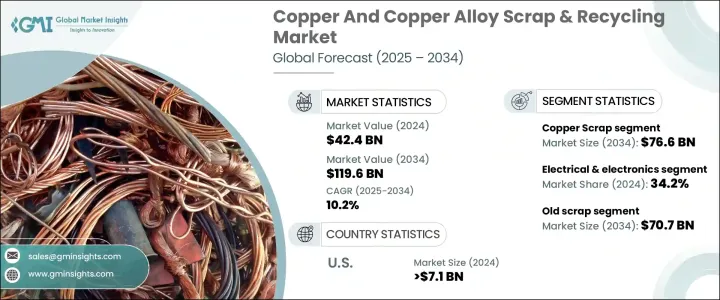
电气和电子产业在推动再生铜需求方面发挥关键作用,因为它消耗了全球60%的铜。由于铜具有无与伦比的导电性,该行业需要铜来製造从电线到电路板的各种产品。此外,随着电动车、再生能源和相关基础设施的兴起,全球电气化进程持续推进,铜回收已成为供应链中的关键组成部分。此外,铜在建筑领域的作用日益扩大,尤其是在亚太和中东等新兴市场,它被用于管道、覆层、屋顶和电线。
| 市场范围 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 预测年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 424亿美元 |
| 预测值 | 1196亿美元 |
| 复合年增长率 | 10.2% |
2024年,废铜市场价值为275亿美元,预计2034年将大幅成长至766亿美元。废铜仍然是再生铜的主要来源,由于其储量丰富、价值高且性能优异,在各行各业都至关重要。铜凭藉其优异的导电性、耐腐蚀性和可重复利用的特性,备受青睐,尤其是在电气和建筑等行业。随着各行各业对更永续解决方案的需求不断增长,废铜的使用有助于减少对原生铜开采的需求,这与全球回收和优化资源的努力相一致。
电气和电子产业在铜及铜合金废料及回收市场中占据主导地位,2024 年将占据 34.2% 的份额,这得益于铜在手机、智慧型平板电脑、电脑和其他现代电子产品中的关键作用,铜在这些产品中被广泛用于电线、电路板和连接器。铜作为可靠的电导体,使其成为该行业不可或缺的材料,支撑了对原生铜和再生铜的需求。随着技术创新的持续,尤其是在行动和智慧设备生产领域,电子产品对铜的需求将持续成长,进一步推动废铜市场的成长。
2024年,美国铜及铜合金废料及回收市场产值达71亿美元,这得益于美国日益重视永续发展与循环经济。随着企业和产业转向更环保的营运模式,对铜回收的重视程度也日益加深。铜以其可多次回收且品质不受影响而闻名,是理想的再利用材料。这不仅减少了对原生铜的需求,也支持了日益增长的减少浪费和资源节约的趋势。
全球铜及铜合金废料及回收市场的主要参与者包括 Aurubis AG、Umicore、Commercial Metals Company、European Metal Recycling (EMR) 和 Sims Metal Management。这些公司采取了多项策略来巩固其市场地位,包括扩大回收能力、投资先进技术以及与供应商和客户建立牢固的关係。透过专注于提高效率和改进回收流程,这些公司旨在满足日益增长的再生铜需求,同时与全球永续发展目标保持一致。此外,他们正在扩大业务覆盖范围,以开拓新市场并利用循环经济中的新兴机会。
目录
第一章:方法论与范围
第二章:执行摘要
第三章:行业洞察
- 市场概况与动态
- 市场定义和范围
- 产业价值链分析
- 市场规模与成长预测(2025-2033)
- 历史市场演变(2018-2024)
- 市场驱动因素
- 再生能源对铜的需求不断增长
- 更加重视循环经济
- 再生铜的成本优势
- 不断成长的电动车市场
- 都市化和基础设施发展
- 市场限制
- 铜市场价格波动
- 收集和分类挑战
- 再生材料的品质不一致
- 技术限制
- 供应链中断
- 市场机会
- 回收製程的技术进步
- 发展中经济体尚未开发的潜力
- 电子垃圾回收扩张
- 人工智慧与自动化的融合
- 策略伙伴关係与合作
- 市场挑战
- 监理合规的复杂性
- 来自原生铜生产的竞争
- 再生铜的污染问题
- 高初始投资要求
- 熟练劳动力短缺
- 大环境分析
- 波特五力分析
- 川普政府关税
- 对贸易的影响
- 贸易量中断
- 报復措施
- 对产业的影响
- 供给侧影响(原料)
- 主要材料价格波动
- 供应链重组
- 生产成本影响
- 需求面影响(售价)
- 价格传导至终端市场
- 市占率动态
- 消费者反应模式
- 供给侧影响(原料)
- 受影响的主要公司
- 策略产业回应
- 供应链重构
- 定价和产品策略
- 政策参与
- 展望与未来考虑
- 对贸易的影响
- 贸易统计(HS编码)
- 主要出口国(2021-2024年)
- 主要进口国(2021-2024年)
註:以上贸易统计仅提供重点国家
- 铜回收价值链分析
- 收集系统和基础设施
- 正式蒐集网络
- 非正式收集网络
- 存款系统
- 生产者责任延伸计划
- 排序和预处理
- 手动排序
- 自动分类技术
- 粉碎和尺寸减小
- 分离技术
- 加工和精炼
- 冶炼作业
- 精炼工艺
- 品质控制措施
- 副产品回收
- 分销和终端市场
- 市场通路
- 定价机制
- 品质标准和规范
- 客户要求
- 价值链整合与优化策略
- 价值链挑战与瓶颈
- 价值链的未来演变
- 规范架构与政策分析
- 全球法规
- 巴塞尔公约
- 国际贸易法规
- 全球永续发展倡议
- 区域监理框架
- 北美洲
- 美国环保署法规
- 资源保护与回收法案(RCRA)
- 州级法规
- 欧洲联盟
- 废弃电子电气设备(WEEE)指令
- 报废车辆(ELV)指令
- 循环经济行动计划
- REACH法规
- 亚太
- 中国废料进口政策
- 日本的回收法
- 印度电子垃圾管理条例
- 北美洲
- 其他区域法规
- 法规对市场动态的影响
- 产业参与者的合规策略
- 未来监管趋势及其影响
- 全球法规
- 永续性和环境影响分析
- 铜回收的环境效益
- 节能
- 温室气体减量
- 资源节约
- 减少废弃物
- 再生铜与原生铜的生命週期评估
- 碳足迹分析
- 水资源利用与管理
- 铜回收中的循环经济原则
- 企业永续发展计划
- ESG(环境、社会、治理)考量
- 永续性认证和标准
- 未来永续发展趋势与机会
- 铜回收的环境效益
- 技术格局与创新分析
- 目前的回收技术
- 收集和分类技术
- 加工技术
- 炼油技术
- 新兴技术与创新
- 人工智慧和机器学习应用
- 机器人与自动化
- 先进的感测器技术
- 区块链用于供应链可追溯性
- 新型冶金工艺
- 科技采用趋势
- 研发投资与创新中心
- 专利分析
- 技术成功案例分析
- 未来技术路线图
- 目前的回收技术
- 未来市场趋势和预测
- 短期市场展望(1-2年)
- 中期市场预测(3-5年)
- 长期市场预测(6-8年)
- 新兴趋势
- 城市采矿
- 回收业的数位转型
- 回收业务在地化
- 与再生能源系统的整合
- 先进材料回收
- 情境分析
- 乐观情境
- 现实场景
- 悲观情景
- 外在因素的影响
- 经济因素
- 技术发展
- 监管变化
- 环境问题
- 社会和人口结构的变化
- 投资分析与市场机会
- 铜回收的投资趋势
- 创投与私募股权活动
- 併购格局
- 投资报酬分析
- 各地区投资热点
- 投资风险及缓解策略
- 未来投资机会
- 利害关係人分析
- 主要利害关係人群体
- 回收公司
- 铜生产商
- 最终用途产业
- 技术提供者
- 监管机构
- 投资者和金融机构
- 研究与学术机构
- 产业协会
- 利害关係人利益及影响分析
- 利害关係人参与策略
- 合作机会
- 主要利害关係人群体
- 策略建议
- 对于回收公司
- 技术采用策略
- 市场拓展机会
- 营运效率提升
- 策略伙伴关係
- 对于最终用途行业
- 采购策略
- 永续性整合
- 供应链优化
- 对于投资者
- 高潜力投资领域
- 风险评估框架
- 投资组合多元化策略
- 对于政策制定者
- 规范架构增强
- 激励计划
- 基础建设发展支持
- 对于技术提供者
- 创新重点领域
- 市场渗透策略
- 合作研发机会
- 对于回收公司
第四章:竞争格局
- 市占率分析
- 市场集中度分析
- 竞争定位矩阵
- 关键球员简介
- 奥鲁比斯股份公司
- 公司概况
- 财务表现
- 产品组合
- 策略倡议
- SWOT分析
- 优美科
- 商业金属公司
- 欧洲金属回收(EMR)
- 西姆斯金属管理公司
- 同和控股株式会社
- 施尼策钢铁工业
- 库萨科斯基公司
- 纽柯公司
- 大卫·J·约瑟夫公司
- 其他值得注意的球员
- 奥鲁比斯股份公司
- 竞争策略
- 合併与收购
- 合资企业和合作伙伴关係
- 产能扩张
- 技术创新
- 市场进入策略
- 近期发展及其影响
第五章:市场规模及预测:依类型,2021-2034
- 主要趋势
- 废铜
- 裸露亮铜废料
- #1 废铜
- #2 废铜
- 其他废铜
- 铜合金废料
- 黄铜
- 青铜
- 白铜
- 其他铜合金
第六章:市场规模及预测:依来源,2021-2034
- 主要趋势
- 旧废料(消费后)
- 报废车辆
- 电子垃圾
- 建筑和建筑废料
- 产业机械
- 其他消费后来源
- 新废料(消费前/工业废料)
- 製造过程废弃物
- 生产残留物
- 不合格材料
- 其他工业来源
第七章:市场规模及预测:依最终用途,2021-2034
- 主要趋势
- 电气和电子
- 建筑和施工
- 运输
- 汽车
- 铁路
- 航太
- 海洋
- 工业机械设备
- 消费品
- 其他的
第 8 章:市场规模与预测:按加工方法,2021-2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 机械加工
- 火法冶金加工
- 湿式冶金加工
- 电冶金加工
- 其他加工方法
第九章:市场规模及预测:按地区,2021-2034
- 主要趋势
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 英国
- 德国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 荷兰
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 澳洲
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- MEA
- 南非
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿联酋
第十章:公司简介
- Aurubis AG
- Umicore
- Commercial Metals Company
- European Metal Recycling (EMR)
- Sims Metal Management
- Dowa Holdings
- Schnitzer Steel Industries
- Kuusakoski Oy
- Nucor Corporation
- The David J. Joseph Company
The Global Copper And Copper Alloy Scrap & Recycling Market was valued at USD 42.4 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 10.2% to reach USD 119.6 billion by 2034, driven by rising industrial activities and a global push for sustainability. The focus on a circular economy, supported by governments worldwide, has resulted in increased demand for copper scrap and its alloys. Recycled copper is gaining importance as an essential resource in various industries, from electrical to construction, due to its excellent conductivity, recyclability, and high value across applications.

The electrical and electronics sector plays a pivotal role in driving the demand for recycled copper, as it consumes 60% of the world's copper. This sector requires copper for everything from wiring to circuit boards due to its unmatched electrical conductivity. Additionally, as the world continues to undergo significant electrification, spurred by the rise of electric vehicles, renewable energy, and related infrastructure, copper recycling has become a key component of the supply chain. Furthermore, copper's role in construction, especially in emerging markets like Asia-Pacific and the Middle East, is expanding, where it's used in plumbing, cladding, roofing, and wiring.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $42.4 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $119.6 Billion |
| CAGR | 10.2% |
The copper scrap segment, which was valued at USD 27.5 billion in 2024, is anticipated to experience substantial growth, reaching USD 76.6 billion by 2034. Copper scrap remains a primary source of recycled copper, making it essential across various industries due to its abundance, high value, and superior properties. Copper's excellent conductivity, resistance to corrosion, and versatility for reuse make it highly sought after, particularly in sectors like electrical and construction. As industries continue to demand more sustainable solutions, the use of copper scrap helps reduce the need for primary copper mining, aligning with global efforts to recycle and optimize resources.
The electrical & electronics sector dominates the Copper And Copper Alloy Scrap & Recycling Market, holding a 34.2% share in 2024, driven by copper's crucial role in mobile phones, smart tablets, computers, and other modern electronics, where it is used extensively for wiring, circuit boards, and connectors. Copper's role as a reliable conductor of electricity makes it indispensable in this industry, supporting the demand for both primary and recycled copper. As technological innovation continues, especially in mobile and smart device production, the need for copper in electronics is set to rise, further bolstering the growth of the copper scrap market.
United States Copper And Copper Alloy Scrap & Recycling Market generated USD 7.1 billion in 2024, underpinned by the country's increasing focus on sustainability and the circular economy. As businesses and industries move toward more environmentally friendly practices, the emphasis on recycling copper has intensified. Copper is known for its ability to be recycled multiple times without losing quality, making it an ideal material for reuse. This not only reduces the demand for virgin copper but also supports the growing trend of waste reduction and resource conservation.
Key players in the Global Copper And Copper Alloy Scrap & Recycling Market Include Aurubis AG, Umicore, Commercial Metals Company, European Metal Recycling (EMR), and Sims Metal Management. These companies have adopted several strategies to strengthen their positions in the market, including expanding their recycling capacities, investing in state-of-the-art technologies, and building strong relationships with suppliers and customers. By focusing on efficiency improvements and enhancing their recycling processes, these firms aim to meet the growing demand for recycled copper while aligning with global sustainability goals. Additionally, they are expanding their geographic footprints to tap into new markets and leverage emerging opportunities in the circular economy.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology & Scope
- 1.1 Market scope & definition
- 1.2 Base estimates & calculations
- 1.3 Forecast calculation
- 1.4 Data sources
- 1.4.1 Primary
- 1.4.2 Secondary
- 1.4.2.1 Paid sources
- 1.4.2.2 Public sources
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry synopsis, 2021-2034
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Market Overview and Dynamics
- 3.1.1 Market Definition and Scope
- 3.1.2 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 3.1.3 Market Size and Growth Projections (2025-2033)
- 3.1.4 Historical Market Evolution (2018-2024)
- 3.1.5 Market Drivers
- 3.1.5.1 Rising Demand for Copper in Renewable Energy
- 3.1.5.2 Increasing Focus on Circular Economy
- 3.1.5.3 Cost Advantages of Recycled Copper
- 3.1.5.4 Growing Electric Vehicle Market
- 3.1.5.5 Urbanization and Infrastructure Development
- 3.1.6 Market Restraints
- 3.1.6.1 Price Volatility in Copper Markets
- 3.1.6.2 Collection and Sorting Challenges
- 3.1.6.3 Quality Inconsistencies in Recycled Materials
- 3.1.6.4 Technological Limitations
- 3.1.6.5 Supply Chain Disruptions
- 3.1.7 Market Opportunities
- 3.1.7.1 Technological Advancements in Recycling Processes
- 3.1.7.2 Untapped Potential in Developing Economies
- 3.1.7.3 E-Waste Recycling Expansion
- 3.1.7.4 Integration of AI and Automation
- 3.1.7.5 Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
- 3.1.8 Market Challenges
- 3.1.8.1 Regulatory Compliance Complexity
- 3.1.8.2 Competition from Primary Copper Production
- 3.1.8.3 Contamination Issues in Recycled Copper
- 3.1.8.4 High Initial Investment Requirements
- 3.1.8.5 Skilled Labor Shortages
- 3.1.9 PESTLE Analysis
- 3.1.10 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 3.2 Trump Administration Tariffs
- 3.2.1 Impact on Trade
- 3.2.1.1 Trade Volume Disruptions
- 3.2.1.2 Retaliatory Measures
- 3.2.2 Impact on the Industry
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-Side Impact (Raw Materials)
- 3.2.2.1.1 Price Volatility in Key Materials
- 3.2.2.1.2 Supply Chain Restructuring
- 3.2.2.1.3 Production Cost Implications
- 3.2.2.2 Demand-Side Impact (Selling Price)
- 3.2.2.2.1 Price Transmission to End Markets
- 3.2.2.2.2 Market Share Dynamics
- 3.2.2.2.3 Consumer Response Patterns
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-Side Impact (Raw Materials)
- 3.2.3 Key Companies Impacted
- 3.2.4 Strategic Industry Responses
- 3.2.4.1 Supply Chain Reconfiguration
- 3.2.4.2 Pricing and Product Strategies
- 3.2.4.3 Policy Engagement
- 3.2.5 Outlook and Future Considerations
- 3.2.1 Impact on Trade
- 3.3 Trade statistics (HS Code)
- 3.3.1 Major Exporting Countries, 2021-2024 (USD Mn)
- 3.3.2 Major Importing Countries, 2021-2024 (USD Mn)
Note: The above trade statistics will be provided for key countries only
- 3.4 Copper Recycling Value Chain Analysis
- 3.5 Collection Systems and Infrastructure
- 3.5.1 Formal Collection Networks
- 3.5.2 Informal Collection Networks
- 3.5.3 Deposit Systems
- 3.5.4 Extended Producer Responsibility Programs
- 3.6 Sorting and Pre-processing
- 3.6.1 Manual Sorting
- 3.6.2 Automated Sorting Technologies
- 3.6.3 Shredding and Size Reduction
- 3.6.4 Separation Technologies
- 3.7 Processing and Refining
- 3.7.1 Smelting Operations
- 3.7.2 Refining Processes
- 3.7.3 Quality Control Measures
- 3.7.4 By-product Recovery
- 3.8 Distribution and End Markets
- 3.8.1 Market Channels
- 3.8.2 Pricing Mechanisms
- 3.8.3 Quality Standards and Specifications
- 3.8.4 Customer Requirements
- 3.9 Value Chain Integration and Optimization Strategies
- 3.10 Value Chain Challenges and Bottlenecks
- 3.11 Future Evolution of the Value Chain
- 3.12 Regulatory Framework and Policy Analysis
- 3.12.1 Global Regulations
- 3.12.1.1 Basel Convention
- 3.12.1.2 International Trade Regulations
- 3.12.1.3 Global Sustainability Initiatives
- 3.12.2 Regional Regulatory Frameworks
- 3.12.2.1 North America
- 3.12.2.1.1 U.S. EPA Regulations
- 3.12.2.1.2 Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)
- 3.12.2.1.3 State-Level Regulations
- 3.12.2.2 European Union
- 3.12.2.2.1 Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive
- 3.12.2.2.2 End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) Directive
- 3.12.2.2.3 Circular Economy Action Plan
- 3.12.2.2.4 REACH Regulations
- 3.12.2.3 Asia-Pacific
- 3.12.2.3.1 China's Policies on Scrap Imports
- 3.12.2.3.2 Japan's Recycling Laws
- 3.12.2.3.3 India's E-Waste Management Rules
- 3.12.2.1 North America
- 3.12.3 Other Regional Regulations
- 3.12.4 Impact of Regulations on Market Dynamics
- 3.12.5 Compliance Strategies for Industry Participants
- 3.12.6 Future Regulatory Trends and Their Implications
- 3.12.1 Global Regulations
- 3.13 Sustainability and Environmental Impact Analysis
- 3.13.1 Environmental Benefits of Copper Recycling
- 3.13.1.1 Energy Savings
- 3.13.1.2 Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions
- 3.13.1.3 Resource Conservation
- 3.13.1.4 Waste Reduction
- 3.13.2 Life Cycle Assessment of Recycled vs. Primary Copper
- 3.13.3 Carbon Footprint Analysis
- 3.13.4 Water Usage and Management
- 3.13.5 Circular Economy Principles in Copper Recycling
- 3.13.6 Corporate Sustainability Initiatives
- 3.13.7 ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) Considerations
- 3.13.8 Sustainability Certifications and Standards
- 3.13.9 Future Sustainability Trends and Opportunities
- 3.13.1 Environmental Benefits of Copper Recycling
- 3.14 Technological Landscape and Innovation Analysis
- 3.14.1 Current Recycling Technologies
- 3.14.1.1 Collection and Sorting Technologies
- 3.14.1.2 Processing Technologies
- 3.14.1.3 Refining Technologies
- 3.14.2 Emerging Technologies and Innovations
- 3.14.2.1 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications
- 3.14.2.2 Robotics and Automation
- 3.14.2.3 Advanced Sensor Technologies
- 3.14.2.4 Blockchain for Supply Chain Traceability
- 3.14.2.5 Novel Metallurgical Processes
- 3.14.3 Technology Adoption Trends
- 3.14.4 R&D Investments and Innovation Hubs
- 3.14.5 Patent Analysis
- 3.14.6 Case Studies of Technological Success Stories
- 3.14.7 Future Technology Roadmap
- 3.14.1 Current Recycling Technologies
- 3.15 Future Market Trends and Forecasts
- 3.15.1 Short-term Market Outlook (1–2 Years)
- 3.15.2 Medium-term Market Projections (3–5 Years)
- 3.15.3 Long-term Market Forecasts (6–8 Years)
- 3.15.4 Emerging Trends
- 3.15.4.1 Urban Mining
- 3.15.4.2 Digital Transformation in Recycling
- 3.15.4.3 Localization of Recycling Operations
- 3.15.4.4 Integration with Renewable Energy Systems
- 3.15.4.5 Advanced Material Recovery
- 3.15.5 Scenario Analysis
- 3.15.5.1 Optimistic Scenario
- 3.15.5.2 Realistic Scenario
- 3.15.5.3 Pessimistic Scenario
- 3.15.6 Impact of External Factors
- 3.15.6.1 Economic Factors
- 3.15.6.2 Technological Developments
- 3.15.6.3 Regulatory Changes
- 3.15.6.4 Environmental Concerns
- 3.15.6.5 Social and Demographic Shifts
- 3.16 Investment Analysis and Market Opportunities
- 3.16.1 Investment Trends in Copper Recycling
- 3.16.2 Venture Capital and Private Equity Activities
- 3.16.3 Mergers and Acquisitions Landscape
- 3.16.4 Return on Investment Analysis
- 3.16.5 Investment Hotspots by Region
- 3.16.6 Investment Risks and Mitigation Strategies
- 3.16.7 Future Investment Opportunities
- 3.17 Stakeholder Analysis
- 3.17.1 Key Stakeholder Groups
- 3.17.1.1 Recycling Companies
- 3.17.1.2 Copper Producers
- 3.17.1.3 End-Use Industries
- 3.17.1.4 Technology Providers
- 3.17.1.5 Regulatory Bodies
- 3.17.1.6 Investors and Financial Institutions
- 3.17.1.7 Research and Academic Institutions
- 3.17.1.8 Industry Associations
- 3.17.2 Stakeholder Interests and Influence Analysis
- 3.17.3 Stakeholder Engagement Strategies
- 3.17.4 Collaborative Opportunities
- 3.17.1 Key Stakeholder Groups
- 3.18 Strategic Recommendations
- 3.18.1 For Recycling Companies
- 3.18.1.1 Technology Adoption Strategies
- 3.18.1.2 Market Expansion Opportunities
- 3.18.1.3 Operational Efficiency Improvements
- 3.18.1.4 Strategic Partnerships
- 3.18.2 For End-Use Industries
- 3.18.2.1 Sourcing Strategies
- 3.18.2.2 Sustainability Integration
- 3.18.2.3 Supply Chain Optimization
- 3.18.3 For Investors
- 3.18.3.1 High-Potential Investment Areas
- 3.18.3.2 Risk Assessment Framework
- 3.18.3.3 Portfolio Diversification Strategies
- 3.18.4 For Policy Makers
- 3.18.4.1 Regulatory Framework Enhancements
- 3.18.4.2 Incentive Programs
- 3.18.4.3 Infrastructure Development Support
- 3.18.5 For Technology Providers
- 3.18.5.1 Innovation Focus Areas
- 3.18.5.2 Market Penetration Strategies
- 3.18.5.3 Collaborative R&D Opportunities
- 3.18.1 For Recycling Companies
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Market Share Analysis
- 4.2 Market Concentration Analysis
- 4.3 Competitive Positioning Matrix
- 4.4 Key Player Profiles
- 4.4.1 Aurubis AG
- 4.4.1.1 Company Overview
- 4.4.1.2 Financial Performance
- 4.4.1.3 Product Portfolio
- 4.4.1.4 Strategic Initiatives
- 4.4.1.5 SWOT Analysis
- 4.4.2 Umicore
- 4.4.3 Commercial Metals Company
- 4.4.4 European Metal Recycling (EMR)
- 4.4.5 Sims Metal Management
- 4.4.6 Dowa Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 4.4.7 Schnitzer Steel Industries
- 4.4.8 Kuusakoski Oy
- 4.4.9 Nucor Corporation
- 4.4.10 The David J. Joseph Company
- 4.4.11 Other Notable Players
- 4.4.1 Aurubis AG
- 4.5 Competitive Strategies
- 4.5.1 Mergers and Acquisitions
- 4.5.2 Joint Ventures and Partnerships
- 4.5.3 Capacity Expansions
- 4.5.4 Technological Innovations
- 4.5.5 Market Entry Strategies
- 4.6 Recent Developments and Their Impact
Chapter 5 Market Size and Forecast, By Type, 2021-2034 (USD Million) (Tons)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Copper scrap
- 5.2.1 Bare bright copper scrap
- 5.2.2 #1 copper scrap
- 5.2.3 #2 copper scrap
- 5.2.4 Other copper scrap
- 5.3 Copper alloy scrap
- 5.3.1 Brass
- 5.3.2 Bronze
- 5.3.3 Cupronickel
- 5.3.4 Other copper alloys
Chapter 6 Market Size and Forecast, By Source, 2021-2034 (USD Million) (Tons)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Old scrap (post-consumer)
- 6.2.1 End-of-life vehicles
- 6.2.2 Electronic waste
- 6.2.3 Building and construction waste
- 6.2.4 Industrial machinery
- 6.2.5 Other post-consumer sources
- 6.3 New scrap (pre-consumer/industrial)
- 6.3.1 Manufacturing process waste
- 6.3.2 Production residues
- 6.3.3 Off-specification materials
- 6.3.4 Other industrial sources
Chapter 7 Market Size and Forecast, By End Use, 2021-2034 (USD Million) (Tons)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Electrical and electronics
- 7.3 Building and construction
- 7.4 Transportation
- 7.4.1 Automotive
- 7.4.2 Railways
- 7.4.3 Aerospace
- 7.4.4 Marine
- 7.5 Industrial machinery and equipment
- 7.6 Consumer products
- 7.7 Others
Chapter 8 Market Size and Forecast, By Processing Method, 2021-2034 (USD Million) (Tons)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Mechanical processing
- 8.3 Pyrometallurgical processing
- 8.4 Hydrometallurgical processing
- 8.5 Electrometallurgical processing
- 8.6 Other processing methods
Chapter 9 Market Size and Forecast, By Region, 2021-2034 (USD Million) (Tons)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 North America
- 9.2.1 U.S.
- 9.2.2 Canada
- 9.3 Europe
- 9.3.1 UK
- 9.3.2 Germany
- 9.3.3 France
- 9.3.4 Italy
- 9.3.5 Spain
- 9.3.6 Netherlands
- 9.4 Asia Pacific
- 9.4.1 China
- 9.4.2 India
- 9.4.3 Japan
- 9.4.4 South Korea
- 9.4.5 Australia
- 9.5 Latin America
- 9.5.1 Brazil
- 9.5.2 Mexico
- 9.5.3 Argentina
- 9.6 MEA
- 9.6.1 South Africa
- 9.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 9.6.3 UAE
Chapter 10 Company Profiles
- 10.1 Aurubis AG
- 10.2 Umicore
- 10.3 Commercial Metals Company
- 10.4 European Metal Recycling (EMR)
- 10.5 Sims Metal Management
- 10.6 Dowa Holdings
- 10.7 Schnitzer Steel Industries
- 10.8 Kuusakoski Oy
- 10.9 Nucor Corporation
- 10.10 The David J. Joseph Company










