|
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1797764
轨道转移飞行器 (OTV) 市场机会、成长动力、产业趋势分析及 2025 - 2034 年预测Orbital Transfer Vehicle (OTV) Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
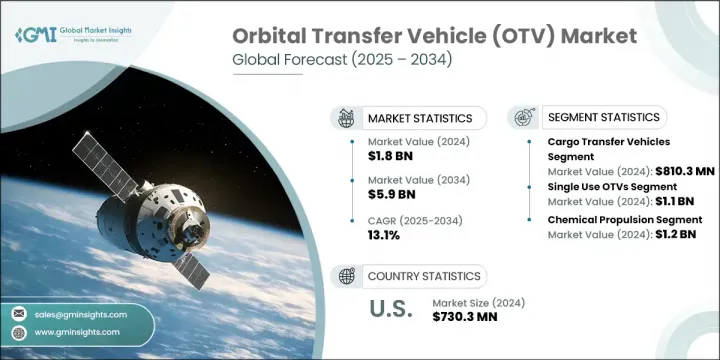
2024 年全球轨道转移飞行器市值为 18 亿美元,预计到 2034 年将以 13.1% 的复合年增长率成长至 59 亿美元。市场成长的动力来自对适应性卫星部署方法日益增长的需求、小型卫星和立方体卫星发射频率的提高、推进系统的快速进步、流入轨道基础设施的资本激增以及商业太空计划的稳步上升。随着产业逐渐摆脱传统发射系统,轨道转移飞行器正在成为不可或缺的太空运载解决方案,能够将有效载荷机动到各种轨道目的地,包括低地球轨道 (LEO)、中地球轨道 (MEO)、地球静止轨道 (GEO) 以及更远的地月空间。公共和私营部门都在投入大量资金开发卫星星座、太空服务舱、轨道栖息地和月球支持结构,进一步推动市场长期成长。
对灵活卫星运输日益增长的需求是推动OTV空间扩张的关键因素。营运商如今寻求能够提供更高反应速度和特定任务轨道定位的部署系统,而非局限于僵化的、预先定义的发射方案。轨道运输飞行器作为太空物流解决方案,正在透过在各种轨道环境中实现按需卫星交付来取代旧系统。与此同时,从国防部门到商业航太新创公司等各种专注于太空的实体正在加紧努力,建立更强大的轨道生态系统。
| 市场范围 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 预测年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 18亿美元 |
| 预测值 | 59亿美元 |
| 复合年增长率 | 13.1% |
2024年,货物转运飞行器细分市场的收入为8.103亿美元。该细分市场继续受益于有效载荷补给任务频率的不断增长,这些任务旨在维护轨道站并为新兴商业平台铺平道路。对卫星服务和轨道资产维护的日益重视也加速了对专用货运飞行器的需求,这些飞行器可确保及时、安全地运输关键任务硬体。自主对接系统的发展以及航太组织之间不断扩大的全球合作,正在推动可重复使用货物运输技术的普及。
2024年,一次性轨道转移飞行器市场规模达11亿美元。这类飞行器因其结构简化、製造成本降低以及适用于一次性有效载荷部署任务而日益受到青睐。由于无需复杂的回收或再利用系统,它们为无法回收的高风险或长距离任务提供了理想的解决方案。这类飞行器在政府机构和国防相关任务中尤其普遍,因为这些任务对战略交付的可靠性至关重要。此外,航太业的新创公司和新进业者通常会在测试、原型验证或进行经济可行的轨道演示的初始阶段选择一次性平台。
2024年,美国轨道转移飞行器 (OTV) 市场产值达7.303亿美元。这一强劲地位得益于政府机构和商业营运商的持续努力,包括提升卫星发射能力、开发在轨维护系统以及实施轨道碎片减缓策略。这些合作投资旨在提高轨道运行效率、增强有效载荷机动性并延长航太资产的使用寿命。对轨道可持续性和任务灵活性的日益重视,进一步巩固了美国在该领域的领导地位。
积极塑造全球轨道转移飞行器 (OTV) 市场的知名参与者包括 Astroscale Holdings Inc.、Virgin Galactic、D-Orbit SpA、Relativity Space、OHB SE、Quantum Space LLC、Northrop Grumman Corporation、ArianeGroup SAS、Space Machines Company Pty Ltd、Sierra Space 订单(CALT)、SpaceX、MaiaSpace SAS、三菱重工、 Altius Space Machines Inc.、Impulse Space Inc.、Roscosmos / Energia、Firefly 航太 、Atomos Space LLC、Gama Space SAS、Rocket Lab USA Inc.、Blue SAigin LLC、Eunch Ltd、CASIC / ExPace、Momentus Inc. 和 Starfish Space Inc. 轨道转移飞行器市场的领先公司正在优先考虑创新和合作,以巩固其竞争优势。许多公司正在投资专有推进系统和模组化运载火箭设计,以支援灵活的任务配置。跨国和跨组织的策略合作正在帮助各公司获得更广泛的发射平台,并将其运载火箭整合到不同的任务架构中。
目录
第一章:方法论与范围
第二章:执行摘要
第三章:行业洞察
- 产业生态系统分析
- 供应商格局
- 利润率
- 成本结构
- 每个阶段的增值
- 影响价值链的因素
- 中断
- 产业生态系统分析
- 产业衝击力
- 成长动力
- 卫星部署灵活性的需求日益增加
- 小型卫星和立方体卫星发射不断增加
- 推进技术的进步
- 增加太空基础设施的投资
- 日益增长的商业太空活动
- 陷阱与挑战
- 技术可靠性和任务保证
- 监理复杂性与空间交通管理
- 成长动力
- 成长潜力分析
- 监管格局
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL分析
- 技术和创新格局
- 当前的技术趋势
- 新兴技术
- 新兴商业模式
- 合规性要求
- 国防预算分析
- 全球国防开支趋势
- 区域国防预算分配
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 中东和非洲
- 拉丁美洲
- 重点国防现代化项目
- 预算预测(2025-2034)
- 对产业成长的影响
- 各国国防预算
- 永续发展倡议
- 供应链弹性
- 地缘政治分析
- 劳动力分析
- 数位转型
- 合併、收购和策略伙伴关係格局
- 风险评估与管理
- 主要合约授予(2021-2024)
第四章:竞争格局
- 介绍
- 公司市占率分析
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 市场集中度分析
- 按地区
- 关键参与者的竞争基准
- 财务绩效比较
- 收入
- 利润率
- 研发
- 产品组合比较
- 产品范围广度
- 科技
- 创新
- 地理位置比较
- 全球足迹分析
- 服务网路覆盖
- 各区域市场渗透率
- 竞争定位矩阵
- 领导者
- 挑战者
- 追踪者
- 利基市场参与者
- 战略展望矩阵
- 财务绩效比较
- 2021-2024 年关键发展
- 併购
- 伙伴关係和合作
- 技术进步
- 扩张和投资策略
- 永续发展倡议
- 数位转型倡议
- 新兴/新创企业竞争对手格局
第五章:市场估计与预测:按类型,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 货物转运车辆
- 机组人员转移车辆
- 为车辆加油
- 卫星服务和碎片清除车辆
- 其他的
第六章:市场估计与预测:按车辆类型,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 一次使用OTV
- 可重复使用的OTV
第七章:市场估计与预测:按推进系统,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 化学推进
- 电力推进
- 核热推进
- 其他的
第八章:市场估计与预测:按有效载荷容量,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 有效载荷较小(最多 200 公斤)
- 中等有效载重(200 公斤至 1,000 公斤)
- 大有效载重(1,000 公斤以上)
第九章:市场估计与预测:按应用,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 卫星部署
- 太空探索
- 在轨服务
- 太空旅游
- 太空站补给和机组人员轮换
- 其他的
第 10 章:市场估计与预测:依最终用途,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 政府航太机构
- 商业航太公司
- 公私部门合作伙伴关係
第 11 章:市场估计与预测:按地区,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 西班牙
- 义大利
- 荷兰
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韩国
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 阿联酋
第十二章:公司简介
- Global Key Players
- Regional Key Players
- 颠覆者/利基市场参与者
- 海星空间公司
- Atomos Space LLC
- Astroscale控股公司
- 维珍银河
The Global Orbital Transfer Vehicle Market was valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 13.1% to reach USD 5.9 billion by 2034. The market growth is driven by an increasing need for adaptable satellite deployment methods, the rising frequency of small satellite and CubeSat launches, rapid progress in propulsion systems, surging capital flow into orbital infrastructure, and a steady uptick in commercial space initiatives. As the industry shifts away from traditional launch systems, OTVs are emerging as indispensable in-space delivery solutions capable of maneuvering payloads to various orbital destinations-including low Earth orbit (LEO), medium Earth orbit (MEO), geostationary orbit (GEO), and beyond to cislunar space. Both public and private sectors are channeling considerable investments into developing satellite constellations, in-space service modules, orbital habitats, and lunar support structures-further fueling long-term growth in the market.

Heightened demand for flexible satellite transportation is a critical factor powering the expansion of the OTV space. Operators now seek deployment systems that offer greater responsiveness and mission-specific orbital placement, rather than being tied to rigid, predefined launch profiles. Orbital transfer vehicles, acting as in-space logistics solutions, are replacing older systems by enabling on-demand satellite delivery across a diverse range of orbital environments. In tandem, various space-focused entities-from national defense divisions to commercial aerospace startups-are ramping up efforts to construct more robust orbital ecosystems.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $1.8 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $5.9 Billion |
| CAGR | 13.1% |
The cargo transfer vehicles segment generated USD 810.3 million in 2024. This segment continues to benefit from the growing frequency of payload resupply missions designed to sustain orbital stations and pave the way for emerging commercial platforms. The growing emphasis on satellite servicing and orbital asset maintenance is also accelerating demand for dedicated cargo vehicles that ensure the timely, secure transport of mission-critical hardware. Developments in autonomous docking systems and expanding global cooperation between aerospace organizations are driving the adoption of reusable cargo transport technologies.
The single-use orbital transfer vehicles segment generated USD 1.1 billion in 2024. These vehicles are increasingly favored due to their simplified structure, reduced manufacturing costs, and suitability for missions involving one-time payload deployments. By eliminating the need for complex retrieval or reuse systems, they provide an ideal solution for high-risk or long-distance missions where vehicle recovery is impractical. Their utilization is particularly prevalent among government bodies and defense-related missions, where strategic delivery reliability is paramount. Additionally, startups and newer entrants to the aerospace industry often opt for single-use platforms during initial stages of testing, prototype validation, or conducting economically viable orbital demonstrations.
United States Orbital Transfer Vehicle (OTV) Market generated USD 730.3 million in 2024. This strong position is underpinned by sustained efforts from both governmental institutions and commercial operators to enhance satellite launch capabilities, develop in-orbit maintenance systems, and implement orbital debris mitigation strategies. These collaborative investments aim to enhance the efficiency of orbital operations, increase payload maneuverability, and extend the useful life of space assets. The growing emphasis on orbital sustainability and mission flexibility continues to strengthen the country's leadership in the sector.
Prominent players actively shaping the Global Orbital Transfer Vehicle (OTV) Market include Astroscale Holdings Inc., Virgin Galactic, D-Orbit S.p.A., Relativity Space, OHB SE, Quantum Space LLC, Northrop Grumman Corporation, ArianeGroup SAS, Space Machines Company Pty Ltd, Sierra Space, Moog Inc., ISRO / Antrix Corporation, China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT), SpaceX, MaiaSpace SAS, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Altius Space Machines Inc., Impulse Space Inc., Roscosmos / Energia, Firefly Aerospace, Atomos Space LLC, Gama Space SAS, Rocket Lab USA Inc., Blue Origin LLC, Epic Aerospace LLC, Thales Alenia Space S.A., United Launch Alliance LLC (ULA), Orbital Operations Ltd, CASIC / ExPace, Momentus Inc., and Starfish Space Inc. Leading companies in the orbital transfer vehicle market are prioritizing innovation and partnerships to solidify their competitive edge. Many are investing in proprietary propulsion systems and modular vehicle designs to support flexible mission configurations. Strategic collaborations-both cross-border and inter-organizational-are helping firms access broader launch platforms and integrate their vehicles into diverse mission architectures.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology and scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast model
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive summary
- 2.1 Industry 3600 synopsis
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Type trends
- 2.2.2 Vehicle type trends
- 2.2.3 Propulsion system trends
- 2.2.4 Payload capacity trends
- 2.2.5 Application trends
- 2.2.6 End use trends
- 2.2.7 Regional trends
- 2.3 TAM Analysis, 2025-2034 (USD Billion)
- 2.4 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 critical success factors
- 2.5 Future outlook and strategic recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.2 Profit margin
- 3.1.3 Cost structure
- 3.1.4 Value addition at each stage
- 3.1.5 Factor affecting the value chain
- 3.1.6 Disruptions
- 3.2 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.3 Industry impact forces
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3.1.1 Increasing demand for satellite deployment flexibility
- 3.3.1.2 Rising small satellite and cubesat launches
- 3.3.1.3 Advancements in propulsion technologies
- 3.3.1.4 Increased investments in space infrastructure
- 3.3.1.5 The growing commercial space activities
- 3.3.2 Pitfalls and challenges
- 3.3.2.1 Technical Reliability and Mission Assurance
- 3.3.2.2 Regulatory Complexity and Space Traffic Management
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.4 Growth potential analysis
- 3.5 Regulatory landscape
- 3.5.1 North America
- 3.5.2 Europe
- 3.5.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.5.4 Latin America
- 3.5.5 Middle East & Africa
- 3.6 Porter's analysis
- 3.7 PESTEL analysis
- 3.8 Technology and Innovation landscape
- 3.8.1 Current technological trends
- 3.8.2 Emerging technologies
- 3.9 Emerging business models
- 3.10 Compliance requirements
- 3.11 Defense budget analysis
- 3.12 Global defense spending trends
- 3.13 Regional defense budget allocation
- 3.13.1 North America
- 3.13.2 Europe
- 3.13.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.13.4 Middle East and Africa
- 3.13.5 Latin America
- 3.14 Key defense modernization programs
- 3.15 Budget forecast (2025-2034)
- 3.15.1 Impact on industry growth
- 3.15.2 Defense budgets by country
- 3.16 Sustainability initiatives
- 3.17 Supply chain resilience
- 3.18 Geopolitical analysis
- 3.19 Workforce analysis
- 3.20 Digital transformation
- 3.21 Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships landscape
- 3.22 Risk assessment and management
- 3.23 Major contract awards (2021-2024)
Chapter 4 Competitive landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 By region
- 4.2.1.1 North America
- 4.2.1.2 Europe
- 4.2.1.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.1.4 Latin America
- 4.2.1.5 Middle East & Africa
- 4.2.2 Market concentration analysis
- 4.2.1 By region
- 4.3 Competitive benchmarking of key players
- 4.3.1 Financial performance comparison
- 4.3.1.1 Revenue
- 4.3.1.2 Profit margin
- 4.3.1.3 R&D
- 4.3.2 Product portfolio comparison
- 4.3.2.1 Product range breadth
- 4.3.2.2 Technology
- 4.3.2.3 Innovation
- 4.3.3 Geographic presence comparison
- 4.3.3.1 Global footprint analysis
- 4.3.3.2 Service network coverage
- 4.3.3.3 Market penetration by region
- 4.3.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.3.4.1 Leaders
- 4.3.4.2 Challengers
- 4.3.4.3 Followers
- 4.3.4.4 Niche players
- 4.3.5 Strategic outlook matrix
- 4.3.1 Financial performance comparison
- 4.4 Key developments, 2021-2024
- 4.4.1 Mergers and acquisitions
- 4.4.2 Partnerships and collaborations
- 4.4.3 Technological advancements
- 4.4.4 Expansion and investment strategies
- 4.4.5 Sustainability initiatives
- 4.4.6 Digital transformation initiatives
- 4.5 Emerging/ startup competitors landscape
Chapter 5 Market estimates and forecast, By Type, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Cargo transfer vehicles
- 5.3 Crew transfer vehicles
- 5.4 Refueling vehicles
- 5.5 Satellite servicing & debris removal vehicles
- 5.6 Others
Chapter 6 Market estimates and forecast, By Vehicle Type, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Single Use OTVs
- 6.3 Reusable OTVs
Chapter 7 Market estimates and forecast, By Propulsion System, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Chemical propulsion
- 7.3 Electric propulsion
- 7.4 Nuclear thermal propulsion
- 7.5 Others
Chapter 8 Market estimates and forecast, By Payload Capacity, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Small payload (up to 200 kg)
- 8.3 Medium payload (200 kg to 1,000 kg)
- 8.4 Large payload (1,000 kg and above)
Chapter 9 Market estimates and forecast, By Application, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 Satellite deployment
- 9.3 Space exploration
- 9.4 Inorbit servicing
- 9.5 Space tourism
- 9.6 Space station resupply & crew rotation
- 9.7 Others
Chapter 10 Market estimates and forecast, By End Use, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 Government space agencies
- 10.3 Commercial space companies
- 10.4 Public-private partnerships
Chapter 11 Market estimates and forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million & Units)
- 11.1 Key trends
- 11.2 North America
- 11.2.1 U.S.
- 11.2.2 Canada
- 11.3 Europe
- 11.3.1 Germany
- 11.3.2 UK
- 11.3.3 France
- 11.3.4 Spain
- 11.3.5 Italy
- 11.3.6 Netherlands
- 11.4 Asia Pacific
- 11.4.1 China
- 11.4.2 India
- 11.4.3 Japan
- 11.4.4 Australia
- 11.4.5 South Korea
- 11.5 Latin America
- 11.5.1 Brazil
- 11.5.2 Mexico
- 11.5.3 Argentina
- 11.6 Middle East and Africa
- 11.6.1 Saudi Arabia
- 11.6.2 South Africa
- 11.6.3 UAE
Chapter 12 Company profiles
- 12.1 Global Key Players
- 12.1.1 SpaceX
- 12.1.2 Blue Origin LLC
- 12.1.3 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 12.1.4 Thales Alenia Space S.A.
- 12.1.5 ArianeGroup SAS
- 12.1.6 United Launch Alliance LLC (ULA)
- 12.1.7 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- 12.1.8 China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT)
- 12.1.9 Roscosmos / Energia
- 12.1.10 ISRO / Antrix Corporation
- 12.2 Regional Key Players
- 12.2.1 North America
- 12.2.1.1 Rocket Lab USA Inc.
- 12.2.1.2 Momentus Inc.
- 12.2.1.3 Epic Aerospace LLC
- 12.2.1.4 Quantum Space LLC
- 12.2.1.5 Impulse Space Inc.
- 12.2.1.6 Firefly Aerospace
- 12.2.1.7 Relativity Space
- 12.2.1.8 Sierra Space
- 12.2.1.9 Moog Inc.
- 12.2.1.10 Altius Space Machines Inc.
- 12.2.2 Europe
- 12.2.2.1 D-Orbit S.p.A.
- 12.2.2.2 OHB SE
- 12.2.2.3 Orbital Operations Ltd
- 12.2.2.4 Gama Space SAS
- 12.2.2.5 MaiaSpace SAS
- 12.2.3 Asia-Pacific
- 12.2.3.1 CASIC / ExPace
- 12.2.3.2 Space Machines Company Pty Ltd
- 12.2.1 North America
- 12.3 Disruptors / Niche Players
- 12.3.1 Starfish Space Inc.
- 12.3.2 Atomos Space LLC
- 12.3.3 Astroscale Holdings Inc.
- 12.3.4 Virgin Galactic