 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1876568
碳化硅(SiC)无线电动汽车充电市场机会、成长驱动因素、产业趋势分析及预测(2025-2034年)Silicon Carbide (SiC) for Wireless EV Charging Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
2024 年全球用于电动车无线充电的碳化硅 (SiC) 市场价值为 420 万美元,预计到 2034 年将以 15.1% 的复合年增长率增长至 1700 万美元。
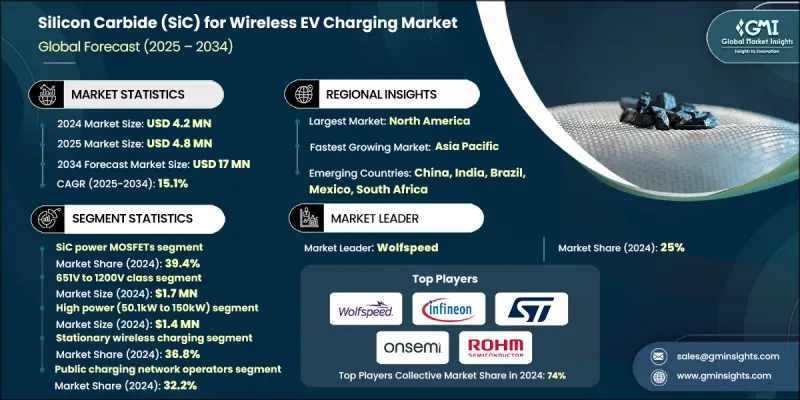
全球电动车普及率的激增推动了无线电动汽车充电系统对碳化硅(SiC)的需求,因为消费者和商业车队越来越倾向于更快、更有效率、更便利的充电解决方案。与传统的硅元件相比,SiC 装置具有更高的功率转换效率和更低的能量损耗,使其非常适合高频无线充电应用。 SiC 能够在更高的电压和温度下工作,这使得充电器设计更加紧凑轻便,也使其成为下一代电动车充电基础设施的关键推动因素。 SiC 半导体材料和製造流程的进步,例如更高的晶圆品质、更高的生产良率和更优化的装置结构,都提高了效率、热稳定性和可靠性。 SiC MOSFET 和二极体的创新进一步降低了能量损耗,并支援更小巧、整合度更高、功率密度和开关频率更高的充电解决方案。
| 市场范围 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 预测年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 420万美元 |
| 预测值 | 1700万美元 |
| 复合年增长率 | 15.1% |
预计到2024年,SiC功率MOSFET元件将占据39.4%的市场份额,这主要得益于其卓越的效率、更低的开关损耗和更高的功率密度。这些特性使得无线电动汽车充电器能够实现更快、更紧凑、散热效率更高的应用。製造商正致力于提升装置的可靠性、闸极氧化层稳定性以及封装性能,以满足高频运作的需求。
由于其适用于中高功率无线电动汽车充电,651V至1200V电压等级的逆变器市场预计在2024年将创造170万美元的销售额。这些组件具有卓越的效率和散热性能,生产商正致力于提升器件的稳健性、栅极可靠性和车规级封装集成,同时与电动汽车OEM厂商合作进行逆变器设计和热建模,以增强产品市场定位。
2024年,北美无线电动汽车充电用碳化硅(SiC)市场份额预计将达到34.5%,这主要得益于电动车普及率的提高、政府扶持政策的出台以及对先进充电基础设施的投资。环保意识的增强和清洁能源激励措施的出台,也推动了对高效SiC技术的需求成长。製造商有机会在城市和郊区扩展无线电动汽车充电网络,透过与公用事业公司建立战略合作伙伴关係以及投资可扩展的SiC基础设施,可以更好地满足日益增长的住宅、商业和公共交通充电需求。
全球电动车无线充电式碳化硅 (SiC) 市场的主要参与者包括英飞凌科技、三菱电机、微芯科技、意法半导体、GeneSiC Semiconductor(Qorvo)、安森美半导体、UnitedSiC(Qorvo)、富士电机、东芝、罗姆半导体、WixelDA. Ltd.、Plugless Power Inc.(Evatran)、高通技术公司(Halo)、InductEV Inc.、ABB Ltd.、罗伯特博世有限公司、丰田汽车公司、西门子公司和大陆集团。这些企业正透过持续的产品创新等策略来巩固其在电动车无线充电碳化硅 (SiC) 市场的领先地位,专注于高效、耐热的 SiC MOSFET 和二极体。许多企业正在与电动车原始设备製造商 (OEM) 和公用事业供应商建立策略合作伙伴关係,以将 SiC 解决方案整合到无线充电网路中。对可扩展製造製程、晶圆品质改进和封装优化的投资提高了可靠性并降低了能量损耗。各公司也致力于扩大区域影响力、参与合作研究并展示高性能应用,以获得竞争优势。行销活动着重强调碳化硅解决方案的能源效率和紧凑设计优势,以吸引住宅和商业客户,从而巩固其在蓬勃发展的电动车生态系统中的地位。
目录
第一章:方法论与范围
第二章:执行概要
第三章:行业洞察
- 产业生态系分析
- 产业影响因素
- 成长驱动因素
- 电动车(EV)的普及率不断提高
- 碳化硅半导体技术的进步
- 政府对永续交通的支持力道不断加大
- 越来越重视快速且有效率的无线充电
- 产业陷阱与挑战
- 碳化硅材料和製造成本高昂
- 复杂的製造和设计要求
- 市场机会
- 全球电动车普及率的提高和政府激励措施将推动全球对高效碳化硅无线充电解决方案的强劲需求。
- SiC半导体技术的进步将使无线充电器速度更快、体积更小、能源效率更高,从而扩大住宅和商业领域的市场机会。
- 成长驱动因素
- 成长潜力分析
- 监管环境
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 北美洲
- 技术格局
- 当前趋势
- 新兴技术
- 管道分析
- 未来市场趋势
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL 分析
第四章:竞争格局
- 介绍
- 公司市占率分析
- 全球的
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 公司矩阵分析
- 主要市场参与者的竞争分析
- 竞争定位矩阵
- 关键进展
- 併购
- 伙伴关係与合作
- 新产品发布
- 扩张计划
第五章:市场估算与预测:依碳化硅产品类型划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- SiC功率MOSFET
- 碳化硅肖特基势垒二极体
- SiC功率模组
- SiC 分立元件
第六章:市场估算与预测:依电压等级划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 最高650V级
- 651V 至 1200V 级
- 1201V 至 1700V 级
- 1700V以上等级
第七章:市场估算与预测:依功率等级划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 低功率(最高 11kW)
- 中等功率(11.1kW 至 50kW)
- 高功率(50.1kW 至 150kW)
- 超高功率(150kW以上)
第八章:市场估算与预测:依应用类型划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 固定式无线充电
- 动态无线充电
- 准动态无线充电
- 其他的
第九章:市场估算与预测:依最终用途划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 住宅用户
- 商业车队营运商
- 大众运输管理局
- 公共充电网路营运商
- 其他的
第十章:市场估计与预测:依地区划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 西班牙
- 义大利
- 荷兰
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韩国
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 中东和非洲
- 南非
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿联酋
第十一章:公司简介
- Wolfspeed
- Infineon Technologies
- STMicroelectronics
- onsemi (ON Semiconductor)
- ROHM Semiconductor
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Fuji Electric
- GeneSiC Semiconductor (Qorvo)
- UnitedSiC (Qorvo)
- Microchip Technology
- Toshiba
- General Electric (GE)
- Littelfuse (IXYS)
- WiTricity Corporation
- InductEV Inc.
- Plugless Power Inc. (Evatran)
- HEVO Inc.
- Electreon Wireless Ltd.
- Qualcomm Technologies (Halo)
- Robert Bosch GmbH
- Continental AG
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- ENRX (Norway)
The Global Silicon Carbide (SiC) for Wireless EV Charging Market was valued at USD 4.2 million in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 15.1% to reach USD 17 million by 2034.

The surge in electric vehicle adoption worldwide is driving demand for SiC in wireless EV charging systems, as consumers and commercial fleets increasingly prefer faster, more efficient, and convenient charging solutions. SiC components provide higher power conversion efficiency and lower energy losses than conventional silicon devices, making them highly suitable for high-frequency wireless charging applications. Their ability to function at elevated voltages and temperatures also allows for compact and lightweight charger designs, positioning SiC as a critical enabler of next-generation EV charging infrastructure. Advancements in SiC semiconductor materials and manufacturing such as higher wafer quality, improved production yield, and refined device architecture have enhanced efficiency, thermal stability, and reliability. Innovations in SiC MOSFETs and diodes further reduce energy losses and support smaller, integrated charging solutions with higher power density and switching frequency.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $4.2 Million |
| Forecast Value | $17 Million |
| CAGR | 15.1% |
The SiC power MOSFETs segment held a 39.4% share in 2024, driven by their superior efficiency, lower switching losses, and higher power density. These features enable faster, more compact, and thermally efficient wireless EV chargers. Manufacturers are focusing on improving device reliability, gate oxide stability, and packaging to meet high-frequency operational demands.
The 651V to 1200V class segment generated USD 1.7 million in 2024, owing to its suitability for mid- to high-power wireless EV charging. These components offer exceptional efficiency and thermal performance, and producers are investing in device robustness, gate reliability, and automotive-grade packaging integration, while collaborating with EV OEMs on inverter design and thermal modeling to enhance product positioning.
North America Silicon Carbide (SiC) for Wireless EV Charging Market held a 34.5% share in 2024, driven by rising EV adoption, supportive government initiatives, and investments in advanced charging infrastructure. Environmental awareness and clean energy incentives are increasing demand for high-efficiency SiC technology. Manufacturers have opportunities to expand wireless EV charging networks in both urban and suburban areas, with strategic partnerships with utilities and investments in scalable SiC infrastructure helping to capture growing residential, commercial, and public transit charging demand.
Leading players in the Global Silicon Carbide (SiC) for Wireless EV Charging Market include Infineon Technologies, Mitsubishi Electric, Microchip Technology, STMicroelectronics, GeneSiC Semiconductor (Qorvo), onsemi (ON Semiconductor), UnitedSiC (Qorvo), Fuji Electric, Toshiba, ROHM Semiconductor, WiTricity Corporation, HEVO Inc., Littelfuse (IXYS), General Electric (GE), Electreon Wireless Ltd., Plugless Power Inc. (Evatran), Qualcomm Technologies (Halo), InductEV Inc., ABB Ltd., Robert Bosch GmbH, Toyota Motor Corporation, Siemens AG, and Continental AG. Companies in the Silicon Carbide (SiC) for Wireless EV Charging Market are strengthening their presence through strategies such as continuous product innovation, focusing on high-efficiency, thermally robust SiC MOSFETs and diodes. Many are forming strategic partnerships with EV OEMs and utility providers to integrate SiC solutions into wireless charging networks. Investments in scalable manufacturing processes, wafer quality improvements, and packaging optimization enhance reliability and reduce energy losses. Firms also focus on expanding regional presence, participating in collaborative research, and demonstrating high-performance applications to gain a competitive edge. Marketing efforts highlight the energy efficiency and compact design advantages of SiC-based solutions to attract both residential and commercial clients, solidifying their foothold in the growing EV ecosystem.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology and Scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast model
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 3600 synopsis
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Regional trends
- 2.2.2 Product type trends
- 2.2.3 Voltage trends
- 2.2.4 Power level trends
- 2.2.5 Application trends
- 2.2.6 End use trends
- 2.3 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.3.1 Key decision points for industry executives
- 2.3.2 Critical success factors for market players
- 2.4 Future outlook and strategic recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.1.1 Growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs)
- 3.2.1.2 Advancements in SiC semiconductor technology
- 3.2.1.3 Rising government support for sustainable mobility
- 3.2.1.4 Increasing focus on fast and efficient wireless charging
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.2.1 High cost of SiC materials and manufacturing
- 3.2.2.2 Complex fabrication and design requirements
- 3.2.3 Market opportunities
- 3.2.3.1 Rising global EV adoption and government incentives will drive strong demand for high-efficiency SiC-based wireless charging solutions worldwide.
- 3.2.3.2 Technological advancements in SiC semiconductors will enable faster, compact, and energy-efficient wireless chargers, expanding market opportunities across residential and commercial sectors.
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4.1 North America
- 3.4.1.1 U.S.
- 3.4.1.2 Canada
- 3.4.2 Europe
- 3.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.4.4 Latin America
- 3.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 3.4.1 North America
- 3.5 Technology landscape
- 3.5.1 Current trends
- 3.5.2 Emerging technologies
- 3.6 Pipeline analysis
- 3.7 Future market trends
- 3.8 Porter's analysis
- 3.9 PESTEL analysis
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 Global
- 4.2.2 North America
- 4.2.3 Europe
- 4.2.4 Asia Pacific
- 4.3 Company matrix analysis
- 4.4 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.5 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.6 Key developments
- 4.6.1 Merger and acquisition
- 4.6.2 Partnership and collaboration
- 4.6.3 New product launches
- 4.6.4 Expansion plans
Chapter 5 Market Estimates and Forecast, By SiC Product Type, 2021 - 2034 ($ Mn)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 SiC power MOSFETs
- 5.3 SiC schottky barrier diodes
- 5.4 SiC power modules
- 5.5 SiC discrete components
Chapter 6 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Voltage Rating, 2021 - 2034 ($ Mn)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Up to 650V class
- 6.3 651V to 1200V class
- 6.4 1201V to 1700V class
- 6.5 Above 1700V class
Chapter 7 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Power Level, 2021 - 2034 ($ Mn)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Low power (Up to 11kW)
- 7.3 Medium power (11.1kW to 50kW)
- 7.4 High power (50.1kW to 150kW)
- 7.5 Ultra-high power (Above 150kW)
Chapter 8 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Application Type, 2021 - 2034 ($ Mn)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Stationary wireless charging
- 8.3 Dynamic wireless charging
- 8.4 Quasi-dynamic wireless charging
- 8.5 Others
Chapter 9 Market Estimates and Forecast, By End Use, 2021 - 2034 ($ Mn)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 Residential users
- 9.3 Commercial fleet operators
- 9.4 Public transit authorities
- 9.5 Public charging network operators
- 9.6 Others
Chapter 10 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 ($ Mn)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 North America
- 10.2.1 U.S.
- 10.2.2 Canada
- 10.3 Europe
- 10.3.1 Germany
- 10.3.2 UK
- 10.3.3 France
- 10.3.4 Spain
- 10.3.5 Italy
- 10.3.6 Netherlands
- 10.4 Asia Pacific
- 10.4.1 China
- 10.4.2 India
- 10.4.3 Japan
- 10.4.4 Australia
- 10.4.5 South Korea
- 10.5 Latin America
- 10.5.1 Brazil
- 10.5.2 Mexico
- 10.5.3 Argentina
- 10.6 Middle East and Africa
- 10.6.1 South Africa
- 10.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 10.6.3 UAE
Chapter 11 Company Profiles
- 11.1 Wolfspeed
- 11.2 Infineon Technologies
- 11.3 STMicroelectronics
- 11.4 onsemi (ON Semiconductor)
- 11.5 ROHM Semiconductor
- 11.6 Mitsubishi Electric
- 11.7 Fuji Electric
- 11.8 GeneSiC Semiconductor (Qorvo)
- 11.9 UnitedSiC (Qorvo)
- 11.10 Microchip Technology
- 11.11 Toshiba
- 11.12 General Electric (GE)
- 11.13 Littelfuse (IXYS)
- 11.14 WiTricity Corporation
- 11.15 InductEV Inc.
- 11.16 Plugless Power Inc. (Evatran)
- 11.17 HEVO Inc.
- 11.18 Electreon Wireless Ltd.
- 11.19 Qualcomm Technologies (Halo)
- 11.20 Robert Bosch GmbH
- 11.21 Continental AG
- 11.22 Toyota Motor Corporation
- 11.23 ABB Ltd.
- 11.24 Siemens AG
- 11.25 ENRX (Norway)










