 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1892709
快速充电电动汽车电池化学市场机会、成长驱动因素、产业趋势分析及预测(2025-2034年)Fast-Charging EV Battery Chemistries Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
2024 年全球快速充电电动车电池化学市场价值为 177 亿美元,预计到 2034 年将以 18.8% 的复合年增长率增长至 986 亿美元。
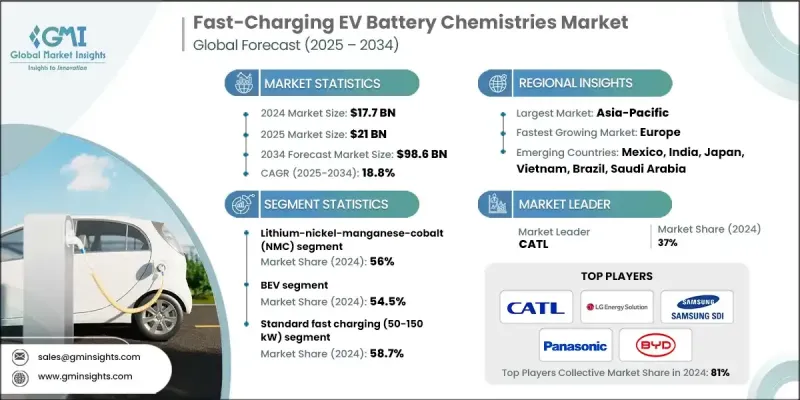
随着世界各国政府和各产业致力于减少温室气体排放并支持净零排放目标,向电动车的快速转型成为关键驱动因素。光是交通运输业就占全球排放量的25%以上,因此,电动车的普及已成为一项迫切需求,而不仅仅是消费者的选择。随着电动车保有量的成长,里程焦虑和充电基础设施的不足推动了对先进电池技术的需求,这些技术能够在10-30分钟内将电量从10%充至80%。超快速充电技术的创新,包括350千瓦以上的系统和800伏特等高压架构,使得在短短10到15分钟内即可显着提升续航里程。这一趋势正在推动对锂镍锰钴(NMC)、磷酸铁锂(LFP)和锂镍钴铝(NCA)等电池技术的投资,这些技术能够提供更高的效率、更长的寿命和更快的充电速度。
| 市场范围 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 预测年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 177亿美元 |
| 预测值 | 986亿美元 |
| 复合年增长率 | 18.8% |
到 2024 年,锂镍锰钴 (NMC) 电池市占率将达到 56%。电动车的普及以及锂成本的下降,正在加速对 NMC 电池的需求,而 NMC 电池因其快速充电能力而受到汽车製造商的广泛青睐。
预计到2024年,纯电动车(BEV)市场份额将达到54.5%。由于纯电动车电池组容量更大,且消费者对充电时间的期望日益提高,因此对快速充电电池技术的需求也随之增长。锂离子电池和磷酸锂电池技术的进步正在提升充电速度、能量储存能力和电池安全性,同时延长电池的整体使用寿命。
预计2024年,美国快速充电电动车电池市场规模将达29亿美元。政府政策,例如《通货膨胀抑制法案》(IRA),透过提供税收优惠和推广使用本地材料,正在加速国内生产。这些措施鼓励汽车製造商在合规的供应链中专注于NMC、LFP和其他先进的快速充电电池技术,以降低成本并支持永续发展。
目录
第一章:方法论
第二章:执行概要
第三章:行业洞察
- 产业生态系分析
- 供应商格局
- 利润率
- 成本结构
- 每个阶段的价值增加
- 影响价值链的因素
- 中断
- 产业影响因素
- 成长驱动因素
- 消费者对缩短充电时间的需求日益增长
- 政府对零排放车辆的强制规定
- 扩展高功率充电基础设施网络
- 电池成本下降推动了快速充电技术的普及。
- 产业陷阱与挑战
- 快速充电带来的电池衰减和循环寿命问题
- 原料供应受限
- 市场机会
- 重型和商用车辆电气化
- 超快速充电技术发展
- 固态电池商业化
- 车网互动(V2G)与快速充电的融合
- 成长驱动因素
- 成长潜力分析
- 监管环境
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL 分析
- 技术与创新格局
- 当前技术趋势
- 新兴技术
- 技术路线图与演进
- 技术采纳生命週期分析
- 价格趋势
- 按地区
- 副产品
- 成本細項分析
- 专利分析
- 消费者认知与接受障碍
- 消费者对充电时间的期望与接受程度
- 里程焦虑与快速充电可用性之间的权衡
- 快速充电功能的价格溢价意愿
- 电池衰减问题及保固预期
- 充电基础设施可近性感知
- 热退化与安全分析
- 全球充电标准格局
- 功率水平标准化
- 通讯协定
- 兆瓦充电系统
- 标准化差距和互通性挑战
- 生命週期成本和总拥有成本 (TCO) 分析
- TCO 方法论及假设
- 快速充电进阶成本分析
- 能源成本和充电效率
- 维护和更换成本
- 案例研究
第四章:竞争格局
- 介绍
- 公司市占率分析
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- MEA
- 主要市场参与者的竞争分析
- 竞争定位矩阵
- 战略展望矩阵
- 关键进展
- 併购
- 合作伙伴关係与合作
- 新产品发布
- 扩张计划和资金
- 供应商选择标准
第五章:市场估计与预测:依电池化学类型划分,2021-2034年
- 磷酸铁锂(LFP)
- 锂镍锰钴(NMC)
- 镍钴铝合金(NCA)
- 其他的
第六章:市场估算与预测:依动力总成划分,2021-2034年
- 纯电动车
- 插电式混合动力汽车
- 戊型肝炎病毒
第七章:市场估价与预测:依车辆类型划分,2021-2034年
- 搭乘用车
- SUV
- 轿车
- 掀背车
- 商用车辆
- 低容量性状
- MCV
- C型肝炎
- 两轮车
第八章:市场估算与预测:依充电技术划分,2021-2034年
- 标准快速充电(50-150千瓦)
- 超快速充电(150度以上)
第九章:市场估算与预测:依销售管道划分,2021-2034年
- OEM
- 售后市场
第十章:市场估计与预测:依地区划分,2021-2034年
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 北欧
- 比荷卢经济联盟
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 澳新银行
- 新加坡
- 马来西亚
- 印尼
- 越南
- 泰国
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 哥伦比亚
- MEA
- 南非
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿联酋
- 土耳其
第十一章:公司简介
- 全球公司
- CATL
- LG Energy Solution
- Samsung SDI
- Panasonic Energy
- SK On
- BYD Company
- Tesla
- Farasis Energy
- BorgWarner
- 区域公司
- Northvolt
- CALB
- Gotion High-Tech
- Envision AESC
- EVE Energy
- Automotive Cells Company
- 新兴公司
- QuantumScape
- StoreDot
- Solid Power
- Sila Nanotechnologies
- Factorial Energy
- Enevate
- Amprius Technologies
- ProLogium Technology
- ONE
- Freyr Battery
- Cuberg
- Sunwoda Electronic
The Global Fast-Charging EV Battery Chemistries Market was valued at USD 17.7 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 18.8% to reach USD 98.6 billion by 2034.

The rapid transition toward electric vehicles is a key driver, as governments and industries worldwide focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and supporting net-zero targets. The transportation sector alone accounts for over 25% of global emissions, making EV adoption a critical necessity rather than just a consumer preference. As EV ownership rises, range anxiety and limited charging infrastructure have pushed the demand for advanced battery chemistries capable of charging from 10% to 80% in 10-30 minutes. Innovations in ultra-fast charging technologies, including 350 kW+ systems and high-voltage architectures like 800V platforms, are enabling substantial range gains in just 10 to 15 minutes. This trend is propelling investments in battery chemistries such as lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC), lithium iron phosphate (LFP), and lithium-nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA), which can deliver higher efficiency, longer life, and faster charge times.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $17.7 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $98.6 Billion |
| CAGR | 18.8% |
The lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) segment held a 56% share in 2024. Increasing EV adoption, combined with declining lithium costs, is accelerating demand for NMC batteries, which are widely preferred by automakers for their rapid charging capabilities.
The battery electric vehicle (BEV) segment held a 54.5% share in 2024. BEVs drive the need for fast-charging battery chemistries due to their larger battery packs and growing consumer expectations for reduced charging times. Advances in lithium-ion and LFP chemistries are enhancing charging speed, energy storage, and battery safety, while extending overall lifespan.
U.S. Fast-Charging EV Battery Chemistries Market reached USD 2.9 billion in 2024. Government policies, such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), are accelerating domestic production by providing tax incentives and promoting the use of local materials. These initiatives are encouraging automakers to focus on NMC, LFP, and other advanced fast-charging battery chemistries within compliant supply chains to reduce costs and support sustainability.
Key players in the Global Fast-Charging EV Battery Chemistries Market include BYD, SK On, Factorial Energy, LG Energy Solution, CATL, Samsung SDI, BorgWarner, Panasonic, Farasis Energy, and EVE Energy. Companies in the Global Fast-Charging EV Battery Chemistries Market are strengthening their positions by investing heavily in R&D to improve energy density, safety, and charge speed. Strategic partnerships with automakers and technology firms help accelerate the commercialization of next-generation chemistries. Many are expanding production capacity in strategic regions to reduce logistics costs and meet local content requirements. Firms are also pursuing patents, licensing agreements, and joint ventures to secure supply chains for critical raw materials while focusing on sustainability and recycling initiatives to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 360° synopsis
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Regional
- 2.2.2 Battery Chemistry
- 2.2.3 Powertrain
- 2.2.4 Vehicle
- 2.2.5 Charging Technology
- 2.2.6 Sales Channel
- 2.3 TAM analysis, 2025-2034
- 2.4 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 Critical success factors
- 2.5 Future outlook and recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.2 Profit margin
- 3.1.3 Cost structure
- 3.1.4 Value addition at each stage
- 3.1.5 Factor affecting the value chain
- 3.1.6 Disruptions
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.1.1 Increasing consumer demand for reduced charging times
- 3.2.1.2 Government mandates for zero-emission vehicles
- 3.2.1.3 Expansion of high-power charging infrastructure networks
- 3.2.1.4 Declining battery costs enabling fast-charging adoption
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.2.1 Battery degradation & cycle life concerns with fast charging
- 3.2.2.2 Raw material supply constraints
- 3.2.3 Market opportunities
- 3.2.3.1 Heavy-duty & commercial vehicle electrification
- 3.2.3.2 Extreme fast-charging technology development
- 3.2.3.3 Solid-state battery commercialization
- 3.2.3.4 Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration with fast-charging
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4.1 North America
- 3.4.2 Europe
- 3.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.4.4 Latin America
- 3.4.5 Middle East & Africa
- 3.5 Porter's analysis
- 3.6 PESTEL analysis
- 3.7 Technology and innovation landscape
- 3.7.1 Current technological trends
- 3.7.2 Emerging technologies
- 3.7.3 Technology roadmaps & evolution
- 3.7.4 Technology adoption lifecycle analysis
- 3.8 Price trends
- 3.8.1 By region
- 3.8.2 By product
- 3.9 Cost breakdown analysis
- 3.10 Patent analysis
- 3.11 Consumer perception & adoption barriers
- 3.11.1 Consumer charging time expectations & acceptance thresholds
- 3.11.2 Range anxiety vs fast-charging availability trade-off
- 3.11.3 Price premium willingness for fast-charging capability
- 3.11.4 Battery degradation concerns & warranty expectations
- 3.11.5 Charging infrastructure accessibility perception
- 3.12 Thermal degradation & safety analysis
- 3.12.1 Global charging standards landscape
- 3.12.2 Power level standardization
- 3.12.3 Communication protocols
- 3.12.4 Megawatt charging system
- 3.12.5 Standardization gaps & interoperability challenges
- 3.13 Life cycle cost & total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis
- 3.13.1 TCO methodology & assumptions
- 3.13.2 Fast-charging premium cost analysis
- 3.13.3 Energy costs & charging efficiency
- 3.13.4 Maintenance & replacement costs
- 3.14 Case studies
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 North America
- 4.2.2 Europe
- 4.2.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.4 LATAM
- 4.2.5 MEA
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategic outlook matrix
- 4.6 Key developments
- 4.6.1 Mergers & acquisitions
- 4.6.2 Partnerships & collaborations
- 4.6.3 New product launches
- 4.6.4 Expansion plans and funding
- 4.7 Vendor selection criteria
Chapter 5 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Battery Chemistry, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
- 5.3 Lithium-Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC)
- 5.4 Nickel-Cobalt-Aluminum (NCA)
- 5.5 Others
Chapter 6 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Powertrain, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 BEV
- 6.3 PHEV
- 6.4 HEV
Chapter 7 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Vehicle, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Passenger Vehicles
- 7.2.1 SUVs
- 7.2.2 Sedans
- 7.2.3 Hatchbacks
- 7.3 Commercial Vehicles
- 7.3.1 LCV
- 7.3.2 MCV
- 7.3.3 HCV
- 7.4 Two-wheelers
Chapter 8 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Charging Technology, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Standard Fast Charging (50-150 kW)
- 8.3 Ultra-Fast Charging (Above 150 kW)
Chapter 9 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Sales Channel, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 OEM
- 9.3 Aftermarket
Chapter 10 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 ($Mn, Units)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 North America
- 10.2.1 US
- 10.2.2 Canada
- 10.3 Europe
- 10.3.1 Germany
- 10.3.2 UK
- 10.3.3 France
- 10.3.4 Italy
- 10.3.5 Spain
- 10.3.6 Russia
- 10.3.7 Nordics
- 10.3.8 Benelux
- 10.4 Asia Pacific
- 10.4.1 China
- 10.4.2 India
- 10.4.3 Japan
- 10.4.4 South Korea
- 10.4.5 ANZ
- 10.4.6 Singapore
- 10.4.7 Malaysia
- 10.4.8 Indonesia
- 10.4.9 Vietnam
- 10.4.10 Thailand
- 10.5 Latin America
- 10.5.1 Brazil
- 10.5.2 Mexico
- 10.5.3 Argentina
- 10.5.4 Colombia
- 10.6 MEA
- 10.6.1 South Africa
- 10.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 10.6.3 UAE
- 10.6.4 Turkey
Chapter 11 Company Profiles
- 11.1 Global companies
- 11.1.1 CATL
- 11.1.2 LG Energy Solution
- 11.1.3 Samsung SDI
- 11.1.4 Panasonic Energy
- 11.1.5 SK On
- 11.1.6 BYD Company
- 11.1.7 Tesla
- 11.1.8 Farasis Energy
- 11.1.9 BorgWarner
- 11.2 Regional companies
- 11.2.1 Northvolt
- 11.2.2 CALB
- 11.2.3 Gotion High-Tech
- 11.2.4 Envision AESC
- 11.2.5 EVE Energy
- 11.2.6 Automotive Cells Company
- 11.3 Emerging companies
- 11.3.1 QuantumScape
- 11.3.2 StoreDot
- 11.3.3 Solid Power
- 11.3.4 Sila Nanotechnologies
- 11.3.5 Factorial Energy
- 11.3.6 Enevate
- 11.3.7 Amprius Technologies
- 11.3.8 ProLogium Technology
- 11.3.9 ONE
- 11.3.10 Freyr Battery
- 11.3.11 Cuberg
- 11.3.12 Sunwoda Electronic







