 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1892869
远距病人监护(RPM)设备市场机会、成长驱动因素、产业趋势分析及预测(2025-2034年)Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Devices Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
2024 年全球远距病人监护设备市场价值为 241 亿美元,预计到 2034 年将以 10.8% 的复合年增长率增长至 659 亿美元。
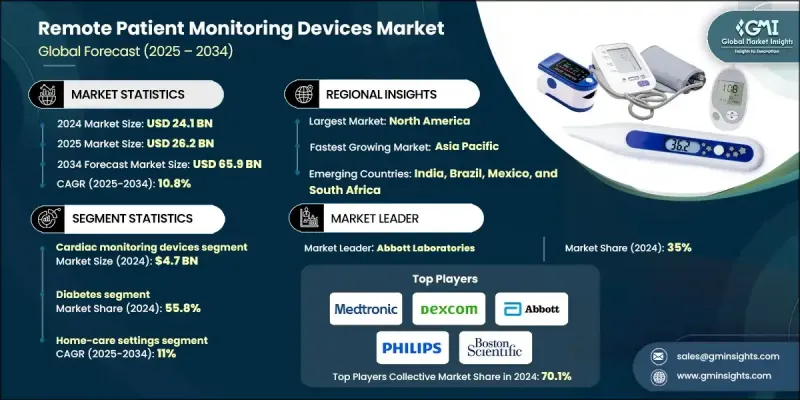
市场成长的驱动因素包括慢性病盛行率的上升、医疗保健的快速数位化以及降低医院再入院率和整体医疗成本的迫切需求。远距患者监护 (RPM) 能够在传统临床环境之外持续追踪患者的生命征象和健康状况,使医生能够更快地做出数据驱动的决策,并提高患者对治疗方案的依从性。智慧型手机、连网医疗设备和云端平台的日益普及显着提升了 RPM 解决方案的可用性、准确性和可扩展性。这些技术共同支持更积极主动的预防性医疗模式,减少急诊就诊次数,减轻医疗基础设施的负担。
| 市场范围 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 预测年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 241亿美元 |
| 预测值 | 659亿美元 |
| 复合年增长率 | 10.8% |
全球向价值医疗和居家医疗模式的转变进一步加速了对远距病患监测(RPM)设备的需求。支付方和医疗服务提供方日益认识到远端监测的经济效益,例如减少住院天数、降低再入院罚款以及更好地管理高风险患者群体。此外,全球人口老化以及糖尿病、心血管疾病和呼吸系统疾病等疾病发生率的上升,也扩大了RPM的目标患者族群。政府推行的促进数位医疗、远距医疗报销以及将远距监测纳入标准诊疗流程的倡议,也在预测期内对提升市场渗透率发挥关键作用。
2024年,心臟监测设备市场规模预计将达47亿美元。该市场涵盖心电图设备、植入式心臟监测器、穿戴式心臟监测器以及用于即时检测心律不整、心臟衰竭加重和其他心臟异常的事件记录仪。全球心血管疾病的高发生率,以及对高风险心臟病患者进行持续监测的迫切需求,是推动该市场成长的核心因素。远距心臟监测能够减少患者频繁的面对面就诊,及早发现危及生命的事件,并有助于更好地调整药物剂量。
随着医疗服务从医院转向患者家中,以提高患者舒适度、降低成本并减少再次入院率,预计到2024年,居家护理市场将占据11%的市场份额。在该领域,远端监测设备,例如生命体征监测仪、血糖仪、心臟穿戴设备和连网血氧仪,被用于持续或定期监测慢性病患者、术后患者和老年人的健康状况。居家监测使患者能够在熟悉的环境中接受医疗专业人员的远端监督,从而提高治疗依从性和生活品质。
2024年,北美远距患者监护设备市占率达到42.3%,位居全球最大。该地区的领先地位得益于其完善的医疗基础设施、高额的医疗支出以及对数位医疗技术的广泛应用。尤其是在美国,远距监护服务的优惠报销政策极大地鼓励了医疗机构将远距患者监护纳入慢性病管理方案。此外,生活方式相关疾病的高发生率、庞大的老龄人口以及互联网和智慧型设备的普及,也为远距监护解决方案的部署创造了理想的环境。
目录
第一章:方法论与范围
第二章:执行概要
第三章:行业洞察
- 产业生态系分析
- 产业影响因素
- 成长驱动因素
- 全球慢性病发生率不断上升
- 新兴国家可支配收入和医疗保健支出不断增长
- 已开发国家的技术进步
- 远距病人监护设备的应用日益普及
- 产业陷阱与挑战
- 设备成本高昂
- 严格的监管框架
- 市场机会
- 人工智慧驱动的预测性监测工具的应用日益普及
- 穿戴式生物感测器的出现,为连续、即时健康追踪提供了可能
- 成长驱动因素
- 成长潜力分析
- 监管环境
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 技术格局
- 未来市场趋势
- 差距分析
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL 分析
第四章:竞争格局
- 介绍
- 公司市占率分析
- 公司矩阵分析
- 主要市场参与者的竞争分析
- 竞争定位矩阵
- 策略仪錶板
第五章:市场估算与预测:依产品划分,2021-2034年
- 心臟监测设备
- 血压监测设备
- 神经监测设备
- 呼吸监测设备
- 多参数监测设备
- 血糖监测设备
- 胎儿及新生儿监护设备
- 睡眠监测设备
- 其他产品
第六章:市场估算与预测:依应用领域划分,2021-2034年
- 心血管疾病
- 癌症
- 糖尿病
- 神经系统疾病
- 传染病
- 呼吸系统疾病
- 其他应用
第七章:市场估算与预测:依最终用途划分,2021-2034年
- 居家照护环境
- 长期照护
- 其他最终用途
第八章:市场估算与预测:依地区划分,2021-2034年
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 波兰
- 瑞士
- 荷兰
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韩国
- 泰国
- 印尼
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 哥伦比亚
- 智利
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 阿联酋
- 以色列
第九章:公司简介
- Abbott Laboratories
- Baxter International
- BIOTRONIK
- Boston Scientific
- Dexcom
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche
- GE Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson
- Koninklijke Philips NV
- Medtronic
- OMRON
- Sotera Wireless
- Vital Connect
The Global Remote Patient Monitoring Devices Market was valued at USD 24.1 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 10.8% to reach USD 65.9 billion by 2034.

Market growth is driven by the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, rapid digitalization of healthcare, and the growing need to reduce hospital readmissions and overall care costs. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) enables continuous tracking of patients' vital signs and health status outside traditional clinical settings, empowering physicians to make faster, data-driven decisions and improving patient adherence to treatment plans. Rising adoption of smartphones, connected medical devices, and cloud-based platforms has significantly enhanced the usability, accuracy, and scalability of RPM solutions. These technologies collectively support more proactive and preventive care models, reducing emergency visits and easing the burden on healthcare infrastructure.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $24.1 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $65.9 Billion |
| CAGR | 10.8% |
The global shift towards value-based care and home-based healthcare is further accelerating the demand for RPM devices. Payers and providers are increasingly recognizing the economic benefits of remote monitoring, such as reduced inpatient days, lower readmission penalties, and better management of high-risk patient cohorts. Additionally, aging populations worldwide and the rising incidence of conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and respiratory disorders are expanding the addressable patient pool for RPM. Government initiatives promoting digital health, telehealth reimbursement, and integration of remote monitoring into standard care pathways are also playing a critical role in enhancing market penetration over the forecast period.
The cardiac monitoring devices segment generated USD 4.7 billion in 2024. This segment includes ECG devices, implantable cardiac monitors, wearable heart monitors, and event recorders used to detect arrhythmias, heart failure exacerbations, and other cardiac abnormalities in real time. The high burden of cardiovascular diseases globally, combined with the critical need for continuous surveillance of high-risk cardiac patients, is a core driver for this segment. Remote cardiac monitoring reduces the need for frequent in-person consultations, enables early identification of life-threatening events, and supports better medication titration.
The home care settings segment held 11% share in 2024 as healthcare delivery shifted from hospitals to patients' homes to improve comfort, reduce costs, and minimize hospital readmissions. In this segment, remote monitoring devices such as vital signs monitors, glucose meters, cardiac wearables, and connected oximeters are used to track patients with chronic conditions, post-operative cases, and elderly individuals on a continuous or scheduled basis. Home-based monitoring enables patients to remain in a familiar environment while still being under the virtual supervision of healthcare professionals, which enhances treatment adherence and quality of life.
North America Remote Patient Monitoring Devices Market held 42.3% share in 2024, accounting for the largest regional share. The region's leadership is supported by a well-established healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and strong adoption of digital health technologies. Favorable reimbursement frameworks for remote monitoring services, particularly in the United States, have significantly encouraged providers to incorporate RPM into chronic disease management programs. Additionally, a high prevalence of lifestyle-related disorders, a large elderly population, and widespread access to the internet and smart devices create an ideal environment for the deployment of remote monitoring solutions.
Key players operating in the Global Remote Patient Monitoring Devices Market include Philips Healthcare, Medtronic plc, GE HealthCare, Abbott Laboratories, Boston Scientific Corporation, Nihon Kohden Corporation, ResMed Inc., Dexcom, Inc., and Masimo Corporation. These companies focus on continuous product innovation, integrating advanced sensors, wireless connectivity, and data analytics into their device portfolios. They are also actively involved in strategic partnerships with hospitals, telehealth platforms, and payers to expand their installed base and enhance recurring revenue streams via monitoring services and software subscriptions. Many of these players are investing in AI-enabled platforms that can automatically flag abnormal readings, support predictive risk scoring, and simplify clinical workflows, making remote monitoring more scalable and effective for large patient populations.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology and Scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definitions
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast model
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 360º synopsis
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Regional trends
- 2.2.2 Product trends
- 2.2.3 Application trends
- 2.2.4 End use trends
- 2.3 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.3.1 Key decision points for industry executives
- 2.3.2 Critical success factors for market players
- 2.4 Future outlook and strategic recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.1.1 Rising incidence of chronic diseases across the globe
- 3.2.1.2 Growing disposable income and healthcare expenditure in emerging countries
- 3.2.1.3 Technological advancement in developed nations
- 3.2.1.4 Growing adoption of remote patient monitoring devices
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.2.1 High cost of devices
- 3.2.2.2 Stringent regulatory framework
- 3.2.3 Market opportunities
- 3.2.3.1 Increasing adoption of AI-powered predictive monitoring tools
- 3.2.3.2 Emergence of wearable biosensors for continuous, real-time health tracking
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4.1 North America
- 3.4.2 Europe
- 3.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.4.4 Latin America
- 3.4.5 Middle East & Africa
- 3.5 Technology landscape
- 3.6 Future market trends
- 3.7 Gap analysis
- 3.8 Porter's analysis
- 3.9 PESTEL analysis
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.3 Company matrix analysis
- 4.4 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.5 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.6 Strategy dashboard
Chapter 5 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Product, 2021 - 2034 ($ Mn)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Cardiac monitoring devices
- 5.3 Blood pressure monitoring devices
- 5.4 Neurological monitoring devices
- 5.5 Respiratory monitoring devices
- 5.6 Multiparameter monitoring devices
- 5.7 Blood glucose monitoring devices
- 5.8 Fetal and neonatal monitoring devices
- 5.9 Sleep monitoring devices
- 5.10 Other products
Chapter 6 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Application, 2021 - 2034 ($ Mn)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Cardiovascular diseases
- 6.3 Cancer
- 6.4 Diabetes
- 6.5 Neurological disorders
- 6.6 Infectious diseases
- 6.7 Respiratory diseases
- 6.8 Other applications
Chapter 7 Market Estimates and Forecast, By End Use, 2021 - 2034 ($ Mn)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Home-care settings
- 7.3 Long-term care
- 7.4 Other end use
Chapter 8 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 ($ Mn)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 North America
- 8.2.1 U.S.
- 8.2.2 Canada
- 8.3 Europe
- 8.3.1 Germany
- 8.3.2 UK
- 8.3.3 France
- 8.3.4 Italy
- 8.3.5 Spain
- 8.3.6 Russia
- 8.3.7 Poland
- 8.3.8 Switzerland
- 8.3.9 Netherlands
- 8.4 Asia Pacific
- 8.4.1 China
- 8.4.2 India
- 8.4.3 Japan
- 8.4.4 Australia
- 8.4.5 South Korea
- 8.4.6 Thailand
- 8.4.7 Indonesia
- 8.5 Latin America
- 8.5.1 Brazil
- 8.5.2 Mexico
- 8.5.3 Argentina
- 8.5.4 Colombia
- 8.5.5 Chile
- 8.6 Middle East and Africa
- 8.6.1 Saudi Arabia
- 8.6.2 South Africa
- 8.6.3 UAE
- 8.6.4 Israel
Chapter 9 Company Profiles
- 9.1 Abbott Laboratories
- 9.2 Baxter International
- 9.3 BIOTRONIK
- 9.4 Boston Scientific
- 9.5 Dexcom
- 9.6 F. Hoffmann-La Roche
- 9.7 GE Healthcare
- 9.8 Johnson & Johnson
- 9.9 Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- 9.10 Medtronic
- 9.11 OMRON
- 9.12 Sotera Wireless
- 9.13 Vital Connect








