 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1906294
全球晶圆厂自动化市场按产品、自动化等级、晶圆尺寸、部署类型、晶圆厂类型、最终用户和地区划分-预测至2032年Fab Automation Market By Offering (Harfware, Software), Wafer Size, End User - Global Forecast to 2032 |
||||||
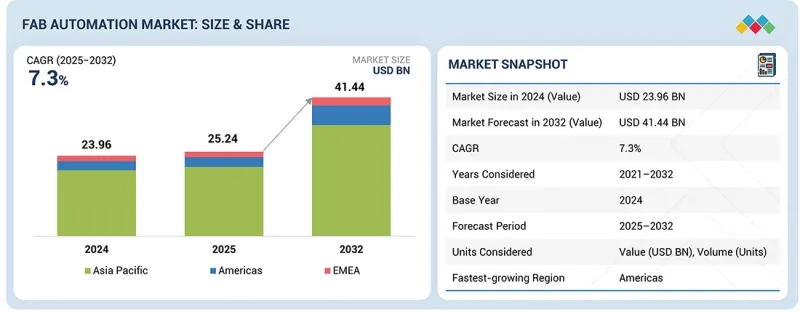
预计到 2025 年,晶圆厂自动化市场规模将达到 252.4 亿美元,到 2032 年将达到 414.4 亿美元,2025 年至 2032 年的复合年增长率为 7.3%。
由于半导体製造的复杂性日益增加,以及全球对更高产量比率、更短週期时间和更高营运一致性的追求,预计市场在预测期内将显着增长。
| 调查范围 | |
|---|---|
| 调查期 | 2020-2032 |
| 基准年 | 2024 |
| 预测期 | 2025-2032 |
| 目标单元 | 金额(十亿美元) |
| 部分 | 依产品、自动化等级、晶圆尺寸、部署类型、晶圆厂类型、最终用户、地区 |
| 目标区域 | 北美、欧洲、亚太地区及其他地区 |
300毫米晶圆产能的扩张、先进製程节点的研发以及异质整合技术的进步,正在加速自动化物料搬运系统(AMHS)、机器人、製造执行系统(MES)、先进製程控制(APC)、产量比率管理软体(YMS)以及基于人工智慧的分析解决方案的普及应用。这些解决方案能够帮助晶圆厂实现精准的物料搬运、即时製程优化、预测性维护,并确保符合超洁净製造标准。对新建待开发区的大规模投资、政府对半导体产业的支持,以及人工智慧、5G、汽车电子和高效能运算等领域对晶片日益增长的需求,都将进一步推动市场成长。然而,高昂的实施成本、复杂的整合以及熟练工程师的短缺也可能构成挑战。加强自动化生态系统的互通性、推广模组化应用以及建立伙伴关係关係,对于维持市场的长期扩张至关重要。
预计在2025年至2032年期间,半导体组装测试外包(OSAT)服务商细分市场将以最高的复合年增长率成长,这主要得益于先进封装、异质整合和晶片级架构的快速发展。 OSAT设施需要高精度、无污染且高吞吐量的自动化解决方案,以支援晶圆级封装(WLP)、扇出型封装技术、2.5D/3D堆迭和进阶测试作业等复杂製程。为了应对日益复杂的装置和不断缩小的公差,OSAT公司正在采用自动化物料搬运系统(AMHS)、机器人、智慧侦测系统、製造执行系统(MES)、进阶製程控制(APC)和人工智慧分析等技术,以提高产量比率、降低操作变异性,并在整个封装和测试工作流程中保持可追溯性。人工智慧、高效能运算(HPC)、汽车电子和5G应用的扩展进一步推动了OSAT客户对更快週期、可扩展生产和更高可靠性的需求。随着封装成为半导体效能的关键差异化因素,OSAT(外包半导体封装测试)公司正在加速投资数位转型、自动化升级和无尘室优化。外包趋势的日益增长、先进封装需求的增加以及对高性价比大批量生产的需求,共同促成了OSAT供应商在全球晶圆厂自动化市场中成为至关重要且快速成长的终端用户群。
在半导体製造能力快速扩张和对高通量、洁净度控制生产环境日益增长的需求的推动下,预计到2032年,硬体领域将占据晶圆厂自动化市场最大的份额。随着晶圆厂向先进节点和300毫米生产线扩展,包括自动化物料搬运系统(AMHS)、机器人、晶圆搬运设备、环境控制系统、电力和公用设施自动化系统以及通讯和网路硬体在内的强大硬体的需求持续增长。这些系统构成了自动化晶圆厂的物理基础,能够实现精确的晶圆运输、维持稳定的无尘室环境、不间断的公用设施管理以及可靠的设备连接。人工智慧、高效能运算、汽车电子和5G应用推动的逻辑、记忆体和先进封装生产激增,进一步加速了对自动化硬体的投资。对于亚太地区、美国和欧洲的待开发区而言,端到端自动化基础设施正成为确保产量比率稳定、缩短週期时间和增强营运韧性的重中之重。此外,现有工厂的现代化改造正在推动下一代机器人技术、自动化物料搬运系统 (AMHS) 升级以及先进污染控制系统的应用。随着半导体製程复杂性的增加和处理容量要求的提高,硬体仍将是全球晶圆厂自动化领域的基础和最重要的投资领域。
预计2025年至2032年,美洲地区晶圆厂自动化市场将呈现最高的复合年增长率,这主要得益于对先进半导体製造的大规模投资、现有晶圆厂的现代化改造以及旨在提升国内晶片产量的政府新倡议。该地区(包括美国和其他美洲国家)正在推动多个待开发区和棕地计划,旨在支援尖端逻辑、记忆体和异质整合技术。新建晶圆厂强调高产能、无污染和节能运行,从而推动了对自动化物料搬运系统(AMHS)、机器人、环境控制系统、先进计量设备和工厂通讯基础设施的需求。美国凭藉整合装置製造商(IDM)、晶圆代工厂和外包半导体测试与製造(OSAT)公司的大量资本投资,以及国家半导体政策(NSP)的激励措施(该政策优先考虑自动化、数位转型和劳动力优化),正在推动该地区的成长。 10奈米以下和极紫外光刻(EUV)製程的日益普及,进一步加速了精密搬运设备和智慧自动化平台的需求。同时,其他美洲国家正在扩大其后端组装、测试和封装能力,从而对可扩展且经济高效的自动化解决方案产生了更大的需求。强有力的政策支持、不断增长的半导体消费量以及产能的大规模扩张,共同使美洲成为下一代晶圆厂自动化领域的高成长中心。
在全球晶圆厂自动化市场拥有重要地位的主要企业包括大福(日本)、村田机械(日本)、阿特拉斯科普柯(瑞典)、罗泽自动化(日本)和荏原(日本)。
调查范围
本报告按产品类型、部署方式、晶圆尺寸、最终用户和地区对晶圆厂自动化市场进行细分,并预测市场规模。该报告还全面分析了影响市场成长的驱动因素、限制因素、机会和挑战,并从定性和定量两个角度对市场进行了全面评估。
购买这份报告的理由:
本报告为市场领导和新参与企业提供晶圆厂自动化市场及其相关细分市场的预期收入资讯。这有助于相关人员了解竞争格局,并提供宝贵的见解,从而帮助他们巩固市场地位并制定有效的打入市场策略策略。此外,报告还透过提供有关关键市场驱动因素、限制、机会和挑战的信息,帮助企业了解市场趋势。
本报告深入分析了以下内容:
- 关键驱动因素分析(先进节点和EUV微影技术的扩展需要高吞吐量自动化;300mm晶圆厂产能的快速成长;逻辑、记忆体和先进封装製程复杂性的增加;人工智慧/机器学习驱动的预测分析阻碍因素数位双胞胎平台的日益普及;政府鼓励待开发区的奖励);动化硬体和整合方面的高额资本支出;旧有系统和下一代系统之间互通性;熟练的自动化和软体专业人员短缺;由于供应商集中导致工厂前置作业时间长);机会分析(2.5D/3D封装和异质挑战(由于严格的超洁净製造要求,污染和可靠性风险增加;跨多个供应商的美国、APC、YMS和AMHS生态系统的整合复杂性;在高晶圆产量和EUV製程敏感性下保持自动化性能;影响半导体设备供应链的永续性动盪;以及在不影响生产的情况下对现有工厂进行现代化改造的高复杂性和高成本)。
- 产品开发/创新:晶圆厂自动化市场新产品发布、扩张、协议、合作和收购的策略,以及对未来技术趋势和研发活动的深入洞察
- 市场发展:关于盈利市场的全面资讯-本报告分析了各个地区的晶圆厂自动化市场。
- 市场多元化:全面介绍晶圆厂自动化市场的新产品、前沿领域、近期趋势和投资状况。
- 主要企业——大福(日本)、村田机械(日本)、阿特拉斯·科普柯(瑞典)、罗泽自动化(日本)、荏原(日本)、发那科(日本)、川崎重工(日本)、平田株式会社(日本)、安川电机(日本)、库卡股份公司(德国)
目录
第一章 引言
第二章执行摘要
第三章重要考察
第四章 市场概览
- 市场动态
- 相互关联的市场与跨产业机会
- 一级/二级/三级公司的策略性倡议
- 市场动态
第五章 产业趋势
- 波特五力分析
- 总体经济指标
- 价值链分析
- 生态系分析
- 定价分析
- 贸易分析
- 2026-2027 年主要会议和活动
- 影响客户业务的趋势/干扰因素
- 2021-2025年投资与资金筹措情景
- 案例研究分析
- 美国关税对2025年晶圆厂自动化市场的影响
第六章:技术进步、人工智慧的影响、专利、创新与未来应用
- 关键新兴技术
- 互补技术
- 邻近技术
- 技术/产品蓝图
- 专利分析
- 人工智慧对晶圆厂自动化市场的影响
第七章 监理环境
- 监管机构、政府机构和其他组织
- 业界标准
- 半标准(GEM、GEM300、E84、E87、EDA/介面 A)
- ISO无尘室及环境管理标准(ISO 14644系列)
- ISO 10218 和 IEC 61508 - 机器人安全与功能安全标准
- 用于製造设备通讯的 OPC UA
- ANSI/ISA-95 - 整合製造标准
- SEMI S2 - 环境、健康与安全 (EHS) 标准
第八章:顾客状况与购买行为
- 决策流程
- 主要相关人员和采购标准
- 招募障碍和内部挑战
- 来自不同终端使用者的未满足需求
9. 晶圆厂自动化市场(依产品/服务分类)
- 硬体
- 软体
- 服务
第十章 晶圆厂自动化市场(依自动化细分市场划分)
- 物料输送自动化
- 设备自动化
- 流程自动化
- 工厂自动化软体
- 人工智慧/分析自动化
第十一章 晶圆厂自动化市场(以晶圆尺寸划分)
- 小于150毫米
- 200毫米
- 300毫米
第十二章 晶圆厂自动化市场(依部署类型划分)
- 待开发区工厂
- 棕地工厂
第十三章 晶圆厂自动化市场(以晶圆厂类型划分)
- 先进节点晶圆厂(7奈米及以下)
- 主流节点晶圆厂(10-28奈米)
- 成熟节点晶圆厂(28-90奈米)
- 传统节点晶圆厂(>90奈米)
第十四章 晶圆厂自动化市场(依自动化程度划分)
- 全自动
- 半自动
第十五章 晶圆厂自动化市场(以最终用户划分)
- 整合设备製造商
- 铸造厂
- 半导体组装和测试外包服务供应商
- 研究工厂
第十六章 各地区晶圆厂自动化市场
- 美洲
- 美国
- 其他的
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 日本
- 韩国
- 台湾
- 印度
- 其他的
- EMEA
- 欧洲
- 中东和非洲
第十七章 竞争格局
- 概述
- 主要参与企业的策略/优势,2021年1月至2025年10月
- 2024年市占率分析
- 2021-2024年收入分析
- 估值和财务指标
- 品牌/产品对比
- 公司估值矩阵:主要参与企业,2024 年
- 公司估值矩阵:Start-Ups/中小企业,2024 年
- 竞争场景
第十八章:公司简介
- 主要参与企业
- DAIFUKU CO., LTD.
- MURATA MACHINERY
- EBARA CORPORATION
- RORZE CORPORATION
- FANUC
- HIRATA CORPORATION
- KUKA AG
- YASKAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION
- KAWASAKI HEAVY INDUSTRIES
- 其他公司
- ATLAS COPCO
- THIRA-UTECH
- DAIHEN CORPORATION
- BROOKS AUTOMATION
- MIRLE AUTOMATION
- SYNUS TECH
- SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES
- MEETFUTURE
- Fab MATICS
- TAIYO INC.
- SINEVA
- CASTEC INTERNATIONAL
- SYSTEMA GMBH
- KYOWA ELECTRIC & INSTRUMENT
- AMHS TECHNOLOGIES
- ATS AUTOMATION
- NIDEC CORPORATION
- GENMARK AUTOMATION
- JEL CORPORATION
- KENSINGTON LABS
- SIEMENS
- ROCKWELL AUTOMATION
- 最终用户
- FOUNDRIES
- IDM FIRMS
- OSAT COMPANIES
第十九章调查方法
第20章附录
The fab automation market is projected to reach USD 25.24 billion in 2025 and USD 41.44 billion by 2032, registering a CAGR of 7.3% between 2025 and 2032. The market is projected to witness substantial growth during the forecast period, driven by the increasing complexity of semiconductor manufacturing and the global push toward higher yields, faster cycle times, and greater operational consistency.
| Scope of the Report | |
|---|---|
| Years Considered for the Study | 2020-2032 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2032 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Billion) |
| Segments | By Offering, Deployment Type, Wafer Size, End User and Region |
| Regions covered | North America, Europe, APAC, RoW |
Expanding 300 mm capacity, advanced-node production, and heterogeneous integration are accelerating the adoption of automated material handling systems (AMHS), robotics, manufacturing execution systems (MES), advanced process control (APC), yield management software (YMS), and AI-enabled analytics. These solutions enable fabs to achieve precision handling, real-time process optimization, and predictive maintenance, ensuring compliance with ultra-clean manufacturing standards. Growth is further supported by large-scale investments in new greenfield fabs, government semiconductor incentives, and the rising demand for chips powering AI, 5G, automotive electronics, and high-performance computing. However, high implementation costs, integration complexity, and the need for skilled technical resources may present operational challenges. Strengthening interoperability, modular deployments, and partnerships across the automation ecosystem will be essential to sustaining long-term market expansion.

"By end user, the outsourced semiconductor assembly & test (OSAT) providers segment is expected to register the highest CAGR between 2025 and 2032."
The outsourced semiconductor assembly and test (OSAT) providers segment is expected to register the highest CAGR in the fab automation market between 2025 and 2032, driven by the rapid growth of advanced packaging, heterogeneous integration, and chiplet-based architectures. OSAT facilities are experiencing rising demand for high-precision, contamination-free, and high-throughput automation solutions to support complex processes such as wafer-level packaging (WLP), fan-out technologies, 2.5D/3D stacking, and advanced test operations. To manage increasing device complexity and shrinking tolerances, OSATs are deploying Automated Material Handling Systems (AMHS), robotics, smart inspection systems, Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Advanced Process Control (APC), and AI-enabled analytics to enhance yield, reduce operational variability, and maintain traceability across packaging and test workflows. The expansion of AI, HPC, automotive electronics, and 5G applications is further driving OSAT customers to demand faster cycle times, scalable production, and higher reliability. As packaging becomes a critical differentiator in semiconductor performance, OSATs are accelerating investments in digital transformation, automation upgrades, and cleanroom optimization. The combination of rising outsourcing trends, advanced packaging demand, and the need for cost-efficient, high-volume production positions OSAT providers as a pivotal and fast-growing end-user segment in the global fab automation market.
"Based on offering, the hardware segment is projected to account for the largest market share in 2032."
The hardware segment is projected to account for the largest share of the fab automation market by 2032, driven by the rapid expansion of semiconductor manufacturing capacity and the increasing demand for high-throughput, contamination-controlled production environments. As fabs scale advanced-node and 300mm lines, demand for robust hardware, including automated material handling systems (AMHS), robotics, wafer-handling equipment, environmental control systems, power and utility automation systems, and communication and networking hardware, continues to rise. These systems form the physical backbone of automated fabs, enabling precise wafer transport, maintaining stable cleanroom conditions, ensuring uninterrupted utility management, and ensuring reliable equipment connectivity. The surge in logic, memory, and advanced packaging production driven by AI, HPC, automotive electronics, and 5G applications is further accelerating investments in automation hardware. Greenfield fabs in the Asia Pacific, the US, and Europe are increasingly prioritizing end-to-end automated infrastructure to ensure yield consistency, reduce cycle time, and enhance operational resilience. Additionally, the modernization of brownfield facilities is boosting the adoption of next-generation robotics, AMHS upgrades, and advanced contamination control systems. As semiconductor processes become more complex and throughput requirements rise, hardware will remain the foundational and most heavily invested offering within the global fab automation landscape.
"The Americas region is projected to exhibit the highest CAGR from 2025 to 2032."
The Americas region is projected to exhibit the highest CAGR in the fab automation market from 2025 to 2032, driven by substantial investments in advanced semiconductor manufacturing, modernization of existing fabs, and renewed government focus on strengthening domestic chip production. The region, comprising the US and the Rest of the Americas, is advancing multiple greenfield and brownfield projects aimed at supporting leading-edge logic, memory, and heterogeneous integration technologies. As new fabs emphasize high-throughput, contamination-free, and energy-efficient operations, demand is rising for automated material handling systems (AMHS), robotics, environmental control systems, advanced metrology hardware, and factory communication infrastructure. The US leads regional growth, fueled by substantial capital expenditure from IDMs, foundries, and OSATs, alongside incentives under national semiconductor policies that prioritize automation, digital transformation, and workforce optimization. Increasing adoption of sub-10 nm and EUV-enabled processes is further accelerating the need for precision handling equipment and intelligent automation platforms. Meanwhile, countries in the Rest of the Americas are expanding backend assembly, test, and packaging capabilities, creating additional demand for scalable, cost-efficient automation solutions. Collectively, strong policy support, rising semiconductor consumption, and large-scale capacity expansion position the Americas as a high-growth hub for next-generation fab automation.
The break-up of the profile of primary participants in the fab automation market-
- By Company Type: Tier 1 - 35%, Tier 2 - 45%, Tier 3 - 20%
- By Designation: C-level Executives - 40%, Directors - 30%, Others - 30%
- By Region: Americas - 40%, EMEA - 25%, Asia Pacific - 35%
Note: Other designations include sales, marketing, and product managers.
The three tiers of the companies are based on their total revenues as of 2024: Tier 1: >USD 1 billion, Tier 2: USD 500 million-1 billion, and Tier 3: USD 500 million.
The major players in the fab automation market with a significant global presence include Daifuku (Japan), Murata Machinery (Japan), Atlas Copco (Sweden), Rorze Automation (Japan), and Ebara (Japan).
Research Coverage
The report segments the fab automation market and forecasts its size by offering, deployment type, wafer size, end user, and region. It also comprehensively reviews the drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges that influence market growth. The report encompasses both qualitative and quantitative aspects of the market.
Reasons to Buy the Report:
The report will help the market leaders/new entrants with information on the closest approximate revenues for the overall fab automation market and related segments. This report will help stakeholders understand the competitive landscape and gain valuable insights to strengthen their market position and develop effective go-to-market strategies. The report also helps stakeholders understand the pulse of the market, providing them with information on key market drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges.
The report provides insights into the following pointers:
- Analysis of key drivers (expansion of advanced-node and EUV-enabled manufacturing requiring high-throughput automation; rapid growth in 300 mm fab capacity; rising process complexity across logic, memory, and advanced packaging; increasing adoption of AI/ML-driven predictive analytics and digital-twin platforms; government incentives accelerating greenfield fab construction), restraints (high capital expenditure for automation hardware and integration; limited interoperability between legacy and next-generation systems; shortages of skilled automation and software specialists; extended equipment lead times due to vendor concentration), opportunities (deployment of advanced automation for 2.5D/3D packaging and heterogeneous integration; emergence of autonomous, AI-enabled fabs; large-scale automation demand from new fabs in the US, Asia, and Europe; adoption of modular AMHS and collaborative robotics; sustainability-focused automation solutions for energy and cleanroom efficiency), and challenges (stringent ultra-clean manufacturing requirements increasing contamination and reliability risks; integration complexity across multi-vendor MES, APC, YMS, and AMHS ecosystems; maintaining automation performance at high wafer volumes and EUV process sensitivities; geopolitical disruptions affecting semiconductor equipment supply chains; high complexity and cost of modernizing brownfield fabs without production impact)
- Product Development/Innovation: Detailed insights on upcoming technologies, research & development activities, and strategies such as new product launches, expansions, contracts, partnerships, and acquisitions in the fab automation market
- Market Development: Comprehensive information about lucrative markets-the report analyses the fab automation market across varied regions
- Market Diversification: Exhaustive information about new products, untapped geographies, recent developments, and investments in the fab automation market
- Competitive Assessment: In-depth assessment of market shares, growth strategies, and product offerings of leading players, including Daifuku (Japan), Murata Machinery (Japan), Atlas Copco (Sweden), Rorze Automation (Japan), Ebara (Japan), FANUC (Japan), Kawasaki Heavy Industries (Japan), Hirata Corporation (Japan), Yaskawa (Japan), and KUKA AG (Germany).
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES
- 1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
- 1.3 STUDY SCOPE
- 1.3.1 MARKETS COVERED AND REGIONAL SCOPE
- 1.3.2 YEARS CONSIDERED
- 1.3.3 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- 1.4 CURRENCY CONSIDERED
- 1.5 UNITS CONSIDERED
- 1.6 STAKEHOLDERS
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- 2.1 MARKET HIGHLIGHTS AND KEY INSIGHTS
- 2.2 KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS: MAPPING OF STRATEGIC DEVELOPMENTS
- 2.3 DISRUPTIVE TRENDS IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 2.4 HIGH-GROWTH SEGMENTS
- 2.5 REGIONAL SNAPSHOT: MARKET SIZE, GROWTH RATE, AND FORECAST
3 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
- 3.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 3.2 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING
- 3.3 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY WAFER SIZE
- 3.4 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT TYPE
- 3.5 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER
- 3.6 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION
- 3.7 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY COUNTRY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 INTRODUCTION
- 4.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.2.1 DRIVERS
- 4.2.1.1 Rising demand for high-throughput, high-yield semiconductor manufacturing across AI, HPC, automotive, and 5G applications
- 4.2.1.2 Expansion of advanced-node fabs requiring deep automation to sustain process stability
- 4.2.1.3 Increasing adoption of AMHS, robotics, and contamination-free transport to reduce human intervention
- 4.2.1.4 Increasing integration of MES, APC, YMS, and ECS platforms to enhance real-time process control and production efficiency
- 4.2.1.5 Government-backed investments and incentive programs accelerating greenfield fabs and capacity expansion
- 4.2.2 RESTRAINTS
- 4.2.2.1 High capital investment requirements for full fab automation deployment, particularly in brownfield facilities
- 4.2.2.2 Interoperability challenges between legacy tools and modern automation systems
- 4.2.2.3 Limited availability of skilled automation engineers for system integration and fab-level optimization
- 4.2.2.4 Supply chain constraints for automation components and cleanroom systems, resulting in extended deployment timelines
- 4.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
- 4.2.3.1 AI/ML-driven automation enabling predictive maintenance, intelligent scheduling, and yield enhancement
- 4.2.3.2 Rising automation demand in OSAT facilities driven by advanced packaging and throughput requirements
- 4.2.3.3 Expansion of 300 mm fabs and modernization of 200 mm facilities, driving long-term automation upgrade cycles
- 4.2.3.4 Growing adoption of digital twins and simulation platforms to optimize fab workflows and equipment layouts
- 4.2.4 CHALLENGES
- 4.2.4.1 Complex coordination and orchestration across multi-layer automation architectures in large semiconductor fabs
- 4.2.4.2 Ensuring real-time, low-latency communication across distributed automation networks under heavy data loads
- 4.2.4.3 Ensuring ultra-clean automated handling as device geometries shrink and contamination sensitivity intensifies
- 4.2.4.4 Long deployment and integration timelines create operational risks in upgrading automation within running fabs
- 4.2.1 DRIVERS
- 4.3 INTERCONNECTED MARKETS AND CROSS-SECTOR OPPORTUNITIES
- 4.3.1 INTERCONNECTED MARKETS
- 4.3.2 CROSS-SECTOR OPPORTUNITIES
- 4.4 STRATEGIC MOVES BY TIER 1/2/3 PLAYERS
- 4.4.1 MARKET DYNAMICS
5 INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 5.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.2 PORTER'S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS
- 5.2.1 THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS
- 5.2.2 THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES
- 5.2.3 BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS
- 5.2.4 BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS
- 5.2.5 INTENSITY OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- 5.3 MACROECONOMIC INDICATORS
- 5.3.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.3.2 GDP TRENDS AND FORECAST
- 5.3.3 TRENDS IN MANUFACTURING & INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION INDUSTRY
- 5.3.4 TRENDS IN SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY
- 5.4 VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 5.5 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
- 5.6 PRICING ANALYSIS
- 5.6.1 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE OF KEY PLAYERS, BY OFFERING, 2024
- 5.6.2 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE, BY REGION, 2021-2024
- 5.7 TRADE ANALYSIS
- 5.7.1 IMPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 8479)
- 5.7.2 EXPORT SCENARIO (HS CODE 8479)
- 5.8 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2026-2027
- 5.9 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESSES
- 5.10 INVESTMENT AND FUNDING SCENARIO, 2021-2025
- 5.11 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
- 5.11.1 TSMC'S CLEANROOM THROUGHPUT IMPROVEMENT WITH DAIFUKU'S NEO-AMHS PLATFORM
- 5.11.2 SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS' AUTOMATION UPGRADE USING MURATA MACHINERY'S WAFER-HANDLING ROBOTICS
- 5.11.3 GLOBALFOUNDRIES' APC/YMS TRANSFORMATION WITH APPLIED MATERIALS AUTOMATION SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS
- 5.12 IMPACT OF 2025 US TARIFF - FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 5.12.1 KEY TARIFF RATES
- 5.12.2 PRICE IMPACT ANALYSIS
- 5.12.3 IMPACT ON COUNTRIES/REGIONS
- 5.12.3.1 US
- 5.12.3.2 Europe
- 5.12.3.3 Asia Pacific
- 5.12.4 IMPACT ON END USERS
6 TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCEMENTS, AI-DRIVEN IMPACT, PATENTS, INNOVATIONS, AND FUTURE APPLICATIONS
- 6.1 KEY EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.1.1 AI-DRIVEN ADVANCED PROCESS CONTROL (APC) & PREDICTIVE AUTOMATION
- 6.1.2 MODULAR & COLLABORATIVE AMHS PLATFORMS
- 6.1.3 DIGITAL TWIN & VIRTUAL FAB SIMULATION PLATFORMS
- 6.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.2.1 EDGE COMPUTING & REAL-TIME DATA INFRASTRUCTURE
- 6.2.2 HIGH-PRECISION CLEANROOM ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL & MONITORING SYSTEMS
- 6.2.3 SECURE FAB COMMUNICATION NETWORKS & INDUSTRIAL IOT CONNECTIVITY
- 6.3 ADJACENT TECHNOLOGIES
- 6.3.1 ADVANCED PACKAGING & HETEROGENEOUS INTEGRATION AUTOMATION
- 6.3.2 SEMICONDUCTOR MATERIALS DELIVERY & CHEMICAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
- 6.4 TECHNOLOGY/PRODUCT ROADMAP
- 6.4.1 SHORT-TERM (2025-2027): AUTOMATION MODERNIZATION & AI-AUGMENTED OPERATIONS
- 6.4.2 MID-TERM (2027-2030): HYPER-AUTOMATION & ADVANCED PACKAGING INTEGRATION
- 6.4.3 LONG-TERM (2030-2035+): AUTONOMOUS FABS & SYSTEM-LEVEL CONVERGENCE
- 6.5 PATENT ANALYSIS
- 6.6 IMPACT OF AI ON FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 6.6.1 TOP USE CASES AND MARKET POTENTIAL
- 6.6.2 BEST PRACTICES IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 6.6.3 CASE STUDIES OF AI IMPLEMENTATION IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- 6.6.4 INTERCONNECTED ADJACENT ECOSYSTEM AND IMPACT ON MARKET PLAYERS
- 6.6.5 CLIENTS' READINESS TO ADOPT GENERATIVE AI IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
7 REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 INTRODUCTION
- 7.1.1 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- 7.2 INDUSTRY STANDARDS
- 7.2.1 SEMI STANDARDS (GEM, GEM300, E84, E87, EDA/INTERFACE A)
- 7.2.2 ISO CLEANROOM & ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL STANDARDS (ISO 14644 SERIES)
- 7.2.3 ISO 10218 & IEC 61508 - ROBOTICS SAFETY & FUNCTIONAL SAFETY STANDARDS
- 7.2.4 OPC UA FOR FAB EQUIPMENT COMMUNICATION
- 7.2.5 ANSI/ISA-95 - MANUFACTURING INTEGRATION STANDARD
- 7.2.6 SEMI S2 - ENVIRONMENTAL, HEALTH & SAFETY (EHS) STANDARD
8 CUSTOMER LANDSCAPE AND BUYER BEHAVIOR
- 8.1 DECISION-MAKING PROCESS
- 8.2 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA
- 8.2.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS
- 8.2.2 BUYING CRITERIA
- 8.3 ADOPTION BARRIERS AND INTERNAL CHALLENGES
- 8.4 UNMET NEEDS FROM VARIOUS END USERS
9 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING
- 9.1 INTRODUCTION
- 9.2 HARDWARE
- 9.2.1 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS
- 9.2.1.1 AI-orchestrated throughput growth to fuel AMHS demand in fab automation
- 9.2.2 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT
- 9.2.2.1 AI-enabled precision and vision integration to drive demand
- 9.2.3 ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL SYSTEMS
- 9.2.3.1 Humidity and AMC control to increase demand for advanced environmental control systems
- 9.2.4 POWER & UTILITY AUTOMATION SYSTEMS
- 9.2.4.1 Power quality and energy-efficiency mandates to accelerate adoption of utility & power automation systems in fabs
- 9.2.5 COMMUNICATION & NETWORKING HARDWARE
- 9.2.5.1 Low-latency, deterministic connectivity requirements to drive market
- 9.2.1 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS
- 9.3 SOFTWARE
- 9.3.1 MANUFACTURING EXECUTION SYSTEMS
- 9.3.1.1 Model-driven traceability and real-time dispatch to accelerate adoption
- 9.3.2 EQUIPMENT CONTROL SOFTWARE
- 9.3.2.1 Real-time tool-state coordination and recipe enforcement to drive adoption
- 9.3.3 ADVANCED PROCESS CONTROL
- 9.3.3.1 Shrinking process windows and high-mix production to drive APC integration
- 9.3.4 YIELD MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE
- 9.3.4.1 Defect density reduction and multi-source data fusion to increase adoption
- 9.3.5 AI/ML & PREDICTIVE ANALYTICS PLATFORMS
- 9.3.5.1 Predictive maintenance and lot-flow optimization to accelerate AI/ML deployment
- 9.3.6 SIMULATION & DIGITAL TWIN SOFTWARE
- 9.3.6.1 Capacity planning and virtual process optimization to expand digital twin usage
- 9.3.7 MIDDLEWARE & COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL SOFTWARE
- 9.3.7.1 Interoperability requirements and multi-vendor tool integration to fuel middleware adoption
- 9.3.1 MANUFACTURING EXECUTION SYSTEMS
- 9.4 SERVICES
- 9.4.1 PROFESSIONAL SERVICES
- 9.4.1.1 System integration complexity and node migration timelines to increase demand
- 9.4.2 MANAGED SERVICES
- 9.4.2.1 Predictive maintenance and 24/7 operational assurance to accelerate managed services adoption
- 9.4.1 PROFESSIONAL SERVICES
10 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY AUTOMATION LAYER
- 10.1 INTRODUCTION
- 10.2 MATERIAL HANDLING AUTOMATION
- 10.3 EQUIPMENT AUTOMATION
- 10.4 PROCESS AUTOMATION
- 10.5 FACTORY AUTOMATION SOFTWARE
- 10.6 AI/ANALYTICS AUTOMATION
11 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY WAFER SIZE
- 11.1 INTRODUCTION
- 11.2 <150 MM
- 11.2.1 INCREASED SPECIALTY-DEVICE PRODUCTION TO DRIVE ADOPTION
- 11.3 200 MM
- 11.3.1 GROWTH IN POWER AND ANALOG DEVICES TO INCREASE DEMAND
- 11.4 300 MM
- 11.4.1 ADVANCED PACKAGING DEMAND AND HIGH-VOLUME TEST REQUIREMENTS TO DRIVE MARKET
12 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT TYPE
- 12.1 INTRODUCTION
- 12.2 GREENFIELD FABS
- 12.2.1 ADVANCED NODE CAPACITY EXPANSION AND HIGH-THROUGHPUT MANUFACTURING REQUIREMENTS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 12.3 BROWNFIELD FABS
- 12.3.1 RETROFIT INVESTMENTS AND LEGACY-ASSET UTILIZATION TO SUPPORT MARKET GROWTH
13 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY FAB TYPE
- 13.1 INTRODUCTION
- 13.2 ADVANCED NODE FABS (<=7 NM)
- 13.3 MAINSTREAM NODE FABS (10-28 NM)
- 13.4 MATURE NODE FABS (28-90 NM)
- 13.5 LEGACY NODE FABS (>90 NM)
14 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY AUTOMATION LEVEL
- 14.1 INTRODUCTION
- 14.2 FULLY AUTOMATED
- 14.3 SEMI-AUTOMATED
15 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER
- 15.1 INTRODUCTION
- 15.2 INTEGRATED DEVICE MANUFACTURERS
- 15.2.1 COMPLEX PRODUCT PORTFOLIOS AND MULTI-FAB MANUFACTURING COORDINATION TO DRIVE MARKET
- 15.3 FOUNDRIES
- 15.3.1 HIGH-MIX PRODUCTION LOADS AND ADVANCED-NODE CAPACITY REQUIREMENTS TO PROPEL MARKET
- 15.4 OUTSOURCED SEMICONDUCTOR ASSEMBLY & TEST PROVIDERS
- 15.4.1 ADVANCED PACKAGING DEMAND AND HIGH-VOLUME TEST REQUIREMENTS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 15.5 RESEARCH FABS
- 15.5.1 HIGH-ACCURACY EXPERIMENTATION AND ACCELERATED PROTOTYPING DEMAND TO DRIVE MARKET
16 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION
- 16.1 INTRODUCTION
- 16.2 AMERICAS
- 16.2.1 US
- 16.2.1.1 Federal incentives and advanced-node capacity expansion to drive adoption
- 16.2.2 REST OF AMERICAS
- 16.2.1 US
- 16.3 ASIA PACIFIC
- 16.3.1 CHINA
- 16.3.1.1 China's 300 mm expansion and localized automation ecosystem to drive market
- 16.3.2 JAPAN
- 16.3.2.1 Government subsidies and new 300 mm fab investments to accelerate demand
- 16.3.3 SOUTH KOREA
- 16.3.3.1 Memory-led capacity expansion and mega-cluster investments to accelerate demand
- 16.3.4 TAIWAN
- 16.3.4.1 Advanced-node expansion and foundry-led manufacturing growth to drive automation
- 16.3.5 INDIA
- 16.3.5.1 Government-backed fab expansion and growing domestic demand to drive adoption
- 16.3.6 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC
- 16.3.1 CHINA
- 16.4 EMEA
- 16.4.1 EUROPE
- 16.4.1.1 Advanced-node investments and power-semiconductor expansion to drive market
- 16.4.2 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA
- 16.4.2.1 Government-led technology initiatives and emerging electronics manufacturing to support market growth
- 16.4.1 EUROPE
17 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 17.1 OVERVIEW
- 17.2 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN, JANUARY 2021-OCTOBER 2025
- 17.3 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2024
- 17.4 REVENUE ANALYSIS, 2021-2024
- 17.5 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS
- 17.6 BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- 17.7 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 17.7.1 STARS
- 17.7.2 EMERGING LEADERS
- 17.7.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
- 17.7.4 PARTICIPANTS
- 17.7.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 17.7.5.1 Company footprint
- 17.7.5.2 Region footprint
- 17.7.5.3 Offering footprint
- 17.7.5.4 Wafer size footprint
- 17.7.5.5 Deployment type footprint
- 17.7.5.6 End user footprint
- 17.8 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 17.8.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
- 17.8.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
- 17.8.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
- 17.8.4 STARTING BLOCKS
- 17.8.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 17.8.5.1 Detailed list of key startups/SMEs
- 17.8.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs
- 17.9 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
- 17.9.1 PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- 17.9.2 EXPANSIONS
18 COMPANY PROFILES
- 18.1 INTRODUCTION
- 18.2 KEY PLAYERS
- 18.2.1 DAIFUKU CO., LTD.
- 18.2.1.1 Business overview
- 18.2.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.1.3 Recent developments
- 18.2.1.3.1 Expansions
- 18.2.1.4 MnM view
- 18.2.1.4.1 Key strengths
- 18.2.1.4.2 Strategic choices
- 18.2.1.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 18.2.2 MURATA MACHINERY
- 18.2.2.1 Business overview
- 18.2.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.2.3 MnM view
- 18.2.2.3.1 Key strengths
- 18.2.2.3.2 Strategic choices
- 18.2.2.3.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 18.2.3 EBARA CORPORATION
- 18.2.3.1 Business overview
- 18.2.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.3.3 MnM view
- 18.2.3.3.1 Key strengths
- 18.2.3.3.2 Strategic choices
- 18.2.3.3.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 18.2.4 RORZE CORPORATION
- 18.2.4.1 Business overview
- 18.2.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.4.3 MnM view
- 18.2.4.3.1 Key strengths
- 18.2.4.3.2 Strategic choices
- 18.2.4.3.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 18.2.5 FANUC
- 18.2.5.1 Business overview
- 18.2.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.5.3 MnM view
- 18.2.5.3.1 Key strengths
- 18.2.5.3.2 Strategic choices
- 18.2.5.3.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 18.2.6 HIRATA CORPORATION
- 18.2.6.1 Business overview
- 18.2.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.7 KUKA AG
- 18.2.7.1 Business overview
- 18.2.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.8 YASKAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION
- 18.2.8.1 Business overview
- 18.2.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.9 KAWASAKI HEAVY INDUSTRIES
- 18.2.9.1 Business overview
- 18.2.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered
- 18.2.1 DAIFUKU CO., LTD.
- 18.3 OTHER PLAYERS
- 18.3.1 ATLAS COPCO
- 18.3.2 THIRA-UTECH
- 18.3.3 DAIHEN CORPORATION
- 18.3.4 BROOKS AUTOMATION
- 18.3.5 MIRLE AUTOMATION
- 18.3.6 SYNUS TECH
- 18.3.7 SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES
- 18.3.8 MEETFUTURE
- 18.3.9 FABMATICS
- 18.3.10 TAIYO INC.
- 18.3.11 SINEVA
- 18.3.12 CASTEC INTERNATIONAL
- 18.3.13 SYSTEMA GMBH
- 18.3.14 KYOWA ELECTRIC & INSTRUMENT
- 18.3.15 AMHS TECHNOLOGIES
- 18.3.16 ATS AUTOMATION
- 18.3.17 NIDEC CORPORATION
- 18.3.18 GENMARK AUTOMATION
- 18.3.19 JEL CORPORATION
- 18.3.20 KENSINGTON LABS
- 18.3.21 SIEMENS
- 18.3.22 ROCKWELL AUTOMATION
- 18.4 END USERS
- 18.4.1 FOUNDRIES
- 18.4.1.1 Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited
- 18.4.1.2 Samsung
- 18.4.1.3 GlobalFoundries
- 18.4.1.4 SMIC
- 18.4.1.5 United Microelectronics Corporation
- 18.4.2 IDM FIRMS
- 18.4.2.1 Intel Corporation
- 18.4.2.2 Texas Instruments Incorporated
- 18.4.2.3 Infineon Technologies AG
- 18.4.3 OSAT COMPANIES
- 18.4.3.1 ASE Technology Holding Co., Ltd.
- 18.4.3.2 Amkor Technology
- 18.4.1 FOUNDRIES
19 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 19.1 RESEARCH DATA
- 19.1.1 SECONDARY AND PRIMARY RESEARCH
- 19.1.2 SECONDARY DATA
- 19.1.2.1 List of key secondary sources
- 19.1.2.2 Key data from secondary sources
- 19.1.3 PRIMARY DATA
- 19.1.3.1 List of primary interview participants
- 19.1.3.2 Breakdown of primaries
- 19.1.3.3 Key data from primary sources
- 19.1.3.4 Key industry insights
- 19.2 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
- 19.2.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 19.2.2 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- 19.3 DATA TRIANGULATION
- 19.4 RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS
- 19.5 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS AND RISK ASSESSMENT
20 APPENDIX
- 20.1 INSIGHTS FROM INDUSTRY EXPERTS
- 20.2 DISCUSSION GUIDE
- 20.3 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS' SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL
- 20.4 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS
- 20.5 RELATED REPORTS
- 20.6 AUTHOR DETAILS
List of Tables
- TABLE 1 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- TABLE 2 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: IMPACT OF PORTER'S FIVE FORCES
- TABLE 3 GDP PERCENTAGE CHANGE, BY KEY COUNTRY, 2021-2029
- TABLE 4 ROLE OF PLAYERS IN FAB AUTOMATION ECOSYSTEM
- TABLE 5 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE OF FAB AUTOMATION SOLUTIONS OFFERED BY KEY PLAYERS, 2024 (USD MILLION, PER SYSTEM/PROJECT),
- TABLE 6 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE OF FAB AUTOMATION SYSTEMS, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION, PER LARGE FAB PROJECT)
- TABLE 7 IMPORT DATA FOR HS CODE 8479-COMPLIANT PRODUCTS, BY COUNTRY, 2020-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 8 EXPORT DATA FOR HS CODE 8479-COMPLIANT PRODUCTS, BY COUNTRY, 2020-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 9 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2026-2027
- TABLE 10 US ADJUSTED RECIPROCAL TARIFF RATES
- TABLE 11 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: LIST OF GRANTED PATENTS, JANUARY 2021-NOVEMBER 2025
- TABLE 12 TOP USE CASES AND MARKET POTENTIAL
- TABLE 13 BEST PRACTICES: COMPANIES IMPLEMENTING USE CASES
- TABLE 14 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: CASE STUDIES RELATED TO AI IMPLEMENTATION
- TABLE 15 INTERCONNECTED ADJACENT ECOSYSTEM AND IMPACT ON MARKET PLAYERS
- TABLE 16 CLIENTS' READINESS TO ADOPT GENERATIVE AI IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- TABLE 17 AMERICAS: REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- TABLE 18 ASIA PACIFIC: REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- TABLE 19 EMEA: REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- TABLE 20 INFLUENCE OF STAKEHOLDERS ON BUYING PROCESS FOR TOP 3 END USERS (%)
- TABLE 21 KEY BUYING CRITERIA FOR TOP THREE END USERS
- TABLE 22 UNMET NEEDS IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER
- TABLE 23 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 24 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 25 HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 26 HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 27 HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 28 HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 29 HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 30 HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 31 HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 32 HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 33 HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 34 HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 35 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 36 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 37 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 38 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 39 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 40 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 41 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 42 AUTOMATED MATERIAL HANDLING SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 43 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 44 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 45 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 46 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 47 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 48 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 49 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 50 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 51 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, 2021-2024 (UNITS)
- TABLE 52 ROBOTICS & HANDLING EQUIPMENT: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, 2025-2032 (UNITS)
- TABLE 53 ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 54 ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 55 ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 56 ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 57 ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 58 ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 59 ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 60 ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 61 POWER & UTILITY AUTOMATION SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 62 POWER & UTILITY AUTOMATION SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 63 POWER & UTILITY AUTOMATION SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 64 POWER & UTILITY AUTOMATION SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 65 POWER & UTILITY AUTOMATION SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 66 POWER & UTILITY AUTOMATION SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 67 POWER & UTILITY AUTOMATION SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 68 POWER & UTILITY AUTOMATION SYSTEMS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 69 COMMUNICATION & NETWORKING HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 70 COMMUNICATION & NETWORKING HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 71 COMMUNICATION & NETWORKING HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 72 COMMUNICATION & NETWORKING HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 73 COMMUNICATION & NETWORKING HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 74 COMMUNICATION & NETWORKING HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 75 COMMUNICATION & NETWORKING HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 76 COMMUNICATION & NETWORKING HARDWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 77 SOFTWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 78 SOFTWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 79 SOFTWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 80 SOFTWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 81 SOFTWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 82 SOFTWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 83 SOFTWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 84 SOFTWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 85 SOFTWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 86 SOFTWARE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 87 SERVICES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 88 SERVICES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 89 SERVICES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 90 SERVICES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 91 SERVICES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 92 SERVICES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN AMERICAS, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 93 SERVICES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 94 SERVICES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 95 SERVICES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 96 SERVICES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET IN EMEA, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 97 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY WAFER SIZE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 98 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY WAFER SIZE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 99 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 100 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 101 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 102 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 103 INTEGRATED DEVICE MANUFACTURERS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 104 INTEGRATED DEVICE MANUFACTURERS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 105 FOUNDRIES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 106 FOUNDRIES: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 107 OUTSOURCED SEMICONDUCTOR ASSEMBLY & TEST PROVIDERS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 108 OUTSOURCED SEMICONDUCTOR ASSEMBLY & TEST PROVIDERS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 109 RESEARCH FABS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 110 RESEARCH FABS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 111 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 112 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 113 AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 114 AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 115 AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 116 AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 117 AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 118 AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 119 AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 120 AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 121 US: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 122 US: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 123 US: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 124 US: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 125 REST OF AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 126 REST OF AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 127 REST OF AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 128 REST OF AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 129 ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 130 ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 131 ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 132 ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 133 ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 134 ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 135 ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 136 ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 137 CHINA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 138 CHINA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 139 CHINA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 140 CHINA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 141 JAPAN: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 142 JAPAN: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 143 JAPAN: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 144 JAPAN: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 145 SOUTH KOREA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 146 SOUTH KOREA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 147 SOUTH KOREA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 148 SOUTH KOREA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 149 TAIWAN: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 150 TAIWAN: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 151 TAIWAN: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 152 TAIWAN: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 153 INDIA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 154 INDIA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 155 INDIA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 156 INDIA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 157 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 158 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 159 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 160 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 161 EMEA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 162 EMEA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 163 EMEA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 164 EMEA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 165 EMEA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 166 EMEA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 167 EMEA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 168 EMEA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 169 EUROPE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 170 EUROPE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 171 EUROPE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 172 EUROPE: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 173 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 174 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 175 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 176 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, BY HARDWARE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 177 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: OVERVIEW OF STRATEGIES ADOPTED BY KEY PLAYERS, JANUARY 2021-OCTOBER 2025
- TABLE 178 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: DEGREE OF COMPETITION, 2024
- TABLE 179 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: REGION FOOTPRINT
- TABLE 180 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: OFFERING FOOTPRINT
- TABLE 181 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: WAFER SIZE FOOTPRINT
- TABLE 182 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: DEPLOYMENT TYPE FOOTPRINT
- TABLE 183 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: END USER FOOTPRINT
- TABLE 184 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: DETAILED LIST OF KEY STARTUPS/SMES
- TABLE 185 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING OF KEY STARTUPS/SMES
- TABLE 186 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: PRODUCT LAUNCHES, JANUARY 2021-OCTOBER 2025
- TABLE 187 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: EXPANSIONS, JANUARY 2021-OCTOBER 2025
- TABLE 188 DAIFUKU CO., LTD.: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 189 DAIFUKU CO., LTD.: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 190 DAIFUKU CO., LTD.: EXPANSIONS
- TABLE 191 MURATA MACHINERY: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 192 MURATA MACHINERY: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 193 EBARA CORPORATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 194 EBARA CORPORATION: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 195 RORZE CORPORATION: BUSINESS OVERVIEW
- TABLE 196 RORZE CORPORATION: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 197 FANUC: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 198 FANUC: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 199 HIRATA CORPORATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 200 HIRATA CORPORATION: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 201 KUKA AG: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 202 KUKA AG: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 203 YASKAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 204 YASKAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 205 KAWASAKI HEAVY INDUSTRIES: BUSINESS OVERVIEW
- TABLE 206 KAWASAKI HEAVY INDUSTRIES: PRODUCTS/SOLUTIONS/SERVICES OFFERED
- TABLE 207 ATLAS COPCO: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 208 THIRA-UTECH: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 209 DAIHEN CORPORATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 210 BROOKS AUTOMATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 211 MIRLE AUTOMATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 212 SYNUS TECH: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 213 SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 214 MEETFUTURE: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 215 FABMATICS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 216 TAIYO INC.: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 217 SINEVA: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 218 CASTEC INTERNATIONAL: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 219 SYSTEMA GMBH: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 220 KYOWA ELECTRIC & INSTRUMENT: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 221 AMHS TECHNOLOGIES: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 222 ATS AUTOMATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 223 NIDEC CORPORATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 224 GENMARK AUTOMATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 225 JEL CORPORATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 226 KENSINGTON LABS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 227 SIEMENS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 228 ROCKWELL AUTOMATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 229 TAIWAN SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING COMPANY LIMITED: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 230 SAMSUNG: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 231 GLOBALFOUNDRIES: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 232 SMIC: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 233 UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 234 INTEL CORPORATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 235 TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INCORPORATED: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 236 INFINEON TECHNOLOGIES AG: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 237 ASE TECHNOLOGY HOLDING CO., LTD.: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 238 AMKOR TECHNOLOGY: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 239 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS
- TABLE 240 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: RISK ASSESSMENT
List of Figures
- FIGURE 1 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET SEGMENTATION AND REGIONAL SCOPE
- FIGURE 2 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: YEARS CONSIDERED
- FIGURE 3 MARKET SCENARIO
- FIGURE 4 GLOBAL FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, 2021-2032
- FIGURE 5 MAJOR STRATEGIES ADOPTED BY KEY PLAYERS IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, 2021-2025
- FIGURE 6 DISRUPTIONS INFLUENCING GROWTH OF FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- FIGURE 7 HIGH-GROWTH SEGMENTS IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET, 2025-2032
- FIGURE 8 ASIA PACIFIC TO ACCOUNT FOR LARGEST MARKET SHARE DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 9 ADVANCED NODE EXPANSION, 300 MM FAB GROWTH, AND AUTOMATION TO INCREASE DEMAND
- FIGURE 10 HARDWARE SEGMENT TO DOMINATE MARKET IN 2032
- FIGURE 11 300 MM SEGMENT TO ACCOUNT FOR LARGEST MARKET SHARE DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 12 BROWNFIELD FABS TO WITNESS FASTEST GROWTH DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 13 FOUNDRIES SEGMENT TO ACCOUNT FOR LARGEST MARKET SHARE DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 14 ASIA PACIFIC TO ACCOUNT FOR LARGEST MARKET SHARE IN 2032
- FIGURE 15 INDIA TO REGISTER HIGHEST CAGR DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 16 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: DRIVERS, RESTRAINTS, OPPORTUNITIES, AND CHALLENGES
- FIGURE 17 IMPACT ANALYSIS: DRIVERS
- FIGURE 18 IMPACT ANALYSIS: RESTRAINTS
- FIGURE 19 IMPACT ANALYSIS: OPPORTUNITIES
- FIGURE 20 IMPACT ANALYSIS: CHALLENGES
- FIGURE 21 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: PORTER'S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS
- FIGURE 22 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
- FIGURE 23 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
- FIGURE 24 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND FOR FAB AUTOMATION SYSTEMS, BY REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION, PER LARGE FAB PROJECT)
- FIGURE 25 IMPORT DATA FOR HS CODE 8479-COMPLIANT PRODUCTS IN TOP 5 COUNTRIES, 2020-2024
- FIGURE 26 EXPORT DATA FOR HS CODE 8479-COMPLIANT PRODUCTS IN TOP 5 COUNTRIES, 2020-2024
- FIGURE 27 TRENDS AND DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
- FIGURE 28 INVESTMENT AND FUNDING SCENARIO, 2021-2025
- FIGURE 29 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: PATENT ANALYSIS, 2015-2024
- FIGURE 30 DECISION-MAKING FACTORS IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET
- FIGURE 31 INFLUENCE OF STAKEHOLDERS ON BUYING PROCESS FOR TOP 3 END USERS
- FIGURE 32 KEY BUYING CRITERIA FOR TOP 3 END USERS
- FIGURE 33 ADOPTION BARRIERS AND INTERNAL CHALLENGES
- FIGURE 34 HARDWARE SEGMENT TO ACCOUNT FOR LARGEST MARKET SHARE DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 35 300 MM SEGMENT IS PROJECTED TO REGISTER HIGHEST CAGR DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 36 BROWNFIELD FABS SEGMENT TO ACCOUNT FOR MAJORITY MARKET SHARE DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 37 FOUNDRIES SEGMENT TO DOMINATE MARKET IN 2032
- FIGURE 38 AMERICAS TO REGISTER HIGHEST CAGR IN FAB AUTOMATION MARKET DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 39 AMERICAS: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 40 ASIA PACIFIC: FAB AUTOMATION MARKET SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 41 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS OF COMPANIES OFFERING FAB AUTOMATION SOLUTIONS, 2024
- FIGURE 42 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: REVENUE ANALYSIS OF TOP FIVE PLAYERS, 2021-2024
- FIGURE 43 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: COMPANY VALUATION
- FIGURE 44 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET PLAYERS: EV/EBITDA
- FIGURE 45 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- FIGURE 46 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX (KEY PLAYERS), 2024
- FIGURE 47 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: COMPANY FOOTPRINT
- FIGURE 48 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX (STARTUPS/SMES), 2024
- FIGURE 49 DAIFUKU CO., LTD.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 50 EBARA CORPORATION: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 51 FANUC: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 52 HIRATA CORPORATION: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 53 YASKAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 54 KAWASAKI HEAVY INDUSTRIES: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 55 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: RESEARCH DESIGN
- FIGURE 56 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: RESEARCH APPROACH
- FIGURE 57 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- FIGURE 58 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- FIGURE 59 FAB AUTOMATION MARKET: DATA TRIANGULATION








