 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1277028
智能商业建筑中的物联网:市场规模和竞争格局(2023-2028)The Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings 2023 to 2028: Market Sizing & Competitive Landscape |
||||||
本报告总结并提供了全球商业建筑物联网市场规模(至 2028 年)和竞争格局的最新分析结果。
本报告重点关注商业房地产市场,全面评估了物联网市场的市场规模、应用和机会,以及主要促进因素和障碍。
主要问题
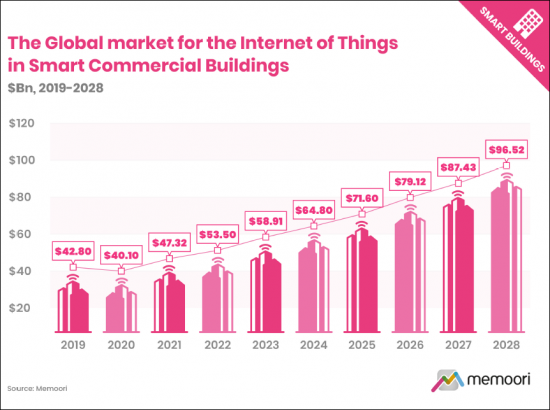
- 用于智能商业建筑 (BIoT) 的 IoT(物联网)市场规模有多大? : 根据最新分析,到 2022 年,BIoT 市场将增长至 535 亿美元,较 2021 年增长 13%。 包括整体经济復苏慢于预期、芯片组短缺和供应链中断在内的几个因素低于我们 13.8% 的预测。 BIoT 的市场规模预计将在 2022 年至 2028 年间以 10.33% 的复合年增长率增长,达到 965 亿美元。
- BIoT 市场采用的促进因素是什么? :房地产企业的投资不仅是为了让他们的资产更具可持续性,也是为了提高他们的业绩并推动更高的租金和收益率。 随着能源成本预计将继续上升,对节能技术和可持续解决方案的关注仍将是许多公司的首要任务。
- BIoT 市场面临哪些挑战和障碍? :网络安全是越来越多越来越容易受到网络攻击的智能建筑的重要考虑因素。 智能建筑系统和设备通常缺乏动态修补功能,设施管理团队可能缺乏必要的 IT 技能来管理网络安全。
建筑行业正朝着可持续发展和降低能源消耗的方向发展。 根据 EIA 的 2018 年 CBECS 消费和支出调查,与 2012 年相比,2018 年商业建筑每平方英尺建筑面积的能源消耗下降了 12%。 然而,由于建筑和建筑施工占全球能源消耗的三分之一和二氧化碳排放量的近 40%,建筑行业尚未达到未来可持续发展所需的目标。
要到 2050 年实现净零排放,建筑业主和运营商需要加大新建和翻新力度。 国际能源署呼吁到 2030 年将改造率从目前的不到 1% 每年提高 2.5%。

本报告中提及的物联网公司:(节选)
|
|
内容
前言
执行摘要
第 1 章简介
- 智能商业建筑物联网市场概览
- BIOT供应链
第 2 章市场规模和区域分析
- 全球 BIoT 市场预测
- 市场收入:按硬件、按软件、按服务
- 市场收入:按行业分类
- 市场收入:按应用分类
- BIoT 市场分析:按地区
- 按地区比较
- 北美
- 拉丁美洲
- 亚太地区
- 欧洲
- 中东和非洲
第 3 章BIoT市场应用
- 安全和访问控制
- 影像监控
- 影像管理系统 (VMS)
- VSaaS(视频监控即服务)
- 访问控制
- 用于安全和访问控制的 AI 应用程序
- 能源管理和环境控制
- 物联网和人工智能在能源管理中的作用
- 实时能源跟踪和分析
- 暖通空调优化
- 平衡优先级并集成多个系统
- 能源管理和环境控制的未来
- 网格互动建筑
- 需求响应和负载管理
- 需求侧管理策略
- 减载和调峰
- 可再生能源与 PEV 的整合
- 网格交互构建领域的领先公司
- 智能运维
- 空间、占用率、人员流动
- 空气质量
- 卫生/健康/保健
- 智能照明
- 租户和工作经验
- 消防与安全
- 废物和水管理
- 水资源管理
- 废物管理
- 数位孪生
- 数位孪生定义
- 数位孪生、BIM(建筑资讯模型)和物联网之间的关係
- 数位孪生的 3D 建模
- 挑战和批评
- 成功的数位孪生的先决条件
- 市场认可度和采用率
- 数位孪生供应商
第 4 章智能建筑物联网平台
- 物联网平台
- BIoT平台生态系统
- BIoT平台产品
第 5 章市场展望和用例:按市场部门分类
- 商业办公室
- 零售
- 零售业务业绩
- 零售业的未来
- 零售业的物联网机遇
- 酒店业
- 酒店
- 餐厅/餐饮服务
- 数据中心
- 其他行业
- 交通
- 公共集会/场所
- 仓库
- 小建筑
第 6 章 BIoT 市场 - 采用的促进因素
- 经济和商业促进因素
- 降低运营成本并提高效率
- 租户优先级和资产价值
- 工作场所的要求和期望
- 技术促进因素
- 技术成本
- 数据量和可访问性
- 新技术
- 能源效率和可持续性的促进因素
- 商业建筑领域的可持续发展记录
- 翻新的重要性
- 企业立场、投资和举措
- 与能源成本相关的因素
- ESG报告
- 应对物联网的不利影响
- 促进健康和福祉的因素
- 政府政策和法规
- 环境和可持续发展法规
- 政府奖励和补贴
- 物联网、数据、网络安全法规
- 其他投资和政策促进因素
- 标准和认证
- 建筑标准和认证的变化
- 智能数位连接
- 可持续性、能源和 ESG 绩效
- 健康与幸福
- 网络安全标准和要求
第 7 章 BIoT 市场:挑战与障碍
- 技术问题
- 网路安全
- 网路保险
- 数据隐私
- 系统复杂性和互操作性
- 数据相关问题
- 抵制行业的变化和发展
- 抵制 CRE 行业的变革
- 行业发展和转型的促进因素
- 领导、调试、采购
- 物联网项目负责人和决策者
- 构建生命週期
- 利益相关方的调试、采购和协调
- 调试和采购挑战
- 利益相关者在整个建筑生命週期中的优先事项
- 利益相关者之间实现协调
- 物联网技术与建筑设计的有效融合
- IT/OT 利益相关者
- 每位房东/房客的奖励
- 成本趋势和业务案例
- 物联网项目成本
- 商业案例中的趋势
第 8 章竞争格局
This Report is a new 2023 Study which Makes an Objective Assessment of the Commercial Building IoT Market Size & Competitive Landscape to 2028
Our new report focuses on market sizing, applications and opportunities in the Internet of Things market, as well as a comprehensive evaluation of the drivers and barriers to adoption that are specific to the Commercial Real Estate sector.
New for 2023, it INCLUDES at no extra cost, a spreadsheet containing the data from the report AND high-resolution presentation charts showing the key findings. It is the second instalment of a two-part series, with the first report (published last month) covering IoT Device Projections, Adoption & Meta-Trends Analysis. These reports are included in our 2023 Premium Subscription Service.

KEY QUESTIONS ADDRESSED:
- What is the Size of the Internet of Things Market in Smart Commercial Buildings (BIoT)? Our latest analysis indicates that the BIoT market grew to $53.5 billion in 2022, representing a 13% rise from 2021. Performance was slightly down from our forecast of 13.8% for the year due to several factors, including a slower-than-anticipated overall economic recovery, a lack of chipsets, and disrupted supply chains. Memoori forecasts that the BIoT market size will grow at a CAGR of 10.33% to $96.5 billion between 2022 and 2028.
- What is Driving BIoT Market Adoption? Real estate stakeholders are investing not only to improve the sustainability credentials of their assets but also to enhance their performance, resulting in better rent and yields. As rising energy costs are expected to continue increasing, the focus on energy-efficient technologies and sustainable solutions is likely to remain a significant priority for many companies.
- What Challenges & Barriers Does the BIoT Market Face? Cybersecurity is a crucial consideration for the growing number of smart buildings, which are increasingly susceptible to cyber attacks. Smart building systems and devices often lack dynamic patching capabilities, and facilities management teams may lack the IT skills required to manage cybersecurity.
The building sector is making progress towards sustainable development and reducing energy consumption. The EIA's 2018 CBECS consumption and expenditures survey found that commercial buildings consumed 12% less energy per square foot of floorspace in 2018 than in 2012. However, the building sector still falls short of the targets required for sustainable future development, as buildings and building construction contribute to one-third of global energy consumption and almost 40% of CO2 emissions.
To achieve net zero by 2050, building owners and operators must redouble their efforts in new construction and retrofits. The IEA is now calling for an increase in retrofit rates of 2.5% annually by 2030, up from less than 1% today.
WITHIN ITS 236 PAGES AND 26 CHARTS AND TABLES, THE REPORT FILTERS OUT ALL THE KEY FACTS AND DRAWS CONCLUSIONS, SO YOU CAN UNDERSTAND EXACTLY WHAT IS SHAPING THE FUTURE OF THIS GLOBAL IOT MARKET
- The Building Internet of Things market is complex and multifaceted, involving a wide range of players from traditional building automation companies to specialized manufacturers, ICT vendors, property firms, and software vendors offering middleware, platforms, and cloud-based data analytics services. While some companies offer end-to-end BIoT solutions, others specialize in specific areas such as data intelligence, automation, or energy optimization and analytics.
- The smart building startup landscape is also expanding rapidly, with a 20% increase in the number of new entrants founded since 2021. Consolidation is expected in the wider platforms space, but there remain considerable market opportunities for cloud-based software offerings for specialist applications or vertical markets.
- While the level of fragmentation in the BIoT market can act as a source of confusion and frustration for buyers, leading platform solution providers are beginning to emerge, and the user base seems likely to coalesce around a more limited number of platform providers.
This report provides valuable information to companies so they can improve their strategic planning exercises AND look at the potential for developing their business through mergers, acquisitions and alliances.
WHO SHOULD BUY THIS REPORT?
The information contained in this report will be of value to all those engaged in managing, operating and investing in commercial smart buildings (and their advisers) around the world. In particular, those wishing to understand exactly how the Internet of Things is impacting commercial real estate will find it most useful.
ALIGNING STAKEHOLDER PRIORITIES
The infographic below illustrates key stakeholders in a smart building project, their priorities and KPIs, and the project phases they might be involved in under traditional and best practice approaches. Encouraging collaboration, communication, and standardized practices among stakeholders can help bridge the gap and foster innovation.
The integration of Internet of Things technology into building design is a complex process that requires coordination and alignment among all parties involved. A comprehensive and cohesive design approach involving key stakeholders from the earliest stages leads to improved decision-making and better outcomes .

Internet of Things Companies Mentioned INCLUDE: (but NOT limited to)
|
|
Table of Contents
Preface
The Executive Summary
1. Introduction
- 1.1. Overview of the IoT Market in Smart Commercial Buildings
- 1.2. The BIOT Supply Chain
2. Market Sizing and Regional Analysis
- 2.1. BIoT Global Market Forecasts
- 2.1.1. Market Revenue by Hardware, Software & Services
- 2.1.2. Market Revenue by Vertical
- 2.1.3. Market Revenue by Application
- 2.2. BIoT Market Analysis by Region
- 2.2.1. Regional Comparisons
- 2.2.2. North America
- 2.2.3. Latin America
- 2.2.4. Asia Pacific
- 2.2.5. Europe
- 2.2.6. Middle East & Africa
3. BIoT Market Applications
- 3.1. Security & Access Control
- 3.1.1. Video Surveillance
- 3.1.2. Video Management Systems (VMS)
- 3.1.3. Video Surveillance as a Service (VSaaS)
- 3.1.4. Access Control
- 3.1.5. AI Applications for Security & Access Control
- 3.2. Energy Management & Environmental Control
- 3.2.1. The Role of IoT and AI in Energy Management
- 3.2.2. Real-Time Energy Tracking and Analysis
- 3.2.3. HVAC Optimization
- 3.2.4. Balancing Priorities and Integrating Multiple Systems
- 3.2.5. The Future of Energy Management and Environmental Control
- 3.3. Grid Interactive Buildings
- 3.3.1. Demand Response and Load Management
- 3.3.2. Demand-Side Management Strategies
- 3.3.3. Load Shedding and Peak Shaving
- 3.3.4. Integrating Renewables and PEV's
- 3.3.5. Leading Players in Grid Interactive Buildings
- 3.4. Smart Operations & Maintenance
- 3.5. Space, Occupancy & People Movement
- 3.6. Air Quality
- 3.7. Hygiene, Health & Wellness
- 3.8. Smart Lighting
- 3.9. Tenant & Workplace Experience
- 3.10. Fire & Safety
- 3.11. Waste & Water Management
- 3.11.1. Water Management
- 3.11.2. Waste Management
- 3.12. Digital Twin
- 3.12.1. Defining Digital Twins
- 3.12.2. The Relationship Between Digital Twins, BIM & IoT
- 3.12.3. 3D Modelling for Digital Twins
- 3.12.4. Challenges & Criticisms
- 3.12.5. Prerequisites for Successful Digital Twins
- 3.12.6. Market Perceptions & Adoption Rates
- 3.12.7. Digital Twin Vendors
4. Smart Building IoT Platforms
- 4.1. IoT Platforms
- 4.2. The BIoT Platform Eco-System
- 4.3. BIoT Platform Offerings
5. Prospects & Use Cases by Market Vertical
- 5.1. Commercial Offices
- 5.2. Retail
- 5.2.1. Retail Sector Performance
- 5.2.2. The Future of Retail
- 5.2.3. Retail Sector IoT Opportunities
- 5.3. Hospitality
- 5.3.1. Hotels
- 5.3.2. Restaurants & Food Services
- 5.4. Data Centers
- 5.5. Other Verticals
- 5.5.1. Transport
- 5.5.2. Public Assembly/Venues
- 5.5.3. Warehouses
- 5.6. Smaller Buildings
6. BIoT Market - Adoption Drivers
- 6.1. Economic & Business Drivers
- 6.1.1. Operational Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains
- 6.1.2. Tenant Priorities & Property Value
- 6.1.3. Workplace Demands & Expectations
- 6.2. Technology Drivers
- 6.2.1. Technology Costs
- 6.2.2. Data Volume & Accessibility
- 6.2.3. Emerging Technologies
- 6.3. Energy Efficiency & Sustainability Drivers
- 6.3.1. Sustainability Performance in the Commercial Building Sector
- 6.3.2. The Critical Importance of Retrofits
- 6.3.3. Corporate Attitudes, Investments, and Initiatives
- 6.3.4. Energy Cost-related Drivers
- 6.3.5. ESG Reporting
- 6.3.6. Countering the Adverse Impacts of the IoT
- 6.4. Health & Wellbeing Drivers
- 6.5. Government Policies & Regulations
- 6.5.1. Environmental and Sustainability Regulations
- 6.5.2. Government Incentives and Subsidies
- 6.5.3. IoT, Data & Cybersecurity Regulations
- 6.5.4. Other Investment or Policy Drivers
- 6.6. Standards & Certification
- 6.6.1. The Evolving Landscape of Building Standards & Certifications
- 6.6.2. Smart & Digital connectivity
- 6.6.3. Sustainability, Energy & ESG performance
- 6.6.4. Health & Wellbeing
- 6.6.5. Cybersecurity Standards and Requirements
7. BIoT Market - Challenges & Barriers
- 7.1. Technology Challenges
- 7.1.1. Cybersecurity
- 7.1.2. Cyber Insurance
- 7.1.3. Data Privacy
- 7.1.4. Systems Complexity & Interoperability
- 7.1.5. Data Related Challenges
- 7.2. Resistance to Change and Industry Evolution
- 7.2.1. Resistance to Change in the CRE Industry
- 7.2.2. Industry evolution and transition drivers
- 7.3. Leadership, Commissioning & Procurement
- 7.3.1. IoT Project Leadership & Decision Makers
- 7.4. Building Life Cycles
- 7.5. Commissioning, Procurement & Stakeholder Alignment
- 7.5.1. Commissioning & Procurement Challenges
- 7.5.2. Stakeholder Priorities Across the Building Life Cycle
- 7.5.3. Achieving Stakeholder Alignment
- 7.5.4. Effective Integration of IoT Technology into Building Design
- 7.5.5. IT vs OT Stakeholders
- 7.5.6. Landlord/Tenant split incentives
- 7.6. Costs & Business Case Development
- 7.6.1. IoT Project Costs
- 7.6.2. Business Case Development
8. The Competitive Landscape
List of Charts and Figures
- Fig 1.1 - The Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings 2023 v5.1
- Fig 1.2 - The BIoT Supply Chain
- Fig 2.1 - The Global Market for the Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings, $Bn 2019-2028
- Fig 2.2 - The Global Market for the Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings, Breakdown by Hardware, Software, & Services, $Bn 2022-2028
- Fig 2.3 - Market Breakdown by Hardware, Software & Services, Market Size $Bn, % of Total Market
- Fig 2.4 - The Market for the Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings Market by Vertical, $Bn 2022 & 2028
- Fig 2.5 - The Market for the Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings Market by Application, $Bn 2022 & 2028
- Fig 2.6 - Regional Growth Indicators
- Fig 2.7 - The Market for the Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings Market by Region 2022 to 2028, % of Global Market
- Fig 2.8 - BIoT Related Patent Applications by Country, May 2023
- Fig 2.9 - Percentage Share of Academic Publications, Selected Technologies
- Fig 2.10 - Frontier Technology Readiness by Region
- Fig 2.11 - The Market for the Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings North America, $Bn 2022 - 2028
- Fig 2.12 - The Market for the Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings Latin America, $Bn 2022 - 2028
- Fig 2.13 - The Market for the Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings Asia Pacific, $Bn 2022 - 2028
- Fig 2.14 - The Market for the Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings Europe, $Bn 2022 - 2028
- Fig 2.15 - The Market for the Internet of Things in Smart Commercial Buildings Middle East & Africa, $Bn 2022 - 2028
- Fig 4.1 - Typical IoT Platform Functionality
- Fig 6.1 - Price Inflation for Information Technology, Hardware & Services since 1988
- Fig 6.2 - Non-Residential Building Sector CO2 Emissions 2010 - 2030
- Fig 6.3 - Buildings Share of Global Final Energy & CO2 Emissions 2021
- Fig 6.4 - Average Electricity & Gas Prices for Non-Household Consumers
- Fig 7.1 - Building Component Life Cycles
- Fig 7.2 - Aligning Stakeholder Priorities Across the Building Life Cycle










