 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1331219
互联农业市场规模和份额分析 - 增长趋势和预测(2023-2028)Connected Agriculture Market Size & Share Analysis - Growth Trends & Forecasts (2023 - 2028) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
互联农业市场规模预计将从 2023 年的 52 亿美元增长到 2028 年的 88 亿美元,预测期内(2023-2028 年)复合年增长率为 11.10%。
需要先进的农业技术来优化作物产量,同时最大限度地减少水、肥料和种子等资源,这是推动互联农业市场增长的关键因素。 通过实施各种互联农业技术,农民和企业可以更有效地管理他们的农业时间,同时使用更少的资源。
主要亮点
- 农业用水管理对于提高农业产量、降低成本并促进环境稳定至关重要。 农业利益相关者担心水资源短缺,并正在努力加强农业用水管理。 融合了物联网 (IoT)、移动应用、大数据分析和决策支持系统的互联农业水管理解决方案正在帮助为不断增长的人口生产环保且优质的农产品。Masu。
- 互联农业使农民能够最大限度地提高作物产量,同时减少与传统耕作方法相关的费用和劳动力。 互联农业使农民能够熟练地将时间和资源投入到正确的组合中,以更准确地评估最佳播种密度、估计肥料并预测作物产量,从而提高产量。 农民现在依赖最新的农业进步,例如移动电话和其他联网设备的使用。 低功耗广域通信 (LPWA)、Zigbee、WiFi 和新型无线传感器技术等先进的连接技术正在帮助农民规划和执行各种农业任务,例如采购物资、管理库存以及及时种植和收穫。 。
- 数据收集是精准农业的第一步,因此也是研究最多的一步。 这主要是通过测定土壤肥力(来自田地、多边形、区域的一个样本)来实现的。 区域是使用航空和卫星图像创建的,并基于多年来对同一作物拍摄的产量图和照片。 这样做是为了最终提高产量。 1公顷多边形网格是最常用的土壤测试方法。 这个网格大小足以了解场变化及其内部发生的情况。 最后,根据土壤扫描,创建任务图以实现精确施肥和石灰施用。
- 人们对联网农场技术知之甚少,而且安装成本高昂。 这些是技术在预期时间范围内的限制。 世界各地的大多数农民都是小规模农民,买不起如此昂贵的设备。 这项技术需要有能力和知识渊博的农民、大量的初始投资、有效的农具,而农民不愿意通过这项技术收集信息。 由于成本较高,只适合大型工业化农场。
- 由于新冠肺炎 (COVID-19) 大流行,人工智能 (AI) 的使用引起了人们的关注。 人工智能和机器学习模型使用实时数据来提供富有洞察力的知识,例如何时播种、选择哪些作物以及选择哪些杂交品种以获得更高的产量。您可以获得。 精准农业,通常被称为人工智能係统,有助于提高收成的整体质量和准确性。 人工智能技术有助于检测农场的害虫、植物病害和营养缺乏症。 人工智能 (AI) 传感器可以在决定使用哪种除草剂之前识别并瞄准杂草。
互联农业市场的趋势
智能水管理系统的需求激增
- 智能水管理 (SWM) 利用信息和通信技术 (ICT) 以及实时数据和响应,是解决水管理挑战的基本要素。 智能係统在水管理方面的潜在应用非常广泛,包括水质、水量、高效灌溉、渗漏、压力和流量、洪水、干旱等的解决方案。 根据联合国报告,到2025年,水资源短缺将直接影响近20%的人类,并可能间接影响地球上的其他居民。 基于物联网、大数据和人工智能技术相结合的智能水系统可以帮助阻止这些预测,并扭转因不小心使用水资源而造成的损害。
- 世界银行和非营利组织 Imagine H2O 最近合作,资助推动全球水资源可持续发展的技术。 许多新公司的目标是为偏远或以前无法到达的地区的农民提供实时数字信息,例如田地的湿度或天气变化。 农民还获得一个移动管理平台。 世界银行和 Imagine H2O 支持的创新技术包括洪水风险检测、寻找水污染源的 DNA 指纹技术,以及小岛屿社区的自主波浪驱动海水淡化厂。
- 在智利和秘鲁,“水智能”技术正在帮助果农适应日益严重的干旱和水资源短缺。 这些创新技术的重点是提高灌溉效率和恢復土壤健康。 AQUA4D 是一项改善水中矿物质溶解和分布的技术。 这种方法增加了土壤的保水期,减少了农民的用水量。 另一方面,改善水中矿物质的平衡可以改善土壤质量和盐度。
- 自来水公司和水处理厂可以通过确保其监控设备是最新的且尽可能准确来儘自己的一份力量。 虽然 SCADA 系统在现代运营中变得更加普遍,但水处理设施和工厂中基于云的 SCADA 系统预计将在预测期内进一步提高运营的可扩展性。 除此之外,智能电錶的技术进步及其与SCADA 等通信解决方案的集成将有助于解决水务公司、农民、居民和工业面临的不正确计费和水管理的挑战。我们已经实现了管理转型。
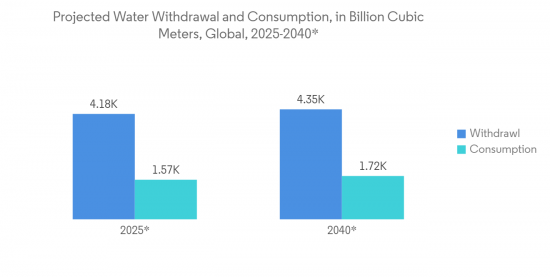
- IEA预测,到2040年需要抽取的水总量将达到4.35万亿立方米。 近几十年来,用水量的增加使人口增长增加了一倍多。 如此巨大的用水量和取水量将为智能水管理系统创造机会。
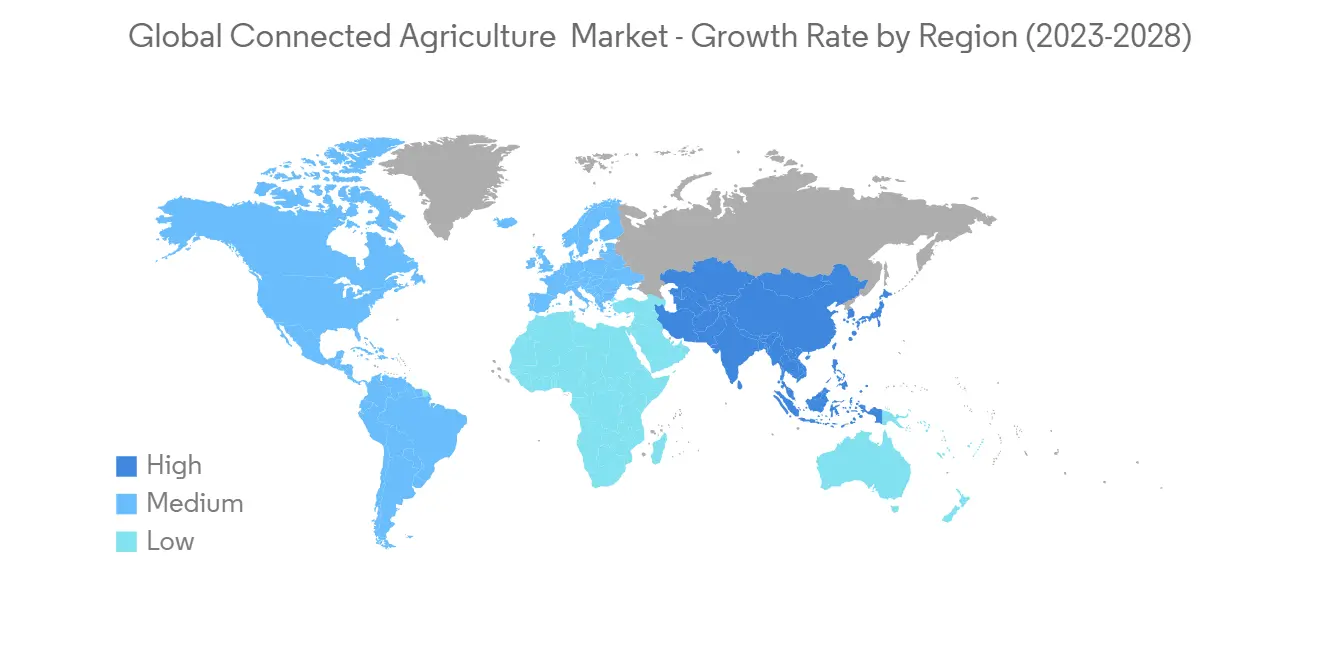
亚太地区将经历最高的增长
- 由于肥料和农业设备等农业投入成本较高,日本的农业生产成本高于其他国家。 根据农林水产省的数据,去年生产60公斤大米的平均总投入成本为9,180日元。 其中,13%是肥料成本,其余32%是农业机械及其引进成本。 因此,减少化肥浪费和降低机器成本的互联农业进步可能会让日本农民受益匪浅。
- 马哈拉施特拉邦政府自 2022 年 10 月允许无人机喷洒农药以来,尚未制定政策。 州政府正在等待澄清,然后再批准对中心批准的无人机购买计划的补贴。 无人机正在被推广作为应对劳动力危机和提高农业机械化的一种方式。 国际农化公司先正达週一宣布,其两种杀菌剂配方已获得负责喷洒法规的中央农药委员会的无人机喷洒批准。
- 菲律宾农业部 (DA) 正在评估无人机改变我们播种、施肥和杀虫剂以及监测作物方式的潜力。 此外,日本农林水产省还制定了到2022年将农业无人机引入日本约一半水稻、小麦和大豆种植面积的目标。
- 2022 年 8 月,印度灌溉喷头、过滤设备和施肥设备製造商 Oatmat 宣布将参加拉贾斯坦邦展会。今天,我们宣布为农民推出五种全新智能灌溉解决方案。 为了解决拉贾斯坦邦灌溉水位低的问题,Automat India 推出了五种基于物联网的自主灌溉系统,帮助农民明智地监测、控制和用水。 MachClean(砂介质过滤器)、Turbo(自动筛网过滤器)、Hydromat(控制阀)、Auto Drop(低成本自动化套件)和Aqua Disc(自动盘式过滤器)等品牌帮助农民方便灌溉,同时节省时间和成本。
- 2022 年 4 月,泰国政府承诺加快该国粮食和农业部门的数字化转型计划,特别强调大数据、智慧农业、电子商务和农业综合企业发展。泰国政府确实做到了。 自采用泰国4.0和20年国家战略框架以来,泰国更加註重食品和农业供应链的数字化。
互联农业行业概述
由于存在多个参与者,互联农业市场的竞争力较弱。 市场参与者正在采取产品创新、兼併和收购等策略来扩大产品组合、扩大地域覆盖范围,并主要保持市场竞争力。
2023 年 1 月,通过知识转移合作伙伴关係 (KTP),阿斯顿大学将与工程公司 Solargen Technologies (SGT) 和内罗毕大学合作,利用太阳能和风能全年灌溉土地。提高肯尼亚农作物产量的灌溉系统。 SGT 是肯尼亚最大的能源、水和灌溉解决方案及服务提供商。 我们与非政府组织、政府和人民合作,为东非农村和受衝突影响的社区提供定制的能源、水和粮食安全解决方案。
2022 年 2 月,Agrology 计划将 Wyld Networks 基于卫星的物联网连接纳入其预测农业平台,以进行全球 24/7 数据收集。 Agrology 和 Wyld Networks 今天宣布合作,将 Wyld Connect 整合到 Agrology 的地面实况预测农业技术中。 Wyld Connect 是一种基于低轨道卫星技术的低成本物联网 (IoT) 全球连接网络。 该解决方案将使 Agrology 的地面实况传感器能够继续从最偏远的位置收集数据,并快速将数据传送给 Agrology 的客户,无论网络条件如何。
其他好处:
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章简介
- 调查结果
- 调查的先决条件
- 调查范围
第二章研究方法
第 3 章执行摘要
第 4 章市场动态
- 市场概览
- 市场促进因素和市场约束因素介绍
- 市场驱动因素
- 互联农业中 BYOD(自带无人机)的出现
- 智能水管理系统的需求激增
- 市场製约因素
- 互联农业的深度学习曲线
- 价值链分析
- 行业吸引力 - 波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买家/消费者的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争公司之间敌对关係的强度
第五章市场细分
- 按组件
- 解决方案
- 网络管理
- 农业资产管理
- 监督和控制
- 服务
- 解决方案
- 按用途
- 智能物流
- 智能灌溉
- 农业规划和管理
- 按地区
- 北美
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 欧洲其他地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 日本
- 印度
- 其他亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- 中东/非洲
- 北美
第六章竞争态势
- 公司简介
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- IBM Corporation
- SAP SE
- Trimble Navigation Ltd
- Microsoft Corporation
- Vodafone Group PLC
- Accenture PLC
- SWIIM System
- Orange Business Services
- Link Labs LLC
第7章 投资分析
第8章 市场机会与今后动向
The Connected Agriculture Market size is expected to grow from USD 5.20 billion in 2023 to USD 8.80 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 11.10% during the forecast period (2023-2028).
The demand for advanced agricultural techniques to optimize crop yields while using the least amount of resources, such as water, fertilizer, and seeds, is the key factor driving the growth of the connected agriculture market. Farmers and businesses will be able to manage their time more effectively on the farm while using fewer resources by putting various linked agricultural technologies into practice.
Key Highlights
- Water management in agriculture is critical for increasing agricultural yields while decreasing costs and contributing to environmental stability. Agriculture officials are concerned about water scarcity and are working to enhance agricultural water management. Water management solutions in linked agriculture, which incorporate the Internet of Things (IoT), mobile applications, Big Data analytics, and decision support systems, are assisting in the production of environmentally friendly and optimum agricultural outputs for a growing population.
- Connected agriculture enables farmers to maximize crop cultivation while reducing expenses and effort associated with traditional agricultural methods. Connected agriculture boosts production by allowing farmers to expertly invest time and resources in the right combination to more precisely evaluate optimum sowing density, estimate fertilizers, and predict crop yields. Farmers currently rely on the most recent agricultural advancements, such as the usage of cell phones and other linked equipment. Sophisticated connected technologies such as low power wide area (LPWA), Zigbee, WiFi, and new wireless sensor technologies aid farmers in the planning and execution of various agricultural operations such as purchasing supplies, inventory control, timely planting and harvesting, and so on.
- Data collection is the first stage of precision agriculture and, thus, the most researched. This is accomplished mostly through the determination of soil fertility (one sample from the field, a polygon, or a zone). Zones are created using aerial or satellite imagery and are based on yield maps or photographs of the same crop over numerous years. It is done to boost yields eventually. A one-hectare polygon grid is the most often used soil testing method. This grid dimension is adequate for understanding the field's variability and what is going on in it. Finally, based on the soil scan, task maps are created for precise fertilizer and liming applications.
- There is a lack of understanding of connected farm technology, and installation is prohibitively expensive. These are the technology's constraints over the anticipated timeframe. The majority of farmers worldwide are small-scale farmers who cannot afford such costly equipment. This technique necessitates competent and knowledgeable farmers, large initial investments, and effective farming instruments, making farmers unwilling to gather information from it. Because of its high cost, it is only suitable for large and industrialized farms.
- The Covid pandemic brought attention to using artificial intelligence (AI). Data is used in real-time by artificial intelligence and machine learning models to get insightful knowledge, such as when to plant seeds, which crops to choose, which hybrid seeds to select for higher yields, and other things. Precision agriculture, often known as artificial intelligence systems, is assisting in enhancing the overall quality and accuracy of harvests. AI technology aids in the detection of pests, plant diseases, and undernutrition in farms. Artificial intelligence (AI) sensors can identify and target weeds before deciding which herbicide to use.
Connected Agriculture Market Trends
Upsurge in Demand for Smart Water Management Systems
- Smart water management (SWM) uses information and communication technology (ICT) and real-time data and responses, which is an integral part of the solution for water management challenges. The potential application of smart systems in water management is vast and includes solutions for water quality, water quantity, efficient irrigation, leaks, pressure and flow, floods, droughts, and much more. Water scarcity may directly affect nearly 20% of the human population by 2025, UN reports state, and indirectly influence the rest of the planet's inhabitants. Smart water systems based on the combination of the IoT, big data, and AI technologies may help stop these predictions and undo the damage the imprudent usage of water resources has already caused.
- The World Bank and Imagine H2O, a non-profit organization, partnered recently to fund technologies that promote global water sustainability. Many new enterprises aim at providing real-time digital information to farmers in remote and previously unavailable regions, such as moisture levels in their fields and impending weather conditions. Farmers received mobile management platforms as well. Flood risk detection, DNA fingerprinting technology to find the source of water pollution, and wave-driven autonomous desalination facilities for small island settlements are among the innovative technologies backed by the World Bank and Imagine H2O.
- In Chile and Peru, "water-smart" technologies help fruit producers adapt to the increase in droughts and water scarcity. These innovative technologies are focused on enhancing the efficiency of irrigation and restoring the health of soils. AQUA4D is a technology that improves the dissolution and distribution of minerals in the water. By this method, soils retain water for a longer interval, reducing water consumption by farmers. In contrast, a better balance of minerals in the water can improve the quality and salinity of the soil.
- Water usage facilities and water treatment plants can do their part by ensuring that their monitoring equipment is up-to-date and as accurate as possible. While SCADA systems are more commonplace in modern operations, cloud-based SCADA systems in water treatment facilities and plants are further expected to enhance the scalability of operations in the foreseen period. Adding to the scenario, technological advancements in smart meters and their integration with communication solutions like SCADA have transformed water management to address the challenges faced by water utilities, farmers, residents, and industries, in terms of erroneous billing and water management.
- According to IEA, by 2040, it is predicted that the total amount of water that will need to be withdrawn will be 4,350 billion cubic meters. The increase in water consumption in recent decades has outpaced population growth by a factor of two. Such huge water consumption and withdrawal would create an opportunity for smart water management systems.

Asia-Pacific to Witness the Highest Growth
- Japan's agricultural production expenses are high in comparison to other countries, owing to the high cost of agricultural inputs such as fertilizers and agricultural gear. According to the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries, rice cultivation, Japan's principal agricultural commodity, costs, on average, JPY 9,180 in total input costs for every 60kg of rice produced last year. Fertilizer expenditures account for 13% of this total, with agricultural machinery and implementation accounting for the remaining 32%. As a result, advancements in connected agriculture that reduce fertilizer waste or lower machinery costs will tremendously benefit Japanese farmers.
- The Maharashtra government has yet to develop a policy following the Center's clearance of the use of drones to spray pesticides in October 2022. Before approving subsidies under the Center-approved drone purchase program, the state administration is awaiting clarifications. Drones are being promoted as a way to combat the labor crisis and advance agricultural mechanization. International agrochemical company Syngenta said on Monday that two of its fungicide formulations had been given the go-ahead for drone spraying by the central pesticide board, the organization in charge of spraying regulations.
- The Department of Agriculture (DA) in the Philippines is evaluating the potential of drones to change the way seeds are planted, the way fertilizers and pesticides are applied, and the way crops are monitored. Moreover, the Ministry of Japan set a goal to introduce agricultural drones for about half of the land planted with rice, wheat, and soy across Japan by 2022.
- In August 2022, Automat, India's manufacturer of irrigation sprinklers, filtration equipment, and fertilization equipment, today launched five new smart irrigation solutions for Rajasthan farmers at its UDGHOSH event-a first-of-its-kind program to bring innovative technology to Indian farmers. To address the issue of low water levels for irrigation in Rajasthan, Automat India has launched five IoT-based autonomous irrigation systems that would assist farmers in monitoring, controlling, and wisely utilizing water. Each brand's goods, such as MachClean (Sand Media Filter), Turbo (Automatic Screen Filter), Hydromat (control Valves), Auto drip (Low-cost automation kit), and Aqua Disc (Automatic Disc Filter), would make irrigation easier for farmers while saving them time and money.
- In April 2022, the Thai government committed to accelerating its plans for a national digital transformation of the country's food and agricultural sectors, with a particular emphasis on big data, smart agriculture, e-commerce, and agribusiness development. Since the adoption of the national Thailand 4.0 and 20-year National Strategy frameworks, Thailand has expanded its focus on the digitalization of its food and agricultural supply chain.

Connected Agriculture Industry Overview
The connected agriculture market is moderately competitive owing to the presence of multiple players. The players in the market are adopting strategies like product innovation, mergers, and acquisitions in order to expand their product portfolio and expand their geographic reach and primarily to stay competitive in the market.
In January 2023, through a Knowledge Transfer Partnership (KTP), Aston University collaborated with engineering firm Solargen Technologies (SGT) and the University of Nairobi to develop a smart irrigation system that uses solar and wind energy to provide year-round watering of land and improve crop production in Kenya. SGT is Kenya's largest provider of energy, water, and irrigation solutions and services. They collaborate with non-governmental organizations, governments, and people to provide customized energy, water, and food security solutions to communities in rural and conflict-affected areas of Eastern Africa.
In February 2022, Agrology was planning to include Wyld Network's satellite-based IoT connectivity into its predictive agriculture platform for global, 24 hours a day, seven days a week data collection. Agrology and Wyld Networks announced a cooperation today to integrate Wyld Connect into Agrology's ground truth predictive agriculture technology. Wyld Connect is a low-cost Internet of Things (IoT) worldwide connectivity network based on low-orbit satellite technology. The solution assures that Agrology ground truth sensors will continue to collect data from even the most remote areas and will be able to communicate that data to Agrology customers swiftly, regardless of network status.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Introduction to Market Drivers and Restraints
- 4.3 Market Drivers
- 4.3.1 Emergence of BYOD (Bring Your Own Drone) in Connected Agriculture
- 4.3.2 Upsurge in Demand for Smart Water Management Systems
- 4.4 Market Restraints
- 4.4.1 Steep Learning Curve Regarding Connected Agriculture
- 4.5 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Solution
- 5.1.1.1 Network Management
- 5.1.1.2 Agriculture Asset Management
- 5.1.1.3 Supervisory Control
- 5.1.2 Service
- 5.1.1 Solution
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Smart Logistics
- 5.2.2 Smart Irrigation
- 5.2.3 Farming Planning and Management
- 5.3 Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.2.1 Germany
- 5.3.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.2.3 France
- 5.3.2.4 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.3.1 China
- 5.3.3.2 Japan
- 5.3.3.3 India
- 5.3.3.4 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 Latin America
- 5.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Company Profiles
- 6.1.1 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 6.1.2 IBM Corporation
- 6.1.3 SAP SE
- 6.1.4 Trimble Navigation Ltd
- 6.1.5 Microsoft Corporation
- 6.1.6 Vodafone Group PLC
- 6.1.7 Accenture PLC
- 6.1.8 SWIIM System
- 6.1.9 Orange Business Services
- 6.1.10 Link Labs LLC













