 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1438550
杀幼虫剂:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2024-2029)Larvicides - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
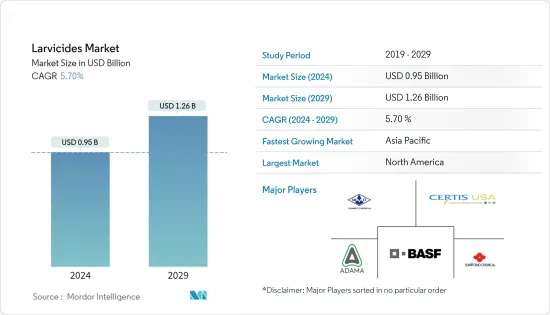
杀幼虫剂市场规模预计到 2024 年为 9.5 亿美元,预计到 2029 年将达到 12.6 亿美元,在预测期内(2024-2029 年)增长 5.70%,复合年增长率为
新型冠状病毒感染疾病(COVID-19)的突然爆发导致多个国家推出了严格的封锁规定,导致杀幼剂进出口活动受到干扰。疫情期间,地方政府部门和防蚊区将主导大规模灭蚊行动。其中一项活动是散布幼虫剂。持有执照的灭蚊专业人员根据受影响区域的大小,使用背包式喷雾器、卡车或飞机使用经环境保护局 (EPA)散布的杀幼虫剂。
据世界卫生组织称,开发中国家40% 的人口面临感染疟疾等严重的风险。疟疾是一种危及生命的疾病,由雌性疟蚊传播的寄生虫所引起。例如,2017年,87个国家估计有2.19亿例疟疾病例,疟疾控制总资金估计为31亿美元。热带国家的国家捐款达9亿美元,占资金总额的28%。疾病爆发、媒介传播流行病和害虫袭击数量的增加是推动全球杀幼虫剂市场的一些关键因素。其中,由于气候变迁的影响以及城市害虫对公众健康的威胁,亚太地区在杀幼虫剂市场中占据较大份额。
杀幼剂市场趋势
蚊媒疾病推动杀幼剂市场
蚊媒疾病在包括南美洲在内的大多数国家造成了毁灭性的破坏。委内瑞拉报告 2019 年有 126 人死于疟疾。疟疾、基屈公病和登革热等致命疾病可以用杀幼虫剂治疗。例如,兹卡病毒等疾病的爆发使欧洲地区的蚊子数量更加猖獗。撒哈拉以南非洲、中东、拉丁美洲、亚洲和欧洲部分地区是受疟疾影响的地区。因此,对登革热和疟疾病例增加的担忧为目标地区的杀幼虫剂市场创造了机会。此外,政府支出和跨国公司在发展中产业的参与正在推动杀幼虫剂市场的发展。
媒介传播疾病、传染病、气候变迁、害虫数量增加以及生态学永续性等因素正在推动市场成长。
北美市场占据主导地位
由于许多跨国公司在该地区的存在,北美估计是最大的消费国。由于有效的监测和病媒控制计划,美国和加拿大的市场庞大。 2017年,北美占比最大,其次是欧洲。由于蚊媒疾病的流行,亚太地区预计将维持最高的复合年增长率。高度都市化和公众对害虫不容忍的增加预计将加速未来杀幼剂市场的发展。
使用喷雾器将液体杀幼虫剂产品直接涂布水中。锭剂、丸剂、颗粒剂和木炭块等杀幼虫製剂也被繁殖区的灭蚊人员广泛使用。在美国,美国环保署(美国 EPA)註册了三种主要类型的幼虫控製剂:微生物杀幼虫剂、昆虫生长抑制剂和化学杀虫剂(主要是替美磷)。苏云金芽孢桿菌(Bti)是一种天然土壤细菌,可以有效杀死水中的蚊子幼虫。 Aquabac、Teknar、Baltimore 和 Vectobac 是一些市售 Bti 菌株。
杀幼虫剂产业概况
杀幼虫剂市场高度分散。领先公司采用合资、新产品发布、合作、协议、扩张、併购等各种策略来扩大其在市场上的影响力。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月分析师支持
目录
第一章简介
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章市场动态
- 市场概况
- 市场驱动因素
- 市场限制因素
- 波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代产品的威胁
- 竞争公司之间敌对的强度
第五章市场区隔
- 目的
- 农业
- 非农
- 控制方式
- 生物防治剂
- 化学品
- 昆虫生长调节剂
- 产品类别
- 合成杀幼虫剂
- 天然杀幼虫剂
- 生物杀幼虫剂
- 目标昆虫
- 蚊子
- 苍蝇
- 其他目标昆虫
- 地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地区
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 俄罗斯
- 西班牙
- 其他欧洲国家
- 亚太地区
- 印度
- 中国
- 日本
- 其他亚太地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 其他非洲
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争形势
- 最采用的策略
- 市场占有率分析
- 公司简介
- Adama
- BASF
- Sumitomo Chemical
- Certis
- Summit Chemical
- Nufarm
- Russell IPM
- Central Garden &Pet Co.
- Eli Lily and Company
- Syngenta
第七章市场机会与未来趋势
第 8 章 评估 COVID-19 对市场的影响
The Larvicides Market size is estimated at USD 0.95 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 1.26 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5.70% during the forecast period (2024-2029).

The sudden outbreak of COVID-19 led to the implementation of stringent lockdown regulations across several nations, resulting in disruptions in the import and export activities of larvicides. Local government departments and mosquito control districts lead large-scale mosquito control activities during an outbreak. One activity is to apply larvicides. Licensed mosquito control professionals apply Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)-registered larvicides using backpack sprayers, trucks, or airplanes, depending on the size of the area being affected.
According to the WHO, 40% of the population living in underdeveloped countries is at risk of serious diseases, such as malaria, which is one of the life-threatening diseases caused by parasites transmitted by female anopheles mosquitoes. For instance, in 2017, there were an estimated 219 million malaria cases in 87 countries, and the total funding for malaria control was estimated at USD 3.1 billion. State contributions from tropical countries contributed to USD 900 million, accounting for 28% of total funding. An increasing number of disease outbreaks, vector-based epidemics, and growing pest attacks are some of the major factors driving the larvicides market globally. Among the regions, Asia-Pacific holds the major share in the larvicides market due to climate change, which poses a threat to public health caused by urban pests.
Larvicides Market Trends
Mosquito-borne Diseases Drive the Larvicides Market
Mosquito-borne diseases have become devastating in most countries, such as South America. Venezuela reported 126 deaths in 2019 due to malaria. Deadly diseases such as malaria, chikungunya, and dengue can be managed by larvicide. For example, the disease outbreaks such as the Zika virus have made the European region more susceptible to the spread of mosquito populations. Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle-East, Latin America, Asia, and several parts of Europe are malaria-affected regions. Thus, the concerns about increasing dengue and malaria cases create an opportunity for the larvicides market in the target region. Additionally, government spending in the developing sector and the involvement of multinational companies drive the larvicides market.
Factors such as the increasing prevalence of vector-borne diseases, epidemics, climatic changes, rising pest population, and ecological sustainability are driving the market's growth.
North America Dominates the Market
North America is estimated as the largest consumer due to the presence of many multinational companies in the region. The US and Canadian markets are huge due to effective surveillance and vector control programs. North America accounted for the largest share in 2017, followed by Europe. Asia-Pacific is projected to record the highest CAGR due to the spread of mosquito-borne diseases. High urbanization and rising public intolerance of pests are anticipated to fuel the larvicides market in the future.
Liquid larvicide products are applied directly to water using sprayers. Tablet, pellet, granular, and briquet formulations of larvicides are also widely applied by mosquito controllers to breeding areas. In the United States, the Environment Protection Agency (US EPA) registered three major types of larval control agents, i.e., microbial larvicides, insect growth inhibitors, and chemical insecticides (mainly temephos). Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti) is a naturally occurring soil bacterium that can effectively kill mosquito larvae present in water. Aquabac, Teknar, Baltimore, and Vectobac are some of the commercially available Bti strains.
Larvicides Industry Overview
The larvicides market is highly fragmented. The major players use various strategies such as joint ventures, new product launches, partnerships, agreements, expansions, and mergers and acquisitions to increase their footprint in the market.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Application
- 5.1.1 Agriculture
- 5.1.2 Non-agriculture
- 5.2 Control Method
- 5.2.1 Bio Control Agent
- 5.2.2 Chemical Agent
- 5.2.3 Insect Growth Regulator
- 5.3 Product Type
- 5.3.1 Synthetic Larvicides
- 5.3.2 Natural Larvicides
- 5.3.3 Biological Larvicides
- 5.4 Target Insect
- 5.4.1 Mosquitoes
- 5.4.2 Flies
- 5.4.3 Other Target Insects
- 5.5 Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Russia
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 India
- 5.5.3.2 China
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 Rest of the Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Africa
- 5.5.5.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Most Adopted Strategies
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Adama
- 6.3.2 BASF
- 6.3.3 Sumitomo Chemical
- 6.3.4 Certis
- 6.3.5 Summit Chemical
- 6.3.6 Nufarm
- 6.3.7 Russell IPM
- 6.3.8 Central Garden & Pet Co.
- 6.3.9 Eli Lily and Company
- 6.3.10 Syngenta






