 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1636554
欧洲塑胶废弃物管理:市场占有率分析、行业趋势和统计、成长预测(2025-2030 年)Europe Plastic Waste Management - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
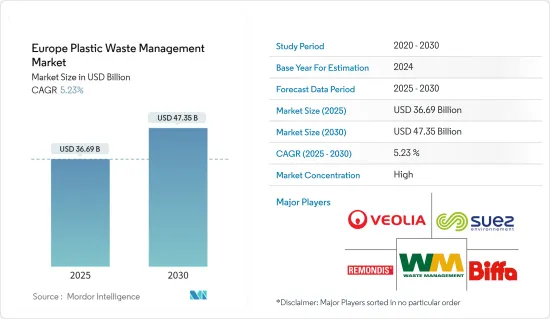
欧洲塑胶废弃物管理市场规模预计在2025年为366.9亿美元,预计到2030年将达到473.5亿美元,预测期内(2025-2030年)的复合年增长率为5.23%。
主要亮点
- 欧洲塑胶废弃物管理市场主要受到政府遏制快速废弃物产生措施和对永续性的偏好的推动。
- 塑胶废弃物污染是一个迫切的全球性问题。作为塑胶的主要消费国,欧洲在加剧这个问题方面发挥关键作用。该地区每年产生的塑胶废弃物不断增加,尤其是包装等一次性物品。但回收率却落后,凸显欧洲实现塑胶循环经济还有很长的路要走。
- 2023年,欧盟预计将排放6,000万吨塑胶废弃物。预测表明,这一趋势将持续下去,到 2060 年塑胶废弃物产生量可能会翻一番,达到每年 1 亿多吨。
- 包装是欧洲塑胶废弃物的主要来源,总合欧盟成员国2023年将产生超过1,600万吨塑胶垃圾。过去十年,欧盟的塑胶包装废弃物激增了30%左右。
- 在欧洲,掩埋和焚烧能源回收回收仍然是塑胶废弃物管理的主导方式,而回收则落后,仅占欧洲大陆废弃物处理的不到15%。虽然取得了一些进展,但欧盟塑胶包装的回收率仍低于50%,没有达到欧盟2025年的回收目标。
- 出口到欧盟以外地区的塑胶废弃物被纳入回收率,假设将在欧盟内部进行加工。然而,由于接收国废弃物基础设施不足,这些出口经常面临管理不善的情况。儘管如此,该地区的塑胶废弃物出口仍在下降。这是因为越来越多的国家禁止或限制进口塑胶废弃物。
- 塑胶污染已成为欧洲的迫切问题,促使该地区推出新的政策。例如,欧盟的《一次性塑胶指令》禁止使用欧洲海滩上常见的许多一次性塑胶产品。欧洲正大力推行更广泛禁止一次性塑胶的措施。特别是,欧盟于2023年11月承诺在2026年停止向非经合组织国家出口塑胶废弃物,但要求全面禁止出口的呼声依然存在。
欧洲塑胶废弃物管理市场趋势
欧盟新政策将改变包装产业,推动 2050 年实现气候中和
欧盟已于 2023 年修改了有关包装和包装废弃物的法案。该修正案是2050年使包装产业实现气候中立的更广泛目标的一部分。
自 2023 年起,餐饮服务、宅配服务和餐厅将被要求提供可重复使用的容器作为外带食品的选择,不再使用一次性塑胶。在英国,预计到 2025 年,一次性饮料瓶必须含有至少 25% 的再生塑胶。
这些新政策将特别有利于中小企业,它们将释放出新一轮的商机。这也将减少对原料的依赖,增强欧洲的回收能力,并减少欧洲大陆对主要来源和外部供应商的依赖。重要的是,这些努力将使包装产业在 2050 年之前实现气候中立目标。
在努力实现雄心勃勃的净零和净正目标的同时,塑胶产业依赖三大支柱:速度、劳动力和政策。实现这些里程碑将增强欧洲的竞争力,并代表欧洲在应对气候变迁方面向前迈出的重要一步。未来三到五年对于我们能否在本世纪中叶达到脱碳至关重要。
随着世界变化,英国加大力度应对塑胶废弃物
塑胶因其价格低廉、耐用且用途广泛而受到讚誉,已在全球社会中根深蒂固。然而,其处理的限制对环境构成了重大威胁。英国是排放塑胶废弃物最多的国家,其家庭每年丢弃的塑胶包装数量高达 1000 亿件。 2021年产生了250万吨塑胶包装废弃物。
儘管人们的环保意识不断增强,但 2021 年塑胶包装废弃物的回收率在过去的半个世纪中保持相对稳定,仅为 44%。该比率包括直接回收和透过焚烧进行的能源回收。令人震惊的是,英国近一半的塑胶废弃物被焚烧以获取能源,而只有 12% 在国内回收,25% 被垃圾掩埋场,其余的则被运往海外。
由于国内加工能力不足,英国越来越依赖出口,尤其是对荷兰的出口,2022 年荷兰占英国塑胶废弃物进口量的四分之一。然而,全球格局正在改变。传统废弃物进口国中国等国家正在严厉打击此类行为,并加强对英国的压力,要求其重新审查其废弃物管理策略。越来越多的人呼吁加强回收基础设施和引进先进的回收技术。
由于塑胶分解速度缓慢,其污染问题在英国引起了人们的担忧。对此,英国政府推出了包括对一次性塑胶购物袋收费在内的多项政策,大幅减少了超级市场的塑胶购物袋发放。有人呼吁进一步实施禁令,苏格兰率先禁止使用有问题的一次性塑料,包括刀叉餐具、盘子和咖啡杯。英格兰也将效仿并从 2023 年 10 月 1 日起实施类似的禁令。此外,原定于 2023 年实施的全国饮料容器押金返还计画 (DRS) 因财政挑战而推迟至 2025 年。
欧洲塑胶废弃物管理产业概况
欧洲塑胶废弃物管理市场比较分散。以下主要企业正在塑造竞争格局:威立雅环境公司、苏伊士、Remondis、Biffa、Waste Management Inc. 和Renewi。中心宗旨,并减少塑胶垃圾对环境造成的伤害。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月的分析师支持
目录
第 1 章 简介
- 调查前提条件
- 研究范围
第二章调查方法
- 分析方法
- 研究阶段
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场动态与洞察
- 当前市场状况
- 市场动态
- 驱动程式
- 永续性需求不断成长推动市场
- 人们对环境问题的兴趣日益浓厚
- 限制因素
- 影响市场的监管因素
- 影响市场的基础建设挑战
- 市场机会
- 市场驱动的技术进步
- 驱动程式
- 价值链/供应链分析
- 政府法规、贸易协定与倡议
- 产业吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 消费者议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
- 塑胶废弃物管理市场的先锋技术
- COVID-19 市场影响
第五章 市场区隔
- 按聚合物
- 聚丙烯(PP)
- 聚乙烯 (PE)
- 聚氯乙烯(PVC)
- 聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)
- 其他聚合物
- 按排放分类
- 住宅
- 商业的
- 工业的
- 其他(建筑、医疗保健)
- 透过处理
- 回收利用
- 化学处理
- 垃圾掩埋场
- 其他处理
- 按地区
- 英国
- 德国
- 西班牙
- 法国
- 义大利
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲国家
第六章 竞争格局
- 市场集中度概览
- 公司简介
- Veolia Environment
- Suez Environment
- Biffa Group
- Waste Management Inc.
- REMONDIS
- Renewi
- FCC Environment
- Viridor
- DS Smith
- TOMRA
- 其他公司
第七章:市场的未来
第 8 章 附录
The Europe Plastic Waste Management Market size is estimated at USD 36.69 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 47.35 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.23% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- The European plastic waste management market is mainly driven by government initiatives to curb rapid waste generation and a growing preference for sustainability.
- Plastic waste pollution is a pressing global concern. As a significant consumer of plastics, Europe plays a pivotal role in exacerbating this issue. The region's annual plastic waste production, notably from single-use items like packaging, is on the rise. However, recycling rates are lagging, underscoring the considerable distance Europe must traverse to achieve a circular economy for plastics.
- In 2023, the European Union produced an estimated 60 million metric tons of plastic waste. Projections suggest this trend will persist, potentially leading to a doubling of plastic waste generation by 2060, exceeding 100 million metric tons annually.
- Within Europe, packaging represents the primary source of plastic waste, with EU Member States collectively producing over 16 million metric tons in 2023. Over the last decade, plastic packaging waste in the European Union surged by approximately 30%.
- In Europe, landfilling and incineration for energy recovery continue to dominate plastic waste management, while recycling lags, making up less than 15% of the continent's waste disposal. Despite some progress, the plastic packaging recycling rate in the European Union has struggled to breach the 50% mark, falling short of the bloc's 2025 recycling goal.
- The plastic waste exported from the European Union to countries outside the bloc intended for treatment is factored into recycling rates. However, these shipments often face mismanagement due to inadequate waste infrastructure in the receiving nations. Despite this, plastic waste exports in the region have been on a downward trend, attributed to an increasing number of countries enforcing bans and restrictions on such imports.
- Plastic pollution is a pressing issue in Europe, prompting the region to enact new policies. For instance, the Single-use Plastics Directive of the European Union includes bans on various disposable plastic items commonly found on European beaches. The momentum for a broader single-use plastics ban in Europe is gaining traction. Notably, in November 2023, the European Union committed to halting plastic waste exports to non-OECD nations by 2026, although calls for a total export ban persist.
Europe Plastic Waste Management Market Trends
The European Union's New Policies Set to Transform the Packaging Industry and Drive Climate Neutrality by 2050
The European Union revised its legislation on packaging and packaging waste, effective 2023. This revision is part of a broader goal to steer the packaging industry toward climate neutrality by 2050.
From 2023, eateries, delivery services, and restaurants were mandated to provide reusable containers as an option for takeout food, moving away from single-use plastics. By 2025, the United Kingdom is projected to require disposable beverage bottles to contain a minimum of 25% recycled plastic content.
These new policies are poised to usher in a wave of business opportunities, particularly benefiting smaller enterprises. They will also reduce the reliance on virgin materials, bolster Europe's recycling capabilities, and lessen the continent's dependence on primary resources and external suppliers. Crucially, these initiatives are set to align the packaging industry with climate neutrality targets by 2050.
While striving for ambitious net-zero and net-positive goals, the plastics industry hinges on three pillars, i.e., speed, workforce, and policy. Achieving these milestones positions Europe competitively and marks a significant stride in combating climate change. The upcoming three to five years will be pivotal in gauging the industry's ability to decarbonize by mid-century.
The United Kingdom Ramps up Efforts to Tackle Plastic Waste Amid Global Shifts
Plastics, lauded for their affordability, durability, and versatility, have entrenched themselves in the global society. However, the limitations in their disposal pose a significant environmental threat. The United Kingdom stands out in its plastic waste production, with its households discarding a monumental 100 billion plastic packaging pieces annually, averaging 66 per week. In 2021, the country generated 2.5 million metric tons of plastic packaging waste.
Despite heightened environmental awareness, the country's recycling rate for plastic packaging waste lingered at 44% in 2021, which remained relatively static for half a decade. This rate encompasses both direct recycling and energy recovery from incineration. Alarmingly, nearly half of the United Kingdom's plastic waste is incinerated for energy, while a mere 12% is recycled domestically, with 25% ending up in landfills and the rest shipped overseas.
With insufficient domestic processing capabilities, the United Kingdom has increasingly turned to exports, notably channeling a significant portion to the Netherlands, which accounted for a quarter of UK plastic waste imports in 2022. However, the global scenario is shifting. Countries like China, a traditional waste importer, have clamped down on such practices, intensifying the pressure on the United Kingdom to revamp its waste management strategies. Calls for bolstered recycling infrastructure and the adoption of advanced recycling technologies have grown louder.
Given the slow decomposition rate of plastic, concerns over pollution are mounting in the United Kingdom. In response, the UK government has initiated various policies, including the single-use carrier bag charge, which has notably curbed supermarket plastic bag issuance. Calls for further bans have emerged, with Scotland leading the way by prohibiting problematic single-use plastics like cutlery, plates, and coffee cups. Following suit, England was set to implement a similar ban starting October 1, 2023. Additionally, a nationwide deposit return scheme (DRS) for beverage containers, initially slated for 2023, has been delayed to 2025, citing economic challenges.
Europe Plastic Waste Management Industry Overview
The European plastic waste management market is fragmented in nature. It boasts a competitive landscape shaped by key players such as Veolia Environnement SA, Suez, Remondis, Biffa, Waste Management Inc., and Renewi. These industry leaders vie for market share through pioneering recycling technologies, streamlined collection and sorting, and eco-conscious waste disposal methods. Their strategies pivot on adhering to regulations, championing circular economy tenets, and curbing the environmental toll of plastic waste.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS AND INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.2.1.1 Increasing Demand for Sustainability Driving the Market
- 4.2.1.2 Environmental Concerns Driving the Market
- 4.2.2 Restraints
- 4.2.2.1 Regulatory Factors Affecting the Market
- 4.2.2.2 Infrastructure Challenges Affecting the Market
- 4.2.3 Opportunities
- 4.2.3.1 Technological Advancements Driving the Market
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.3 Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Government Regulations, Trade Agreements, and Initiatives
- 4.5 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.6 Technological Developments in the Plastic Waste Management Market
- 4.7 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Polymer
- 5.1.1 Polypropylene (PP)
- 5.1.2 Polyethylene (PE)
- 5.1.3 Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- 5.1.4 Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
- 5.1.5 Other Polymers
- 5.2 By Source
- 5.2.1 Residential
- 5.2.2 Commercial
- 5.2.3 Industrial
- 5.2.4 Other Sources (Construction and Healthcare)
- 5.3 By Treatment
- 5.3.1 Recycling
- 5.3.2 Chemical Treatment
- 5.3.3 Landfill
- 5.3.4 Other Treatments
- 5.4 By Region
- 5.4.1 The United Kingdom
- 5.4.2 Germany
- 5.4.3 Spain
- 5.4.4 France
- 5.4.5 Italy
- 5.4.6 Russia
- 5.4.7 Rest of Europe
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Veolia Environment
- 6.2.2 Suez Environment
- 6.2.3 Biffa Group
- 6.2.4 Waste Management Inc.
- 6.2.5 REMONDIS
- 6.2.6 Renewi
- 6.2.7 FCC Environment
- 6.2.8 Viridor
- 6.2.9 DS Smith
- 6.2.10 TOMRA*
- 6.3 Other Companies











