 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851094
固定无线存取:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Fixed Wireless Access - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
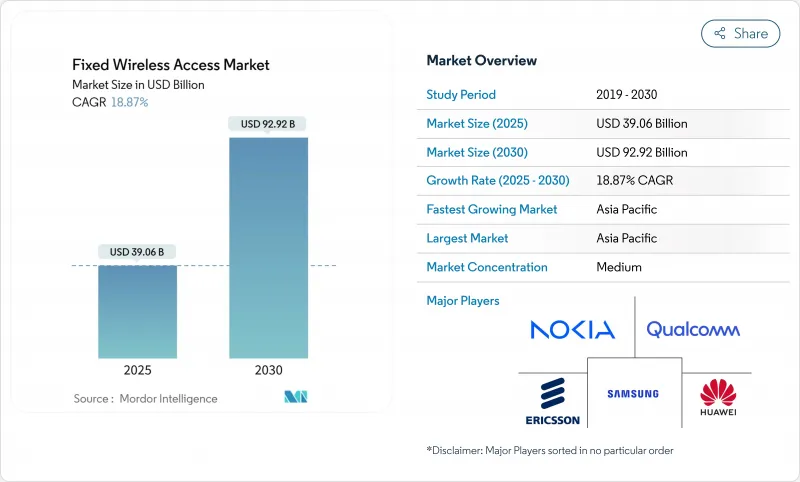
预计到 2025 年,固定无线接取市场规模将达到 390.6 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 927.2 亿美元,复合年增长率为 18.87%,证实了固定无线接入市场是成长最快的宽频细分市场之一。
此次扩张由三大支柱驱动:加速部署5G,将现有行动基地台改造为住宅宽频;农村地区对经济实惠的「最后一公里」连接的需求日益增长;以及用户端设备持续创新,提供接近光纤的速度。北美和亚太地区的营运商已将资金从传统的「光纤到户」转向固定无线,从而缩短了部署週期并显着降低了每户成本。 6GHz以下频段频谱的分配以及毫米波在都市区密集城区的推出,使营运商能够更灵活地平衡覆盖范围和容量。同时,工业IoT试点计画正在透过将固定无线存取链路转变为工厂和物流中心的安全、低延迟骨干网,创造新的收入来源。
全球固定无线接取市场趋势与洞察
5G部署加速Gigabit级固定无线存取(FWA)。
5G的广泛部署将使通讯业者能够在同一无线网路上迭加固定无线接入,从而将行动宏基地台转变为社区宽频节点。美国通讯业者报告称,其新增宽频用户主要来自固定无线套餐,这凸显了固定无线存取市场对传统有线基础设施的蚕食作用。对大规模MIMO和波束成形技术的投资将提高室外CPE的吞吐量,同时在非视距环境下维持服务。爱立信的软体升级无需新硬体即可扩展覆盖范围,简化农村地区的覆盖范围。诺基亚等厂商展示了毫米波接收器,能够在最远7公里的距离上维持1Gbps的链路,证明了其在人口稠密的城市和人口稀少的郊区的可行性。这些进步将把用户体验提升到光纤水平,并推动家庭和企业采用5G网路。
农村宽频推广计划
公共资金正透过资助无线接入设备和用户终端设备 (CPE) 的建设,缩小光纤线路未覆盖城镇的数位落差。在美国,联邦和州政府津贴数十亿美元用于服务不足的普查区,通常优先发展固定无线接入,因为基地台的部署只需几週而非几个月。华盛顿州监管机构已证实,固定无线存取 (FWA) 解决方案的安装成本更低、速度更快,儘管速度比光纤降低。欧洲的「数位十年」计画也采用了类似的策略,透过灵活的频谱规则吸引无线网路服务供应商使用农村频宽。布拉特尔集团 (Brattle Group) 的一项成本效益研究发现,宽频扩展(包括固定无线存取)可带来数兆美元的房产价值和收入成长,这进一步支持了相关政策。
频谱短缺和监管不确定性
中频段频谱兼具覆盖范围和容量优势,但大部分已被传统用途占用或被现有广播公司争夺。美国围绕着低频段3GHz频谱的游说之争,凸显了政策决策的拖延如何阻碍营运商的投资。谷歌的频谱存取系统等动态共享系统能够实现灵活使用,但设备生态系统仍依赖明确的授权协议。区域性规则使全球设备设计复杂化,推高了成本,并延缓了大规模生产。包括美国国家电信和资讯管理局(NTIA)的《国家频谱战略》在内的国家蓝图承诺增加频谱分配,但由于竞标延迟和优先事项的调整,仍然存在不确定性。
细分市场分析
到2024年,硬体仍将占据固定无线存取市场65%的份额,这主要得益于早期对无线电和CPE(网路部署的核心组件)的重点投资。虽然室内设备将占出货量的60%,但由于室外设备单价较高且需要专业安装,室外设备将占大部分收入。营运商和供应商持续在热感、天线增益和路由器软体方面进行创新,为客户提供类似Wi-Fi Mesh套件的自助安装体验。由硬体驱动的固定无线接取市场规模预计将以低于订阅用户成长的速度成长。
到2030年,服务板块的复合年增长率将达到19.60%,超过固定无线存取产业的其他板块,主要得益于营运商向託管Wi-Fi、 Over-the-Top视讯和云端安全性捆绑服务等领域的多元化发展。超过40%的营运商正在转向基于速度的定价模式,类似于光纤分级定价,这将加速提升每位用户平均收入。网路API很快就会支援在实况活动和电竞比赛期间按需提升吞吐量,进一步提高服务利润率。随着普及规模的扩大,获利能力将取决于经常性费用,而非设备销售。
到2024年,住宅宽频将占总收入的52%,这反映了顶级通讯业者积极的消费者宣传活动。这些宣传活动通常将串流媒体订阅与免费硬体捆绑销售,从而降低用户流失率。相较之下,到2030年,住宅宽频的复合年增长率将达到22.32%。工厂正在生产线和边缘伺服器之间部署固定无线网关,以支援即时机器视觉、机器人和安全系统。试验显示,使用载波聚合频谱,下行链路的平均速度可达648 Mbps,峰值速度超过1 Gbps。这些指标满足了汽车和半导体工厂通常严格的可用性目标。
快餐店等商业场所需要快速推出和灵活的合约来连接销售点系统数位电子看板,而教育和医疗行业则更倾向于快速部署而非申请线路许可。因此,这些行业的公司正在客製化垂直行业套餐,将专用 5G 核心网与零接触配置相结合。
区域分析
亚太地区维持了37%的收入份额,并以21.07%的复合年增长率实现了最快增长,这主要得益于中国、韩国和日本超过85%的5G人口覆盖率。印度两大业者将AirFiber服务与每日储值券捆绑销售,在不到一年的时间内吸引了数百万首次宽频用户。印度政府在「数位印度」计画下的激励措施,为未覆盖村庄的基地台安装提供高达80%的报销,进一步加速了部署。固定无线接入市场参与者也受益于全部区域的设备製造地,从而缩短了供应链。
北美地区正受到大规模5G独立组网核心网和频谱政策的推动。随着通讯业者重新部署从卫星服务中释放出来的中频段频谱资源,美国固定无线存取市场规模正在不断扩大。营运商通常报告每季净新增用户60万至70万,这一趋势迫使有线电视营运商实施对称分级服务。加拿大大力推动农村宽频建设,为农场和旅游旅馆的屋顶无线网路提供资金,因为在这些地方,挖掘穿过永久冻土层的光纤线路是不切实际的。
欧洲呈现出碎片化的格局。光纤覆盖率高的北部国家主要利用固定无线网路来实现冗余,而南部和东部国家则利用固定无线网路直接跳过铜缆升级阶段。 26GHz频段的监管弹性促进了跨境设备协调,降低了用户端设备(CPE)的成本。中东和非洲的新兴市场正在采用无线优先解决方案来实现最后一公里接取。各国宽频计画将在两年内将固定无线网路作为连接学校和诊所的主要方式,这将使固定无线接入市场成为推动整个欧洲大陆数位包容性的催化剂。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 5G部署加速Gigabit级固定无线存取(FWA)。
- 农村宽频推广计划
- FWA 作为一种经济高效的「最后一公里」光纤替代方案
- 企业SD-WAN备援连线的需求
- 市场限制
- 频谱稀缺性和监管不确定性
- 毫米波密集化资本支出
- 价值链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- FWA采用的关键推动因素
- 供应商计画与伙伴关係
- 商业考量和前提条件
- FWA与FTTH/FTTdp的比较
- 农村、半都市区和都市区用例模型
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按类型
- 硬体
- 消费性电子产品(CPE)
- 接入单元(飞毫微微蜂窝和微微型基地台)
- 服务
- 硬体
- 透过使用
- 住宅
- 商业的
- 工业的
- 按频宽
- 6 GHz 以下频段
- 毫米波(24 GHz 以上)
- 透过部署模式
- 室内CPE
- 户外CPE
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 南美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 中东和非洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- Nokia Corporation
- Ericsson AB
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- ATandT Inc.
- T-Mobile US Inc.
- US Cellular Corp.
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- Siklu Communication Ltd.
- Starry Group Holdings Inc.
- Arqiva Ltd.
- Inseego Corp.
- ZTE Corporation
- Deutsche Telekom AG
- Vodafone Group Plc
- Telstra Corp. Ltd.
- Orange SA
- Globe Telecom Inc.
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The fixed wireless access market is valued at USD 39.06 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 92.72 billion by 2030, reflecting an 18.87% CAGR and confirming the fixed wireless access market size as one of the most rapidly expanding broadband segments.

Expansion rests on three pillars: accelerated 5G roll-outs that repurpose existing mobile towers for home broadband, growing demand for affordable last-mile connectivity in rural districts, and continuous innovation in customer-premises equipment that delivers near-fiber speeds. Operators in North America and Asia Pacific have redirected capital from traditional fiber-to-the-home toward fixed wireless, trimming deployment timelines and reducing per-household costs by wide margins. Spectrum allocations in Sub-6 GHz, coupled with millimeter-wave launches in dense urban zones, give providers the flexibility to balance coverage and capacity. Meanwhile, industrial IoT pilots are turning fixed wireless access links into secure, low-latency backbones for factories and logistics hubs, thereby opening fresh revenue streams.
Global Fixed Wireless Access Market Trends and Insights
5G Roll-out Accelerating Gigabit-class FWA
Widespread 5G deployment allows operators to layer fixed wireless access on the same radio network, turning mobile macro sites into neighborhood broadband nodes. U.S. carriers report the majority of net broadband additions coming from fixed wireless packages, underscoring how the fixed wireless access market is eating into cable's traditional base. Investments in massive MIMO and beamforming raise outdoor CPE throughput while sustaining service in non-line-of-sight environments. Ericsson software upgrades extend usable range without new hardware, simplifying rural coverage. Vendors such as Nokia have showcased mmWave receivers that hold a 1 Gbps link at distances up to 7 km, proving viability in both dense cities and sparsely populated fringes. Taken together, these advances lift customer experience to fiber-like benchmarks and boost adoption across homes and enterprises.
Rural Broadband Stimulus Programmes
Public funding is narrowing digital divides by underwriting radio access equipment and CPE for towns bypassed by fiber trenching. In the United States, federal and state grants funnel billions into unserved census blocks, and fixed wireless access often receives priority because towers are deployed in weeks rather than months. Washington State regulators confirm that FWA solutions can be installed rapidly at lower cost, albeit with modest speed trade-offs compared with fiber. Europe's Digital Decade agenda mirrors this approach through flexible spectrum rules that invite wireless internet service providers into rural bands. Cost-benefit studies from The Brattle Group link broadband expansion, including fixed wireless, to trillions in property-value and income gains, fueling more policy support.
Spectrum Scarcity & Regulatory Uncertainty
Mid-band spectrum sits at the sweet spot between coverage and capacity, yet much of it is tied up in legacy use or contested by incumbent broadcasters. Lobbying battles over the lower 3 GHz block in the U.S. illustrate how protracted policymaking can stall operator investment. Dynamic sharing systems such as Google's Spectrum Access System allow opportunistic use, but device ecosystems still rely on clear, licensed holdings. Varied regional rules complicate global equipment design, raising costs and slowing volume manufacturing. Although national road maps, including the NTIA National Spectrum Strategy, promise additional allocations, uncertainty lingers through auction delays and shifting priorities.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- FWA as Cost-effective Last-mile Alternative to Fibre
- Enterprise SD-WAN Back-up Connectivity Demand
- High mmWave Densification CAPEX
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Hardware retained a 65% share of the fixed wireless access market in 2024 thanks to intensive early-stage spending on radios and CPE that anchor network roll-outs. Indoor devices make up 60% of units shipped, while outdoor models dominate revenue because of higher unit pricing and professional installation. Operators and vendors continue to innovate on thermals, antenna gains, and router software, giving customers a self-install experience that parallels Wi-Fi mesh kits. The fixed wireless access market size attributable to hardware is projected to expand, yet at a slower clip than subscriptions.
The services segment is set for a 19.60% CAGR through 2030, outstripping the rest of the fixed wireless access industry as providers diversify into managed Wi-Fi, over-the-top video, and cloud security bundles. More than 40% of operators have migrated to speed-based tariff menus that mimic fiber grade tiers, accelerating average revenue per user. Network APIs will soon enable on-demand throughput boosts during live events or e-sports tournaments, further lifting service margins. As adoption reaches scale, recurring fees rather than equipment sales will define earnings power.
Residential broadband accounted for 52% of overall revenue in 2024, reflecting aggressive consumer campaigns by Tier-1 mobile carriers. Promotions often bundle streaming subscriptions and zero-cost hardware, which compresses churn. Industrial deployments, in contrast, record a 22.32% CAGR to 2030. Factories insert fixed wireless gateways between production lines and edge servers, supporting real-time machine vision, robotics, and safety systems. Trials have demonstrated a median downlink of 648 Mbps and peaks above 1 Gbps using carrier-aggregated spectrum. These metrics satisfy stringent availability targets common in automotive and semiconductor plants.
Commercial sites such as quick-service restaurants rely on fast turn-ups and flexible contracts to connect point-of-sale systems and digital signage. Education and healthcare settings also favor rapid deployment over trenching permits. Consequently, fixed wireless access market players tailor vertical packages that integrate private 5 G cores with zero-touch provisioning.
The Fixed Wireless Access Market Report is Segmented by Type (Hardware [Consumer Premise Equipment (CPE), Access Units [Femto and Picocells]] and Services), Application (Residential, Commercial, and Industrial), Frequency Band (Sub-6 GHz and MmWave (above 24 GHz), Deployment Mode (Outdoor CPE and Indoor CPE), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific keeps a 37% revenue share and posts the fastest 21.07% CAGR as 5 G population coverage exceeds 85% in China, South Korea, and Japan. India's top two operators have bundled AirFiber services with pay-per-day vouchers, capturing millions of first-time broadband users in less than a year. Government incentives under Digital India reimburse up to 80% of tower equipment in unserved villages, further accelerating roll-out. Fixed wireless access market players also benefit from device-manufacturing hubs across the region that shorten supply chains.
North America follows, fueled by large-scale 5 G standalone cores and supportive spectrum policy. The fixed wireless access market size in the United States is climbing as telecoms redeploy mid-band holdings cleared from satellite services. Operators routinely report 600,000 to 700,000 net additions per quarter, a trend that has forced cable incumbents to introduce symmetrical tiers. Canada's rural broadband drive funds rooftop radios for farms and tourist lodges where fiber trenching through permafrost is impractical.
Europe shows a fragmented pattern. Northern nations with high fiber coverage use fixed wireless mainly for redundancy, while Southern and Eastern countries leverage it to leapfrog copper upgrades. Regulatory flexibility in the 26 GHz band encourages cross-border equipment harmonization, which lowers CPE cost. Emerging markets in the Middle East and Africa rely on wireless first solutions for last-mile access. National broadband plans treat fixed wireless as the primary method to connect schools and clinics within two years, positioning the fixed wireless access market as a catalyst for digital inclusion across the continent.
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- Nokia Corporation
- Ericsson AB
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- ATandT Inc.
- T-Mobile US Inc.
- US Cellular Corp.
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- Siklu Communication Ltd.
- Starry Group Holdings Inc.
- Arqiva Ltd.
- Inseego Corp.
- ZTE Corporation
- Deutsche Telekom AG
- Vodafone Group Plc
- Telstra Corp. Ltd.
- Orange S.A.
- Globe Telecom Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 5G roll-out accelerating gigabit-class FWA
- 4.2.2 Rural broadband stimulus programmes
- 4.2.3 FWA as cost-effective last-mile alternative to fibre
- 4.2.4 Enterprise SD-WAN back-up connectivity demand
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Spectrum scarcity and regulatory uncertainty
- 4.3.2 High mmWave densification CAPEX
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.6.1 Key enablers for FWA adoption
- 4.6.2 Vendor initiatives and partnerships
- 4.6.3 Business considerations and prerequisites
- 4.6.4 FWA vs FTTH / FTTdp comparison
- 4.6.5 Rural, semi-urban and urban use-case models
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.1.1 Consumer Premise Equipment (CPE)
- 5.1.1.2 Access Units (Femto and Picocells)
- 5.1.2 Services
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Residential
- 5.2.2 Commercial
- 5.2.3 Industrial
- 5.3 By Frequency Band
- 5.3.1 Sub-6 GHz
- 5.3.2 mmWave ( above 24 GHz)
- 5.4 By Deployment Mode
- 5.4.1 Indoor CPE
- 5.4.2 Outdoor CPE
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Nokia Corporation
- 6.4.3 Ericsson AB
- 6.4.4 Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.5 Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Verizon Communications Inc.
- 6.4.7 ATandT Inc.
- 6.4.8 T-Mobile US Inc.
- 6.4.9 US Cellular Corp.
- 6.4.10 Airspan Networks Inc.
- 6.4.11 Siklu Communication Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Starry Group Holdings Inc.
- 6.4.13 Arqiva Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Inseego Corp.
- 6.4.15 ZTE Corporation
- 6.4.16 Deutsche Telekom AG
- 6.4.17 Vodafone Group Plc
- 6.4.18 Telstra Corp. Ltd.
- 6.4.19 Orange S.A.
- 6.4.20 Globe Telecom Inc.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment











