 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1684102
德国肥料:市场占有率分析、行业趋势和统计、成长预测(2025-2030 年)Germany Fertilizer - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
价格
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
简介目录
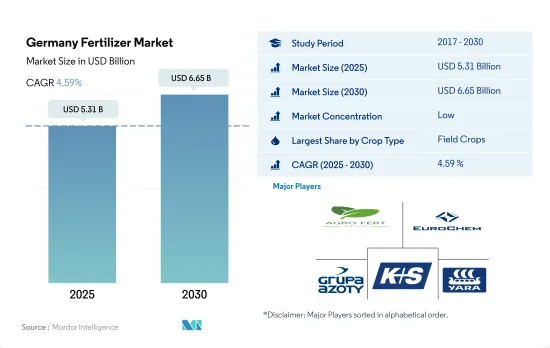
预计 2025 年德国肥料市场规模将达到 53.1 亿美元,到 2030 年预计将达到 66.5 亿美元,预测期内(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 4.59%。
集约化农业实践增加了肥料消耗
- 德国是欧洲第四大农业国,农业覆盖全国57%以上的土地面积。全国有近 276,000 个小农场,平均每个农场占地 61 公顷。由于土壤类型多种多样,农民会调整肥料的使用来解决营养缺陷并优化作物的生长和品质。
- 近年来,德国的化肥使用量大幅增加。 2022 年的化肥使用量预计与前一年同期比较增加 2.9%,这在很大程度上是由于该国的气候条件。农民遭受干旱和热浪的侵袭,严重依赖化肥和农作物保护产品来确保粮食安全。
- 2022年,田间作物占化肥消费的大部分,为56.4%。这主要是因为需要解决耕作面积扩大、密集耕作方法和连续耕作造成的营养缺乏问题。小麦、大麦、油菜籽和大豆是主要作物。德国透过扩大种植面积专注于国内豆科植物作物,预计将引领田间作物市场,预计 2023 年至 2030 年的复合年增长率为 3.7%。
- 草坪和观赏作物部分占据德国第二大市场占有率,到 2022 年将达到 35.9%。这些作物在多种用途上需求量大。同时,农民越来越依赖作物营养来确保作物的生长和品质。预计这种不断增长的需求将在未来几年推动市场发展。
德国肥料市场趋势
干旱和热浪影响田间作物种植
- 2022年,田间作物占德国耕地面积的78.2%。这一优点在于它对确保粮食安全和作为农业部门的重要经济作物具有双重意义。研究期间,田间作物种植面积大幅减少。 2017年,田间作物种植总面积为735万公顷,预计2022年将减少161万公顷,至574万公顷。田间作物种植面积的大幅减少是由于近年来干旱和极端高温的不利影响,导致产量大幅下降。因此,农民选择减少种植面积以应对恶劣的气候条件。主要种植作物为小麦、油菜籽、玉米和大豆。
- 小麦是该地区主导最广泛的作物,也是第二大产粮作物。 2022年,小麦种植面积占全国耕地面积的49.8%。这一优势主要归因于国内和国际市场对小麦的需求不断增长。小麦种植面积与2017年相比大幅下降约7%,2022年为298万公顷,主要原因是受天气干燥炎热影响,夏小麦收穫面积减少45%,冬小麦收穫面积减少1.4%。
- 2022 年豆类作物种植面积增加了 46.3%,主要原因是依赖国内生产。
氮是田间作物消耗的主要营养元素。
- 2022年,德国田间作物平均养分施用量为每公顷177.2公斤。其中,玉米、水稻、小麦、高粱、大豆、油菜籽和棉花等都是需要高营养水平来支持其生长的主要田间作物。集约化耕作方式和持续种植小麦等主要作物造成的营养缺乏需要增加营养施用。在这种情况下,需要更多的营养投入来维持土壤肥力。
- 在所有主要营养物质中,氮是田间作物消耗的主要营养物质。平均氮肥施用量为每公顷274.7公斤。由于pH值过高、土壤沙质以及反覆干旱导致的持续干燥条件,该国的土壤面临氮缺乏的问题。这些因素综合起来导致该国农业对氮营养的需求增加。钾肥是第二大消费量的主要养分,平均施用量为每公顷 142.9 公斤,而磷消费量为 114.1 公斤。
- 该国是该地区主要的油菜籽生产国之一。油菜平均养分施用量最高,达每公顷290.5公斤。油菜籽对氮的依赖性很强。重要营养元素氮的平均施用量为每公顷393.7公斤。此作物的养分利用效率低,因此高度依赖氮肥来增加蛋白质含量。
德国肥料产业概况
德国肥料市场较为分散,前五大公司的市占率为32.74%。该市场的主要企业是:AGROFERT、EuroChem Group、Grupa Azoty SA (Compo Expert)、K+S Aktiengesellschaft 和 Yara International ASA(按字母顺序排列)。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月的分析师支持
目录
第 1 章执行摘要和主要发现
第二章 报告要约
第 3 章 简介
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 研究范围
- 调查方法
第四章 产业主要趋势
- 主要作物种植面积
- 田间作物
- 园艺作物
- 平均养分施用量
- 微量营养素
- 田间作物
- 园艺作物
- 主要营养物质
- 田间作物
- 园艺作物
- 次要营养素
- 田间作物
- 园艺作物
- 微量营养素
- 灌溉农田
- 法律规范
- 价值链与通路分析
第五章 市场区隔
- 类型
- 复合型
- 直的
- 微量营养素
- 硼
- 铜
- 铁
- 锰
- 钼
- 锌
- 其他的
- 氮
- 尿素
- 其他的
- 磷酸
- DAP
- MAP
- SSP
- TSP
- 钾
- MoP
- SoP
- 次要营养物质
- 钙
- 镁
- 硫
- 形式
- 传统的
- 特别的
- CRF
- 液体肥料
- SRF
- 水溶性
- 施肥方法
- 受精
- 叶面喷布
- 土壤
- 作物类型
- 田间作物
- 园艺作物
- 草坪和观赏植物
第六章 竞争格局
- 主要策略趋势
- 市场占有率分析
- 业务状况
- 公司简介
- AGLUKON Spezialduenger GmbH & Co.
- AGROFERT
- EuroChem Group
- Grupa Azoty SA(Compo Expert)
- ICL Group Ltd
- K+S Aktiengesellschaft
- Nouryon
- PhosAgro Group of Companies
- Sociedad Quimica y Minera de Chile SA
- Yara International ASA
第七章:执行长的关键策略问题
第 8 章 附录
- 世界概况
- 概述
- 五力分析框架
- 全球价值链分析
- 市场动态(DRO)
- 资讯来源和进一步阅读
- 图片列表
- 关键见解
- 资料包
- 词彙表
简介目录
Product Code: 50002250
The Germany Fertilizer Market size is estimated at 5.31 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 6.65 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 4.59% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Intensive agricultural practices are increasing fertilizer consumption
- Germany ranks as the fourth largest agricultural nation in the European region, with agriculture occupying over 57% of its land. The country boasts nearly 276,000 small farms, averaging 61 hectares each. Given the diverse soil types, farmers tailor their fertilizer usage to address nutrient deficiencies and optimize crop growth and quality.
- In recent years, Germany has seen a notable surge in fertilizer utilization. In 2022, fertilizer usage rose by 2.9% compared to the previous year, largely influenced by the country's climatic conditions. Farmers struggled with droughts and heatwaves and relied heavily on fertilizers and crop protection products to safeguard food security.
- In 2022, field crops dominated fertilizer consumption, accounting for 56.4%. This is primarily due to their expansive cultivation areas, intensive agricultural practices, and the need to address nutrient deficiencies resulting from continuous cultivation. Wheat, barley, rapeseed, and soybean take the lead as major crops. Germany's emphasis on domestic legume production, achieved through expanding cultivation areas, is set to drive the field crops market with a projected CAGR of 3.7% from 2023 to 2030.
- The turf and ornamental crop segment claims the second-largest market share in Germany, standing at 35.9% in 2022. These crops are witnessing heightened demand across various applications. Farmers, in response, are increasingly relying on crop nutrition to ensure robust growth and quality. This rising demand is poised to propel the market in the coming years.
Germany Fertilizer Market Trends
Droughts and heat waves impacted the cultivation of field crops
- In 2022, field crops dominated Germany's cultivation area, accounting for 78.2%. This prominence can be attributed to their dual significance in guaranteeing food security and serving as economically vital crops for the agricultural sector. A substantial decline in the cultivation area of field crops was observed during the study period. In 2017, the total cultivation area dedicated to field crops accounted for 7.35 million hectares, but by 2022, it had reduced by 1.61 million hectares and reached 5.74 million hectares. This noteworthy reduction in the country's field crop acreage can be attributed to the adverse impacts of recent droughts and persistent heat waves, which led to significant yield losses. Consequently, farmers opted to reduce their cultivation areas in response to these challenging climatic conditions. Wheat, rapeseed, corn, and soybean are major cultivating crops.
- Wheat takes the lead as the most extensively cultivated crop and is the region's second-largest producer. In 2022, the wheat cultivation area comprised a substantial 49.8% of the total cultivated land. This predominance can be majorly attributed to the escalating demand for wheat both within the domestic market and on the international market. The wheat cultivation area reduced drastically by approximately 7% compared to the year 2017. In 2022, it accounted for 2.98 million hectares, which is majorly due to a reduction in summer wheat harvesting area, down by 45%, and winter wheat harvesting area by 1.4%, due to dry and hot climatic conditions.
- The legume crop cultivation area increased in 2022 by 46.3%, which was majorly due to the country's dependence on domestic production.
Nitrogen is the main primary nutrient consumed by the field crops
- In the year 2022, the average nutrient application rate of field crops stood at 177.2 kg per hectare in Germany. Notably, corn, rice, wheat, sorghum, soybean, rapeseed, and cotton represent the primary field crops cultivated, and they demand higher nutrient levels to support their growth. The nutrient deficiency arising from intensive agricultural practices and the continuous cultivation of major crops, such as wheat, necessitates an increased application of nutrients. This situation calls for higher nutrient input to maintain soil fertility.
- Nitrogen stands out as the predominant nutrient consumed by field crops among all the primary nutrients. The average nutrient application rate for nitrogen is a substantial 274.7 kg per hectare. The country's soils experience nitrogen deficiency due to its high pH levels, sandy soil composition, and persistent dry conditions resulting from recurrent droughts. These factors collectively drive an increased demand for nitrogen nutrients in the country's agricultural practices. Potash is the second most consumed primary nutrient, with an average nutrient application rate of 142.9 kg per hectare, and phosphorus consumption accounts for 114.1 kg per hectare.
- The country holds a prominent position as a leading producer of oil rapeseed within the region. The rapeseed crop exhibits the highest average nutrient application rate, reaching 290.5 kilograms per hectare. The oil rapeseed crop relies heavily on nitrogen. It is notable that the average nutrient application rate for this crucial nutrient stands at 393.7 kilograms per hectare. This crop heavily depends on nitrogen fertilization due to its lower nutrient use efficiency, and while this enhances protein content.
Germany Fertilizer Industry Overview
The Germany Fertilizer Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 32.74%. The major players in this market are AGROFERT, EuroChem Group, Grupa Azoty S.A. (Compo Expert), K+S Aktiengesellschaft and Yara International ASA (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Acreage Of Major Crop Types
- 4.1.1 Field Crops
- 4.1.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2 Average Nutrient Application Rates
- 4.2.1 Micronutrients
- 4.2.1.1 Field Crops
- 4.2.1.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2.2 Primary Nutrients
- 4.2.2.1 Field Crops
- 4.2.2.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2.3 Secondary Macronutrients
- 4.2.3.1 Field Crops
- 4.2.3.2 Horticultural Crops
- 4.2.1 Micronutrients
- 4.3 Agricultural Land Equipped For Irrigation
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD and Volume, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Type
- 5.1.1 Complex
- 5.1.2 Straight
- 5.1.2.1 Micronutrients
- 5.1.2.1.1 Boron
- 5.1.2.1.2 Copper
- 5.1.2.1.3 Iron
- 5.1.2.1.4 Manganese
- 5.1.2.1.5 Molybdenum
- 5.1.2.1.6 Zinc
- 5.1.2.1.7 Others
- 5.1.2.2 Nitrogenous
- 5.1.2.2.1 Urea
- 5.1.2.2.2 Others
- 5.1.2.3 Phosphatic
- 5.1.2.3.1 DAP
- 5.1.2.3.2 MAP
- 5.1.2.3.3 SSP
- 5.1.2.3.4 TSP
- 5.1.2.4 Potassic
- 5.1.2.4.1 MoP
- 5.1.2.4.2 SoP
- 5.1.2.5 Secondary Macronutrients
- 5.1.2.5.1 Calcium
- 5.1.2.5.2 Magnesium
- 5.1.2.5.3 Sulfur
- 5.2 Form
- 5.2.1 Conventional
- 5.2.2 Speciality
- 5.2.2.1 CRF
- 5.2.2.2 Liquid Fertilizer
- 5.2.2.3 SRF
- 5.2.2.4 Water Soluble
- 5.3 Application Mode
- 5.3.1 Fertigation
- 5.3.2 Foliar
- 5.3.3 Soil
- 5.4 Crop Type
- 5.4.1 Field Crops
- 5.4.2 Horticultural Crops
- 5.4.3 Turf & Ornamental
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 AGLUKON Spezialduenger GmbH & Co.
- 6.4.2 AGROFERT
- 6.4.3 EuroChem Group
- 6.4.4 Grupa Azoty S.A. (Compo Expert)
- 6.4.5 ICL Group Ltd
- 6.4.6 K+S Aktiengesellschaft
- 6.4.7 Nouryon
- 6.4.8 PhosAgro Group of Companies
- 6.4.9 Sociedad Quimica y Minera de Chile SA
- 6.4.10 Yara International ASA
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR FERTILIZER CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219








