 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1686603
农业薄膜-市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2025-2030)Agriculture Films - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
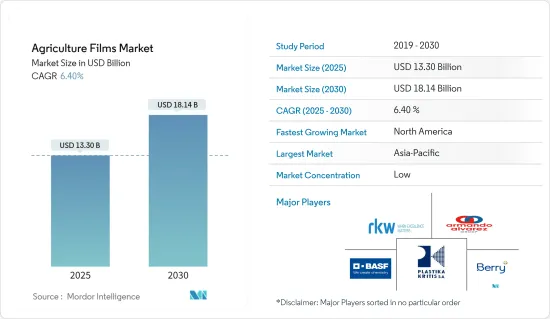
预计 2025 年农用薄膜市场规模为 133 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 181.4 亿美元,预测期内(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 6.4%。
农用薄膜是农业中广泛使用的材料,用于土壤保护、温室栽培和覆盖等目的。这些薄膜具有许多好处,包括减少土壤侵蚀和压实、调节温度、保留养分、提高种子发芽率、抑制杂草和防紫外线。农业薄膜市场受到多种因素的推动,例如越来越多地采用保护性耕作方法、注重提高作物产量、广泛使用地膜以及对生物分解性产品的需求不断增长。由于人口成长和可耕地面积减少,人们对全球粮食安全的担忧进一步推动了对农业薄膜的需求,因为农业薄膜是提高农业生产力的一种手段。
农膜的主要用途是覆盖,在世界各地的农业中,用薄膜覆盖土壤正变得越来越普遍。由于环保问题,消费者对生物分解性薄膜的偏好增加,也是这个市场成熟的一个主要驱动力。地膜广泛应用于玉米和大豆种植。大学和研究人员正在积极研究如何加强地膜在农业中的应用,并专注于寻找更永续的解决方案。 2024年,利哈伊大学的研究人员开发出一种生物分解性的地膜,可以为作物提供养分,为传统塑胶薄膜提供环保替代品。此外,美国农业部 (USDA) 及其国家食品和农业研究所还为题为“合作伙伴关係:设计营养增强覆盖膜以改善退化和土壤健康”的计划提供了 744,000 美元的研究津贴。这项多年期研究将于 2024 年 7 月至 2028 年 6 月进行,由麻萨诸塞大学洛威尔分校、美国农业部亚利桑那州马里科帕农业研究服务处和以色列本古里安大学的专家共同进行合作研究。
农业薄膜广泛应用于各种农业实践,例如温室和动物饲料包装,以保护作物免受低温影响。加拿大冬季漫长,气温较低,不利于农作物生长。因此,越来越多地使用温室等保护性栽培方法来减少进口依赖,从而推动了对温室薄膜的需求。加拿大的温室种植面积几年来一直在扩大。据加拿大农业部称,2023 年,加拿大共有 920 个商业温室蔬菜经营场所,生产蔬菜 802,163 吨。与2022年相比,产量增加了7%。 2023年,安大略省继续成为温室蔬菜市场的领导者,占加拿大总产量的72%。其次是不列颠哥伦比亚省(14%)和魁北克省(8%)。其余各州总合占总产量的 6%。温室产业的成长推动了市场对温室薄膜的需求。
对环境问题的关注正在推动对生物分解性农用薄膜的需求不断增加。这些环保替代品有助于抑制杂草、调节温度、维持土壤中的养分和水分,并提高植物的稳定性。世界各国政府都在推广永续农业和环境友善农业实践,预计这将在未来几年支持市场成长。
农用薄膜市场趋势
温室应用占市场主导地位
温室薄膜越来越受到种植者的欢迎,因为它们可以在任何季节提高作物的产量。与传统农业方法相比,温室的生产能力更高,再加上人口成长和气候变迁带来的粮食需求增加,预计将推动该产业的成长。温室环境为作物种植提供了可控的环境,有可能增强植物遗传并促进更健康品种的生长。温室中使用的聚碳酸酯基透明塑胶薄膜比玻璃结构具有更好的温度调节和隔热性能。这些因素加上温室薄膜的成本效益,预计将推动该领域的需求。
世界人口的成长和对粮食安全的日益关注推动了保护性农业的采用。这种方法延长了作物的生长季节并提高了产量,从而增加了对农业塑胶的需求。这些材料对于确保并显着提高每公顷产量以及改善作物品质至关重要。农用薄膜有助于降低因天气、害虫和杂草而导致的作物腐败风险,提高作物整个生命週期的质量,尤其是在温室中。聚乙烯是农用薄膜中常用的一种材料,可以保护温室和隧道中的作物并提高产量。
此外,一些国家,特别是海湾合作委员会地区的国家,正在扩大温室生产以提高自给自足能力。该地区已经开发了许多温室设施,从而提高了产量。例如,根据农业部预测,2023年卡达温室生产面积将达666.4公顷,产量将达67,263.6吨。同样,根据俄罗斯联邦农业部预测,2023年俄罗斯温室蔬菜产量将达到创纪录的158万吨,温室面积将达3,280公顷。主要作物有番茄、小黄瓜、茄子、辣椒、绿叶蔬菜、生菜等。水果和蔬菜温室产量的增加推动了该领域的投资,从而增加了对农业薄膜的需求。
製造商加入各种添加剂来提高农用薄膜的性能和使用寿命。这些添加剂包括抗农药剂、紫外线(UV)吸收剂和防雾化合物,可提高温室薄膜的耐久性和功效。预计在预测期内,利用奈米技术和超高温材料等技术开发的先进农业薄膜将推动温室应用中对这些产品的需求。
亚太地区是最大的市场
亚太地区占全球温室蔬菜种植面积的近一半。推动该地区农用薄膜市场发展的关键因素包括大规模温室蔬菜种植、对高价值出口型水果和蔬菜生产的日益关注以及蓬勃发展的农业产业。不断增强的环保意识推动了消费者对生物分解性薄膜的偏好,进一步刺激了市场成长。随着人均耕地面积不断减少,提高生产力至关重要。根据联合国粮食及农业组织(FAO)统计年鑑《2023年世界粮食及农业》预测,2023年越南人均可用耕地面积约0.3公顷,为全球最低。这反映了该国人口密度高和土地资源有限。透过温室种植可以满足对产量作物的需求,解决农业用地短缺问题,同时又不影响产量,从而有可能增加农用薄膜在该领域的使用。
覆盖仍然是印度农业中广泛采用的传统做法。然而,非政府组织 Toxic Links 和马尼帕尔高等教育学院 2022 年的一项研究表明,印度农地存在严重的微塑胶污染问题。这问题的根源在于大量使用地膜来保护作物。这些用作田地和温室覆盖物的薄膜会分解并释放出直径小于 5 毫米的塑胶颗粒。这些微塑胶可以渗透到土壤深处,影响作物,最终影响人类健康。预计这些担忧将推动印度采用生物分解性和可堆肥的薄膜。
青贮饲料生产作为传统饲料的经济替代品在亚洲各国越来越受欢迎。地方政府积极推广青贮饲料生产,为牛提供优质饲料,提升畜牧业生产效率。例如,2021年,富安省经济厅与越南国家种子股份公司合作,在该省实施玉米青贮饲料生产和消费合作模式。这些措施预计将促进该地区青贮饲料的生产,从而推动该领域对农业薄膜的需求。此外,新加坡南洋理工大学 2020 年的一项研究发现,聚己内酯、聚乙烯、聚乙烯醇和丙烯酸酯基聚合物等合成聚合物可用作覆盖物,覆盖土壤并防止水分流失。该领域活性化的研究和开发活动进一步促进了农业薄膜市场的成长。
此外,亚太地区,尤其是澳洲的农民越来越多地采用保护性农业实践来提高作物的产量和品质。 2022年,合作研究中心进行了题为「智慧玻璃薄膜对温室生菜能源使用和生产力的影响」的计划。本研究评估了节能智慧玻璃和光变 LLEAF 薄膜在温室生菜生产中的表现。西悉尼大学 (WSU) 的作物科学家与 Hort Innovation 合作开展该计划,并得到行业合作伙伴 LLEAF Pty Ltd 和 Rijk Zwaan 的支持。预计此类有关农用薄膜的研究将对市场产生正面影响。
农膜业概况
农用薄膜市场较为分散,只有少数几家主要企业和几家规模较小的区域性企业。 Berry Global Inc.、 BASF SE、Armando Alvarez Group、RKW Group、Plastika Kritis SA 等是该市场的主要企业。主要产业参与者正在大力投资研发,以将生物分解性且保质期长的产品商业化。主要企业正在与生物技术公司合作,以确保未来永续的产品创新。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 研究范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场动态
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 温室种植农产品收穫面积增加
- 扩大地膜在农业的应用
- 主要企业技术创新
- 市场限制
- 初期投资高
- 塑胶对环境的有害影响
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买家的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争强度
第五章市场区隔
- 类型
- 低密度聚乙烯
- 线型低密度聚乙烯
- 高密度聚苯乙烯
- 乙烯醋酸乙烯酯 (EVA)/乙烯丁基丙烯酸酯 (EBA)
- 翻新产品
- 其他类型(聚丙烯农膜、聚酰胺农膜、乙烯 - 乙烯醇共聚物树脂、聚氯乙烯)
- 应用
- 温室
- 青贮饲料
- 覆盖
- 地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地区
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 西班牙
- 义大利
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲国家
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 澳洲
- 日本
- 其他亚太地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他非洲国家
- 北美洲
第六章竞争格局
- 最受欢迎的策略
- 市场占有率分析
- 公司简介
- AB Rani Plast Oy
- BASF SE
- Berry Global Inc.
- Plastika Kritis SA
- Novamont SpA
- ExxonMobil Chemical
- Armando Alvarez Group
- Group Barbier
- RKW Group
- INDVECO Group
第七章 市场机会与未来趋势
The Agriculture Films Market size is estimated at USD 13.30 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 18.14 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.4% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Agricultural films are materials used extensively in farming for soil protection, greenhouse cultivation, and mulching. These films provide numerous benefits, including reduced soil erosion and compaction, temperature regulation, nutrient retention, improved seed germination, weed suppression, and protection against UV radiation. The agricultural film market is driven by several factors, including the increasing adoption of protected cultivation practices, a focus on enhancing crop yields, the widespread use of mulching films, and the growing demand for biodegradable options. Global food security concerns, stemming from a rising population and declining arable land, are further bolstering the demand for agricultural films as a means to improve agricultural productivity.
Mulching is a key application of agricultural films, with soil mulching using films becoming increasingly common in global agriculture. The growing consumer preference for biodegradable films, driven by environmental concerns, serves as a significant driver for this mature market. Mulch films are widely used in corn and soybean cultivation. Universities and researchers are actively studying ways to enhance the use of mulch films in agriculture, focusing on more sustainable solutions. In 2024, Lehigh University researchers developed biodegradable mulch films that deliver nutrients to crops, offering an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional plastic films. Additionally, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and its National Institute of Food and Agriculture awarded a USD 744,000 research grant for a project titled "PARTNERSHIP: Engineering Nutrient-Enhanced Mulch Film to Improve Degradation and Soil Health." This multi-year initiative, running from July 2024 through June 2028, involves collaboration among experts from the University of Massachusetts Lowell, the USDA Agricultural Research Service in Maricopa, Arizona, and Ben Gurion University in Israel.
Agricultural films are widely used in various farming practices, including greenhouses and fodder packaging, to protect crops from cold temperatures. Canada's predominantly low temperatures due to long winters hinder crop growth, leading to a reliance on imports to meet demand. Consequently, the use of protected cultivation methods like greenhouses is increasing to reduce import dependency, driving the demand for greenhouse films. The area under greenhouse cultivation in Canada has been expanding for several years. According to the Ministry of Canada, in 2023, Canada had 920 commercial greenhouse vegetable operations, producing 802,163 metric tons of vegetables. This represented a 7% increase in production compared to 2022. Ontario remained the leader in the greenhouse vegetable market in 2023, accounting for 72% of Canada's total production. British Columbia followed with 14%, and Quebec with 8%. The remaining provinces collectively contributed 6% to the total production. This growth in the greenhouse industry is fueling the demand for greenhouse films in the market.
Environmental concerns are driving increased demand for biodegradable agricultural films. These eco-friendly alternatives help suppress weeds, regulate temperature, preserve soil nutrients and moisture, and enhance plant stability. Governments worldwide are promoting sustainable agriculture and eco-friendly farming practices, which is projected to support market growth in the coming years.
Agriculture Films Market Trends
Greenhouse Applications Dominate the Market
Greenhouse films are gaining popularity among growers due to their ability to increase crop yields across all seasons. The higher production capacity of greenhouses compared to traditional farming methods, coupled with the rising food demand from population growth and climate change challenges, is expected to drive the growth of this segment. Greenhouse environments provide a controlled setting for crop cultivation, potentially enhancing plant genetics and promoting the growth of healthier varieties. Polycarbonate-based clear plastic films used in greenhouses offer superior temperature regulation and insulation compared to glass structures. These factors, combined with the cost-effectiveness of greenhouse films, are likely to fuel demand in this segment.
The growing global population and increasing food security concerns are driving the adoption of protected agriculture. This method extends crop growing seasons and increases yields, consequently boosting the demand for agricultural plastics. These materials are crucial for securing and significantly increasing output per hectare while enhancing crop quality. Agricultural films help reduce crop spoilage risks associated with weather, pests, and weeds, improving overall crop quality throughout the lifecycle, particularly in greenhouses. Polyethylene is a commonly used material for agricultural films, protecting crops and improving yields in greenhouses and tunnels.
In addition, several countries have expanded greenhouse production to enhance self-sufficiency, particularly in the GCC region. This area has seen the development of numerous greenhouse facilities, leading to increased production. For example, according to the Department of Agriculture, Qatar's greenhouse production in 2023 covered 666.4 hectares and yielded 67,263.6 metric tons. Similarly, the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation reported that greenhouse vegetable production in Russia reached a record 1.58 million tons in 2023, across 3.28 thousand hectares of greenhouse space. The primary crops included tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplants, bell peppers, greens, and lettuce. This growth in fruit and vegetable production through greenhouses is driving investments in the sector, consequently increasing the demand for agricultural films.
Manufacturers are incorporating various additives into agricultural films to enhance their performance and longevity. These additives include agrochemical resistance agents, ultraviolet (UV) absorbers, and anti-fogging compounds, which improve the durability and efficacy of greenhouse films. The development of advanced agricultural films using technologies such as nanotechnology and ultra-thermic materials is expected to drive demand for these products in greenhouse applications during the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific is the Largest Market
The Asia-Pacific region accounts for nearly half of the global greenhouse vegetable cultivation area. Key factors driving the agricultural film market in the region include extensive greenhouse vegetable cultivation, growing emphasis on high-value and export-oriented fruit and vegetable production, and a thriving agriculture industry. Rising environmental awareness has led consumers to prefer biodegradable films, further stimulating market growth. Increasing productivity has become crucial due to the continuous decline in per capita farmland availability. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization's (FAO) Statistical Yearbook World Food and Agriculture 2023, Vietnam's per capita agricultural land availability in 2023 was approximately 0.3 hectares per person, one of the world's lowest rates. This reflects the country's high population density and limited land resources. The need for high-yielding crops to address farmland scarcity without compromising production volumes may be met through greenhouse farming, potentially increasing the use of agricultural films in this sector.
Mulching remains a traditional and widely used method in Indian agriculture. However, a 2022 research study by NGO Toxic Links and Manipal Academy of Higher Education revealed a significant microplastic contamination problem in India's agricultural fields. This issue stems from the extensive use of mulch films for crop protection. These films, used in fields or as greenhouse covers, degrade and release plastic particles smaller than 5 millimeters in diameter. These microplastics can penetrate deep into the soil, potentially affecting crops and, subsequently, human health. These concerns are projected to drive the adoption of biodegradable and compostable films in India.
Silage production is gaining traction in various Asian countries as an economical alternative to traditional forage. Local authorities are actively promoting silage production to provide high-quality forage for cattle and enhance livestock production. For instance, in 2021, the Economic Office of Pho Yen collaborated with the Vietnam National Seed Joint Stock Company to implement a corn silage production and consumption linkage model in the province. These initiatives are boosting silage production in the region, which is anticipated to drive the demand for agricultural films in this segment. Additionally, a 2020 study by Nanyang Technological University in Singapore found that synthetic polymers such as polycaprolactone, polyethylene, polyvinyl alcohol, and acrylate-based polymers can be used as mulch to cover soil and prevent moisture loss. The increasing research and development activities in this area are further contributing to the growth of the agricultural film market.
Moreover, Farmers in Asia-Pacific, especially in Australia, are increasingly adopting protected agricultural practices to improve crop productivity and quality. In 2022, the Cooperative Research Centre conducted a project titled 'Smart Glass film impacts on energy use and Productivity in greenhouse lettuce'. This study evaluated the performance of energy-saving smart glass and light-shifting LLEAF film in greenhouse lettuce production. Crop scientists at Western Sydney University (WSU) collaborated with Hort Innovation on this project, supported by industry partners LLEAF Pty Ltd and Rijk Zwaan. Such research studies on agriculture films are anticipated to positively impact the market.
Agriculture Films Industry Overview
The agricultural films market is fragmented due to the presence of a few prominent players and several small-scale and regional players. Berry Global Inc., BASF SE, Armando Alvarez Group, RKW Group, and Plastika Kritis SA are some of the major players in the market. Major industry participants have been investing heavily in R&D for commercializing biodegradable and longer shelf-life products. The key companies are partnering with biotechnology firms to ensure sustainable product innovation in the future.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Harvested Area of Greenhouse Produce
- 4.2.2 Growing Use of Mulch Films in Agriculture
- 4.2.3 Innovations by Major Players
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Initial Investment
- 4.3.2 Adverse Effects of Plastics on Environment
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Type
- 5.1.1 Low-Density Polyethylene
- 5.1.2 Linear Low-Density Polyethylene
- 5.1.3 High-Density Polyethylene
- 5.1.4 Ethyl Vinyl Acetate (EVA)/Ethylene Butyl Acrylate (EBA)
- 5.1.5 Reclaims
- 5.1.6 Other Types (Polypropylene Agricultural Films, Polyamide Agricultural Films, Ethylene Vinyl-Alcohol Copolymer Resins, and PVC)
- 5.2 Application
- 5.2.1 Greenhouse
- 5.2.2 Silage
- 5.2.3 Mulching
- 5.3 Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Mexico
- 5.3.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.2.1 Germany
- 5.3.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.2.3 France
- 5.3.2.4 Spain
- 5.3.2.5 Italy
- 5.3.2.6 Russia
- 5.3.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.3.1 China
- 5.3.3.2 India
- 5.3.3.3 Australia
- 5.3.3.4 Japan
- 5.3.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Africa
- 5.3.5.1 South Africa
- 5.3.5.2 Egypt
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Most Adopted Strategies
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 AB Rani Plast Oy
- 6.3.2 BASF SE
- 6.3.3 Berry Global Inc.
- 6.3.4 Plastika Kritis SA
- 6.3.5 Novamont SpA
- 6.3.6 ExxonMobil Chemical
- 6.3.7 Armando Alvarez Group
- 6.3.8 Group Barbier
- 6.3.9 RKW Group
- 6.3.10 INDVECO Group










