 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1687454
全球导航卫星系统晶片:市场占有率分析、行业趋势和统计数据、成长预测(2025-2030 年)Global Navigation Satellite System Chip - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
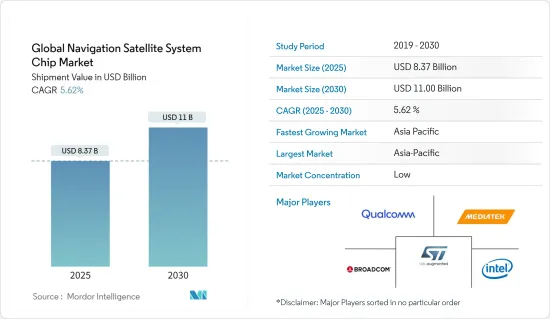
根据出出货收益,全球导航卫星系统晶片市场预计将从 2025 年的 83.7 亿美元成长到 2030 年的 110 亿美元,预测期间(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 5.62%。
2020年初,新冠疫情爆发,严重扰乱了半导体供应链和生产,对一些晶片製造商而言,影响更为严重。由于人手不足,亚太地区许多封装测试工厂已经缩减甚至停止运作。这也为依赖半导体的最终产品公司带来了瓶颈。
全球导航卫星系统 (GNSS) 基本上是指从太空提供讯号并向 GNSS接收器传输定位和资料计时的卫星卫星群。接收器使用这些资料,结合多个感测器,来确定位置、速度和高度等各种因素。
这种晶片的精度和准确度主要取决于其可见范围内卫星的可用性。因此,一些国家渴望部署区域卫星群,以实现更好的导航和测绘。然而,只有中国、俄罗斯、美国、印度和日本五个国家以及欧盟部署了 GNSS 系统。
GNSS 使用者期望近乎即时的定位共用速度。标准定位通常无法做到这一点,因为它需要识别和接收至少四颗卫星的完整资料。不利的讯号条件和恶劣的环境可能意味着资料传输或接收可能需要几分钟、几小时,甚至失败。然而,将 GNSS接收器资料与行动网路单元的资讯结合可以提高效能,使物联网产业的许多应用受益。
2021 年 1 月,U-Blox 宣布推出 ALEX-R5 模组,将低功耗广域 (LPWA) 蜂窝通讯和 GNSS 技术整合到一个系统级封装中。两个关键要素是该公司具有安全云端功能的 UBX-R5 LTE-M/NB-IoT 晶片组和 U-Blox M8 GNSS 晶片,可为医疗保健应用提供足够的定位精度。
配备导航和定位功能的消费性电子设备数量不断增加,预计将大幅推动对低功耗 GNSS 晶片的需求。目前,对技术先进的可穿戴设备的需求日益增长。目前,全球近 50% 的人口使用健身带和智慧型手錶等技术先进的可穿戴设备。 GNSS 晶片主要内建在这些设备中,因为它们为使用者在跑步、行走或驾驶时提供准确的位置信息,使他们能够与亲人保持联繫。
2020年8月,SONY发布了用于物联网和穿戴式装置的高精度GNSS接收器LSI。新型 LSI 支援传统 L1 频段和 L5 频段的接收,目前正在 GNSS卫星群中扩展,使其适合双频定位。
全球GNSS晶片市场趋势
智慧型手机预计将占据很大市场占有率
儘管欧盟28国、北美和中国等成熟市场已经相当饱和,但智慧型手机的出货量仍超过使用 GNSS 晶片的设备数量。智慧型手机已经使用 GNSS 晶片很长一段时间了。大多数情况下,这些晶片支援所有公开可用的卫星网络,包括 GPS、GLONASS 和 Galileo。然而,与专用导航设备相比,这些解决方案的准确性较低。
此外,智慧型手机硬体市场的一定程度的垄断限制了GNSS晶片的范围。大多数情况下,高通硬体没有博通 GNNS 晶片,反之亦然。但近年来,这种情况正在改变。
欧盟委员会已核准法规,要求新上市的智慧型手机必须包含卫星和 Wi-Fi定位服务。根据该规定,具有全球导航卫星系统 (GNSS) 功能的晶片组可能可以存取伽利略,这是欧盟提供精确位置和时间资讯的卫星系统。八个欧盟国家遵守该规定并使用符合伽利略标准的晶片组。
根据欧洲GNSS机构统计,目前卫星导航晶片市场超过95%的企业在其新产品中支援伽利略系统,其中包括博通、高通、联发科等多家智慧型手机晶片厂商。随着主要 GNSS 晶片组供应商生产支援伽利略的晶片组,并且全球智慧型手机品牌已将这些晶片组纳入其最新的智慧型手机型号,预计市场在预测期内将进一步机会。
此外,新一代安卓智慧型手机配备了高性能全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)晶片,能够追踪双频多卫星群资料。从 Android 9 版本开始,使用者可以停用占空比省电选项,从而获得更高品质的伪距和载波相位原始资料。此外,应用PPP(精密单点定位)演算法也变得更加有趣。本研究旨在评估小米首款搭载博通BCM47755的双频GNSS智慧型手机的PPP效能。透过比较小米与单频智慧型手机三星S8的效能,可以凸显双频资料取得的优势。小米的垂直和水平精度分别达到 0.51 米和 6 米,而三星的水平精度达到 5.64 米,垂直精度达到 15 米。
亚太地区预计将占据主要市场占有率
北斗于 2000 年首次发射,由中国国家太空总署 (CNSA) 营运。二十年后,北斗已拥有48颗在轨卫星。北斗卫星发射的讯号包括B1I(1561.098MHz)、B1C(1575.42MHz)、B2a(1175.42MHz)、B2I和B2b(1207.14MHz)、B3I(1268.52MHz)。
中国对全球导航卫星系统 (GNSS) 的做法与欧洲不同。虽然欧洲有 11 个广受认可的 GNSS 技术集团,涵盖从消费产品到关键基础设施等领域,但中国的情况要复杂得多。主要分为三大类:工业市场、大众消费市场、利基市场。
2021年3月11日,中国发布「十四五」规划。该计划将涉及未来五年发展的各个方面,并规划中国2035年的愿景。 「十四五」规划持续重视研发和技术创新,这对中国GNSS产业产生了深远的影响。 「深化北斗系统推广应用,推动产业高品质发展」被提出为国家重大战略计划和规划政策指南。该战略可望推动全球导航卫星系统产业研发,促进北斗产业应用,加速核心技术关键突破。
此外,据韩国太空技术委员会称,韩国希望在2021年之前进行地面测试,在2022年之前掌握基础卫星导航技术,在2024年之前实现卫星实际製造。这两颗卫星将被送入朝鲜半岛上空的地球静止轨道,使KPS成为一个拥有七颗卫星星系。
2021 年 2 月,科学与通讯部累计为太空活动拨款 6,150 亿韩元(5.531 亿美元),以提高卫星、火箭和其他关键设备的製造能力。
导航卫星系统晶片(GNSS)产业概况
GNSS 晶片市场由多家公司组成。从市场占有率来看,没有一家公司能够垄断市场。主要公司包括 Qualcomm Technologies Inc.、Mediatek Inc. 和 STMicroelectronics NV。市场参与企业正在考虑建立策略伙伴关係和联盟来增加市场占有率。最近的一些市场发展趋势包括:
- 2021 年 12 月 - 联发科宣布,其用于下一代旗舰智慧型手机的 5G 智慧型手机晶片 Dimensity 9000 已获得 OPPO、Vivo、小米和荣耀等多个智慧型手机品牌的设备製造商的认可和购买。首批搭载天玑 9000 的旗舰智慧型手机预计将于 2022 年第一季上市。该处理器支援最新的 Wi-Fi、蓝牙和 GNSS 标准,为智慧型手机用户提供无缝的通讯体验。
- 2021 年 1 月 - Qualcomm Technologies Inc. 和 Alps Alpine 宣布推出 ViewPose,这是一款基于摄影机的感测和定位设备,支援绝对车道级车辆定位。阿尔卑斯阿尔派正在利用高通技术公司的多种解决方案,包括支援多频 GNSS 的高通骁龙汽车 5G 平台,以及用于处理多摄影机影像和视觉增强精确定位 (VEPP) 软体的骁龙汽车驾驶舱平台。这为电动前侧视镜、高清地图众包、蜂窝车联网 (C-V2X) 的车道级导航以及高级驾驶辅助系统 (ADAS) 和自动驾驶应用的车道级精度提供了经济高效的解决方案。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 研究范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场洞察
- 市场概览
- 产业吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 消费者议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争强度
- 产业价值链分析
- COVID-19疫情对市场的影响评估
第五章市场动态
- 市场驱动因素
- 采用绿色交通解决方案、永续农业和天气监测
- 对准确、即时资料的需求不断增加
- GNSS基础设施的演变,包括新讯号和频率的出现
- 市场挑战
- GNSS 无法提供精确的地下、水下和室内导航
- 功耗复杂度高
第六章 GNSS 关键统计数据
- GNSS接收器出货量(依价格类别)
- 高端接收器出货量(以价格类别)
- GNSS 设备出货量(依轨道子区隔)
- 依最终使用者安装的 GNSS 设备数量
第七章市场区隔
- 设备类型
- 智慧型手机
- 平板电脑和穿戴式装置
- 个人追踪设备
- 低功耗资产追踪器
- 车载系统
- 无人机
- 其他设备类型
- 最终用户产业
- 车
- 家电
- 航空
- 其他最终用户产业
- 地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 欧洲
- 俄罗斯
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 日本
- 韩国
- 拉丁美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 北美洲
第八章竞争格局
- 公司简介
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Mediatek Inc.
- STMicroelectronics NV
- Broadcom Inc.
- Intel Corporation
- U-blox Holdings AG
- Thales Group
- Quectel Wireless Solutions Co. Ltd
- Skyworks Solutions Inc.
- Furuno Electric Co. Ltd
- Hemisphere GNSS
- Trimble Inc.
- Sony Group Corporation
第九章投资分析
第十章:市场的未来
The Global Navigation Satellite System Chip Market size in terms of shipment value is expected to grow from USD 8.37 billion in 2025 to USD 11.00 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.62% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted the supply chain and production of semiconductors in the initial phase of 2020. For multiple chipmakers, the impact was more severe. Due to labor shortages, many packages and testing plants in the Asia-Pacific region reduced or even suspended operations. This also created a bottleneck for end-product companies that depend on semiconductors.
Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) essentially refers to the constellation of satellites that provide signals from space, transmit positioning, and data timing to the GNSS receivers. The receivers then use such data to determine various factors, such as location, speed, and altitude, combined with several sensors.
The precision and accuracy of such chips are primarily dependent on the satellites in the visibility range. As a result, multiple countries are eagerly trying to deploy regional constellations for better navigation and mapping. However, in the market, only five countries (China, Russia, the United States, India, and Japan) and the European Union have their GNSS systems.
GNSS users expect near-instantaneous position sharing speeds. This is often impossible with standard positioning as at least four satellites must be identified, and their complete data should be received. In adverse signal conditions or harsh environments, transmitting and receiving data can take minutes, hours, or even fail. However, the performance can be improved by integrating the GNSS receiver data with information from mobile network cells to benefit numerous applications in the IoT industry.
In January 2021, U-Blox announced its ALEX - R5 module, which integrates low-power wide-area (LPWA) cellular communication and GNSS technology into the system-in-package. The two key elements are the company's UBX - R5 LTE - M/NB-IoT chipset with a secure cloud functionality and the U-Blox M8 GNSS chip for adequate location accuracy for healthcare applications.
The increasing volume of consumer electronics equipped with navigation and positioning features is expected to create a considerable demand for low-power GNSS chips. Technologically advanced wearable devices are in the demand trend currently. At present, almost 50% of the global population has been using tech-advanced wearable devices, such as fitness bands and smartwatches. GNSS chips are majorly being integrated into these devices to give precise locations to the user even while running, walking, or driving, allowing them to stay connected with their close ones.
In August 2020, Sony Corporation announced the release of high-precision GNSS receiver LSIs for IoT and wearable devices. The new LSIs support the conventional L1 band reception and L5 band reception, which are currently being expanded across GNSS constellations, making them suitable for dual-band positioning.
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Chip Market Trends
The Smartphones Segment is Expected to Hold a Significant Market Share
Despite considerable saturation of mature markets, such as EU28, North America, and China, the shipments of smartphones still outnumber devices using GNSS chips. Smartphones have been using GNSS chips for a considerable time. In most cases, these chips support all publicly available satellite networks, such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, etc. However, compared to dedicated navigation devices, these solutions were less accurate.
Additionally, a degree of monopoly in the smartphone hardware market limited the scope for GNSS chip installations. Most of the time, Qualcomm hardware does not include Broadcom GNNS chips and vice versa, as they are prime competitors. However, in recent years, this scenario has been changing.
The European Commission has approved a regulation mandating that new smartphones launched in the market will have to include satellite and Wi-Fi location services. According to the regulation, chipsets enabled with the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) capabilities are likely to have access to the EU's satellite system Galileo, which provides accurate positioning and timing information. Eight EU countries have been following this regulation and are using Galileo-compatible chipsets.
According to the European GNSS Agency, over 95% of the satellite navigation chipset supply market supports Galileo in new products, including various manufacturers of smartphone chipsets like Broadcom, Qualcomm, and Mediatek. With leading GNSS chipset providers producing Galileo-ready chipsets and global smartphone brands already integrating these chipsets in their latest smartphone models, the market is expected to have further growth opportunities during the forecast period.
Further, the new generation of Android smartphones is equipped with high-performance global navigation satellite system (GNSS) chips capable of tracking dual-frequency multi-constellation data. Starting from Android version 9, users can disable the duty cycle power-saving option; thus, better quality pseudo-range and carrier phase raw data are available. Also, the application of the Precise Point Positioning (PPP) algorithm has become more enjoyable. This work aims to assess the PPP performance of the first dual-frequency GNSS smartphone produced by Xiaomi equipped with a Broadcom BCM47755. The advantage of acquiring dual-frequency data is highlighted by comparing the performance obtained by Xiaomi with that of a single-frequency smartphone, the Samsung S8. The vertical and horizontal accuracy achieved by Xiaomi is 0.51 m and 6 m, respectively, while those achieved by Samsung is 5.64 m for 15 m for horizontal and vertical.
Asia-Pacific is Expected to Account for a Significant Market Share
BeiDou, first launched in 2000 and operated by the China National Space Administration, is based in China (CNSA). BeiDou has 48 satellites in orbit after 20 years. B1I (1561.098 MHz), B1C (1575.42 MHz), B2a (1175.42 MHz), B2I and B2b (1207.14 MHz), and B3I are among the signals being transmitted by BeiDou satellites (1268.52 MHz).
China's attitude to GNSS differs from that of Europe. While there are 11 widely acknowledged GNSS-enabled technical groupings in Europe, ranging from consumer products to vital infrastructure, the situation in China is far more complicated. There were three broad sectors - industrial market, mass consumer market, and specific market.
On March 11, 2021, China rolled out its 14th five-year plan. It is a plan that touches on all aspects of development over the next five years and presents China's 2035 vision. The 14th Five-Year Plan's persistent emphasis on R&D and innovation substantially impacts China's GNSS industry. "Deepen the promotion and use of BeiDou systems; Promote the industry's high-quality growth" is advocated as a policy guideline in the plan as an important national strategic project. The strategy is expected to signify a boost in the GNSS industry's research and development, promote BeiDou's industrial application and accelerate significant core technology advancements.
Further, the Korean Committee of Space Technology hopes to build a ground test by 2021, fundamental satellite navigation technology by 2022, and actual satellite manufacturing by 2024, according to the Korean Committee of Space Technology. Three satellites will be put in the geostationary orbit above the Korean Peninsula, making the KPS a seven-satellite constellation.
In February 2021, the Ministry of Science and ICT announced a budget of KRW 615 billion (USD 553.1 million) for space activities to increase the country's capacity to create satellites, rockets, and other critical equipment.
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Chip Industry Overview
The GNSS chip market consists of several players. In terms of market share, none of the players dominate the market. Significant players include Qualcomm Technologies Inc., Mediatek Inc., and STMicroelectronics NV, among others. The market players are considering strategic partnerships and collaborations to expand their market shares. Some of the recent developments in the market are:
- December 2021 - MediaTek announced device maker acceptance and endorsements from some smartphone brands, including OPPO, Vivo, Xiaomi, and Honor, for its Dimensity 9000 5G smartphone chip for next-generation flagship smartphones. The first flagship smartphones powered by the Dimensity 9000 will hit the market in the first quarter of 2022. Since the processor supports the newest Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and GNSS standards, smartphone users can experience seamless communication.
- January 2021 - Qualcomm Technologies Inc. and Alps Alpine Co. Ltd announced a camera-based sensing and positioning device called ViewPose to support absolute lane-level vehicle positioning. Alps Alpine is leveraging multiple solutions from Qualcomm Technologies like the Qualcomm Snapdragon Automotive 5G platform, which supports Multi-Frequency GNSS and a Snapdragon Automotive Cockpit Platform for processing multiple camera images and Vision Enhanced Precise Positioning (VEPP) software. This provides a cost-effective solution to lane-level accuracy for the electric front, rear- and side-view mirrors, high-definition map crowdsourcing, lane-level navigation for cellular vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X), and advanced driving assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving applications.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.2.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.2.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.2.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.3 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Assessment of the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Adoption of Environment-friendly Transport Solutions, Sustainable Agriculture, and Meteorological Monitoring
- 5.1.2 Increasing Demand for Accurate Real-time Data
- 5.1.3 Evolution of GNSS Infrastructure, such as the Appearance of New Signals and Frequencies
- 5.2 Market Challenges
- 5.2.1 Inability of GNSS to Offer Accurate Underground, Underwater, and Indoor Navigation
- 5.2.2 Complexity Regarding High Power Consumption
6 KEY GNSS STATISTICS
- 6.1 GNSS Receiver Shipments (in billion units), by Price Categories
- 6.2 High-end Receiver Shipments (in million units), by Price Categories
- 6.3 Shipment of GNSS Devices (in thousand units), by Orbital Sub-segment
- 6.4 Installed Base of GNSS Devices (in billion Units) by End User
7 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 7.1 Device Type
- 7.1.1 Smartphones
- 7.1.2 Tablets and Wearables
- 7.1.3 Personal Tracking Devices
- 7.1.4 Low-power Asset Trackers
- 7.1.5 In-vehicle Systems
- 7.1.6 Drones
- 7.1.7 Other Device Types
- 7.2 End-user Industry
- 7.2.1 Automotive
- 7.2.2 Consumer Electronics
- 7.2.3 Aviation
- 7.2.4 Other End-user Industries
- 7.3 Geography
- 7.3.1 North America
- 7.3.1.1 United States
- 7.3.2 Europe
- 7.3.2.1 Russia
- 7.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 7.3.3.1 China
- 7.3.3.2 Japan
- 7.3.3.3 South Korea
- 7.3.4 Latin America
- 7.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 7.3.1 North America
8 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 8.1 Company Profiles
- 8.1.1 Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- 8.1.2 Mediatek Inc.
- 8.1.3 STMicroelectronics NV
- 8.1.4 Broadcom Inc.
- 8.1.5 Intel Corporation
- 8.1.6 U-blox Holdings AG
- 8.1.7 Thales Group
- 8.1.8 Quectel Wireless Solutions Co. Ltd
- 8.1.9 Skyworks Solutions Inc.
- 8.1.10 Furuno Electric Co. Ltd
- 8.1.11 Hemisphere GNSS
- 8.1.12 Trimble Inc.
- 8.1.13 Sony Group Corporation









