 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1687782
东协低温运输物流:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2025-2030 年)ASEAN Cold Chain Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
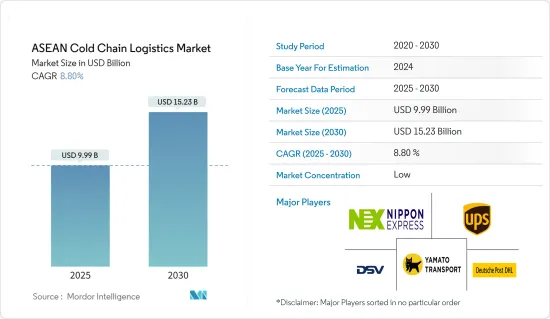
2025年东协低温运输物流市场规模预估为99.9亿美元,预估至2030年将达152.3亿美元,预测期间(2025-2030年)复合年增长率为8.8%。
主要亮点
- 城市人口的增加和消费者态度的改变正在推动对冷藏保管和运输的需求。东南亚的冷藏/冷冻产品市场正在快速成长。
- 食品分销正迅速从传统市场转向超级市场和便利商店。冷藏和冷冻产品很容易采购,主要经销商都提供冷藏卡车运输服务。
- 各地低温运输服务品质参差不齐。由于缺乏冷藏,食物也可能变质。据估计,东南亚90%的食物废弃物发生在运输过程中。
- 虽然印度的低温运输业务尚处于起步阶段,但它是低温运输仓储和物流领域最有前景的行业之一。
- 到2027年,印度将成为世界第五大经济体。作为全球市场上成熟且重要的参与者,印度对供应链基础设施的投资可能会在未来几年增加。
- 幸好,印度政府正在透过各种补贴和激励措施推动低温运输产业的发展,并鼓励私人参与。食品加工工业部(MoFPI)启动了低温运输、加值和保鲜基础设施计画。
- 东南亚国协收入水准的提高和生活方式的改变是这些地区肉类消费和生产成长的重要因素。印尼和越南是主要的成长动力。
东协低温运输物流市场趋势
清真食品推动市场
- 近年来,全球品牌开始转向伊斯兰经济,以利用不断上升的购买力和不断变化的消费者支出重点。东协地区约有2.6亿穆斯林,主要居住在印尼、马来西亚、泰国、菲律宾、新加坡、缅甸和汶莱。过去十年,全部区域举办了一系列清真生活方式活动和宣传活动,激发了人们对伊斯兰旅行、食品、时尚和化妆品的兴趣。
- 韩国食品巨头 SPC 集团有意进军马来西亚,以期抢占全球清真食品产业 2 兆美元的市场。在与新加坡接壤的马来西亚柔佛州,SPC集团宣布计划投资 400 亿韩元(约 3,000 万美元)建造清真认证工厂。根据韩国媒体报道,该设施将设有一个港口,为货物运往东南亚和中东地区提供路线。
- 由于清真食品大部分为肉类,因此必须存放在经过各国政府清真认证的低温运输仓库中。最近,政府推出了多项旨在发展清真产业的政策,包括为清真产业建立经济特区(KEK)。
- 此外,国家伊斯兰教经济和金融委员会 (KNEKS) 与联合利华印尼等公司之间的合作预计将促进该国的清真产业的发展。马来西亚政府也正在采取多项措施,力争成为清真市场的全球市场领导者。清真产业总体规划和清真园区是政府最近的进展。所有这些清真倡议正在推动东南亚国协的低温运输物流。
肉类消费成长推动东协低温运输物流
- 东南亚人口不断增长、收入不断提高、都市化和零售业的发展,导致肉类消费和饲料进口量增加。该地区五大新兴市场为印尼、马来西亚、菲律宾、泰国和越南。
- 近年来肉类消费量不断增加,鱼贝类是肉类消费和生产的最大来源,同时也满足了部分饲料需求。每个东南亚国家对肉类的偏好各有不同,这从消费量和生产量就可以看出。
- 马来西亚是东南亚国家中家禽业产值最高的国家,并且拥有大型生产设施。
- 东南亚国协对清真食品的需求不断增长,原因有很多。一个重要因素是该地区穆斯林人口的成长。随着越来越多的人遵守伊斯兰饮食习惯,对清真认证食品的需求也日益增长。
- 此外,消费者对食品来源及其加工方式的认识和意识也不断增强。许多人(不仅是穆斯林)都选择清真认证的产品,因为人们认为这些产品品质更高、更卫生、更安全。
- 东协地区的旅游业也正在显着成长,其中包括来自穆斯林占多数国家的游客。这些游客在旅行时寻找清真食品,从而产生了对清真认证餐厅和食品的需求。
- 为了满足日益增长的需求,东南亚国协的公司正在积极寻求食品清真认证。清真认证保证产品符合要求的标准并依照伊斯兰饮食法规进行製作。该认证为消费者提供了保证,并帮助公司进入利润丰厚的清真市场。
东协低温运输物流产业概况
东协低温运输物流市场是一个分散的市场,由全球和本地参与者混合组成。本地中小型企业以较小的车队和储存空间服务市场。在一些国家,例如新加坡,DHL、日本通运等全球性企业占有强大的市场份额。此外,全球参与者正在投资市场并收购当地企业,以扩大在该地区的业务。
此外,日本物流企业也加强在东协地区的活动,透过在东南亚国协各国家为製造业和流通业建立陆上运输枢纽,推动供应链建构。该公司也参与低温运输开发,并积极投资新鲜农产品、鲜花、化妆品和消费品的物流。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月的分析师支持
目录
第 1 章 简介
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 市场覆盖
第二章调查方法
- 分析方法
- 研究阶段
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场洞察
- 当前市场状况
- 市场动态
- 驱动程式
- 低温运输物流需求不断增加
- 扩大该地区的国际贸易
- 限制因素
- 缺乏适当的基础设施和设施
- 低温运输物流高成本
- 机会
- 生鲜产品需求不断增加
- 市场驱动的技术进步
- 驱动程式
- 冷冻设施的技术趋势和自动化
- 政府法规和倡议
- 日本在东协低温运输产业中的作用思考与说明
- 产业价值链洞察
- 产业吸引力-波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 购买者/消费者的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争强度
- 排放标准和法规对低温运输产业的影响
- 深入了解冷藏仓库使用的冷媒和包装材料
- 深入了解印尼和马来西亚的清真标准和认证
- 气候和温度控制储存见解
- COVID-19 市场影响
第五章 市场区隔
- 按服务
- 贮存
- 运输
- 附加价值服务(速冻、贴标、库存管理等)
- 按温度
- 常温
- 冷藏
- 冷冻
- 按应用
- 园艺(新鲜水果和蔬菜)
- 乳製品(牛奶、冰淇淋、奶油等)
- 肉类和鱼类
- 加工食品
- 製药、生命科学、化学
- 其他用途
- 按地区
- 新加坡
- 泰国
- 越南
- 印尼
- 马来西亚
- 菲律宾
- 其他东南亚国协
第六章 竞争格局
- 市场集中度概览
- 公司简介
- Nippon Express
- United Parcel Service of America
- Deutsche Post DHL
- Yamato Transport Co. Ltd
- DSV Agility Logistics
- NYK(Yusen Logitics & TASCO)
- Tiong Nam Logistics
- Sinchai Cold Storage
- Jentec Storage Inc.
- JWD Logistics
- KOSPA
- PT. Pluit Cold Storage
- PT. Wahana Cold Storage
- Havi Logistics
- Royal Cargo
- Thai Max Co. Ltd
- MGM Bosco*
第七章:市场的未来
第 8 章 主要供应商和供货商
- 储存设备製造商
- 承运商
- 技术提供者
第 9 章 附录
- 冷藏仓库年度统计
- 冷冻食品进出口贸易资料
- 深入了解主要国家的食品运输和储存法规结构
- 洞察东南亚食品饮料产业
The ASEAN Cold Chain Logistics Market size is estimated at USD 9.99 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 15.23 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 8.8% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- The growing urban population and changing consumer perception have boosted refrigerated storage and transport demand. The market for refrigerated/frozen products is rapidly growing in Southeast Asia.
- The distribution of food products is rapidly shifting from traditional markets toward supermarkets and convenience stores. Refrigerated and frozen products are easier to procure, as major distributors offer shipping via insulated trucks.
- The quality of local cold-chain services varies widely. Food products have been damaged due to the lack of refrigeration. It is estimated that 90% of Southeast Asia's food waste is created during transport.
- Indian cold chain business is still in its early stages, it is one of the most promising industries in the cold chain warehousing and logistics industry.
- By 2027, India will have the world's fifth-largest economy. Investment in India's supply chain infrastructure is likely to increase year on year since it is a well-established, important player in the global market.
- Fortunately, the Indian government is a driving factor in the development of the cold chain industry, encouraging private participation through a variety of subsidy programs and incentives. The Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) has initiated a cold chain, value addition, and preservation infrastructure program.
- Rising income levels in ASEAN countries and lifestyle changes are key factors for the growth of meat consumption and production in these regions. Indonesia and Vietnam are mainly driving the growth.
ASEAN Cold Chain Logistics Market Trends
Hallal Food is offering traction to the market
- In recent years, global brands have begun to focus on the Muslim economy to capitalize on rising purchasing power and shifting consumer spending priorities. Around 260 million Muslims live in the ASEAN region, most of whom live in Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, the Philippines, Singapore, Myanmar, and Brunei. The number of halal lifestyle events and campaigns held across the region in the last decade stimulates interest in Islamic travel, foods, fashion, and cosmetics.
- SPC Group, a major South Korean food company, intends to grow into Malaysia to capture a portion of the USD 2 trillion worldwide halal food industry. In Johor, a Malaysian state bordering Singapore, SPC Group announced plans to invest 40 billion won (about USD 30 million) in the construction of a halal-certified factory. According to South Korean media, the facility will have a route to send goods throughout Southeast Asia and into the Middle East thanks to the location's ports.
- Since most halal food is meat products, they need to be stored in cold chain warehouses that are Halal-certified by the respective Governments. In recent times, several policies aimed at developing the halal industry have been demonstrated by the government, including the establishment of a Special Economic Zone (KEK) for the industry.
- In addition, the collaboration between the National Committee for Sharia Economics and Finance (KNEKS) and companies such as Unilever Indonesia is expected to boost the country's halal industry. The Malaysian government is also making many advancements to become a global market leader in the halal market. The halal industry's master plan and halal park are the recent advancements made by the government. All these halal initiatives are driving the cold chain Logistics in ASEAN countries.
Increase in Meat Consumption Propelling Cold Chain Logistics in ASEAN Countries
- Southeast Asia's expanding population and increasing incomes, urbanization, and retail sectors are contributing to rising meat consumption and growing imports of feedstuffs. The five key emerging markets within the region are Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- In recent years, meat consumption has also increased, although fish and seafood are the largest meat sources consumed and produced and are partially responsible for feedstuffs demand. Every Southeast Asian country has different meat preferences, as reflected by their levels of consumption and production.
- Malaysia has a sizable production apparatus in the poultry sector, which has the best production values among these Southeast Asian nations.
- The increasing demand for halal food products in ASEAN countries can be attributed to various factors. One of the key factors is the growing Muslim population in the region. As more people adhere to Islamic dietary practices, the demand for halal-certified food products has increased.
- Moreover, there has been a rise in awareness and consciousness among consumers regarding the source and preparation of their food. Many people, not just Muslims, are opting for halal-certified products as they perceive them to be of higher quality, more hygienic, and safer to consume.
- The ASEAN region has also witnessed a significant increase in tourism, including visitors from predominantly Muslim countries. These tourists seek halal food options during their travels, creating a demand for halal-certified restaurants and food products.
- To cater to this growing demand, businesses in ASEAN countries have been actively pursuing halal certification for their food products. Halal certification ensures that the products meet the required standards and are prepared in accordance with Islamic dietary laws. This certification assures consumers and helps businesses tap into the lucrative halal market.
ASEAN Cold Chain Logistics Industry Overview
The ASEAN cold chain logistics market's landscape is fragmented in nature, with a mix of global and local players. Small- and medium-sized local players still serve the market with small fleets and storage spaces. Some of the countries, like Singapore, have a strong presence of global players, like DHL and Nippon Express. Additionally, global players are investing in the market and acquiring local companies to increase their footprint in the region.
Furthermore, Japanese logistics companies strengthen their activities in the ASEAN region by setting up bases of land transportation in ASEAN countries for each country within the manufacturing and distribution industries, thereby pushing the construction of a supply chain. The companies are also involved in developing the cold chain and actively investing in logistics related to fruits and vegetables, flowers, cosmetics, and consumer goods.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Market
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.2.1.1 Increasing demand for cold chain logistics
- 4.2.1.2 Expansion of international trade in the region
- 4.2.2 Restraints
- 4.2.2.1 Lack of proper infrastructure and facilities
- 4.2.2.2 High cost associated to cold chain logistics
- 4.2.3 Opportunities
- 4.2.3.1 Growing demand for perishable goods
- 4.2.3.2 Technological advancements driving the market
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.3 Technological Trends and Automation in Cold Storage Facilities
- 4.4 Government Regulations and Initiatives
- 4.5 Review and Commentary on Role of Japan in the ASEAN Cold Chain Industry
- 4.6 Insights into Industry Value Chain
- 4.7 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Emission Standards and Regulations in the Cold Chain Industry
- 4.9 Insights into Refrigerants and Packaging Materials Used in Refrigerated Warehouses
- 4.10 Insights into Halal Standards and Certifications in Indonesia and Malaysia
- 4.11 Insights into Ambient/Temperature-controlled Storage
- 4.12 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Storage
- 5.1.2 Transportation
- 5.1.3 Value-added Services (Blast Freezing, Labeling, Inventory Management, etc.)
- 5.2 By Temperature
- 5.2.1 Ambient
- 5.2.2 Chilled
- 5.2.3 Frozen
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Horticulture (Fresh Fruits and Vegetables)
- 5.3.2 Dairy Products (Milk, Ice-cream, Butter, etc.)
- 5.3.3 Meats and Fish
- 5.3.4 Processed Food Products
- 5.3.5 Pharma, Life Sciences, and Chemicals
- 5.3.6 Other Applications
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 Singapore
- 5.4.2 Thailand
- 5.4.3 Vietnam
- 5.4.4 Indonesia
- 5.4.5 Malaysia
- 5.4.6 Philippines
- 5.4.7 Rest of ASEAN
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Nippon Express
- 6.2.2 United Parcel Service of America
- 6.2.3 Deutsche Post DHL
- 6.2.4 Yamato Transport Co. Ltd
- 6.2.5 DSV Agility Logistics
- 6.2.6 NYK (Yusen Logitics & TASCO)
- 6.2.7 Tiong Nam Logistics
- 6.2.8 Sinchai Cold Storage
- 6.2.9 Jentec Storage Inc.
- 6.2.10 JWD Logistics
- 6.2.11 KOSPA
- 6.2.12 PT. Pluit Cold Storage
- 6.2.13 PT. Wahana Cold Storage
- 6.2.14 Havi Logistics
- 6.2.15 Royal Cargo
- 6.2.16 Thai Max Co. Ltd
- 6.2.17 MGM Bosco*
7 FUTURE OF THE MARKET
8 KEY VENDORS AND SUPPLIERS
- 8.1 STORAGE EQUIPMENT MANUFACTURERS
- 8.2 CARRIER MANUFACTURERS
- 8.3 TECHNOLOGY PROVIDERS
9 APPENDIX
- 9.1 Annual Statistics on Refrigerated Storage Facilities
- 9.2 Import and Export Trade Data of Frozen Food Products
- 9.3 Insights into Regulatory Framework on Food Transportation and Storage in Key Countries
- 9.4 Insights into the Food and Beverage Sector in Southeast Asia











