 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1687894
南美洲废弃物管理-市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2025-2030)South American Waste Management - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
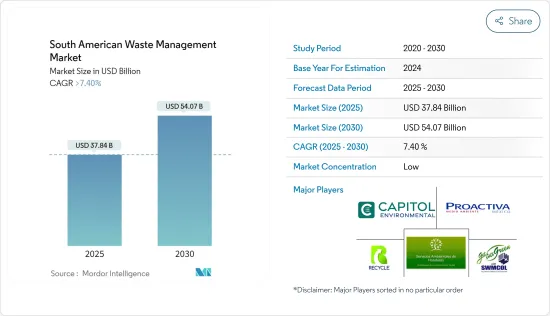
南美废弃物管理市场规模预计在 2025 年为 378.4 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将达到 540.7 亿美元,预测期内(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率将超过 7.4%。
该地区废弃物产量的增加正在推动市场的发展。此外,人们对废弃物管理中 3R 原则以及循环经济的认识不断提高也在推动市场的发展。
拉丁美洲为回收商提供了一个有趣的使用案例。儘管该地区面临一些废弃物处理挑战,但它无疑是一个具有巨大潜力的新兴市场。回收率一般不超过 10%,并且有许多露天垃圾场在运作。其他问题包括职场非正规就业率高以及废弃物管理不当(超过 40%)。新的变革大趋势,例如对永续经营模式的需求和与间接节俭一致的立法,使得寻找这些问题的解决方案变得迫切。随着拉丁美洲寻求提高废弃物管理的有效性、增加私营部门参与以刺激投资并拥抱数位化成果,其对废弃物管理的需求正在增长。电子产品回收是一个利基市场,需要投入巨大的精力。然而,该地区尚未解决废料回收的基本问题,即建立适当的收集网络和环保设施。罗萨莱斯指出,虽然小规模作业和手动拆卸在拉丁美洲仍然很常见,但巴西和墨西哥的回收商现在能够部署更「先进的技术」。例如,这意味着塑胶可以在更远的距离内分解。拉丁美洲的废弃物管理产业多年来一直稳步成长和发展。
拉丁美洲面临多项废弃物处理挑战,回收率最多仅 10% 左右。找到这个问题的解决方案对于永续性和间接节俭等新的变革大趋势至关重要。拉丁美洲废弃物管理市场正在扩大,因为它寻求提高效率、增加私人参与以推动投资并拥抱数位化成果。联合国拉丁美洲和加勒比海经济委员会经济发展司估计,到2030年,全部区域可创造480万个就业机会。根据联合国环境规划署的报告,到2050年,这可创造770万个新就业岗位,每年节省6,210亿美元。例如,智利已设定目标,到2040年在循环经济领域创造超过18万个全职就业机会。次要问题是将废弃物分类机整合到结构化的废弃物系统中。根据区域包容性回收倡议,非正规部门僱用了大约四百万人。该产业约占该地区外部废弃物收集总量的25-50%。
在当前情况下,废弃物管理是利用重要材料的绝佳机会。如果回收不当,宝贵的资源就会流失。在拉丁美洲,有些国家产生废弃物,有些国家则进口垃圾,形成了一种本土化的水闸,一般存在于指引的边缘。随着该地区迅速定位于金融发展和增强,废弃物测量比其他地区更快变得重要。不断发展的电子废弃物已成为拉丁美洲各地公共规划中备受关注的议题。私人社区和一般社会组织也越来越热衷于参与解决废弃物问题。这不仅是因为政治压力和公众对危险废弃物走廊的担忧,也因为废弃物负责人提供的诱人的工业潜力。拉丁美洲国家越来越多地将废弃物视为新的绿色倡议和商业机会的来源。拉丁美洲特别令人担忧的是偷偷摸摸、随意地分类和处理废弃物。这些问题可以透过建立正确的框架来解决:方法、指导方针、电子垃圾专家、健康的后备和运作良好的商业部门、充足的技术创新和能力、具有重要教育和意识的社会秩序,以及显然良好的监测、控制和许可机构。
南美洲废弃物管理市场的趋势
回收需求的增加推动了市场
- 在 TOMRA 的帮助下,阿根廷回收商 Reciclar 的产能已提高到每次处理超过 6 亿个宝特瓶。 TOMRA和Reciclar为加速拉丁美洲宝贵金融资源的间接处理树立了榜样。阿根廷工厂面积超过22000平方公尺,配备了最新一代的TOMRA回收分选设备和各部门。 AUTOSORT™ 和 AUTOSORT™ FLAKE 使回收商能够根据颜色和材料类型对每次运行的 30,000 多吨 PET 容器进行分类和收集,以生产小型咖啡色、绿色和浅蓝色 PET 薄片,以及各种尺寸和颜色的 HDPE 薄片。 Reciclar 也利用消费后的宝特瓶来生产食品级 PET 回收材料。
- 所实现的纯净情况使得回收商能够进一步将其重新利用为高品质的 PET 和 HDPE 再生材料,以生产回收率更高的新包装和瓶子。塑胶回收再利用的挑战是一个影响每个人的全球性问题,而在拉丁美洲,这个挑战并不小。
- 这就是为什么回收领域的两大主要参与者 TOMRA Recycling Sorting 和 Reciclar, SA 联手为该地区延长塑胶生命週期的环保工作做出贡献。透过承诺、创新和诚信,两家公司致力于最大限度地利用再生塑胶。 Recicra 最近安装了一个新的 TOMRA 设施来应对阿根廷的回收挑战。根据ECOPLAS报告,2021年再生塑胶总量达30.7万吨,较2020年增加11吨。
- 该工厂由 Marcelino Casella 创新,过去 28 年来一直专注于废弃物的收集、分类和回收,最近又增加了两个新的 AUTOSORT(TM) 薄片装置,用于生产小咖啡杯、绿色或浅蓝色 PET 薄片以及各种尺寸和颜色的 HDPE 薄片。 TOMRA Recycling Sorting 先进的宝特瓶和 PET 包装分选设备和技术使这家阿根廷公司实现了每次行程 6 亿个宝特瓶和 18,000 吨塑胶托盘的处理能力,成为阿根廷 PET废弃物处理领域的主要企业。
废弃物产量增加推动市场
- 拉丁美洲是世界粮食生产的宝贵贡献者。然而,我们也无法免于食物废弃物问题的影响。拉丁美洲约占全球农业和水产品出口的四分之一。根据经济合作暨发展组织(OECD)的资料,该国38%的土地用于农业,其中9.5%用于种植业,28.5%用于畜牧业。农业部门对拉丁美洲人民的生活至关重要,占 GDP 的 4.7%,并为该地区至少 14% 的人口提供就业。防止粮食损失和浪费仍然是世界面临的最大挑战之一。
- 这项挑战也延伸至拉丁美洲。粮农组织估计,全球 6% 的食物浪费发生在拉丁美洲和加勒比地区,每次约有 15% 的食物被损失和浪费。泛美卫生组织指出,“到2030年,该地区将有6700万人遭受饥饿。此外,这一数字还反映了乌克兰战争导致的全球粮食供应延迟。因此,我们可以预见一些真正令人尴尬的饥饿资料。”
南美洲废弃物管理产业概况
南美洲废弃物管理市场本质上是分散的,有许多区域和本地参与者以及少数全球参与企业。主要参与企业包括 RECYCLE S. DE RL、Proactiva SDRL、S.DE RL、Proactiva Medio Ambiente、洪都拉斯环境服务公司、Capitol 环境服务公司和特立尼达和多巴哥固体废物管理有限公司 (SWMCOL)。南美洲的废弃物管理市场竞争非常激烈,各国政府正在实施新的立法,以有效管理废弃物并制定更好的废弃物回收倡议。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 调查前提条件
- 研究范围
第二章调查方法
- 分析方法
- 研究阶段
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场动态
- 当前市场状况
- 市场概览
- 市场动态
- 驱动程式
- 南美洲快速的都市化和人口成长导致城市垃圾的产生量不断增加。
- 减少垃圾掩埋场的使用和产生清洁能源的需求正在推动对垃圾焚化发电设施的投资。
- 限制因素
- 非正规废弃物部门
- 有限的财政资源
- 机会
- 国际贸易及废弃物进出口
- 官民合作关係和私营部门对废弃物管理基础设施和服务的投资有助于满足日益增长的废弃物管理需求。
- 驱动程式
- 价值链/供应链分析
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买家/消费者的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争强度
- 深入了解拉丁美洲废弃物管理产业的物流支援与发展
- 洞察新兴企业进入拉丁美洲废弃物管理产业的策略
- 有效废弃物管理的技术进步与创新
第五章市场区隔
- 废弃物类型
- 工业废弃物
- 都市固态废弃物
- 电子废弃物
- 塑胶废弃物
- 医疗废弃物
- 按加工方式
- 收集
- 掩埋
- 焚化
- 回收利用
第六章 竞争格局
- 公司简介
- RECYCLE S. DE RL
- Proactiva Medio Ambiente
- Honduras Environmental Services
- The Trinidad and Tobago Solid Waste Management Company Limited(SWMCOL)
- Capitol Environmental Services, Inc
- Inciner8 Limited
- Casella Waste Systems, Inc.
- US Ecology, Inc.
- Waste Management, Inc
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- Republic Services, Inc*
7. 拉丁美洲废弃物管理产业未来成长前景
第 8 章 附录
- 各州都市区固态废弃物产生量统计
- 拉丁美洲人口规模(百万)
- 拉丁美洲GDP
- 拉丁美洲通货膨胀率
- 拉丁美洲消费者物价指数(绝对值)
- 拉丁美洲外汇
The South American Waste Management Market size is estimated at USD 37.84 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 54.07 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of greater than 7.4% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The increasing waste production in the region drives the market. Furthermore, the market is driven by the increasing awareness about the 3 R's of waste management, which intends to create a circular economy.
Latin America presents an intriguing case study for recyclers. It's an emerging market with great eventuality, indeed, though the region is facing several waste operation problems. Recycling rates generally don't exceed 10, with numerous open-air dumps in operation. Other issues include high situations of informality in the workplace and further than 40 of inaptly managed waste. Finding a result of these problems is imperative due to new transformative megatrends, similar to calls for sustainable business models and legislation in line with indirect frugality. The waste operation request in Latin America is expanding as it seeks to facilitate effectiveness, increase private participation to boost investment and incorporate digital results. Electronics recycling is a niche showing a significant pledge. However, our region is still dealing with the basics of scrap recycling in terms of setting up proper collection networks and environmentally sound establishments. While small-scale operations and homemade disassembly are still common across Latin America, Rosales notes that recyclers in Brazil and Mexico have been able to install more ' sophisticated technology.' This allows farther bracket of plastics, for example. The waste operation sector in Latin America has been growing and developing steadily over the last many times.
Latin America faces several waste operation problems, with recycling rates that are at most 10, a large number of open-air dumps, high levels of informality in the plant, and further than 40 of inaptly managed waste. Finding a result to this problem is imperative due to new transformative Mega Trends, similar to sustainability and indirect frugality. The waste operation market in Latin America is expanding as it seeks to improve effectiveness, increase private participation to boost investment and incorporate digital results. At a rough estimate, better waste operation could produce up to 4.8 million jobs across the region by 2030, the UN's Economic Development Division of the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean reported. By 2050, it would be suitable to generate 7.7 million new jobs and save up to 621 billion US- Dollars annually, a UN Environment Programme report states. Chile, for example, has set a target of creating further than 180,000 formal jobs in the circular economy by 2040. A secondary problem is the integration of waste selectors into a systematized waste operation system. The informal sector consists of around four million people, according to the Regional Initiative for Inclusive Recycling. The sector contributes roughly 25 to 50 percent of all external waste collection in the region.
In the current situation, overseeing waste presents a faultless chance to use the important materials that can be set up in multitudinous kinds of inclined widgets. On the off chance that reusing is not meetly done, precious means can be lost. In Latin America, nations both produce and import-waste, shaping the indigenous sluice that exists generally on the edges of the guideline. Because of the locale's quickened financial development and position of enhancement, the measure of-waste is getting more important quicker than in other regions. On ongoing occasions, e-waste has become an extremely conspicuous issue in public plans across Latin America. Private area and common society associations also have a developing enthusiasm for diving into waste issues. This is not just because of political weight and public worries about the dangerous corridor of waste but also because of the appealing industry openings that waste directors offer. Progressively Latin American nations are seeing waste on the board as a creator of new green endeavours and business. Of specific solicitude in Latin America is the sneaking and casual assortment and destroying of waste, which prompts unreasonable contest and unusual pitfalls. These difficulties can be tended to by having the correct framework set up, including approaches and guidelines, e-waste specialist-ops, sound backing and meetly working business sectors, suitable innovation and abilities, social orders that are very important educated and aware, and obviously great observing, control, and authorization bodies.
South American Waste Management Market Trends
Increasing demand for recycling driving the market
- Argentinian recycler Reciclar has improved its capacity of over 600 million plastic bottles per time thanks to TOMRA's outfit. TOMRA and Reciclar set an example of accelerating an indirect treatment of precious coffers in Latin America. The Argentinian factory, with a face area of further than 22,000 m2, features the rearmost generation of TOMRA Recycling Sorting outfit and ministry. AUTOSORT (TM) and AUTOSORT (TM) FLAKE allow the recycler business to sort and recover further than 30,000 tons/ time of PET holders by color and material type and produce demitasse, green, or light blue PET flakes and HDPE flakes of different sizes and colors. Also, Reciclar produces food-grade PET recyclates from post-consumer PET bottles.
- Thanks to the chastity situations achieved, recyclers can further reuse them into high-quality PET and HDPE recyclates for the product of new packaging and bottles with increased recycled content, thus supporting an environmentally friendly resource operation and product in Argentina. The plastic recycling challenge is a global problem in which all are involved, and in Latin America, the task isn't a minor bone.
- For this reason, TOMRA Recycling Sorting and Reciclar, S.A., two important companies in the recycling sector, are joining forces to contribute to environmental conduct in the region to extend the life cycle of plastics. Both companies seek to maximize the use of recycled plastic through commitment, invention, and fidelity. According to this charge, Reciclar recently installed fresh TOMRA outfits to meet the recycling challenges in Argentina. An ECOPLAS report estimates that the total volume of plastic reclaimed in 2021 amounted to 307,000 tonnes of plastics, an increase of 11 compared to 2020.
- The factory innovated by Marcelino Casella, which has specialized in collecting, sorting, and recovering waste for the last 28 times, only recently added 2 new AUTOSORT (TM) FLAKE units to its operation to produce demitasse, green or light blue PET flakes and HDPE flakes of different sizes and colors. Thanks to TOMRA Recycling Sorting's advanced PET bottle and PET packaging sorting outfit and technology, the Argentinean company has reached a processing capacity of 600 million plastic bottles and a product of 18,000 tons of plastic pallets per time, becoming the leading company in Argentina in PET waste processing.
Increasing waste production driving the market
- Latin America is inestimable for global food production. Yet it's no stranger to the food waste issue. Latin America accounts for about a quarter of global exports in agricultural and fisheries products. According to the OECD data, 38 of its available area is used for agriculture, out of which 9.5 is devoted to crops and 28.5 to pasturage. The agricultural sector is crucial for Latin American livelihoods, contributing to a normal of 4.7 of GDP and employing at least 14 of the region's population. Precluding food loss and waste is one of the topmost remaining global challenges.
- This challenges enterprises also Latin America. The FAO estimates that 6 of global food losses occur in Latin America and the Caribbean, and the region loses and/ or wastes each time about 15 of its food each. The Pan American Health Organization estimates that " in 2030, hunger will affect 67 million people in the region, a figure that doesn't take into account the impacts of the COVID-19 epidemic ". In addition, this figure represents the global food supply lapses caused by the war in Ukraine. So, indeed, advanced shameful hunger data are anticipated.
South American Waste Management Industry Overview
The South American waste management market is fragmented in nature, with a lot of regional and local players and a few global players. Some of the major players include RECYCLE S. DE R.L, Proactiva Medio Ambiente, Honduras Environmental Services, Capitol Environmental Services, Inc., The Trinidad and Tobago Solid Waste Management Company Limited (SWMCOL), and many more. The South American waste management market is highly competitive, with newer laws being implemented by the governments for effective waste management and the development of better waste recycling initiatives.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Method
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Overview
- 4.3 Market Dynamics
- 4.3.1 Drivers
- 4.3.1.1 The rapid urbanization and population growth in South America have led to increased municipal waste generation.
- 4.3.1.2 The need to reduce landfill usage and generate clean energy has led to investments in waste-to-energy facilities.
- 4.3.2 Restraints
- 4.3.2.1 Informal Waste Sector
- 4.3.2.2 Limited Financial Resources
- 4.3.3 Opportunities
- 4.3.3.1 International Trade and Waste Import/Export
- 4.3.3.2 Public-private partnerships and private sector investments in waste management infrastructure and services are helping to address the growing waste management needs
- 4.3.1 Drivers
- 4.4 Value Chain / Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.6 Insights on the Logisitcs support and development in the waste management industry in Latin America
- 4.7 Insights on the strategies of the rising startups venturing into the Latin American waste management industry
- 4.8 Technological advancement and innovation in the effective waste management
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Waste type
- 5.1.1 Industrial waste
- 5.1.2 Municipal solid waste
- 5.1.3 E-waste
- 5.1.4 Plastic waste
- 5.1.5 Bio-medical waste
- 5.2 By Disposal methods
- 5.2.1 Collection
- 5.2.2 Landfill
- 5.2.3 Incineration
- 5.2.4 Recycling
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Overview (Market Concentration and Major Players)
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 RECYCLE S. DE R.L
- 6.2.2 Proactiva Medio Ambiente
- 6.2.3 Honduras Environmental Services
- 6.2.4 The Trinidad and Tobago Solid Waste Management Company Limited (SWMCOL)
- 6.2.5 Capitol Environmental Services, Inc
- 6.2.6 Inciner8 Limited
- 6.2.7 Casella Waste Systems, Inc.
- 6.2.8 US Ecology, Inc.
- 6.2.9 Waste Management, Inc:
- 6.2.10 Covanta Holding Corporation
- 6.2.11 Republic Services, Inc*
7 FUTURE GROWTH PROSPECTS OF LATIN AMERICAN WASTE MANAGEMENT INDUSTRY
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Statistics on the state-wise solid waste generation in urban areas
- 8.2 Latin America size of population (million)
- 8.3 Latin America GDP
- 8.4 Latin America inflation
- 8.5 Latin America Consumer Price Index (absolute)
- 8.6 Latin America exchange rate








