 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1844528
玻璃纤维增强聚合物:市场份额分析、产业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030)Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
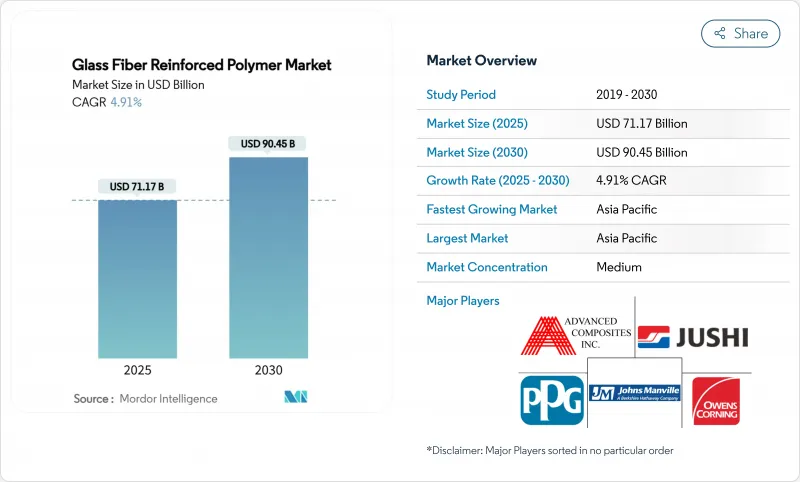
预计 2025 年玻璃纤维增强聚合物市场价值将达到 711.7 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将达到 904.5 亿美元,预测期内(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 4.91%。
随着交通运输、可再生能源、航太和建筑行业的原始设备製造商 (OEM) 用防腐蚀复合材料取代较重的金属,以减轻重量、提高耐用性并满足更严格的永续性发展目标,对复合材料的需求也在不断增长。快速的都市化,尤其是在亚太地区,正在刺激基础设施投资,这些投资指定用于钢筋、桥面和管道衬里的玻璃纤维增强聚合物解决方案。生物基环氧化学正在进入批量生产,而四针增强材料和混合碳玻璃纤维正在实现新的结构应用。跨国公司正在削减低利润生产线并与回收商合作,而区域製造商正在扩大靠近客户的产能,以对冲物流风险和外汇波动。然而,突破性技术——热解和碳化硅升级再造——正在提高循环性,并缓解北美和欧洲的监管压力。
全球玻璃纤维增强聚合物市场趋势与洞察
汽车产业需求不断成长
电动车专案正在加速复合材料的应用,因为每减轻一公斤重量,就能增加续航里程并缩小电池尺寸。玻璃纤维增强热塑性塑胶目前正在取代电池机壳中的压製钢材,减轻了40%的重量,同时提高了防火性和绝缘性。原始设备製造商正在采用碳玻混合变速箱壳体,在保持刚性以实现精确齿轮对准的同时,实现了30%的重量减轻。玻璃纤维增强聚合物市场参与企业也利用较低的模具成本,实现诸如张紧板簧等利基零件的本地化,这可以为商用车减轻高达50公斤的重量,并提高有效负载容量。
风力发电机中玻璃纤维增强聚合物的使用日益增多
在风电领域,随着塔架和叶片越来越高,对更轻、更坚固材料的需求正在快速成长。涡轮机原始设备製造商正在整合碳玻混合翼樑和根部插件,以限制叶尖挠度,从而实现15MW平台。立陶宛研究人员检验了热解方法,与掩埋掩埋相比,可将处置影响减少高达51%。这些进展提高了生命週期可靠性,而这在国家竞标中的需求日益增加。
製造成本高
与普通金属相比,专用纤维上浆剂、严格的製程控制以及高能耗的熔炼製程导致成本更高。欧文斯科宁复合材料业务的销售额在2024年第一季下降了11%,至5.23亿美元,这迫使其对玻璃纤维增强部门进行策略评估。资本密集熔炉以及新兴地区有限的规模经济导致单位成本居高不下,减缓了其在成本敏感型领域的应用。
細項分析
聚酯树脂在玻璃纤维增强聚合物市场中占据主导地位,由于其价格低廉以及与压缩和喷射製程的广泛相容性,到 2024 年将占据 62.15% 的市场份额。儘管环氧树脂的市场规模较小,但预计到 2030 年将以 5.03% 的最高复合年增长率增长,这要归功于其出色的附着力、抗疲劳性和低空隙率加工性,符合严格的航太、风能和汽车计划。乙烯基酯填补了中等性能的空白,它比聚酯具有更好的耐化学性,而成本低于环氧树脂,这使其对海洋和化学品围堵计划具有吸引力。最近一种含有 23%可再生乙二醇的生物基环氧树脂可在不牺牲机械强度的情况下将製造排放减少 21%,支持 ESG 记分卡和采购指南。奈米填料改质环氧树脂用作固体聚合物电解质,为结构电池和超级电容器开闢了使用案例。在玻璃纤维增强聚合物市场,随着下游客户寻求低碳替代品,传统聚酯的成本压力预计将持续存在。
乙烯基酯製造商正在提高固化速度,以适应高速树脂输送线。聚氨酯化学物质正应用于减震面板,这类面板的韧性比刚性更重要。像PEEK这样的小众热塑性塑胶对于工作温度高达240°C的井下油气工具至关重要。中国的大型聚酯工厂运作着专用的熔炉网络,可根据需求波动快速调整生产,从而缓解了供应过剩的担忧。环氧树脂供应商正在透过双酚A和环氧氯丙烷的期货合约对冲原料波动,从而稳定主要航太应用的价格。连续加工领域的创新,例如脱模时间仅为60秒的快速固化环氧树脂,正在缩短生产週期,并支持玻璃纤维增强聚合物市场的销售成长。
压缩成型(包括片状模塑胶和玻璃纤维毡热塑性塑胶)由于其高重复性和中等产量下的经济效益,将在2024年占据市场收入的31.03%。到2030年,射出成型的复合年增长率将达到4.94%,因为高流动性、长纤维热塑性复合材料能够生产薄壁复杂部件,且无需二次加工。真空辅助树脂转注成形正在不断发展,透过在固化过程中施加压力,纤维体积可增加高达62%,拉伸强度可提高至760 MPa,同时厚度可减少4%。手工积层法仍在继续应用于建筑面板和游艇船体,其设计自由度超过了生产节拍时间。
连续拉挤生产线整合了线上打磨和底漆涂装功能,减少了窗框和电网横臂的下游劳动力。可在热固性材料和热塑性材料之间切换的混合生产单元提高了资产利用率,并支持玻璃纤维增强聚合物市场的多材料模组生产。机器人搬运减少了废料,封闭式数位孪生即时检测树脂富集区域,防止出现分层热点。由于循环时间低于55秒,大量生产的汽车门槛樑的成本与铝挤型持平。在新兴经济体,在支持技术转移的优惠贷款的支持下,本地压机正在满足当地需求。
区域分析
预计到2024年,亚太地区将占全球销售额的48.91%,到2030年复合年增长率将达到4.98%。中国正在加速产能扩张,例如BASF投资108亿美元的湛江整合基地等大型工厂。基地100%使用可再生电力,供应汽车和电子复合材料。BASF宣布进一步扩大聚酰胺和PBT产能,以满足下游加工商的需求。东南亚国协正在利用近岸外包的优势,因为供应链多元化使玻璃纤维增强聚合物市场参与企业更接近最终用户。
在北美,美国在涡轮叶片、航太和基础设施领域处于领先地位。巨石集团正在美国兴建待开发区反应器,承诺保障地区供应安全并避免进口关税。联邦「购买美国货」条款日益倾向于国内采购,使老牌製造商和新参与企业都能从中受益。加拿大正专注于轻型客车和电池机壳,以满足零排放汽车的要求。
欧洲颁布循环经济立法,鼓励可回收树脂和叶片间玻璃回收的投资。 Carbon Rivers 的多级热解可回收纤维,用于隔热材料和片状成型塑料,吸引了许多品牌商的津贴和合作。德国支持维修需要耐腐蚀内衬的氢气管道,北海的离岸风力发电支持了对高模量粗纱的需求。虽然南美洲、中东和非洲仍是利基市场,但随着巴西港口维修以及沙乌地阿拉伯为交通和可再生能源领域的大型企划,玻璃纤维增强聚合物市场正在蓬勃发展。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场状况
- 市场概况
- 市场驱动因素
- 汽车产业需求不断成长
- 风力发电机中玻璃纤维增强聚合物的使用日益增多
- 玻璃纤维增强聚合物在航太工业中的应用日益广泛
- 建筑和基础设施领域的扩张
- 建设产业越来越重视能源效率和轻量化
- 市场限制
- 製造成本高
- 回收能力的限制
- 替代材料的可用性
- 价值链分析
- 五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争程度
第五章市场规模及成长预测
- 依树脂类型
- 聚酯纤维
- 乙烯基酯
- 环氧树脂
- 聚氨酯
- 其他树脂类型(PEEK树脂、酚醛树脂等)
- 按工艺
- 手动流程
- 压缩成型
- 片状成型塑胶工艺
- 玻璃纤维毡热塑性工艺
- 连续製程
- 射出成型
- 按纤维形状
- 粗纱
- 切股毡
- 连续纤维丝毡
- 织物
- 按最终用户产业
- 活力
- 车
- 海洋
- 建筑和基础设施
- 电气和电子
- 航太/国防
- 其他终端使用者产业(医疗保健、消费品)
- 按地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 其他亚太地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 其他欧洲国家
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地区
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 亚太地区
第六章 竞争态势
- 市场集中度
- 策略倡议
- 市占率(%)/排名分析
- 公司简介
- Advanced Composites Inc.
- BASF SE
- BGF Industries
- Binani Industries Ltd.
- Celanese Corporation
- China Beihai Fiberglass Co. Ltd
- China Jushi Co. Ltd
- Chongqing Polycomp International Corp.(CPIC)
- Gurit Services AG, Zurich
- Jiuding New Material Co., Ltd
- Johns Manville
- Nippon Electric Glass Co.,Ltd.
- Owens Corning
- PPG Industries Inc.
- Reliance Industries Limited
- SAERTEX GmbH & Co. KG
- Scott Bader Company Ltd.
- The Composite Group
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Market size is estimated at USD 71.17 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 90.45 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.91% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Demand is rising as OEMs in transportation, renewable energy, aerospace, and construction replace heavier metals with corrosion-free composites to lower weight, boost durability, and meet stricter sustainability targets. Rapid urbanization, especially in Asia-Pacific, is stimulating infrastructure investments that specify glass fiber reinforced polymer solutions for rebar, bridge decks, and pipeline liners. Material innovation is widening the performance envelope: bio-based epoxy chemistries are entering series production, while quadaxial stitched reinforcements and hybrid carbon-glass fabrics are enabling new structural applications. Competition is intense but fragmented; multinationals are pruning low-margin lines and partnering with recyclers, whereas regional producers expand capacity close to customers to hedge logistics risk and currency volatility. End-of-life hurdles remain; nevertheless, breakthroughs in pyrolysis and silicon-carbide up-cycling are improving the circularity narrative and easing regulatory pressure in Europe and North America.
Global Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Market Trends and Insights
Growing Demand from the Automotive Sector
Electric-mobility programs are accelerating composite uptake because every kilogram saved extends driving range and shrinks battery size. Glass fiber reinforced thermoplastics now replace stamped steel in battery enclosures, trimming mass by 40% while improving fire resistance and thermal insulation. OEMs deploy hybrid carbon-glass transmission housings that cut 30% weight yet keep stiffness for precise gear alignment. Glass fiber reinforced polymer market participants also exploit lower tooling costs to localize niche parts such as tension leaf springs that remove up to 50 kg from commercial vehicles, thereby permitting higher payloads.
Increasing Usage of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers in Wind Turbines
The wind sector is the fastest-growing end-user because taller towers and longer blades mandate lighter yet stronger materials. Turbine OEMs integrate carbon-glass hybrid spars and root inserts to keep tip deflection within limits, thereby enabling 15-MW platforms. Lithuanian researchers have validated pyrolysis routes that reclaim fibers and toxic styrene from end-of-life blades, reducing disposal impacts by up to 51% versus landfill. These advances improve the life-cycle credentials that national tenders increasingly require.
High Manufacturing Cost
Specialized fiber sizing, tight process controls, and energy-intensive melting raise costs versus commodity metals. Price declines during 2024 squeezed margins; Owens Corning's Composites sales fell 11% to USD 523 million in Q1 2024, prompting a strategic review of its glass reinforcements unit. Capital-intensive furnaces and limited economies of scale in emerging regions keep unit costs elevated, delaying adoption in cost-driven segments.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Increasing Adoption of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers in the Aerospace Industry
- Expansion of Construction and Infrastructure Sector
- Limited Recycling Capabilities
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Polyester resins dominated 2024 demand with a 62.15% share of the glass fiber reinforced polymer market size, thanks to low price and broad compatibility with compression and spray-up processes. Epoxy, though smaller, will register the highest 5.03% CAGR to 2030 because its superior adhesion, fatigue resistance, and low-void processing meet stringent aerospace, wind, and automotive specifications. Vinyl ester fills the mid-performance niche, combining better chemical resistance than polyester with lower cost than epoxy, and thus appeals to marine and chemical containment projects. Recent bio-based epoxies containing 23% renewable glycol cut manufacturing emissions by 21% without sacrificing mechanical strength, supporting ESG scorecards and procurement guidelines. Nanofiller-modified epoxies that double as solid polymer electrolytes open structural battery and supercapacitor use cases. The glass fiber reinforced polymer market expects continued cost pressure on conventional polyester as downstream customers seek lower embedded carbon alternatives.
Vinyl ester producers are enhancing cure kinetics to suit high-speed resin transfer lines, while polyurethane chemistries gain adoption in impact-absorption panels where toughness outweighs stiffness. Niche thermoplastics such as PEEK remain essential in oil-and-gas downhole tools requiring 240 °C service temperatures. Oversupply concerns are limited because large polyester plants in China run captive furnace networks, allowing quick output throttling during demand swings. Epoxy suppliers hedge raw-material volatility through forward contracts on bisphenol-A and epichlorohydrin, stabilizing pricing to aerospace primes. Innovations in continuous processing, such as snap-cure epoxies that reach demold in 60 seconds, will compress cycle time and support volume ramp-ups in the glass fiber reinforced polymer market.
Compression molding, including Sheet Molding Compound and Glass Mat Thermoplastic, accounted for 31.03% of 2024 revenue due to high repeatability and favorable economics at medium volumes. Injection molding will post a 4.94% CAGR through 2030 as high-flow, long-fiber thermoplastic compounds allow thin-wall complex parts without secondary finishing. Vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding has evolved; adding pressure during cure boosts fiber volume to 62% and lifts tensile strength to 760 MPa while trimming thickness by 4%. Manual lay-up persists for architectural panels and yacht hulls where design freedom overrules takt time.
Continuous pultrusion lines now integrate inline sanding and priming, reducing downstream labor for window frames and power-grid crossarms. Hybrid production cells that switch between thermoset and thermoplastic matrices extend asset utilization and enable multimaterial modules in the glass fiber reinforced polymer market. Robotic handling lowers scrap, and closed-loop digital twins detect resin-rich zones in real time, preventing delamination hot spots. Cost parity with aluminum extrusion is within reach for high-volume automotive sill beams once cycle times fall below 55 seconds, a benchmark that major Tier-1 suppliers target by 2027. In emerging economies, localized compression presses fill regional demand, aided by concessional financing that supports technology transfer.
The Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Market Report Segments the Industry by Resin Type (Polyester, Vinyl Ester, Epoxy, and More), Process (Manual Process, Compression Molding, and More), Fiber Form (Rovings, Chopped Strands Mats, and More), End-User Industry (Energy, Automotive, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific dominated with 48.91% revenue in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 4.98% CAGR through 2030. China accelerates capacity with mega-plants such as BASF's USD 10.8 billion Zhanjiang Verbund, which will operate on 100% renewable electricity and supply automotive and electronics composites. India's rail and road modernization campaigns stimulate local demand; BASF has announced additional polyamide and PBT expansions to serve downstream converters. ASEAN countries leverage near-shoring as supply-chain diversification pushes glass fiber reinforced polymer market participants to locate closer to end users.
In North America, the United States leads turbine blade, aerospace, and infrastructure uptake. Jushi Group is finalizing a greenfield furnace in the country, promising regional supply security and import duty avoidance. Federal Buy-America clauses increasingly favor domestic sourcing, benefitting incumbent producers and new entrants. Canada focuses on lightweight buses and battery enclosures to meet zero-emission vehicle mandates.
Europe enforces circular-economy legislation that spurs investment in recyclable resins and blade-to-blade glass reclamation. Carbon Rivers' multi-stage pyrolysis recovers fiber for reuse in insulation and sheet molding compounds, attracting grants and brand-owner partnerships. Germany supports hydrogen pipeline retrofits that require corrosion-resistant liners, while offshore wind build-out in the North Sea sustains high-modulus roving demand. South America and Middle East & Africa remain niche but are gaining momentum as Brazil upgrades ports and Saudi Arabia funds mega-projects in transport and renewable energy, opening new arenas for the glass fiber reinforced polymer market.
- Advanced Composites Inc.
- BASF SE
- BGF Industries
- Binani Industries Ltd.
- Celanese Corporation
- China Beihai Fiberglass Co. Ltd
- China Jushi Co. Ltd
- Chongqing Polycomp International Corp. (CPIC)
- Gurit Services AG, Zurich
- Jiuding New Material Co., Ltd
- Johns Manville
- Nippon Electric Glass Co.,Ltd.
- Owens Corning
- PPG Industries Inc.
- Reliance Industries Limited
- SAERTEX GmbH & Co. KG
- Scott Bader Company Ltd.
- The Composite Group
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing Demand from the Automotive Sector
- 4.2.2 Increasing Usage of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers in Wind Turbines
- 4.2.3 Increasing Adoption of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers in the Aerospace Industry
- 4.2.4 Expandion of Construction and Infrastructure Sector
- 4.2.5 Growing Emphasis on Energy Efficent and Low-Weight Materials in Construction Industry
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Manufacturing Cost
- 4.3.2 Limited Recycling Capabilities
- 4.3.3 Availability of Alternative Materials
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Resin Type
- 5.1.1 Polyester
- 5.1.2 Vinyl Ester
- 5.1.3 Epoxy
- 5.1.4 Polyurethane
- 5.1.5 Other Resin Types (PEEK Resin, Phenolic Resin, etc.)
- 5.2 By Process
- 5.2.1 Manual Process
- 5.2.2 Compression Molding
- 5.2.2.1 Sheet Molding Compound Process
- 5.2.2.2 Glass Mat Thermoplastic Process
- 5.2.3 Continuous Process
- 5.2.4 Injection Molding
- 5.3 By Fiber Form
- 5.3.1 Rovings
- 5.3.2 Chopped Strands Mats
- 5.3.3 Continuous Filament Mats
- 5.3.4 Woven Rovings/Fabrics
- 5.4 By End User Industry
- 5.4.1 Energy
- 5.4.2 Automotive
- 5.4.3 Marine
- 5.4.4 Construction and Infrastructure
- 5.4.5 Electrical and Electronics
- 5.4.6 Aerospace and Defence
- 5.4.7 Other End User Industries (Healthcare, Consumer Goods)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 India
- 5.5.1.3 Japan
- 5.5.1.4 South Korea
- 5.5.1.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 North America
- 5.5.2.1 United States
- 5.5.2.2 Canada
- 5.5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share(%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Advanced Composites Inc.
- 6.4.2 BASF SE
- 6.4.3 BGF Industries
- 6.4.4 Binani Industries Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Celanese Corporation
- 6.4.6 China Beihai Fiberglass Co. Ltd
- 6.4.7 China Jushi Co. Ltd
- 6.4.8 Chongqing Polycomp International Corp. (CPIC)
- 6.4.9 Gurit Services AG, Zurich
- 6.4.10 Jiuding New Material Co., Ltd
- 6.4.11 Johns Manville
- 6.4.12 Nippon Electric Glass Co.,Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Owens Corning
- 6.4.14 PPG Industries Inc.
- 6.4.15 Reliance Industries Limited
- 6.4.16 SAERTEX GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.17 Scott Bader Company Ltd.
- 6.4.18 The Composite Group
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment
- 7.2 Increasing Applications in Marine Industry










