 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1849943
工业机器人:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Industrial Robotics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
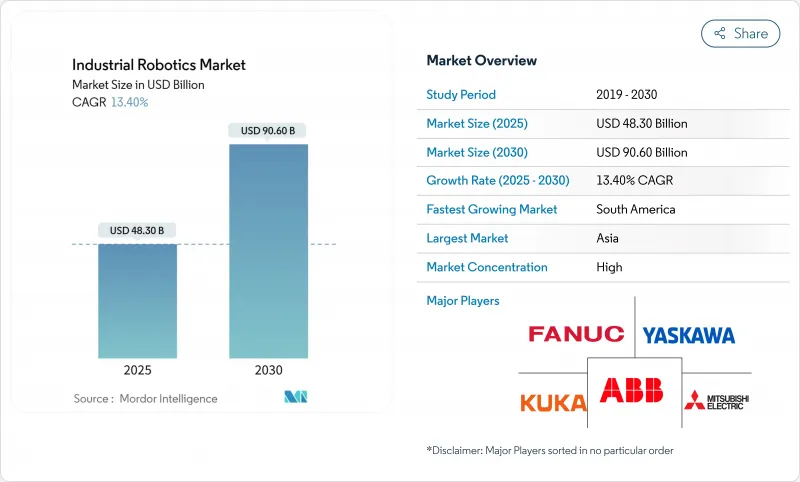
预计到 2025 年,工业机器人市场规模将达到 483 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 906 亿美元,年复合成长率为 13.4%。
人工智慧的快速融合、劳动力短缺的加剧以及关税主导的製造业回流,正将机器人从孤立的自动化工具转变为能够在动盪的供应链中维持生产的中央自适应系统。亚洲对工厂自动化的持续需求、美国不断加快的成本激励措施以及欧洲的永续性指令,共同支撑着即使在宏观经济放缓的情况下,需求週期仍然保持强劲。政府激励措施,例如中国的「十四五」规划和日本的新机器人策略,降低了投资风险,而嵌入式人工智慧和5G网路则提高了整体设备效率。随着协作机器人先驱挑战现有企业,竞争日益激烈,但ABB、发那科、安川电机和库卡等公司的规模优势仍然在工业机器人市场中主导着价格体系和服务预期。
全球工业机器人市场趋势与洞察
人事费用上升和劳动力老化
薪资上涨和劳动力萎缩正促使製造商将曾经依赖大量人力完成的任务自动化。到2024年,日本的机器人密度将达到每万名工人390台,而德国的密度则上升至429台。这清楚地表明,已开发经济体正如何转向机器人以维持生产力。中国製造业薪资的上涨正在改变整体拥有成本(TCO)模式,使得机器人单元的投资回收期比2019年更短。企业也正在对人体工学要求较高的工位部署协作机器人,以留住那些无法再从事重复性搬运工作的经验丰富的员工。机器人执行标准化的工作流程,为下一代员工保留流程记忆,并降低风险。
人工智慧和工业物联网协助智慧工厂快速发展
人工智慧将机器人转变为能够从感测器回馈中学习的自优化资产。 NVIDIA 的 Isaac 平台使西门子等製造商能够开发数位双胞胎,缩短试运行时间,并将计划外停机时间减少高达 30%。机器学习视觉技术无需离线编程即可对新 SKU 进行分类,从而实现电子商务履约中完全相同的换班。边缘运算能够处理高频扭矩数据,并在灾难性故障发生之前预测轴承磨损。这些功能正在将工业机器人市场从简单的重复性操作主导为数据驱动的适应性操作,这对于准时制、多品种工厂至关重要。
中小企业初始投资额高
一套承包的机器人单元成本仍在 5 万至 50 万美元之间,而这还不包括安装期间生产线停机的机会成本。机器人即服务 (Robot-as-a-Service) 将资本支出转化为每月营运费用,但小型企业对多年订阅债务心存顾虑。在新兴市场,商业信贷利差超过两位数,融资压力巨大,公共补贴计画也更倾向大型出口商而非本地製造企业。由于缺乏规模优势来分摊跨多个地点的工程投入,许多中小企业推迟了自动化进程,儘管工业机器人具有潜在的生产力提升空间,但其整体普及速度仍然缓慢。
细分市场分析
到2024年,关节型机器人仍将占据工业机器人市场67%的份额,其六轴灵活性能够支援汽车工厂近乎连续的焊接、喷漆和密封作业。其庞大的装机量确保了备件供应,从而保障了原始设备製造商(OEM)对设备执行时间的承诺。同时,协作机器人占了10.5%的市场份额,年复合成长率(CAGR)为14.0%。整合商目前正将协作机器人安装在自主移动平台上,以创建可重构的工作单元,从而解决多条生产线上的劳动力短缺问题。
轻型机械手臂持续推动成长,实现了先前依赖人工灵巧操作的15公斤以下重物的自动化任务。食品加工商使用卫生级不锈钢协作机器人包装已调理食品,而电子产品组装则能在几分钟内教导机器人新的人工引导式取放点。儘管SCARA机器人和Delta机器人仍然主导着高速取放任务,但由于缺乏内建安全功能,它们的销售成长落后于协作机器人。在整个预测期内,人工智慧驱动的程式设计将降低非熟练工人的操作门槛,确保协作平台继续引领工业机器人市场的销售成长。
到2024年,额定重量在16-225公斤之间的机器人将占据工业机器人市场42%的份额,用于执行诸如汽车底盘焊接、发动机缸体搬运和饮料厂码垛等任务。製造商重视的是有效载荷范围、惯性控制和每公斤承重能力成本之间的平衡。另一方面,由于智慧型手机和医疗设备等零件尺寸不断缩小,需要更高的循环速率和微米级精度,预计到2030年,额定重量≤15公斤的机器人将以15.2%的复合年增长率增长。这些小型机器人结合了真空吸盘和先进的视觉系统,实现了以往自动化系统无法实现的灵活物料搬运。
重量超过226公斤的重型机器人对于铆接航太和精加工大型铸件至关重要,因为目前尚无其他自动化系统可替代。然而,由于高昂的投资支出以及与长期资本财订单相关的需求週期,重型机器人的成长速度较为缓慢。随着力矩感测器和高强度复合材料的出现,机械手臂的重量得以减轻,原本由中型机器人承担的任务正在向轻型机器人转移,从而在不蚕食现有类别核心市场份额的情况下,拓展了轻型机器人市场的潜在机会。
工业机器人市场按机器人类型(例如,关节型机器人、线性机器人、 SCARA机器人、协作机器人)、承重能力(例如,小于15公斤、16-225公斤)、应用领域(例如,物料输送和包装)、终端用户行业(例如,汽车、电气和电子)以及地区进行细分。以上所有细分市场的规模和预测均以美元计价。
区域分析
到2024年,亚洲将占据工业机器人市场70%的收入份额,其中中国已安装276,288台机器人,占全球产量的51%。补贴、国内零件生态系统以及不断上涨的工资水准正在推动这一成长势头。日本凭藉其强大的供应商网路和工业4.0蓝图,保持着每万名工人拥有390台机器人的机器人密度。韩国以超过1,000台的机器人密度位居榜首,这反映了其大型企业集团积极部署智慧工厂的倡议。
南美洲是成长最快的区域,预计复合年增长率将达到11.5%。巴西的肉类加工商和汽车组装纷纷采用机器人来降低人事费用波动并提高出口合规性。墨西哥毗邻美国消费市场,正吸引利用回流奖励的电动车零件製造商。阿根廷正在部署农业包装机器人,以提高加工能力、减少收穫后损失,并为其他市场区隔中树立典范。
北美和欧洲的工业机器人市场虽然已经成熟,但远未饱和。美国在全球排名第十,每万名工人拥有295台机器人,但製造业回流立法和第179条款激励措施正在刺激其持续两位数的成长。德国每万名工人拥有429台机器人,这主要得益于其汽车产业丛集和中小企业出口商,而欧盟的碳中和目标则为节能型机器人开闢了一片市场。中东和非洲的製造商继续走在前列,专注于石化包装生产线和太阳能电池板生产,预示着随着物流基础设施的成熟,工业机器人市场将迎来长期成长。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 劳动成本上升和劳动力老化
- 人工智慧和工业物联网赋能的智慧工厂快速普及
- 政府对自动化领域的资本投资补贴(中国、韩国、德国)
- 关税促使製造业回流美国,刺激美国自动化支出
- ESG推动节能、低碳机器人技术的发展
- 加速折旧规则将推动机器人即服务的发展
- 市场限制
- 中小企业初始投资额高
- 机器人整合人才短缺
- 负责互联生产单元的网路安全
- 稀土元素伺服马达供应波动
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监管格局
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按机器人类型
- 关节机器人
- SCARA机器人
- 直角坐标/龙门机器人
- 并联/ Delta机器人
- 圆柱形机器人
- 协作机器人(cobots)
- 按负载容量
- 15公斤以下
- 16~225kg
- 226~500 kg
- 500公斤以上
- 透过使用
- 物料输送和包装
- 焊接和焊焊
- 组装和配送
- Machine Tending和CNC
- 油漆和涂层
- 品质检验
- 按最终用户产业
- 车
- 电气和电子
- 饮食
- 机械和金属
- 製药和医疗保健
- 建筑材料
- 其他(橡胶、光学)
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 俄罗斯
- 亚洲
- 中国
- 日本
- 韩国
- 印度
- 中东和非洲
- GCC
- 南非
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- ABB Ltd.
- FANUC Corporation
- Yaskawa Electric Corp.
- KUKA AG
- Mitsubishi Electric Corp.
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries(Robotics)
- DENSO Corporation
- Omron/Adept Technologies
- Panasonic Corp.
- Epson Robots
- Staubli Robotics
- Comau SpA
- Yamaha Robotics
- Universal Robots(Teradyne)
- Nachi-Fujikoshi Corp.
- Techman Robot Inc.
- Siasun Robot & Automation
- Doosan Robotics
- Seiko-Epson
- Hanwha Robotics
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The industrial robotics market stands at USD 48.3 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 90.6 billion by 2030, advancing at a 13.4% CAGR.

Rapid integration of artificial intelligence, mounting labor shortages, and tariff-driven reshoring have moved robots from isolated automation tools to central, adaptive systems that keep production running amid volatile supply chains. Asia's sustained appetite for factory automation, the United States' accelerated expensing incentives, and European sustainability mandates together underpin a demand cycle that remains resilient even during macroeconomic slowdowns. Government incentives such as China's 14th Five-Year Plan and Japan's New Robot Strategy continue to lower investment risk while embedded AI and 5G networks lift overall equipment effectiveness. Competitive intensity is growing as collaborative robot pioneers challenge incumbents, yet scale advantages held by ABB, FANUC, Yaskawa, and KUKA still shape price discipline and service expectations in the industrial robotics market.
Global Industrial Robotics Market Trends and Insights
Rising Labor Costs & Ageing Workforce
Escalating wages and shrinking labor pools push manufacturers to automate tasks that once relied on abundant human labor. Japan's robot density reached 390 units per 10,000 workers in 2024, while Germany's density climbed to 429, underscoring how advanced economies lean on robots to preserve productivity China's climb in manufacturing wages has re-tilted total cost of ownership models, making payback periods for robotic cells shorter than in 2019. Companies also deploy collaborative robots in ergonomically demanding stations to retain experienced workers who can no longer perform repetitive lifting. The demographic squeeze simultaneously drives up turnover and erodes tacit knowledge; robots mitigate that risk by executing standardized workflows that preserve process memory for the next generation of employees.
Rapid Adoption of AI & IIoT-Enabled Smart Factories
Artificial intelligence turns robots into self-optimizing assets that learn from sensor feedback. NVIDIA's Isaac platform allows manufacturers such as Siemens to develop digital twins, cut commissioning time, and reduce unplanned downtime by up to 30%. Machine learning vision now classifies new SKUs without offline programming, enabling same-shift changeovers in e-commerce fulfillment. Edge computing processes high-frequency torque data, predicting bearing wear before catastrophic failure, while private 5G networks push control loops closer to actuators. These capabilities transform the industrial robotics market from simple repeatability toward data-driven adaptability, which is critical for just-in-time, high-mix factories.
High Upfront Cap-ex for SMEs
Turnkey robotic cells still cost between USD 50,000 and USD 500,000, and that range excludes opportunity costs from line downtime during installation. While Robot-as-a-Service converts capital outlays into monthly operating expenses, smaller plants remain wary of multi-year subscription liabilities. Financial constraints are tighter in emerging markets where commercial credit spreads exceed double digits, and public subsidy schemes focus on large exporters rather than local job shops. Without scale to amortize engineering effort across multiple sites, many SMEs delay automation, slowing overall penetration of the industrial robotics market despite compelling productivity gains.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Cap-ex Subsidies for Automation
- Tariff-Driven Reshoring Fuels US Automation Spend
- Scarcity of Robot-Integration Talent
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Articulated systems retained 67% share of the industrial robotics market in 2024 as six-axis flexibility supports welding, painting, and sealant application in automotive plants that run near-continuous shifts. Extensive installed bases guarantee spare-parts availability, protecting uptime commitments for OEMs. Meanwhile, collaborative robots held 10.5% share but are riding a 14.0% CAGR, driven by safety-rated force sensors that allow operators to work shoulder-to-shoulder without cages. Integrators now mount cobots on autonomous mobile platforms, creating re-deployable workcells that address labor gaps on multiple lines.
Growth momentum continues as lightweight arms automate tasks below 15 kg that previously relied on manual dexterity. Food processors use hygienic stainless-steel cobots to package ready-to-eat meals, while electronics assemblers teach robots new pick points via hand-guiding within minutes. SCARA and delta robots still dominate high-speed pick-and-place operations, yet their unit growth trails cobots because they lack built-in safety functions. Over the forecast period, AI-powered programming lowers barriers for non-experts, ensuring collaborative platforms remain the vanguard of volume expansion in the industrial robotics market.
Robots rated 16-225 kg captured 42% of the industrial robotics market size in 2024, underpinning automotive under-body welding, engine block handling, and palletizing in beverage plants. Manufacturers appreciate the balance between reach, inertia control, and cost per kilogram of payload. Conversely, the <=15 kg class will post a 15.2% CAGR through 2030 because shrinking component geometries in smartphones and medical devices necessitate micron-level precision at higher cycle rates. Vacuum grippers paired with advanced vision enable these smaller robots to handle flexible materials once thought impossible in automated systems.
Heavy-duty robots above 226 kg remain critical for aerospace fuselage riveting and large casting finishing where no alternative automation exists. However, their growth is modest because investment outlays are higher and demand cycles correlate with long-lead capital goods orders. As force-torque sensors and high-strength composites reduce manipulator weight, tasks once assigned to mid-payload units migrate downward, expanding addressable opportunities for the light segment without cannibalizing core volumes of established categories.
The Industrial Robotics Market is Segmented by Type of Robot (Articulated Robots, Linear Robots, SCARA Robots, Collaborative Robots and More), Payload Capacity (<=15 Kg, 16-225 Kg and More), by Application (Material Handling & Packaging and More), by End-User Industry (Automotive, Electrical & Electronics and More) and Geography. The Market Sizes and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) for all the Above Segments.
Geography Analysis
Asia held 70% revenue share of the industrial robotics market in 2024, underpinned by China's 276,288 installations that equaled 51% of the global total hai-production. Subsidies, domestic component ecosystems, and rising wage levels combine to maintain the momentum. Japan leverages deep supplier networks and Industry 4.0 roadmaps, sustaining a robot density of 390 units per 10,000 workers. South Korea tops density charts above 1,000 units, reflecting aggressive smart-factory roll-outs championed by chaebol conglomerates.
South America represents the fastest-growing bloc with an 11.5% CAGR forecast as Brazilian meat processors and vehicle assemblers introduce robots to rein in labor cost volatility and improve export compliance. Mexico's proximity to US consumer markets attracts EV component makers that capitalize on reshoring incentives. Argentina adopts agricultural packing robots to elevate throughput and reduce post-harvest losses, establishing proof points for other segments within the industrial robotics market.
North America and Europe are mature yet far from saturated. The United States deploys 295 robots per 10,000 workers, placing it tenth globally, but reshoring legislation and Section 179 incentives stimulate sustained double-digit unit growth. Germany's 429-unit density rides on automotive clusters and Mittelstand exporters, while EU carbon-neutrality targets open niches for energy-efficient robot models. Middle East and African manufacturers remain early adopters, focusing on petrochemical packaging lines and increasingly on solar-panel fabrication, indicating long-term upside for the industrial robotics market once logistics infrastructure matures.
- ABB Ltd.
- FANUC Corporation
- Yaskawa Electric Corp.
- KUKA AG
- Mitsubishi Electric Corp.
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries (Robotics)
- DENSO Corporation
- Omron / Adept Technologies
- Panasonic Corp.
- Epson Robots
- Staubli Robotics
- Comau S.p.A.
- Yamaha Robotics
- Universal Robots (Teradyne)
- Nachi-Fujikoshi Corp.
- Techman Robot Inc.
- Siasun Robot & Automation
- Doosan Robotics
- Seiko-Epson
- Hanwha Robotics
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising labor costs & ageing workforce
- 4.2.2 Rapid adoption of AI & IIoT-enabled smart factories
- 4.2.3 Government cap-ex subsidies for automation (China, Korea, Germany)
- 4.2.4 Tariff-driven reshoring fuels US automation spend
- 4.2.5 ESG push for energy-efficient, low-carbon robots
- 4.2.6 Robot-as-a-Service boosted by accelerated depreciation rules
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront cap-ex for SMEs
- 4.3.2 Scarcity of robot-integration talent
- 4.3.3 Cyber-security liabilities in connected production cells
- 4.3.4 Rare-earth servo-motor supply volatility
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE & GROWTH FORECASTS
- 5.1 By Robot Type
- 5.1.1 Articulated Robots
- 5.1.2 SCARA Robots
- 5.1.3 Cartesian/Gantry Robots
- 5.1.4 Parallel/Delta Robots
- 5.1.5 Cylindrical Robots
- 5.1.6 Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
- 5.2 By Payload Capacity
- 5.2.1 <=15 kg
- 5.2.2 16-225 kg
- 5.2.3 226-500 kg
- 5.2.4 >500 kg
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Material Handling & Packaging
- 5.3.2 Welding & Soldering
- 5.3.3 Assembly & Dispensing
- 5.3.4 Machine Tending & CNC
- 5.3.5 Painting & Coating
- 5.3.6 Quality Inspection
- 5.4 By End-user Industry
- 5.4.1 Automotive
- 5.4.2 Electrical & Electronics
- 5.4.3 Food & Beverage
- 5.4.4 Machinery & Metal
- 5.4.5 Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
- 5.4.6 Construction Materials
- 5.4.7 Others (Rubber, Optics)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Russia
- 5.5.4 Asia
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 Japan
- 5.5.4.3 South Korea
- 5.5.4.4 India
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 GCC
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ABB Ltd.
- 6.4.2 FANUC Corporation
- 6.4.3 Yaskawa Electric Corp.
- 6.4.4 KUKA AG
- 6.4.5 Mitsubishi Electric Corp.
- 6.4.6 Kawasaki Heavy Industries (Robotics)
- 6.4.7 DENSO Corporation
- 6.4.8 Omron / Adept Technologies
- 6.4.9 Panasonic Corp.
- 6.4.10 Epson Robots
- 6.4.11 Staubli Robotics
- 6.4.12 Comau S.p.A.
- 6.4.13 Yamaha Robotics
- 6.4.14 Universal Robots (Teradyne)
- 6.4.15 Nachi-Fujikoshi Corp.
- 6.4.16 Techman Robot Inc.
- 6.4.17 Siasun Robot & Automation
- 6.4.18 Doosan Robotics
- 6.4.19 Seiko-Epson
- 6.4.20 Hanwha Robotics
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES & FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment







