 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1850109
收割机:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Harvesting Machinery - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
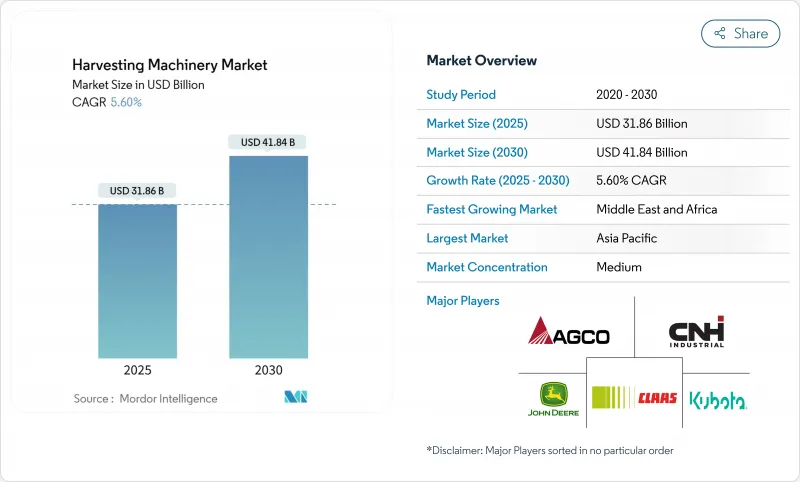
预计到 2025 年,收割机市场规模将达到 318.6 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 418.4 亿美元,预测期内复合年增长率为 5.60%。
机械化进程的稳定推进、精密农业的普及以及减少劳动力依赖的自主化能力的出现,正在推动农业成长。亚太地区仍然是需求中心,而随着补贴和合约收割模式的普及,中东和非洲地区也将快速成长。柴油引擎仍然是主要的动力传动系统多样化,特别是特色作物的兴起,正在拓宽高性能机械的应用范围,并为数据主导服务创造新的收入来源。
全球收割机械市场趋势与洞察
对大容量联合收割机的需求不断增长
在中国和印度,随着大型农业丛集的出现以及政策制定者对现代化设备的补贴,机械化收割正蓬勃发展。使用高效率联合收割机收割大面积作物,可以减少收穫后损失,提高粮食质量,并缩短播种週期。规模、技术和政策的结合有望帮助该地区在中期内保持联合收割机改进的领先地位。
政府奖励加速新兴经济体的机械化进程
公共部门补贴、税收优惠和贷款补贴正在重塑收割机械市场,尤其是在非洲和南美洲部分地区。各国机械化发展蓝图如今将收割机与拖拉机并列为优先事项,认为其对于减少收穫后和实现粮食安全目标至关重要。一些国家将补贴与国内组装选项挂钩,鼓励全球品牌建立散件组装厂,并与当地合作伙伴合作提供售后服务支援。
小农户的初始成本高,收入水准低。
现代联合收割机的价格在30万至50万美元之间。在非洲和南亚,土地所有权分散导致机器利用率低,投资回收期长。巨大的融资缺口加剧了技术普及的差距,催生了老旧、高排放气体次市场。
细分市场分析
联合收割机将在2024年成为收入最高的收割机,占据收割机市场65%的份额。感测模组和自动化系统的不断改进,使得操作员可以将大部分脱粒、分离和清理工作交给软体完成,从而在提高产量的同时节省燃油。成本效益的提案正在推动劳动市场紧张的商业农场对联合收割机的更换需求。人工收割造成的产量损失,以及相关的健康和安全法规,正在推动这些地区对自走式甘蔗收割机的需求。
相较之下,甘蔗收割机虽然数量仍较少,但预计到2030年将以7.5%的复合年增长率成长,因为巴西、印度和泰国正在扩大其机械化甘蔗种植面积。人工收割甘蔗造成的产量损失日益增加,以及健康和安全法规的日益严格,正在推动这些地区采用自走式甘蔗收割机。製造商正在针对窄行、陡坡和潮湿土壤等情况客製化甘蔗收割机型号,并整合远端资讯处理系统,用于报告甘蔗段长度均匀性和抽吸风扇转速。这些针对特定作物的改良措施支撑了其溢价。对乳牛品质至关重要的牧草收割机,随着操作人员升级到具有精确切碎长度控制和青贮接种剂施用器的型号,正保持着中等个位数的增长。
区域分析
亚太地区占全球收割机市场份额的45%,并将于2030年之前继续保持高于全球平均的成长速度。中国土地集约化程度的快速提高以及印度合约收割车队的成长将刺激车队的持续更新。中国各省的补贴政策可报销符合条件的机械设备成本的30%,促使技术选择倾向采用精准导航的机型,以符合国家提高产量的目标。
中东和非洲:中东和非洲是成长最快的地区,儘管目前基数不大,但预计2025年至2030年复合年增长率将达到8%。各国政府优先发展机械化,以确保粮食自给自足并减少收穫后后损失,小农户的损失率可能超过20%。零件进口关税豁免和合作社车队的信贷担保旨在发挥规模效应。中东仍是一个新兴地区,该地区的温室番茄、叶菜类蔬菜和椰枣等作物需要专门的收割机械。投资奖励措施和自由区物流使跨国品牌能够设立区域分销中心,缩短前置作业时间,并确保零件供应。
北美和欧洲合计占全球销售量的四分之一,但两地的车辆更换趋势却截然不同。北美生产商致力于将自动驾驶和互联功能整合到现有车队中,这促使改装套件既能延长车辆寿命,又能提供更先进的功能。而欧洲则在严格的排放法规和通用农业政策奖励的推动下,加速采用混合动力和电动车。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 对大容量联合收割机的需求不断增长
- 政府奖励加速新兴经济体的机械化进程
- 劳动力短缺和工资上涨正在推动自动化
- 拓展合约收割经营模式
- 将精密农业和远端资讯处理技术整合到收割机中
- 原厂融资和租赁方案可减轻资本支出负担
- 市场限制
- 与小农户的收入水准相比,前期投入成本较高。
- 商品价格波动导致机械设备采购放缓
- 在中东和非洲的经销商和服务网络有限
- 柴油排放气体引发的环境问题
- 波特五力模型
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按机器类型
- 结合
- 饲料收割机
- 其他收割机(甘蔗收割机、马铃薯收割机、甜菜收割机、棉花收割机等)
- 透过动力来源
- 柴油引擎
- 油电混合/电动车
- 按作物类型
- 谷物和谷类
- 饲料作物
- 园艺作物
- 特色作物(甘蔗、棉花等)
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地区
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 亚太其他地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 土耳其
- 南非
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial NV
- AGCO Corporation
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- Kubota Corporation
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.
- Yanmar Co., Ltd.
- SDF Group(Same Deutz-Fahr)
- Tractors & Farm Equipment Ltd.
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Harvesting Equipment Market size is estimated at USD 31.86 billion in 2025, and is anticipated to reach USD 41.84 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.60% during the forecast period.

Growth is propelled by steady mechanization, the spread of precision agriculture, and the arrival of autonomous functions that reduce labor dependence. The Asia-Pacific remains the center of demand, while the Middle East and Africa post the quickest gains as subsidy programs and contract-harvesting models take hold. Diesel engines still dominate powertrains, yet double-digit growth for hybrid and electric solutions signals an important transition that aligns with tightening emissions rules. Crop diversification, particularly the rise of specialty crops, is broadening the application base for sophisticated machinery and creating new revenue streams for data-driven service offerings.
Global Harvesting Machinery Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand for High-Capacity Combine Harvesters
Mechanical harvesting is gaining momentum across China and India as larger farm clusters emerge and policymakers channel subsidies toward modern equipment. Broad-acre crops harvested with high throughput combine lower post-harvest losses, improve grain quality, and shorten turnaround times between planting cycles. This confluence of scale, technology, and policy is projected to maintain the region's leadership in combined upgrades through the medium term.
Government Incentives Accelerating Mechanization in Developing Economies
Public-sector grants, tax rebates, and subsidized loans are reshaping the harvesting equipment market, particularly in Africa and parts of South America. National mechanization roadmaps now prioritize harvesters alongside tractors, viewing them as essential to post-harvest loss reduction and food-security targets. Several countries are linking subsidies to domestic assembly conditions, nudging global brands to establish knock-down facilities and engage local partners for after-sales support.
High Upfront Cost Versus Small-Farm Income Levels
Modern combines can cost between USD 300,000 and USD 500,000, a figure beyond the reach of most smallholders. Fragmented land holdings in Africa and South Asia dilute machinery utilization rates and elongate payback periods. Acute financing gaps widen technology adoption divides and sustain a secondary market for aging, high-emission machines that underperform on fuel and grain quality.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Labor Scarcity And Wage Inflation Are Pushing Automation
- Integration of Precision Agriculture and Telematics into Harvesters
- Limited Dealer and Service Networks in Africa and the Middle East
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Combine harvesters generated the highest revenue in 2024, accounting for 65% of the harvesting equipment market. Continuous improvements in sensing modules and automation packages now enable operators to delegate most threshing, separation, and cleaning adjustments to software, which raises throughput while conserving fuel. The cost-benefit proposition drives replacement demand among commercial farms facing tighter labor markets. Rising yield penalties from manual cutting, plus health and safety rules, strengthen the case for self-propelled cane machines in these regions.
In contrast, sugar-cane harvesters, though smaller in volume, are forecast to post a 7.5% CAGR to 2030 as Brazil, India, and Thailand expand the acreage under mechanized cane. Rising yield penalties from manual cutting, plus health and safety rules, strengthen the case for self-propelled cane machines in these regions. Manufacturers tailor sugar-cane models for narrow-row layouts, steep slopes, and wetter soils, integrating telematics that report billet length uniformity and extractor-fan speed. Such crop-specific refinements support premium pricing. Forage harvesters, essential for dairy ration quality, maintain mid-single-digit growth as operators upgrade to models with precision chop length control and silage-inoculant applicators.
The Harvesting Machinery Market Report is Segmented by Machinery Type (Combine Harvester, Forage Harvester, and More), by Power Source (Diesel and Hybrid/Electric), by Crop Type (Grains and Cereals, Forage Crops, and More), and by Geography (North America, Europe, South America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific anchors 45% of the harvesting equipment market and continues to outpace global averages through 2030. Rapid consolidation of cropland in China and growing contract-harvesting fleets in India stimulate continual fleet renewal. Provincial subsidies in China reimburse up to 30% of eligible machine costs, influencing technology choices toward models with precision guidance that aligns with national yield-improvement targets.
Middle East and Africa, while representing a modest base today, is the fastest-growing region at an 8% CAGR between 2025 and 2030. Governments prioritize mechanization to secure grain self-sufficiency and reduce post-harvest losses that can exceed 20% in smallholder systems. Import-duty waivers on components and credit guarantees for cooperative fleets aim to leverage scale effects. The Middle East remains an emerging locale where controlled-environment agriculture and government-backed desert farming require specialized harvesters for greenhouse tomatoes, leafy greens, and date palms. Investment incentives and free-zone logistics encourage multinational brands to position regional distribution hubs, closing lead-time gaps and fostering parts availability.
North America and Europe contribute a combined quarter of global sales but differ in replacement dynamics. North American growers focus on integrating autonomy and connectivity into existing fleets, leading to a rise in retrofit kits that extend asset life while delivering advanced functionality. Europe, guided by stringent emissions rules and Common Agricultural Policy incentives, accelerates the adoption of hybrid and electric units.
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- AGCO Corporation
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- Kubota Corporation
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.
- Yanmar Co., Ltd.
- SDF Group (Same Deutz-Fahr)
- Tractors & Farm Equipment Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising demand for high-capacity combine harvesters
- 4.2.2 Government incentives accelerating mechanization in developing economies
- 4.2.3 Labor scarcity and wage inflation are pushing automation
- 4.2.4 Expansion of contract-harvesting business models
- 4.2.5 Integration of precision agriculture and telematics in harvesters
- 4.2.6 OEM financing and leasing programmes easing capital expenditures burden
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront cost versus small-farm income levels
- 4.3.2 Volatility in commodity prices dampening machinery purchases
- 4.3.3 Limited dealer and service networks in Africa and the Middle East
- 4.3.4 Environmental concerns over diesel emissions
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value and Volume)
- 5.1 By Machinery Type
- 5.1.1 Combine Harvesters
- 5.1.2 Forage Harvesters
- 5.1.3 Other Harvesters (Sugarcane Harvesters, Potato Harvesters, Beet Harvesters, Cotton Harvesters, etc.)
- 5.2 By Power Source
- 5.2.1 Diesel
- 5.2.2 Hybrid/Electric
- 5.3 By Crop Type
- 5.3.1 Grains and Cereals
- 5.3.2 Forage Crops
- 5.3.3 Horticultural Crops
- 5.3.4 Speciality Crops (Sugarcane, Cotton, and Others)
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Spain
- 5.4.2.5 Russia
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 UAE
- 5.4.5.3 Turkey
- 5.4.5.4 South Africa
- 5.4.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Deere & Company
- 6.3.2 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.3.3 AGCO Corporation
- 6.3.4 CLAAS KGaA mbH
- 6.3.5 Kubota Corporation
- 6.3.6 Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.
- 6.3.7 Yanmar Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.8 SDF Group (Same Deutz-Fahr)
- 6.3.9 Tractors & Farm Equipment Ltd.









