 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1850286
农场管理软体:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Farm Management Software - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
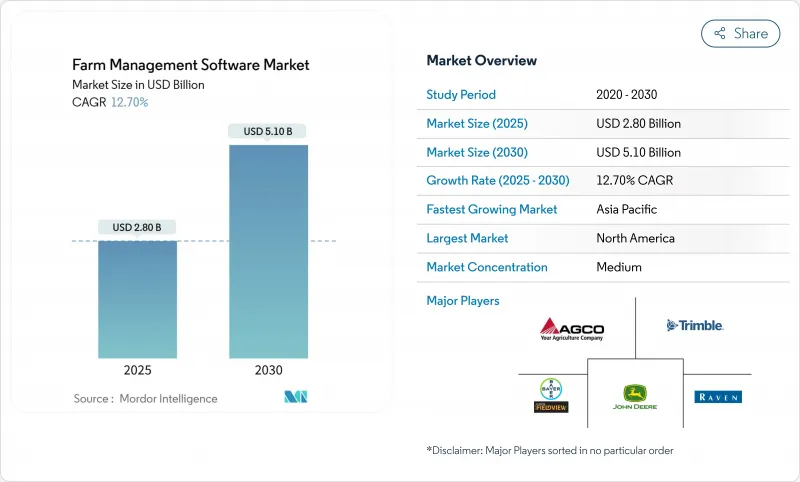
预计到 2025 年,农场管理软体市场规模将达到 28 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 51 亿美元,年复合成长率为 12.70%。
全球农业面临多重压力,推动了两位数的强劲成长:结构性农业劳动力短缺、耕地面积减少、气候相关的生产风险,以及下游买家对永续性指标的检验需求。云端交付平台占据了目前部署的大部分份额,因为它们可以降低前期投资成本、实现自动升级,并支援各种规模农场即时整合感测器、机械、卫星和气象数据。虽然精密农业仍然是主要应用场景,但水产养殖软体的成长速度最快,因为对永续蛋白质的需求促使生产者转向数据主导的水质和饲料效率管理。亚太地区是成长最快的地区,这得益于大规模的公共数位农业项目,而北美地区凭藉早期采用的优势和成熟的经销商支持网络,仍然是收入领先者。设备製造商、投入品供应商和新兴企业正在建立开放API生态系统,以产生持续的订阅收入,并竞相将农场管理软体市场定位在更广泛的农业技术体系的核心位置。
全球农场管理软体市场趋势与洞察
农业劳动力短缺和耕地减少正在推动农业机械化。
农场管理软体作为数位骨干,协调自动驾驶拖拉机、机器人收割机和精准喷药机,从而实现全天候运作,且人事费用低于传统人工。 Bluewhite 的售后自动化套件透过云端控制面板进行集成,可规划设备路线并近乎即时地监控机器运行状况,从而展现出整个作业季的投资回报。随着土地资源日益稀缺,种植者利用基于精细地理空间分析的变数施肥方案,最大限度地提高单位面积产量。全球收割自动化倡议旨在十年内实现美国一半特种作物收割的机械化。这目标的前提是广泛部署资料编配平台,以便在动态的田间条件下同步多个自主单元。劳动力短缺和土地稀缺的双重困境,使得农场管理软体市场成为关键基础设施,而非可有可无的技术。
精密农业技术的快速整合创造了平台需求
农场感测器、无人机影像和机器遥测技术的爆炸性增长正在产生Petabyte的数据。早期采用变数播种结合感测器驱动的施肥调整技术的农户报告称,在保持产量的同时,农药和养分用量最多可节省80%,软体订阅成本可在两年内收回。农场管理平台正日益成为整合中心,将土壤湿度探头、气象站和引擎CAN总线资料整合到一个统一的控制面板中。约翰迪尔的「See and Spray」技术已在超过一百万英亩的土地上部署,证明演算法定向喷洒可以减少除草剂的使用,同时降低碳排放。欧盟已累计「地平线欧洲」计画的资金,用于在2024年至2027年间将类似的数位基础设施扩展到27.4万个农场。随着硬体多样性的增加,基于开放API的农场管理软体自然成为控制中心。
小农户的主导地位限制了软体投资报酬率
小农户耕种面积占全球农业用地面积的80%,但耕地面积通常不到5公顷,收入不足以支付综合软体订阅费用。撒哈拉以南非洲的纵向研究表明,信贷取得、数位素养和推广支持是技术采纳的关键驱动因素,任何一个因素的缺失都会减缓采纳速度。肯塔基州的一项研究证实了耕地面积与精准农业技术采纳之间存在正相关关係,而老农户即使被告知成本效益,仍然抵制数位化介面。拉丁美洲的评估报告指出,根深蒂固的文化习俗和不稳定的网路连结也是阻碍技术采纳的因素。因此,农场管理软体市场将呈现两极化的成长模式:一方面,大型商业生产者的需求强劲;另一方面,以自给自足为导向的小农户(他们在亚洲和非洲的粮食系统中占据主导地位)的采纳速度较慢。
细分市场分析
云端部署将在2024年创造最大收益,占据农场管理软体市场52%的份额,当年达到14.6亿美元,并预计到2030年将以17.40%的复合年增长率成长。在云端环境中,软体即服务(SaaS)订阅模式占据主导地位。自动更新消除了停机时间,而多租户架构则将固定成本分摊到数千用户身上。虽然本地和基于Web的系统仍然服务于那些对资料主权有严格要求的公司,但区域频宽的升级正在缩小这个市场。约翰迪尔的营运中心展示了云端聚合如何实现单一租户本地部署无法实现的跨农场基准化分析。包括现场级加密和多因素身份验证在内的日益成熟的安全通讯协定,也缓解了先前用户对云端技术的犹豫。
由于机器学习演算法会随着资料量的增加而变得更加精准,网路效应放大了云端运算的价值。一个基于500万个匿名样本训练的土壤有机碳预测工具,可将实验室检测成本降低60%,使用户无需离开原有生态系统即可受益。受平台即服务(PaaS)层驱动的农场管理软体市场规模预计将在2030年前持续成长,因为独立开发者会部署微服务(例如,在地化灌溉调度器),这些微服务无需大量编码即可连接到综合仪表板。现今,供应商之间的竞争主要围绕着开放API库和第三方应用收益分成框架展开,这使得云端运算模式的战略意义日益凸显。
区域分析
北美仍是最大的收入贡献者,占市场份额的34%。这部分归功于当地田间设备已具备遥测功能,且平台启动简便。美国农业部「气候智慧型商品」配额政策推动了对合规模块的需求,经销商网路也提供现场培训以弥补技能缺口。玉米带地区企业的云端渗透率超过70%,农场将2-5%的收入用于数位化工具,巩固了该地区的市场主导地位。随着早期采用者逐渐饱和市场,成长将放缓至11.10%的复合年增长率,但特种作物和再生农业实践检验领域仍有成长机会。
亚太地区以16.20%的复合年增长率引领全球成长,这得益于中国、印度和东南亚国家政策支持的数位化项目。印度耗资64亿美元的「数位农业计画」旨在整合覆盖400个地区的感测器数据和卫星影像,从而有效地为数千万小农户承担平台费用。中国各省的试点计画正在将农业软体融入金融服务流程,使投入贷款与检验的产量预测挂钩。儘管整体农业食品科技领域的资金筹措有所萎缩,但创投仍保持韧性,预计2024年,区域农业软体新兴企业将筹集3亿美元资金。然而,农场规模通常小于5公顷,限制了技术的规模化应用。每月30美元的套餐费用往往超过农场净收入,减缓了自给自足型农民的接受度。
欧洲9.40%的复合年增长率反映了精准农业技术的持续成熟应用,这主要得益于通用农业政策中关于数位化记录保存的规定。 「地平线欧洲」津贴拨款7亿欧元(约8.03亿美元)用于精密农业试点项目,这些项目需要一个整合的软体平台。法国的「大规模田间倡议」等国家计画将设备补贴与强制性数据共用框架结合,进一步巩固了开放标准平台。小型家庭农场面临传承方面的挑战,因此需要支持能够简化代际知识传承的数位化工具。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 农业劳动力短缺和耕地减少
- 快速整合精密农业技术
- 政府数位农业奖励和补贴
- 对即时农业决策支援的需求
- 透过FMS平台实现碳信用货币化
- 一个开放的 API 生态系统,可建立超级应用农场平台
- 市场限制
- 小农场的优势
- 软体、硬体和培训的前期成本很高
- 农民的资料隐私和网路安全问题
- 农村地区农业资料科学人才短缺
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按类型
- 本地/网路
- 云端基础的
- Software as a Service(SaaS)
- Platform as a Service(PaaS)
- 透过使用
- 精密农业
- 牲畜监测
- 智慧温室
- 水产养殖
- 其他用途
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 亚太其他地区
- 中东
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 土耳其
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 肯亚
- 其他非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Trimble Inc.
- Climate LLC.(Bayer AG)
- Farmers Edge Inc.
- Deere & Company
- AGCO Corporation
- Raven Industries(CNH Industrial)
- Topcon Corp.
- AGRIVI Ltd.
- CropX Technologies Ltd.
- Traction Ag Inc.
- SemiosBio Technologies
- CropZilla Software Inc.
- BASF Digital Farming GmbH(BASF SE)
- Ag Leader Technology(Ag Leader)
- Eagle IoT(Bentley Systems)
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The farm management software market size is valued at USD 2.80 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 5.10 billion by 2030, expanding at a 12.70% CAGR.

Solid double-digit growth stems from converging pressures on global agriculture: structural farm-labor shortages, shrinking arable land, climate-induced production risk, and the need to verify sustainability metrics for downstream buyers. Cloud-delivered platforms dominate current deployments because they lower upfront capital outlays, automate upgrades, and allow farms of every size to integrate sensor, machine, satellite, and weather data in real time. Precision farming remains the primary use case, yet aquaculture software is registering the fastest growth as demand for sustainable protein pushes producers toward data-driven water-quality and feed-efficiency management. Asia-Pacific is the highest-growth region thanks to large-scale public digital-agriculture programs, while North America remains the revenue leader on the strength of early adoption and entrenched dealer support networks. Competitive intensity is rising as equipment manufacturers, input suppliers, and start-ups race to build open-API ecosystems that lock in recurring subscription revenue and position the farm management software market at the center of the broader ag-tech stack.
Global Farm Management Software Market Trends and Insights
Farm-Labor Shortage and Decreasing Arable Land Push Mechanization
Farm management software acts as the digital backbone that coordinates autonomous tractors, robotic harvesters, and precision sprayers, allowing 24-hour operation with lower labor costs than traditional crews. Bluewhite's aftermarket autonomy kits demonstrate a full season payback when integrated through cloud dashboards that schedule equipment routes and monitor near-real-time machine health. As land availability tightens, producers maximize yield per acre through variable rate prescriptions driven by detailed geospatial analytics. The Global Harvest Automation Initiative targets mechanizing half of the United States specialty-crop harvesting within a decade, a goal that presumes wide deployment of data-orchestrating platforms able to synchronize multiple autonomous units across dynamic field conditions. The intersection of labor shortages and land pressure cements the farm management software market as critical infrastructure rather than optional technology.
Rapid Integration of Precision-Agriculture Technologies Creates Platform Demand
The explosive growth of on-farm sensors, drone imagery, and machine telemetry generates petabytes of data that must be harmonized before it can guide timely field decisions. Early adopters who combined variable rate seeding with sensor-driven fertilizer adjustments reported pesticide and nutrient savings up to 80% while maintaining yield, enabling two-year payback periods on software subscriptions. Farm management platforms increasingly serve as integration hubs, merging soil-moisture probes, weather stations, and engine CAN bus feeds into cohesive dashboards. John Deere's See and Spray technology, deployed on more than 1 million acres, underscores how algorithm-controlled targeting slashes herbicide use while simultaneously reducing carbon footprint. The European Union earmarked Horizon Europe funds to extend similar digital infrastructure to 274,000 farms between 2024 and 2027, amplifying demand for software layers that maintain data interoperability across mixed fleets and vendor ecosystems. As hardware diversity expands, open-API-oriented farm management software becomes the natural control center.
Dominance of Smallholder Farms Limits Software Return on Investment
Smallholders account for 80% of global farm holdings, yet often cultivate plots under five hectares, generating revenue insufficient to offset comprehensive software subscriptions. Longitudinal studies in Sub-Saharan Africa show that credit access, digital literacy, and extension support are decisive factors in technology uptake, and deficits in any one dimension derail adoption. Surveys in Kentucky confirm positive correlations between acreage and precision-tech adoption, while older farmer demographics resist digital interfaces even after cost-benefit explanations. Latin American evaluations highlight entrenched cultural practices and unreliable connectivity as additional barriers. Consequently, the farm management software market sees bifurcated growth, with robust demand from large commercial growers and slower penetration among subsistence-oriented smallholders that dominate food systems in Asia and Africa.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Digital-Agriculture Incentives Accelerate Platform Adoption
- Demand for Real-Time Agronomic Decision Support Drives Platform Sophistication
- High Upfront Software, Hardware, and Training Costs Create Adoption Barriers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Cloud deployment registered the largest 2024 revenue and held 52% of the farm management software market share, translating to USD 1.46 billion that year, and is forecast to expand at a 17.40% CAGR through 2030. Within the cloud, Software-as-a-service subscriptions dominate because automatic updates eliminate downtime, and multi-tenant architecture spreads fixed costs over thousands of users. Local and web-based systems continue to serve enterprises with strict data sovereignty requirements, yet bandwidth upgrades across rural corridors shrink that niche. John Deere's Operations Center illustrates how cloud aggregation allows cross-farm benchmarking that single-tenant local deployments cannot match. Security protocols have matured to include field-level encryption and multi-factor authentication, easing earlier adoption hesitations.
Network effects amplify the value of the cloud because machine-learning algorithms grow more accurate as data volumes compound. A soil-organic-carbon predictor trained on 5 million anonymized samples cut lab-testing costs by 60%, an advantage that keeps users inside the originating ecosystem. The farm management software market size attributed to Platform as a Service layer is projected to climb through 2030 as independent developers roll out micro-services, for example, localized irrigation schedulers, that plug into overarching dashboards without heavy coding requirements. Vendor competition now centers on open-API libraries and revenue-sharing frameworks for third-party apps, reinforcing the cloud model's strategic importance.
The Farm Management Software Market is Segmented by Type (Local/Web-based and Cloud-Based), Application (Precision Farming, Livestock Monitoring, Smart Greenhouse, Aquaculture, and Other Applications), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America remains the largest revenue contributor, accounting for 34% in market revenue, in part because field equipment already arrives telemetry-ready, making platform activation straightforward. The USDA's Climate-Smart Commodities allocations drive demand for compliance modules, while dealer networks provide on-site training that bridges skill gaps. Cloud penetration exceeds 70% among corn belt enterprises, and farms devote 2-5% of revenue to digital tools, cementing the region's primacy. Growth moderates to 11.10% CAGR because early adopters saturate the market, yet opportunities persist in specialty crops and regenerative-practice verification.
Asia-Pacific propels global growth with a 16.20% CAGR and benefits from policy-backed digitalization programs in China, India, and Southeast Asian nations. India's USD 6.40 billion Digital Agriculture Mission aims to integrate sensor data and satellite imagery across 400 districts, effectively underwriting platform costs for tens of millions of smallholders. Chinese provincial pilots embed farm software into financial services workflows, enabling input loans contingent on verified yield forecasts. Venture investment remained resilient, with regional farm-software start-ups raising USD 300 million in 2024 despite broader agrifood-tech funding contraction. Nevertheless, sub-five-hectare farm structures constrain addressable penetration; packages priced at USD 30 per month often exceed net farm income, explaining slower uptake among subsistence operators.
Europe's 9.40% CAGR reflects consistent but mature adoption, bolstered by Common Agricultural Policy stipulations for digital record keeping. Horizon Europe grants channel EUR 700 million (USD 803 million) into precision-farming pilots that require integrated software backbones. National programs such as France's Large-Scale Field Demo initiative couple equipment subsidies with mandatory data-sharing frameworks, further entrenching open-standards platforms. Smaller family farms face succession challenges, and digital tools that simplify multi-generational knowledge transfer gain traction.
- Trimble Inc.
- Climate LLC. (Bayer AG)
- Farmers Edge Inc.
- Deere & Company
- AGCO Corporation
- Raven Industries (CNH Industrial)
- Topcon Corp.
- AGRIVI Ltd.
- CropX Technologies Ltd.
- Traction Ag Inc.
- SemiosBio Technologies
- CropZilla Software Inc.
- BASF Digital Farming GmbH (BASF SE)
- Ag Leader Technology (Ag Leader)
- Eagle IoT (Bentley Systems)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Farm-labor shortage and decreasing arable land
- 4.2.2 Rapid integration of precision-agriculture technologies
- 4.2.3 Government digital-agriculture incentives and subsidies
- 4.2.4 Demand for real-time agronomic decision support
- 4.2.5 Monetization of carbon credits through FMS platforms
- 4.2.6 Open-API ecosystems enabling super-app farm platforms
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Dominance of smallholder farms
- 4.3.2 High upfront software, hardware and training costs
- 4.3.3 Farmer data-privacy and cyber-security concerns
- 4.3.4 Shortage of ag-data science talent in rural areas
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Local/Web-based
- 5.1.2 Cloud-based
- 5.1.2.1 Software as a Service (SaaS)
- 5.1.2.2 Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Precision Farming
- 5.2.2 Livestock Monitoring
- 5.2.3 Smart Greenhouse
- 5.2.4 Aquaculture
- 5.2.5 Other Applications
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Mexico
- 5.3.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.3.2 South America
- 5.3.2.1 Brazil
- 5.3.2.2 Argentina
- 5.3.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.3 France
- 5.3.3.4 Spain
- 5.3.3.5 Russia
- 5.3.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4.1 China
- 5.3.4.2 India
- 5.3.4.3 Japan
- 5.3.4.4 Australia
- 5.3.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.5 Middle East
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 Turkey
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.3.6 Africa
- 5.3.6.1 South Africa
- 5.3.6.2 Kenya
- 5.3.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes global overview, market-level overview, core segments, financials as available, strategic information, market rank/share, products and services, and recent developments)
- 6.4.1 Trimble Inc.
- 6.4.2 Climate LLC. (Bayer AG)
- 6.4.3 Farmers Edge Inc.
- 6.4.4 Deere & Company
- 6.4.5 AGCO Corporation
- 6.4.6 Raven Industries (CNH Industrial)
- 6.4.7 Topcon Corp.
- 6.4.8 AGRIVI Ltd.
- 6.4.9 CropX Technologies Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Traction Ag Inc.
- 6.4.11 SemiosBio Technologies
- 6.4.12 CropZilla Software Inc.
- 6.4.13 BASF Digital Farming GmbH (BASF SE)
- 6.4.14 Ag Leader Technology (Ag Leader)
- 6.4.15 Eagle IoT (Bentley Systems)









