 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1850306
可再生能源复合材料:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Composite Materials In Renewable Energy - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
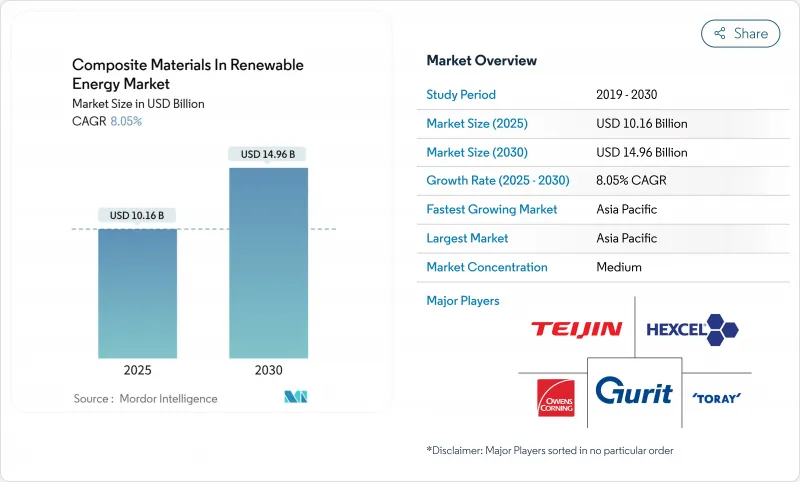
预计到 2025 年,可再生能源复合材料市场规模将达到 101.6 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 149.6 亿美元,年复合成长率为 8.05%。
风能、太阳能和氢能计划的快速产能扩张,对更轻、更坚固的结构提出了更高的要求,以延长零件寿命并减少碳排放。政府的清洁能源政策、可回收热塑性平台的兴起,以及对能够承受恶劣海上和沙漠气候的轻量材料的需求,都在加速采购週期。自动化纤维铺放、3D列印和其他工业4.0製程正在缩短生产週期并减少废料。同时,垂直整合的供应商正在将纤维纺丝、树脂配製和零件製造相结合,以确保在供应链紧张的情况下获得关键原材料。这些因素的交汇有望推动可再生能源复合材料在未来十年实现稳定、创新主导的成长。
全球可再生能源复合材料市场趋势与洞察
比金属结构更轻
在离岸风力发电、氢气罐和潮汐发电设备领域,复合材料的替代可以减轻结构质量,提高负载效率并简化运输物流。潮汐叶片重量减轻13.76%,与钢製替代方案相比,功率输出提高了46.1%。在航太领域,无内衬V形碳复合材料储槽的开发支援向液氢推进的过渡,间接增加了对可再生级纤维的需求。三菱化学的C/SiC陶瓷基质复合材料可承受1500°C的高温,为定日镜接收器和核融合反应器硬体的应用铺平了道路。这些进展凸显了为什么在高温、高腐蚀性环境中,可再生能源领域的复合材料正在不断取代铝和钢。
对更长风力发电机叶片的需求不断增长
西门子能源公司21兆瓦原型机转子直径达276米,显示叶片长度接近150米时,需要使用碳纤维翼梁帽才能达到玻璃纤维无法达到的刚度重量比目标。采用高韧性环氧树脂黏合的分段式叶片结构,既便于运输,又能保持气动弹性完整性。 ZEBRA联盟利用阿科玛公司的Elium树脂,完成了全球最大的完全可回收热塑性叶片,证明了闭合迴路平台的工业化应用已准备就绪。混合积层法,即天然纤维和合成纤维的混合,提高了抗衝击性并降低了体积碳含量。
高昂的研发和模具成本
自动化纤维铺放生产线每条造价500万至1000万美元,而用于生产100米以上叶片的模具每套造价超过200万美元,这意味着在投资回收期到来之前,企业需要投入数年资金。认证课程通常需要五到七年,这会加剧中型创新企业的流动资金压力。 Hexcel公司计划在2025年发行3亿美元债券,这便是其维持製程技术领先地位所需雄厚财力的一个例证。热塑性塑胶的生产成本较高,是因为其烘箱、压机和焊接设备与热固性塑胶生产线截然不同。
细分市场分析
到2024年,玻璃纤维增强复合材料(GFRP)将占可再生能源复合材料市场55.25%的份额,成为该细分市场最大的收入贡献者。碳纤维的复合年增长率(CAGR)为8.62%,这主要反映了转子直径超过120米的市场需求,因为在这些应用中,碳纤维的刚度和疲劳性能使其5-10倍的成本溢价是合理的。 SGL Carbon公司签订的80公尺以上叶片的供应合约表明,碳纤维的应用正从航太垂直扩展到能源领域。混合玄武岩纤维和天然纤维的纤维混铺层积层法,在保持所需模量的同时降低了体积碳含量,从而拓展了中型涡轮机的选择范围。德国对生物基木质素纤维的研究虽然目前商业性规模有限,但具有未来降低成本的潜力。透过机械回收,再生碳纤维可以保留其60-70%的原始拉伸强度,这种再生碳纤维正被逐步应用于二次结构中,从而实现原料多样化并降低原材料价格波动。
由于环氧树脂拥有成熟的供应链和优异的抗疲劳性能,预计到2024年,其市占率将维持在45.86%。然而,随着原始设备製造商(OEM)竞相满足循环经济的需求,生物基和再生树脂的年可再生材料含量高达35%。热塑性基材(例如Elium)还具有可修復性和熔融回收性等优势,推动可再生能源复合材料朝向闭合迴路经济模式发展。
区域分析
至2024年,亚太地区将占可再生能源复合材料市场规模的44.68%,并在2030年之前以8.12%的复合年增长率成长。中国以端到端的供应链支持该地区的发展,但2024年实施的回收标准将增加合规成本,这将有利于当地的一体化企业。印度24亿美元的氢能计画和国防领域对碳纤维的大力投入将增强国内生产的奖励。日本的钙钛矿蓝图旨在2040年利用柔性复合材料基板实现38.3吉瓦的装置容量,这可能是重塑全球太阳能组件架构的关键因素。韩国正利用其造船技术进军离岸风电复合材料领域,而澳洲正在内陆水库上测试浮体式太阳能,展现了该地区终端应用案例的多样性。
北美地区受益于《通膨抑制法案》提供的3,690亿美元资金筹措,而在地化奖励政策则刺激了德克萨斯州、纽约州和安大略省的工厂扩张。通用电气Vernova公司投资6亿美元的製造扩张项目便是将生产迁回国内以降低跨太平洋物流风险的一个例子。加拿大的航太复合材料丛集正协助其从高压釜转型至潮汐涡轮机外壳生产,而墨西哥具有成本竞争力的劳动力资源正吸引拉挤成型企业前来生产太阳能支架出口产品。该地区面临的挑战是扩大纺织品生产规模,以避免过度依赖进口,而多家合资企业的目标是在2027年前弥合这一缺口。
欧洲正利用其监管影响力引导全球在可回收性和体积碳排放方面的标准。 ZEBRA计划热塑性叶片的成功使欧洲大陆成为该领域的技术领导者。德国的木质素纤维试点生产线代表研发领域的领先地位,而法国则正利用其航太的传统优势来改善高模量预浸料。英国国家复合材料中心的SusWIND计画正在检验多种回收途径,并为原始设备製造商(OEM)提供设计弹性。北海和波罗的海离岸风力发电的建设正在推动纤维需求的持续成长,但不断上涨的能源成本迫使企业采用自动化技术来确保利润。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 与金属结构相比,重量更轻
- 对更长寿命风力发电机叶片的需求不断增长
- 政府关于引入可再生能源的意图
- 热塑性可回收叶片平台的商业化
- 3D列印复合材料零件在浮体式太阳能和潮汐能装置的应用日益广泛
- 市场限制
- 高额研发与工具投资
- 回收和掩埋合规成本
- 人们对某些复合材料的耐久性和耐火性表示担忧
- 价值链分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争程度
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 依纤维类型
- 玻璃纤维增强塑胶(GFRP)
- 碳纤维增强塑胶(CFRP)
- 纤维增强聚合物(FRP)
- 其他纤维类型(例如,混纺织物和其他纤维)
- 树脂基
- 环氧树脂
- 聚酯纤维
- 聚氨酯
- 热塑性塑料
- 生物树脂和再生树脂
- 透过製造工艺
- 真空喷射
- 预浸料/高压釜
- 拉挤成型
- 自动化纤维铺放/3D列印
- 压缩成型(SMC、BMC)
- 透过使用
- 风力
- 太阳能发电
- 水力发电
- 其他应用(绿氢能和储能)
- 按地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 亚太其他地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 其他欧洲地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 亚太地区
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率(%)/排名分析
- 公司简介
- Changzhou Tiansheng New Materials Co. Ltd
- EPSILON Composite SAS
- EURO-COMPOSITES
- Evonik Industries AG
- Exel Composites
- GE Vernova
- Gurit Services AG
- Jiangsu Hengshen Co.,Ltd
- Hexcel Corporation
- HS HYOSUNG ADVANCED MATERIALS
- LM WIND POWER
- Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation
- Norco Composites & GRP
- Owens Corning
- Plastic Reinforcement Fabrics Ltd
- SGL Carbon
- Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, SAU
- Solvay
- TEIJIN LIMITED
- TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The composite materials in the renewable energy market were valued at USD 10.16 billion in 2025 and are forecast to expand at an 8.05% CAGR, reaching USD 14.96 billion by 2030.

Rapid capacity additions in wind, solar, and hydrogen projects demand lighter, stronger structures that extend component lifetimes and shrink carbon footprints. Government clean-energy mandates, breakthroughs in recyclable thermoplastic platforms, and the need for lightweight materials that endure harsh offshore and desert climates combine to accelerate procurement cycles. Automated fibre placement, 3D printing, and other Industry 4.0 processes are compressing production timelines while trimming manufacturing scrap. At the same time, vertically integrated suppliers are consolidating fibre spinning, resin synthesis, and part fabrication to secure critical inputs amid supply-chain tension. These intersecting forces position the composite materials in the renewable energy market for a decade of steady, innovation-driven growth.
Global Composite Materials In Renewable Energy Market Trends and Insights
Reduced Weight Versus Metallic Structures
Composite substitution cuts structural mass in offshore wind, hydrogen tanks, and tidal devices, boosting payload efficiency and easing transport logistics. Weight savings of 13.76% on tidal blades have lifted power output by 46.1% versus steel alternatives. In aerospace, the development of liner-less Type V carbon-composite tanks supports the transition to liquid-hydrogen propulsion, indirectly increasing demand for renewable-grade fibres. Mitsubishi Chemical's C/SiC ceramic matrix composite endures 1,500 °C, opening paths for heliostat receivers and fusion-reactor hardware. These advances underline why the composite materials in the renewable energy market continue to displace aluminum and steel in high-temperature, corrosive environments.
Growing Demand for Longer Wind-Turbine Blades
Siemens Energy's 21 MW prototype with a 276 m rotor diameter illustrates how blade lengths nearing 150 m require carbon-fibre spar caps for stiffness-to-weight targets unattainable with glass fibre alone. Segmented blade architectures, enabled by high-toughness epoxy joints, ease transport while maintaining aeroelastic integrity. The ZEBRA consortium completed the world's largest fully recyclable thermoplastic blade using Arkema's Elium resin, signalling industrial readiness for closed-loop platforms. Hybrid lay-ups that mix natural and synthetic fibres improve impact resistance and lower embodied carbon, aligning with EU offshore wind targets of 150 GW by 2050 that could double global carbon-fibre demand.
High Research and Development and Tooling CAPEX
Automated fibre-placement lines cost USD 5-10 million each, while molds for >100 m blades exceed USD 2 million per set, tying up capital for years before payback. Certification programs often run 5-7 years, stretching working-capital needs for mid-tier innovators. Hexcel's USD 300 million bond issue in 2025 exemplifies the financial firepower required to retain process-technology leadership. Thermoplastic adoption compounds costs, since ovens, presses, and welding equipment differ from thermoset lines, creating parallel asset footprints that hamper small manufacturers' competitiveness.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Inclination Towards Adoption of Renewable Energy
- Commercialization of Thermoplastic Recyclable Blade Platforms
- Recycling & Landfill-Ban Compliance Costs
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The segment generated the largest revenue contribution in 2024, when GFRP held 55.25% of composite materials in the renewable energy market share. Carbon fibre's 8.62% CAGR reflects rotor diameters that eclipse 120 m, where stiffness and fatigue performance justify its 5-10X cost premium. SGL Carbon's supply agreements for 80 m-plus blades illustrate vertical moves into energy from aerospace. Fibre-hybrid lay-ups blending basalt and natural fibre reduce embodied carbon yet maintain required modulus, expanding options for mid-range turbine classes. Bio-based lignin fibre research in Germany offers a future cost-reduction lever, although commercial volumes remain limited. Recycled carbon fibre is steadily integrating into secondary structures as mechanical recycling preserves 60-70% original tensile strength, further diversifying feedstocks and tempering raw material price swings.
Epoxy maintained a 45.86% revenue share in 2024 thanks to mature supply chains and high fatigue resistance. Yet bio-resins and recycled resins are expanding at an 8.04% CAGR as OEMs race to satisfy circular-economy mandates. Dow and Vestas have qualified polyurethane spar-cap chemistries that enable rapid pultrusion while elevating interlaminar toughness. Sicomin's SGi 128 bio-epoxy gel coat demonstrates fire-safe solutions with 35% renewable content. Thermoplastic matrices such as Elium offer the added benefit of repairability and melt recycling, pivoting the composite materials in the renewable energy market toward closed-loop economics.
The Composite Materials in Renewable Energy Market Report Segments the Industry by Fibre Type (Glass-Fibre-Reinforced Plastics (GFRP), and More), Resin Matrix (Epoxy, Polyester, and More), Manufacturing Process (Vacuum Infusion, Prepreg/Autoclave, and More), Application (Wind Power, Solar Power, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific commanded 44.68% of the composite materials in the renewable energy market size in 2024 and is on track for an 8.12% CAGR through 2030. China anchors the region with end-to-end supply chains, yet its 2024 recycling standards raise compliance costs that favor integrated local champions. India's USD 2.4 billion Hydrogen Mission and defense-sector carbon-fibre push reinforce domestic production incentives. Japan's perovskite roadmap aims for 38.3 GW by 2040 via flexible composite substrates, a pivot that may recalibrate global solar module architectures. South Korea leverages shipbuilding know-how to enter offshore wind composites, while Australia tests floating solar on inland reservoirs, showcasing regional diversity in end-use cases.
North America benefits from USD 369 billion of Inflation Reduction Act funding, with domestic-content bonuses catalyzing plant expansion in Texas, New York, and Ontario. GE Vernova's USD 600 million manufacturing buildout exemplifies reshoring moves that cut trans-Pacific logistics risk. Canada's aerospace-composite cluster supports the transfer of out-of-autoclave methods to tidal-turbine shells, while Mexico's cost-competitive labor pool draws pultruders for solar-rack exports. The region's challenge is scaling fibre production to prevent over-dependence on imports, a gap several joint ventures aim to close by 2027.
Europe wields regulatory clout, steering global norms on recyclability and embodied carbon. The ZEBRA project's thermoplastic blade success positions the continent as a technology frontrunner. Germany's lignin-fibre pilot lines symbolize R&D leadership, whereas France leverages aerospace heritage to refine high-modulus prepregs. The UK National Composites Centre's SusWIND program validates multiple recycling routes, giving OEMs design flexibility. Offshore wind buildout in the North Sea and Baltic drives sustained fibre demand, though high energy costs compel automation to defend margins.
- Changzhou Tiansheng New Materials Co. Ltd
- EPSILON Composite SAS
- EURO-COMPOSITES
- Evonik Industries AG
- Exel Composites
- GE Vernova
- Gurit Services AG
- Jiangsu Hengshen Co.,Ltd
- Hexcel Corporation
- HS HYOSUNG ADVANCED MATERIALS
- LM WIND POWER
- Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation
- Norco Composites & GRP
- Owens Corning
- Plastic Reinforcement Fabrics Ltd
- SGL Carbon
- Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, S.A.U
- Solvay
- TEIJIN LIMITED
- TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Reduced weight versus metallic structures
- 4.2.2 Growing demand for longer wind-turbine blades
- 4.2.3 Government inclination towards the adoption of renwable energy
- 4.2.4 Commercialisation of thermoplastic recyclable blade platforms
- 4.2.5 Rising adoption of 3-D printed composite parts in floating solar & tidal devices
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High research and development and tooling CAPEX
- 4.3.2 Recycling & landfill-ban compliance costs
- 4.3.3 Concerns regarding the durability and fire resistance of some composite materials
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Fibre Type
- 5.1.1 Glass-Fibre-Reinforced Plastics (GFRP)
- 5.1.2 Carbon-Fibre-Reinforced Plastics (CFRP)
- 5.1.3 Fibre-Reinforced Polymers (FRP)
- 5.1.4 Other Fibre Types (Hybrid and Other Fibres, etc.)
- 5.2 By Resin Matrix
- 5.2.1 Epoxy
- 5.2.2 Polyester
- 5.2.3 Polyurethane
- 5.2.4 Thermoplastic
- 5.2.5 Bio-resins and Recycled Resins
- 5.3 By Manufacturing Process
- 5.3.1 Vacuum Infusion
- 5.3.2 Prepreg/Autoclave
- 5.3.3 Pultrusion
- 5.3.4 Automated Fibre Placement / 3-D Printing
- 5.3.5 Compression Moulding (SMC, BMC)
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Wind Power
- 5.4.2 Solar Power
- 5.4.3 Hydroelectricity
- 5.4.4 Other Applications (Green-Hydrogen & Energy-Storage Vessels)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 India
- 5.5.1.3 Japan
- 5.5.1.4 South Korea
- 5.5.1.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 North America
- 5.5.2.1 United States
- 5.5.2.2 Canada
- 5.5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share(%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Changzhou Tiansheng New Materials Co. Ltd
- 6.4.2 EPSILON Composite SAS
- 6.4.3 EURO-COMPOSITES
- 6.4.4 Evonik Industries AG
- 6.4.5 Exel Composites
- 6.4.6 GE Vernova
- 6.4.7 Gurit Services AG
- 6.4.8 Jiangsu Hengshen Co.,Ltd
- 6.4.9 Hexcel Corporation
- 6.4.10 HS HYOSUNG ADVANCED MATERIALS
- 6.4.11 LM WIND POWER
- 6.4.12 Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation
- 6.4.13 Norco Composites & GRP
- 6.4.14 Owens Corning
- 6.4.15 Plastic Reinforcement Fabrics Ltd
- 6.4.16 SGL Carbon
- 6.4.17 Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, S.A.U
- 6.4.18 Solvay
- 6.4.19 TEIJIN LIMITED
- 6.4.20 TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment










