 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851022
专用LTE:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030年)Private LTE - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
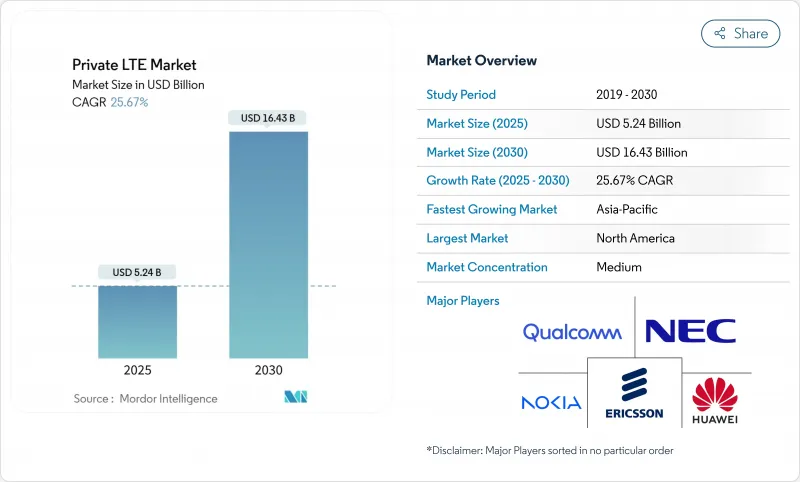
预计到 2025 年,专用 LTE 市场规模将达到 52.4 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 164.3 亿美元,年复合成长率为 25.67%。
随着企业营运数位转型,并将关键业务工作负载部署在专用蜂巢式基础架构上,安全至上、效能确定性是推动其普及的关键因素。共用频谱的早期商业化、工业4.0专案的快速推进,以及在严苛环境下对超可靠、低延迟通讯(URLLC)日益增长的需求,都在推动着私有LTE市场的成长。工业场所现在更倾向于选择私有LTE而非公共LTE,因为私有LTE能够提供可预测的覆盖范围、简化的品管,以及敏感营运资料的完整管理选项。边缘运算的整合是另一个驱动因素,它能够对海量感测器资料流进行本地分析,且无需考虑往返延迟。生态系统创新,特别是开放式小型基地台和CBRS设备的普及,正在降低私有LTE市场的进入门槛,并扩大其潜在用户群。
全球专用LTE市场趋势与洞察
频宽自由化导致企业采用率快速上升。
主要亮点
- 监管机构正在重新分配中频段频谱,使企业能够在类似CBRS的框架下以前所未有的方式获得高品质频谱。到2023年底,预计将部署约37万台CBRS设备,这凸显了共用频宽如何降低许可门槛并实现网路所有权的民主化。经济实惠且干扰可控的存取方式,使得先前缺乏资源取得独家授权的中型企业也能进入专用LTE市场。在美国以外,德国、日本和澳洲正在发放本地许可证,允许工厂、港口和公共设施部署客製化的覆盖范围。这项政策转变正在扩大供应商生态系统,刺激小型基地台创新,并催生出一批新的工业场所,预计未来三年内将在这些场所部署专用LTE网路。
工业IoT推动製造业转型
智慧工厂的部署依赖可靠的无线骨干网,可支援数千个感测器,且延迟低于30毫秒。约79%的早期采用专用LTE网路的用户表示,在部署专用LTE网路以支援自动导引车、扩增实境辅助维护数位双胞胎后的六个月内,他们实现了正向投资回报率。低负载连接提高了线路平衡效率,从而促进了预测性维护、品质分析和全厂能源优化。随着首批网路投入运作,製造商们正在发现越来越多的应用场景,例如场地管理和用于保障工人安全的穿戴式设备,这为专用LTE市场形成了一个自我强化的普及曲线。
资本密集型会造成推广障碍
私有LTE部署需要无线和核心设备、高可靠性回程传输、站点建设,以及在某些地区需要支付频宽使用费。初始成本通常会超过内部预期报酬率,尤其对于中型企业而言。由于营运支出订阅模式可以缓解资本衝击并使支出与生产力提升保持一致,因此人们对网路即服务协议的兴趣日益浓厚。网路安全加固和避免停机等无形收益仍然难以量化,从而延长了预算週期。开放式无线接取网路(Open RAN)硬体可望降低单位成本,但对于缺乏蜂窝网路专业知识的企业而言,整合成本可能会抵销节省的成本。
细分市场分析
2024 年市场细分显示,基础设施产业占市场份额的 63%,反映出其在小型基地台、封包核心网路和传输设备上的大量支出。然而,由于企业依赖系统整合商来规避内部技能短缺问题,服务收入正以 18.4% 的复合年增长率快速成长。託管服务整合了设计、整合和全天候运营,为工厂和公共产业提供可预测的预算,同时加快价值实现速度。绿地计画对专业服务的需求依然旺盛,但经常性託管合约在新订单中占据了相当大的份额。
儘管无线存取网仍然是最大的投资项目,但企业越来越重视在地核心系统,以强化安全策略。将多个工厂区域连接到云端控制套件时,传输回程传输的升级不可或缺。供应商目前正在推广「盒装网路」(预先配置的核心网加小型基地台),并支援当日启用。 Pente Networks 的一款此类套件在 2025 年洛杉矶山火期间保障了应急人员的通讯,凸显了这种承包解决方案如何将专用 LTE 市场拓展到技术型买家之外的更广泛群体。
预计到2024年,时分通讯( TDD)将占总收入的55%,复合年增长率(CAGR)高达17.1%。视讯监控和遥测非对称流量有利于TDD动态分配,从而在稀缺的中频段频道内实现最大吞吐量。 TDD也与CBRS频宽分配一致,进一步巩固了其在新私有LTE市场部署中的预设地位。
频分双工 (FDD) 在对延迟敏感的控制系统中仍然占据一席之地,因为在这些系统中,上行链路和下行链路之间的严格分离至关重要。然而,现代调度器已将 TDD 抖动降低到 10 毫秒以下,缩小了历史差距。即将发布的 5G通讯将进一步优化 TDD 参数,确保企业在向 5G NR 载波聚合过渡的过程中,目前的投资仍然有效。
区域分析
北美将引领潮流,预计到2024年将占全球收入的38%,这主要得益于其CBRS框架以及成熟的无线电、设备和整合商合作伙伴生态系统。到2024年底,全球将有超过4700个专用LTE和5G网路投入使用,其中美国将占据相当大的份额。製造业、医疗保健和公共产业的本地5G试点计画将推动市场需求,而超大规模边缘区域将有助于将低延迟工作负载卸载到主要城市。
亚太地区将在2025年至2030年间实现12.8%的复合年增长率,成为全球5G市场成长最快的地区。中国正在部署国营工厂和矿山网络,日本正在发放毫米波和中频段的本地5G牌照,韩国则利用其密集的光纤骨干网路来建造校园核心网。印度近期调整的频谱政策已在汽车和製药工厂启动了试点计画。澳洲目前已有超过50个私有LTE系统投入运营,主要用于简化偏远地区的铁矿石和锂矿开采作业。澳洲通讯与媒体管理局(ACMA)预测,到2027年,澳洲电信市场规模将达到6.95亿澳元。
根据GSMA的数据,欧洲在5G部署方面位居第二,到2023年中期,将占全球住宅安装量的约40%。德国3.7-3.8 GHz频段的本地牌照正在推动製造业采用5G技术,而英国的共享接入框架则简化了港口和农场的牌照申请流程。欧洲5G观察站的数据显示,截至2024年3月,73%的先锋频段已被分配,为工业网路奠定了坚实的频谱基础。沃达丰承诺在2500个站点部署开放式无线接取网路(Open RAN),预计将降低整个欧洲大陆的建造成本,间接惠及寻求承包计划的企业买家。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 频率自由化与CBRS商业化
- 工业IoT和工业4.0的兴起
- 严苛环境下的关键任务型超可靠低延迟通讯(URLLC)需求
- 向 5G SA 的无缝迁移路径
- 本地边缘 AI频宽需求
- 开放式无线接取网路(Open RAN)小型基地台生态系统可降低整体拥有成本(TCO)。
- 市场限制
- 高额资本支出和不确定的投资报酬率
- 缺乏综合人才
- 颗粒设备频段支持
- 私人5G试办计画蚕食预算
- 价值链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方/消费者的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
- 投资分析
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按组件
- 基础设施
- 无线存取网(RAN)
- 核心(EPC/5GC)
- 回程传输和运输
- 服务
- 专业服务
- 託管服务
- 基础设施
- 透过技术
- 频分双工(FDD)
- 时分双工(TDD)
- 按部署模式
- 集中式(C-RAN)
- 去中心化
- 频谱
- 授权
- 免授权(MulteFire,5GHz)
- 共享(CBRS、LAA)
- 按最终用户行业划分
- 製造业
- 能源与公共产业
- 采矿、石油和天然气
- 运输与物流
- 公共与国防
- 卫生保健
- 公司/校园
- 其他的
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 日本
- 印度
- 韩国
- 亚太其他地区
- 中东和非洲
- 中东
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 卡达
- 以色列
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亚
- 其他非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Nokia
- Ericsson
- Huawei Technologies
- NEC Corp.
- Qualcomm
- Druid Software
- Sierra Wireless
- JMA Wireless
- Ruckus Networks(CommScope)
- Celona
- Airspan Networks
- Cisco Systems
- ZTE Corp.
- Samsung Electronics
- Airspan Networks
- Athonet(HPE)
- Motorola Solutions
- Mavenir Systems
- Amazon AWS Private 5G
- Verizon Business
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The private LTE market is valued at USD 5.24 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 16.43 billion by 2030, expanding at a 25.67% CAGR.

Security-focused, deterministic performance is propelling adoption as enterprises digitize operations and place mission-critical workloads on dedicated cellular infrastructure. Early commercialization of shared spectrum, rapid progress on Industry 4.0 programs, and the rising need for ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC) in harsh settings all reinforce growth. Industrial sites now favour private LTE over public alternatives because it delivers predictable coverage, streamlined quality-of-service management, and the option to retain full control of sensitive operational data. Edge computing integration is another accelerant, enabling local analytics on massive sensor streams without round-trip delays. Ecosystem innovation-in particular, open RAN, small-cell form factors, and CBRS device proliferation-is lowering entry barriers and widening the private LTE market addressable base.
Global Private LTE Market Trends and Insights
Spectrum Liberalization Unlocks Enterprise Deployment Surge
Key Highlights
- Regulators are reallocating mid-band frequencies, giving enterprises unprecedented access to high-quality spectrum under frameworks such as CBRS. Around 370,000 CBRS devices had been deployed by end-2023, underscoring how shared bands reduce licensing hurdles and democratize network ownership.Affordable, interference-managed access has opened the private LTE market to mid-sized firms that previously lacked resources for exclusive licences. Beyond the United States, Germany, Japan, and Australia have issued local licences that let factories, ports, and utilities implement bespoke coverage footprints. The policy shift is expanding vendor ecosystems, stimulating small-cell innovation, and creating a pipeline of new industrial sites expected to deploy private LTE networks over the next three years.
Industrial IoT Drives Manufacturing Transformation
Smart-factory rollouts now hinge on reliable wireless backbones capable of sustaining thousands of sensors with latencies below 30 ms. Nearly 79% of early adopters said they achieved positive ROI within six months after installing private LTE to support automated guided vehicles, AR-assisted maintenance, and digital twins. Low-variance connectivity improves line-balance efficiency, which in turn drives predictive maintenance, quality analytics, and plant-wide energy optimisation. Manufacturers consistently discover incremental use cases, such as yard management and worker-safety wearables, once the initial network is live, creating a self-reinforcing adoption curve inside the private LTE market.
Capital Intensity Creates Adoption Barriers
Private LTE deployments involve radio and core equipment, resilient backhaul, site works and, in some regions, spectrum fees. Upfront costs often exceed internal hurdle rates, especially for mid-tier firms. Interest in network-as-a-service contracts is rising because OPEX subscriptions reduce capital shock and match spending to productivity gains. Quantifying intangible benefits such as cyber-hardening and downtime avoidance remains challenging, prolonging budget cycles. Open RAN hardware promises lower unit prices, yet integration overheads can erase savings for organisations lacking cellular expertise.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Mission-Critical Communications Enable Remote Operations
- Seamless Migration Path Toward 5G SA
- Integration Complexity Slows Implementation Velocity
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The infrastructure segment held 63% of the private LTE market in 2024, reflecting heavy spending on small cells, packet cores, and transport gear. Yet, services revenue is rising faster at an 18.4% CAGR because organisations lean on system integrators to sidestep internal skills shortages. Managed offerings bundle design, integration, and 24/7 operations, giving factories and utilities predictable budgets while accelerating time-to-value. Professional services demand remains high during greenfield projects, but recurring managed contracts are capturing a larger share of new bookings.
Radio access networks still account for the biggest slice of capital, though enterprises increasingly emphasise onsite core systems to enforce security policies. Transport backhaul upgrades are non-negotiable when connecting multiple plant zones to cloud dashboards. Vendors now promote "network-in-a-box" kits-pre-configured core plus small cells-capable of same-day activation. One such kit from Pente Networks maintained communications for emergency crews during the 2025 Los Angeles wildfires, highlighting how turnkey packaging broadens the private LTE market beyond technically-savvy buyers.
Time-division duplexing captured 55% of revenue in 2024 and is projected to sustain the highest 17.1% CAGR. Asymmetric traffic in video surveillance and telemetry favours TDD's dynamic allocation, maximising throughput within scarce mid-band channels. TDD also aligns with CBRS band allocations, reinforcing its position as the default in new private LTE market deployments.
Frequency-division duplexing retains a foothold in latency-sensitive control systems where strict separation of uplink and downlink is prized. However, modern schedulers reduce TDD jitter to sub-10 ms, narrowing the historical gap. Upcoming 5G releases will further refine TDD numerologies, assuring enterprises that today's investment will remain relevant once they transition to 5G NR carrier aggregation.
The Private LTE Market Report is Segmented by Component (Infrastructure and Services), Technology (Frequency-Division Duplexing (FDD) and Time Division Duplex (TDD)), Deployment Model (Centralized (C-RAN), Distributed), End-User Industry (Industrial (Manufacturing, Energy and Utilities, Mining and Oil and Gas, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America led with 38% of 2024 revenue thanks to the CBRS framework and a mature ecosystem of radio, device, and integrator partners. More than 4,700 private LTE and 5G networks were operational worldwide by end-2024, and a substantial share was in the United States. Local 5G pilots in manufacturing, healthcare, and utilities amplify demand, while hyperscaler edge zones make low-latency workload offload straightforward across major metros.
Asia-Pacific records the fastest 12.8% CAGR from 2025 to 2030. China deploys state-backed factory and mine networks, Japan issues local 5G licences in millimetre and mid-bands, and South Korea capitalises on its dense fibre backbone to host campus cores. India's recent spectrum policy changes have unlocked trials in automotive and pharmaceutical plants. Australia already operates more than 50 private LTE systems, primarily to streamline remote-area iron ore and lithium extraction, and its market is forecast to hit AUD 695 million by 2027, according to ACMA.
Europe ranks second in deployment count, holding roughly 40% of global private installations by mid-2023, according to GSMA. Germany's 3.7-3.8 GHz local licences spur manufacturing adoption; the United Kingdom's Shared Access framework simplifies licences for ports and farms. The European 5G Observatory reports that 73% of pioneer bands were assigned by March 2024, forming a solid spectral foundation for industrial networks. Vodafone's pledge to roll out open RAN on 2,500 sites is expected to reduce equipment costs across Continental Europe, indirectly benefiting enterprise buyers seeking turnkey private LTE projects.
- Nokia
- Ericsson
- Huawei Technologies
- NEC Corp.
- Qualcomm
- Druid Software
- Sierra Wireless
- JMA Wireless
- Ruckus Networks (CommScope)
- Celona
- Airspan Networks
- Cisco Systems
- ZTE Corp.
- Samsung Electronics
- Airspan Networks
- Athonet (HPE)
- Motorola Solutions
- Mavenir Systems
- Amazon AWS Private 5G
- Verizon Business
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Spectrum liberalization and CBRS commercialization
- 4.2.2 Industrial IoT and Industry 4.0 uptake
- 4.2.3 Mission-critical URLLC demand in harsh sites
- 4.2.4 Seamless migration path toward 5G SA
- 4.2.5 On-prem edge-AI bandwidth requirements
- 4.2.6 Lower TCO via Open RAN small-cell ecosystems
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High CAPEX and uncertain ROI
- 4.3.2 Scarcity of integration talent
- 4.3.3 Fragmented device-band support
- 4.3.4 Budget cannibalisation by private 5G pilots
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Investment Analysis
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Infrastructure
- 5.1.1.1 Radio Access (RAN)
- 5.1.1.2 Core (EPC/5GC)
- 5.1.1.3 Backhaul and Transport
- 5.1.2 Services
- 5.1.2.1 Professional Services
- 5.1.2.2 Managed Services
- 5.1.1 Infrastructure
- 5.2 By Technology
- 5.2.1 Frequency-Division Duplexing (FDD)
- 5.2.2 Time-Division Duplexing (TDD)
- 5.3 By Deployment Model
- 5.3.1 Centralised (C-RAN)
- 5.3.2 Distributed
- 5.4 By Spectrum
- 5.4.1 Licensed
- 5.4.2 Unlicensed (MulteFire, 5 GHz)
- 5.4.3 Shared (CBRS, LAA)
- 5.5 By End-user Industry
- 5.5.1 Manufacturing
- 5.5.2 Energy and Utilities
- 5.5.3 Mining and Oil and Gas
- 5.5.4 Transportation and Logistics
- 5.5.5 Public Safety and Defense
- 5.5.6 Healthcare
- 5.5.7 Enterprise / Campuses
- 5.5.8 Others
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Spain
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 Japan
- 5.6.4.3 India
- 5.6.4.4 South Korea
- 5.6.4.5 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.3 Qatar
- 5.6.5.1.4 Israel
- 5.6.5.1.5 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Nokia
- 6.4.2 Ericsson
- 6.4.3 Huawei Technologies
- 6.4.4 NEC Corp.
- 6.4.5 Qualcomm
- 6.4.6 Druid Software
- 6.4.7 Sierra Wireless
- 6.4.8 JMA Wireless
- 6.4.9 Ruckus Networks (CommScope)
- 6.4.10 Celona
- 6.4.11 Airspan Networks
- 6.4.12 Cisco Systems
- 6.4.13 ZTE Corp.
- 6.4.14 Samsung Electronics
- 6.4.15 Airspan Networks
- 6.4.16 Athonet (HPE)
- 6.4.17 Motorola Solutions
- 6.4.18 Mavenir Systems
- 6.4.19 Amazon AWS Private 5G
- 6.4.20 Verizon Business
- 6.4.21 General Dynamics Mission Systems
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment










