 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851072
重型卡车:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Heavy Duty Trucks - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
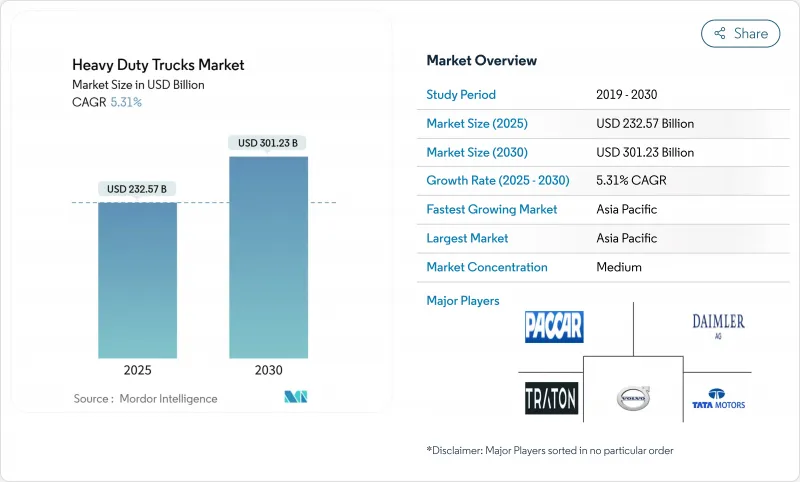
预计到 2025 年,重型卡车市场规模将达到 2,325.7 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 3,012.3 亿美元,复合年增长率为 5.31%。
由于车队需要在满足排放气体即时的排放法规和製定长期电气化计划之间寻求平衡,因此市场需求正处于谨慎增长阶段。全球监管趋严、基础建设投入空前巨大,以及电池和氢能技术的快速发展,正在共同重塑采购决策和资本配置策略。在老牌製造商投资新平台的同时,软体专家和电池供应商也纷纷涌入市场,形成了一个竞争激烈的环境,在这个环境中,作业系统架构的控制与引擎设计同等重要。政策驱动的购车週期将推动短期内柴油车销售成长,但随着成本平衡里程碑的临近,各地区的预测都显示,市场将迅速转向零排放车辆。亚太地区的规模优势、北美地区的政府采购奖励、欧洲地区先进的运输计划,以及部分线路货运量的週期性疲软,共同支撑着市场稳健的成长前景。
全球重型卡车市场趋势与洞察
电子商务货运量的成长
电子商务货运的扩张透过优化最后一公里配送和提高区域配送网路的密度,推动了对重型卡车的需求。线上零售的激增,在零排放法规日益限制柴油车营运的城市环境中,催生了对中型电动卡车的需求。车队营运商优先考虑能够在可预测路线上进行多次每日配送的车辆,这使得电池电动卡车儘管前期成本较高,但在经济上仍然可行。这种转变尤其有利于7级卡车,因为其营运模式符合目前电池技术的限制。随着市政当局实施零排放区,以及消费者对更快、更永续的配送方式的需求不断增长,这一趋势将会加速。亚马逊承诺采购10万辆电动送货车,以及UPS采用可再生天然气卡车,都显示物流巨头正在重塑筹资策略。
更严格的全球排放法规推动车辆更新换代
美国环保署(EPA)的第三阶段标准要求到2032年,50%的专用车辆必须达到零排放。欧盟修订后的二氧化碳排放标准要求在2040年减量90%,而加州的「先进清洁车队」规则则要求从2036年开始,所有车辆销售都必须实现100%零排放。分析师预测,在2027年正式实施前,2025年至2026年间,零排放车辆的订单量将显着成长。随着依赖出口的製造商围绕最严格的要求进行生产标准化,这些法规的连锁效应将超越最初的市场范围。中国电动卡车销量占全球80%以上,其零排放重型车辆的快速普及表明,政策可以如何加速市场转型。
零排放重型卡车的初始成本很高
零排放卡车的购买成本是柴油卡车的两到三倍。儘管锂离子电池价格有所下降,但电池组成本(占车辆价格的30%到40%)仍然是主要的成本驱动因素。车队营运商还需增建基建设施,据估计,到2035年,美国充电基础建设需要300亿美元。总体拥有成本的计算表明,电动卡车仅在特定工况下(例如高利用率和可预测路线)更具优势,这限制了其应用范围,使其仅限于特定用途。这种成本差异对缺乏前期投资资金的中小型车队造成了衝击,并可能加速产业整合,因为大型营运商可以透过早期电气化获得竞争优势。
细分市场分析
到2024年,15吨以上的卡车将占据61.40%的市场份额,这反映出远距货运和需要最大有效负载容量的建筑应用领域的主导地位。然而,10-15吨级卡车市场将以9.50%的复合年增长率(CAGR)实现最快增长,这一增长主要得益于城市配送的优化和中型卡车电气化技术的普及。这种成长模式表明,车队营运商正在策略性地转向更适合特定应用场景的车辆尺寸,而不是一味追求最大有效负载容量。
重型卡车市场的领先地位源于其在单次运输有效载荷经济性方面的监管优势,以及为最大总重车辆设计的成熟基础设施。相反,轻型重型卡车则受益于较低的电气化成本和城市零排放区建设所带来的通行特权。由于电池重量增加对重型卡车的影响尤其显着,因此,对于10-15吨级卡车而言,由于其对负载容量的敏感度低于对行驶灵活性的考量,因此更适合早期采用电气化技术。
8级卡车将继续保持其市场主导地位,到2024年将占据70.80%的市场份额,这反映了它们在远距货运和重型建筑应用领域的重要作用。然而,7级卡车展现出最强劲的成长势头,到2030年复合年增长率将达到8.30%,使其成为有效载荷能力和电气化经济性之间最佳的平衡点。这种差异凸显了监管压力和技术限制如何再形成传统的卡车尺寸偏好。
8级卡车的主导地位反映了其成熟的供应链,该供应链针对远距货运的效率进行了优化,有效负载容量和区域分销网络,在这些应用中,营运弹性比最大运力更为重要。此细分市场受益于电池成本的下降,从而能够实现电气化,同时保持足够的有效负载容量以满足大多数商业应用的需求。 5级和6级卡车则服务于市政和公用事业等特定领域,在这些领域,可预测的运行週期使得即使单位成本较高,也能更早实现电气化。
区域分析
预计到2024年,亚太地区将占全球营收的47.21%,并在2030年之前以9.30%的复合年增长率成长。中国整车製造商凭藉着规模经济优势,使采购价格低于全球平均;而国内电池供应商提供的磷酸锂电池(LFP)则降低了材料成本的波动性。在印度政府透过「印度公路网计画」(Bharatmala)和氢能试点计画提供的支持下,印度的货运走廊正在推动对电池和燃料电池平台的需求。日本在燃料电池系统领域处于领先地位,其产品与上一代产品相比,能量损耗降低了30%。东南亚国家正利用自由贸易协定建立最终组装中心,以满足东协的需求;澳洲则在矿业电气化试验中,检验Megapack电池系统在恶劣环境下的表现。
北美地区在价值方面位居第二,这主要得益于其货运密集型经济和成熟的8级卡车文化。将于2027年生效的EPA第三阶段排放标准,将从2025年开始刺激预购活动,在加速向零排放车型过渡之前,暂时提升柴油车的产量。北美地区的生产布局从五大湖区一直延伸到墨西哥的新莱昂丛集,体现了供应链共享和贸易协定的益处。随着IIJA资助2.5万公里高速公路的翻新工程,与公共基础设施合约相关的重型卡车市场规模将大幅增长,间接带动了对自卸车和混凝土搅拌机车厢更换的需求。加拿大正透过CleanBC和CEPA拨款计画推动港口电气化,而墨西哥则致力于达到出口级合规标准,以确保进入美国市场进入。加州和德克萨斯州的电网改造计划正在分配兆瓦级充电桩容量,以支援燃料电池卡车在I-10和I-5走廊沿线的早期部署。
欧洲制定了最雄心勃勃的脱碳时间表,欧洲议会强制要求到2040年,新卡车的二氧化碳排放量减少90%。德国、法国和荷兰已为每辆零排放卡车提供5万至9.5万欧元的补贴,儘管面临宏观经济逆风,这些补贴仍促进了订单成长。替代燃料基础设施法规确保了充电桩的供应,并缓解了长达1200公里的跨境运输路线上的里程焦虑。斯堪地那维亚的沼气混合燃料强制令允许运输公司在不更换引擎的情况下减少全生命週期排放。东欧车队面临成本壁垒,但受益于欧盟的凝聚基金计划,该计划为购买低碳车辆提供共同融资。在南美洲,前景有所改善,巴西的「Rota 2030」计画为本地生产的电动卡车提供税额扣抵,智利和秘鲁则致力于在铜矿开采走廊建设快速充电网路。中东和非洲仍在发展中,但沙乌地阿拉伯的汽车投资计画和南非的可再生能源竞标表明,未来电气化将迎来发展势头。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 不断扩大的电子商务货运量
- 更严格的全球排放法规促进了车辆更新换代。
- 基础设施奖励策略(美国基础设施投资援助计画、欧盟绿色交易等)
- 亚太氢能走廊试点计划
- 为车队管理者提供OTA支持的TCO优化
- 南美洲矿业电气化承诺
- 市场限制
- 零排放重型卡车的初始成本很高
- 不稳定的柴油价格环境影响购买週期
- 半导体短缺导致ADAS/电动车生产延迟
- 欧盟更严格的轴重规定限制了有效载荷的经济性。
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 消费者议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按吨位类型
- 10~15 T
- 超过15吨
- 按班级
- 七年级
- 八年级
- 依推进类型
- 柴油引擎
- 电池电动
- 燃料电池汽车(FCEV)
- 替代燃料(压缩天然气、液化天然气、生质柴油)
- 透过使用
- 建筑和采矿
- 货运/物流
- 市政和公用事业
- 其他的
- 依卡车车身类型
- 联结车
- 刚性倾卸
- 油船
- 其他的
- 按销售管道
- OEM/首次采购
- 租赁和出租
- 售后改装
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 北美其他地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 澳洲和纽西兰
- 亚太其他地区
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 埃及
- 土耳其
- 南非
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Daimler Truck Holding AG
- Traton SE
- Volvo Group
- PACCAR Inc.
- Dongfeng Motor Corporation
- Tata Motors Ltd
- FAW Group Corp.
- CNHTC(Sinotruk)
- Ashok Leyland Ltd
- Isuzu Motors Ltd
- Hino Motors Ltd
- Navistar International
- Iveco Group NV
- Hyundai Motor Co.
- Nikola Corporation
- JAC Motors
- Kamaz PJSC
- Foton Motor Co. Ltd
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The heavy duty trucks market is valued at USD 232.57 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 301.23 billion by 2030, registering a 5.31% CAGR.

Demand follows a measured growth path as fleets weigh immediate compliance with tightening emission rules against long-term electrification plans. Stricter global regulations, unprecedented infrastructure spending, and rapid advances in battery and hydrogen technologies work together to reshape purchase decisions and capital-allocation strategies. Established manufacturers invest in new platforms while software specialists and battery suppliers enter the ecosystem, creating a competitive environment where control of operating-system architecture matters as much as engine design. Policy-linked pre-buy cycles boost near-term diesel volumes, yet every regional outlook incorporates a rapid pivot toward zero-emission vehicles as cost parity milestones draw closer. Scale advantages in Asia Pacific, government procurement incentives in North America, and progressive timelines in Europe combine to keep the market's growth outlook resilient despite cyclical freight softness in some corridors.
Global Heavy Duty Trucks Market Trends and Insights
Expanding E-commerce Freight Volumes
E-commerce freight expansion drives heavy-duty truck demand through last-mile delivery optimization and regional distribution network densification. The surge in online retail creates demand for medium-duty electric trucks in urban environments, where zero-emission mandates increasingly restrict diesel operations. Fleet operators prioritize vehicles capable of multiple daily delivery cycles with predictable routes, making battery-electric trucks economically viable despite higher upfront costs. This shift particularly benefits Class 7 segments, where operational patterns align with current battery technology limitations. The trend accelerates as municipalities implement zero-emission zones and consumers demand faster, more sustainable delivery options. Amazon's commitment to 100,000 electric delivery vehicles and UPS's adoption of renewable natural gas trucks demonstrate how logistics giants reshape procurement strategies.
Strict Global Emission Mandates Driving Fleet Renewal
Regulatory frameworks across major markets create unprecedented pressure for fleet electrification, with the EPA's Phase 3 standards requiring 50% of vocational vehicles to be zero-emission by 2032. The EU's revised CO2 standards mandate 90% emission reductions by 2040, while California's Advanced Clean Fleet rule requires 100% zero-emission vehicle sales starting in 2036. These regulations create artificial demand spikes as fleets engage in pre-buy strategies to avoid compliance costs, with analysts predicting significant order increases in 2025-2026 ahead of 2027 implementation. The regulatory cascade effect extends beyond initial markets, as export-dependent manufacturers standardize production around the most stringent requirements. China's rapid adoption of zero-emission heavy-duty vehicles, with over 80% of global electric truck sales, demonstrates how policy can accelerate market transformation.
High Upfront Cost of Zero-emission Heavy Trucks
Zero-emission trucks carry acquisition costs 2-3 times higher than diesel equivalents. Battery pack costs, representing 30-40% of vehicle price, remain the primary cost driver despite declining lithium-ion prices. Fleet operators face additional infrastructure investments for charging equipment and grid upgrades, with estimates suggesting USD 30 billion needed for U.S. charging infrastructure by 2035. Total cost of ownership calculations favor electric trucks only in specific duty cycles with high utilization and predictable routes, limiting adoption to specialized applications. The cost differential impacts small and medium-sized fleets lacking capital for upfront investments, potentially accelerating industry consolidation as larger operators gain competitive advantages through early electrification.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Infrastructure Stimulus Packages
- Hydrogen Corridor Pilot Programs in Asia Pacific
- Volatile Diesel Price Environment Impacting Purchase Cycles
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
More than 15-ton trucks commanded 61.40% market share in 2024, reflecting the dominance of long-haul freight operations and construction applications requiring maximum payload capacity. However, the 10-15-ton segment exhibits the fastest growth at 9.50% CAGR through 2030, driven by urban delivery optimization and medium-duty electrification adoption. This growth pattern indicates fleet operators' strategic shift toward right-sizing vehicles for specific applications rather than defaulting to maximum capacity options.
The heavier segment's market leadership stems from regulatory advantages in payload-per-trip economics and established infrastructure designed for maximum gross vehicle weights. Conversely, lighter heavy trucks benefit from lower electrification costs and urban access privileges as cities implement zero-emission zones. Battery weight penalties affect heavier trucks disproportionately, making the 10-15-ton segment more attractive for early electric adoption where payload sensitivity matters less than operational flexibility.
Class 8 vehicles maintain overwhelming market leadership with 70.80% share in 2024, reflecting their essential role in long-haul freight and heavy construction applications. Yet Class 7 trucks demonstrate the strongest growth trajectory at 8.30% CAGR through 2030, positioning themselves as the optimal compromise between payload capacity and electrification economics. This divergence highlights how regulatory pressures and technological constraints reshape traditional size preferences.
Class 8 dominance reflects established supply chains optimized for maximum efficiency in long-distance freight movement, where payload maximization directly impacts per-mile economics. However, Class 7 growth acceleration stems from urban delivery applications and regional distribution networks where operational flexibility outweighs maximum capacity requirements. The segment benefits from lower battery costs for electrification while maintaining sufficient payload for most commercial applications. Classes 5 and 6 serve specialized niches in municipal and utility applications, where predictable duty cycles enable early electric adoption despite higher per-unit costs.
The Heavy Duty Trucks Market Report is Segmented by Tonnage Type (10 To 15 T and More Than 15 T), Class (Class 7 and Class 8), Propulsion Type (Diesel, Battery-Electric, and More), Application (Construction and Mining, and More), Truck Body Type (Tractor-Trailer, and More), Sales Channel (OEM, and More), and Geography (North America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific commanded 47.21% of 2024 revenue and is forecast to expand at 9.30% CAGR through 2030, underpinned by China's policy-backed electric-truck ecosystem. Chinese OEMs deliver scale economies that push purchase prices below global averages, and domestic battery suppliers supply LFP chemistries that reduce material cost volatility. India's freight corridors gain government backing through the Bharatmala program and hydrogen pilots, channeling demand into battery and fuel-cell platforms. Japan leads in fuel-cell systems, with demonstrations achieving 30% lower tank-to-wheel energy loss than earlier generations. South-East Asian nations leverage free-trade agreements to establish final-assembly hubs feeding ASEAN demand, while Australia's mining electrification trials validate mega-pack battery systems in extreme environments.
North America ranks second in value, driven by a freight-intensive economy and a well-established Class 8 culture. EPA Phase 3 standards, effective in 2027, spur pre-buy activity beginning in 2025, temporarily lifting diesel output before an accelerated switch to zero-emission models. Manufacturing footprints stretch from the Great Lakes to Mexico's Nuevo Leon cluster, reflecting supply-chain re-shoring and trade-agreement benefits. The heavy duty trucks market size tied to public-infrastructure contracts spikes as the IIJA funds 25,000 km of highway resurfacing, indirectly lifting replacement demand for dump and concrete-mixer bodies. Canada promotes near-port electrification through CleanBC and CEPA grants, while Mexico targets export-grade compliance to secure U.S. market access. Grid-upgrade projects in California and Texas allocate capacity for multi-megawatt depot chargers, anchoring early fuel-cell truck deployments along I-10 and I-5 corridors.
Europe exhibits the most ambitious decarbonization timetable, with the European Parliament mandating a 90% reduction in new-truck CO2 by 2040. Germany, France, and the Netherlands already subsidize €50,000-95,000 per zero-emission truck, lifting order books despite macroeconomic headwinds. The Alternative Fuel Infrastructure Regulation guarantees charger availability, easing range anxiety in cross-border lanes that span up to 1,200 km. Scandinavia pioneers' biogas blending mandates, ensuring carriers can reduce lifecycle emissions without changing engines. Eastern European fleets face cost barriers but benefit from EU cohesion-fund programs that co-finance low-carbon vehicle purchases. South America's outlook improves as Brazil's Rota 2030 policy grants tax credits for local electric-truck production, while Chile and Peru explore fast-charge networks to serve copper-mining corridors. Middle East and Africa remain nascent; however, Saudi Arabia's automotive investment program and South Africa's renewable-energy auctions signal future electrification momentum.
- Daimler Truck Holding AG
- Traton SE
- Volvo Group
- PACCAR Inc.
- Dongfeng Motor Corporation
- Tata Motors Ltd
- FAW Group Corp.
- CNHTC (Sinotruk)
- Ashok Leyland Ltd
- Isuzu Motors Ltd
- Hino Motors Ltd
- Navistar International
- Iveco Group N.V.
- Hyundai Motor Co.
- Nikola Corporation
- JAC Motors
- Kamaz PJSC
- Foton Motor Co. Ltd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Expanding e-commerce freight volumes
- 4.2.2 Strict global emission mandates driving fleet renewal
- 4.2.3 Infrastructure stimulus packages (e.g., U.S. IIJA, EU Green Deal)
- 4.2.4 Hydrogen corridor pilot programs in Asia Pacific
- 4.2.5 OTA-enabled TCO optimization for fleet managers
- 4.2.6 Mining sector electrification commitments in South America
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront cost of zero-emission heavy trucks
- 4.3.2 Volatile diesel price environment impacting purchase cycles
- 4.3.3 Semiconductor shortages delaying ADAS/EV production
- 4.3.4 Stricter EU axle-weight rules limiting payload economics
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value (USD) and Volume (Units))
- 5.1 By Tonnage Type
- 5.1.1 10 to 15 T
- 5.1.2 More Than 15 T
- 5.2 By Class
- 5.2.1 Class 7
- 5.2.2 Class 8
- 5.3 By Propulsion Type
- 5.3.1 Diesel
- 5.3.2 Battery-Electric
- 5.3.3 Fuel-Cell Electric (FCEV)
- 5.3.4 Alternative Fuels (CNG, LNG, Biodiesel)
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Construction and Mining
- 5.4.2 Freight and Logistics
- 5.4.3 Municipal and Utilities
- 5.4.4 Others
- 5.5 By Truck Body Type
- 5.5.1 Tractor-Trailer
- 5.5.2 Rigid Dump
- 5.5.3 Tanker
- 5.5.4 Others
- 5.6 By Sales Channel
- 5.6.1 OEM / First Purchase
- 5.6.2 Lease and Rental
- 5.6.3 After-market Retrofit
- 5.7 By Geography
- 5.7.1 North America
- 5.7.1.1 United States
- 5.7.1.2 Canada
- 5.7.1.3 Rest of North America
- 5.7.2 South America
- 5.7.2.1 Brazil
- 5.7.2.2 Argentina
- 5.7.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.7.3 Europe
- 5.7.3.1 Germany
- 5.7.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.7.3.3 France
- 5.7.3.4 Italy
- 5.7.3.5 Russia
- 5.7.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.7.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.4.1 China
- 5.7.4.2 India
- 5.7.4.3 Japan
- 5.7.4.4 South Korea
- 5.7.4.5 Australia and New Zealand
- 5.7.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.7.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.7.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.7.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.7.5.3 Egypt
- 5.7.5.4 Turkey
- 5.7.5.5 South Africa
- 5.7.5.6 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.7.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Daimler Truck Holding AG
- 6.4.2 Traton SE
- 6.4.3 Volvo Group
- 6.4.4 PACCAR Inc.
- 6.4.5 Dongfeng Motor Corporation
- 6.4.6 Tata Motors Ltd
- 6.4.7 FAW Group Corp.
- 6.4.8 CNHTC (Sinotruk)
- 6.4.9 Ashok Leyland Ltd
- 6.4.10 Isuzu Motors Ltd
- 6.4.11 Hino Motors Ltd
- 6.4.12 Navistar International
- 6.4.13 Iveco Group N.V.
- 6.4.14 Hyundai Motor Co.
- 6.4.15 Nikola Corporation
- 6.4.16 JAC Motors
- 6.4.17 Kamaz PJSC
- 6.4.18 Foton Motor Co. Ltd
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment











