 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851129
教育机器人:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Educational Robot - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
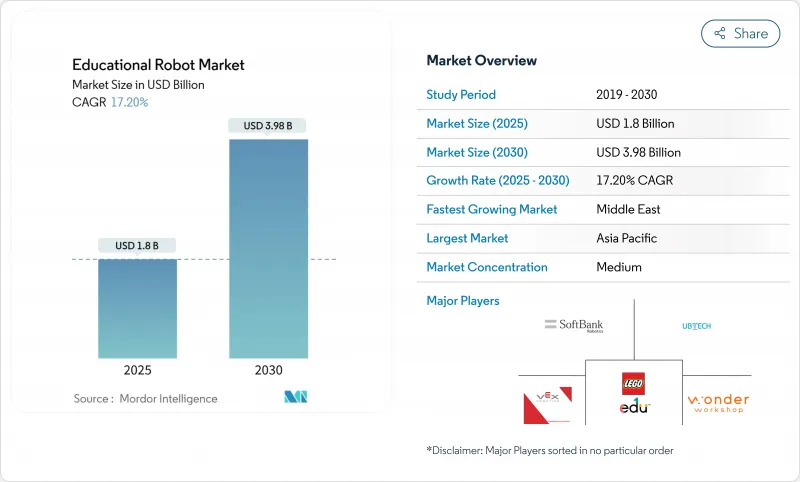
教育机器人市场预计到 2025 年将达到 18 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 39.8 亿美元,在此期间的复合年增长率为 17.2%。
大规模语言模式人工智慧的快速整合正将课堂机器人转变为能够即时调整教学内容和节奏的自适应学习伙伴。硬体价格正在下降,尤其是中国製造的伺服马达和感测器,这使得预算有限的学校也能更容易获得这些设备。东亚、欧洲和北美的政策制定者正在将机器人技术纳入国家STEM(科学、技术、工程和数学)发展议程,从而建立稳固的需求基础。同时,创业投资正涌入专注于特殊教育、多语言内容缺口或机器人即服务模式的新兴企业,重塑竞争动态。
全球教育机器人市场趋势与洞察
在东亚地区,人工智慧社交机器人在幼儿语言教学中的应用日益广泛。
这款机器人搭载了大规模语言模式自然语言处理引擎,能够提供文化适应性强的语言课程,即时修正发音,并根据孩子的情绪讯号调整课程难度。对照研究表明,与教师主导的练习相比,其词彙增长速度提高了28%,记忆维持率提高了34%。出版商只需刷写新的AI模型,即可将相同硬体移植到多种语言。这种扩充性吸引了投资者,并促使地方政府津贴课堂部署,从而强化了教育机器人市场的成长循环。提供与课程相符的分析仪錶板的供应商可以获得更高的价格。
欧洲K-12学校的强制机器人课程
欧洲各国教育部门如今要求中小学各阶段都配备机器人,将零星的试点计画转变为专案预算拨款。学校对能够同时进行教学和评估的机器人的需求日益增长,促使供应商整合安全的资料收集模组,用于记录学生互动并自动批改作业。硬体差异化正逐渐消失,内容丰富度、教师培训方案以及符合GDPR标准的云端架构如今成为合约的主要驱动力。这项政策转变也促使课程出版商与机器人製造商合作开发课程计划,加剧了生态系统的锁定效应,并提高了教育机构的转换成本。
课堂连续使用期间电池组故障率高
热带气候会加速锂离子电池的劣化,导致38%的电池组在课堂负载下一年内失效。频繁的故障维修会加重学校预算负担,扰乱教学计划,并降低学校的采购意愿。供应商正在透过混合动力架构来应对这一问题,该架构可在有充电桩可用时切换到直流供电,并采用被动散热外壳来散热。电池更换方案正逐渐成为采购标准,尤其是在政府竞标中,这些招标通常会规定五年生命週期成本。能够为电池提供度C环境认证的公司正在获得竞争优势。
细分市场分析
到2024年,非人形机器人将占据教育机器人市场68%的份额,其优势在于坚固耐用、操作简单且价格亲民。像Code & Go Mouse这样的课堂热门产品能够承受日常使用,并能大规模地教授程式设计概念。然而,随着学校观察到学生参与度的显着提高,尤其是在自闭症计画中,人形机器人平台正以23.4%的复合年增长率快速成长。早期用户表示,当机器人透过脸部LED灯和柔性关节展现情感时,学生的注意力会更加集中。因此,由于零件成本的下降,人形教育机器人市场规模预计将缩小部分价格差距。
大规模语言模型的整合将使人形机器人能够提供非脚本化的对话和动态回馈。一项于2025年启动的Duet系统试点计画将熟练度评分与基于脸部辨识的参与度指标相结合,使教师能够仅在必要时进行干预。供应商目前已开始交付预先安装了语言、社交情绪学习和特殊需求治疗课程的人形机器人。儘管前期投入成本仍然很高,但诸如「机器人即服务」(Robots-as-a-Service)之类的资金筹措方案正在降低准入门槛,使人形机器人能够在小众但影响巨大的领域迅速占据市场份额。
由于机器人本身俱有实体特性,硬体将在2024年占总收入的74%:底盘、感测器、处理器和电源系统仍然至关重要。组件创新主要集中在紧凑型人工智慧加速器和低成本伺服上,以降低物料清单成本。同时,随着学校转向涵盖维护、软体更新和教师培训的订阅套餐,服务部门正以25%的复合年增长率成长。供应商强调可预测的预算和持续的功能更新,以证明月费的合理性。
自适应学习演算法、云端分析和合规模块正在影响采购决策。因此,硬体利润空间被压缩,迫使企业捆绑终身软体授权或完全转向服务协议。这种转变重新调整了奖励,使收入主要来自于续约而非一次性销售,製造商也因此增加对人工智慧迭代改进的投入。对于学区而言,计量收费模式无需资本支出,并确保教室设备始终保持最新状态。
区域分析
以中国、日本和韩国为首的亚太地区引领机器人产业的发展,预计2024年将占全球收入的38%。北京的「十四五」规划累计4,520万美元用于机器人创新,而东京的新机器人策略也将投入4.4亿美元用于扶持国内产业。韩国每万名工人拥有1,012台机器人,这项高机器人密度造就了技术纯熟劳工队伍和对机器人技术接受度高的教育产业。深圳的供应商出口低成本的零件套件,压缩了全球材料清单,并提升了亚洲製造商在教育机器人市场的影响力。
中东地区到2030年将以22%的复合年增长率成为成长最快的地区。沙乌地阿拉伯的「未来智慧计画」计画培训3万名学生掌握人工智慧技术,而SAMAI倡议的目标对象为100万公民。企业社会责任预算将用于资助公立学校的机器人实验室,以避免购买瓶颈。阿拉伯联合大公国(阿联酋)正在深化与美国和亚洲晶片製造商的合作,以实现供应链独立,并将杜拜和阿布达比打造为针对阿拉伯语课程优化的多语言教育机器人的试验基地。
北美地区在发展的同时日益成熟。白宫发布的2024年CoSTEM报告指出,美国国家科学基金会(NSF)津贴7,000万美元用于机器人技术研究,国防部也支持了超过1,300支FIRST机器人竞赛团队。大学与产业界的合作联盟正在加速从原型到教室的转化,远距临场系统机器人正在帮助解决农村地区教师短缺的问题。与欧洲相比,北美不受GDPR(一般资料保护规范)限制的资料管理模式使得以云端为中心的分析和更快的部署速度成为可能。
欧洲的强制性机器人课程需求稳定,但GDPR合规性将增加整合成本。 「地平线欧洲」计画已拨款1.835亿美元用于机器人研发,而德国的高科技战略也已为教育领域划拨了3.692亿美元。供应商正在整合设备端处理技术以满足资料主权要求。北欧国家正在试行解释人工智慧模组,这些模组会记录每次机器人与学生互动的决策树,为其他国家树立了标竿。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 将人工智慧社交机器人引入东亚幼儿语言教学
- 欧洲K-12学校的强制机器人课程
- 政府资助的STEM倡议(例如美国国家科学基金会DRK-12计划)推动大学采购。
- 中国教育级伺服马达和感测器的平均售价下降
- 北美远距/混合式学习的激增推动了远距临场系统教学机器人的发展
- 企业社会责任预算用于赞助中东公立学校的机器人实验室
- 市场限制
- 课堂连续使用期间电池组故障率高(热带气候)
- 非拉丁语系国家人形机器人多语言内容库的局限性
- GDPR 为欧盟云端连结机器人主导的资料隐私成本
- 非洲农村地区缺乏合格的机器人技术指导员
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监理与技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
- 投资分析(资金筹措、曼德勒、创投趋势)
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按类型
- 人形
- 非人形
- 按组件
- 硬体
- 软体
- 服务
- 依教育程度
- 学前班(幼儿园)
- 小学教育
- 中等教育
- 高等教育
- 特殊教育
- 学习模式/目的
- 程式设计和STEM
- 语言学习
- 人工智慧和机器人调查
- 特殊需求治疗
- 远距临场系统与远距教学
- 最终用户
- 学校
- 大学和学院
- 职业培训机构
- 教育科技公司
- 特殊教育中心
- 创客空间与机器人俱乐部
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 欧洲
- 英国
- 德国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 北欧国家
- 其他欧洲地区
- 中东
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 土耳其
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他非洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 日本
- 韩国
- 印度
- 东南亚
- 亚太其他地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略性倡议(伙伴关係、课程合作、企业社会责任实验室)
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- SoftBank Robotics Corp.
- UBTECH Robotics Inc.
- Hanson Robotics Ltd.
- Lego Education(The Lego Group)
- Wonder Workshop Inc.
- Robotis Co., Ltd.
- VEX Robotics Inc.
- Makeblock Co., Ltd.
- Sphero Inc.
- Modular Robotics(Cubelets)
- Blue Frog Robotics
- Aisoy Robotics
- Sanbot Innovation(Qihan)
- PAL Robotics
- Probotics America
- Robobuilder Co., Ltd.
- Dash Robotics(Kamigami)
- RobotLAB Inc.
- DJI RoboMaster
- Ozobot and Evollve Inc.
- Fischertechnik GmbH
- RoboTerra Inc.
- Roborisen(e-Bo)
- RoboSense(Edu)
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The educational robot market size stands at USD 1.8 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 3.98 billion by 2030, reflecting a brisk 17.2% CAGR during the period.

Rapid integration of large-language-model AI is turning classroom robots into adaptive learning companions that adjust content and pacing in real time. Hardware prices are falling-especially for China-sourced servomotors and sensors-broadening access for budget-constrained schools. Policymakers in East Asia, Europe, and North America are embedding robotics in national STEM agendas, creating assured demand pipelines. Meanwhile, venture capital is flowing to startups that target special education, multilingual content gaps, or Robots-as-a-Service models, reshaping competitive dynamics.
Global Educational Robot Market Trends and Insights
Adoption of AI-enabled Social Robots for Early-Childhood Language Tutoring in East Asia
Robots equipped with large-language-model NLP engines now deliver culturally adaptive language lessons that correct pronunciation in real time and adjust difficulty based on a child's emotional cues. Controlled studies record 28% faster vocabulary gains and 34% higher retention than teacher-led drills. Publishers are porting the same hardware to multiple languages simply by flashing new AI models, enabling manufacturers to chase diverse markets without redesign costs. This scalability is enticing investors and encouraging local governments to subsidize classroom deployments, thereby reinforcing the growth loop for the educational robot market. Suppliers that bundle curriculum-aligned analytics dashboards are capturing premium pricing because schools value quantifiable progress tracking.
Mandatory Robotics Curriculum in K-12 Schools across Europe
European ministries of education now require robotics competencies throughout primary and secondary grades, which has turned sporadic pilot programs into line-item budget allocations. Schools increasingly solicit robots that can both teach and assess, prompting vendors to integrate secure data-collection modules that record student interactions and auto-grade tasks. Hardware differentiation is fading; instead, content depth, teacher-training packages and GDPR-compliant cloud architectures decide contract awards. The policy shift is also inspiring curriculum publishers to co-develop lesson plans with robot makers, tightening ecosystem lock-in and raising switching costs for institutions.
High Failure Rates of Battery Packs in Continuous Classroom Use
In tropical climates, lithium-ion degradation accelerates, with 38% of packs failing within a year under classroom load. Break-fix cycles strain school budgets and disrupt lesson plans, dampening purchase enthusiasm. Suppliers respond with hybrid power architectures that switch to direct current when docks are available and with passive cooling housings to dissipate heat. Battery-swap designs are emerging as a procurement criterion, especially in government tenders that stipulate five-year life-cycle costs. Companies that certify cells for 45 °C environments gain a competitive edge.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government-Funded STEM Initiatives Fueling University Procurement
- Falling ASP of Education-grade Servo Motors & Sensors in China
- Limited Multilingual Content Libraries for Humanoid Robots
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Non-humanoid models retained 68% of the educational robot market in 2024, a position earned through rugged simplicity and entry-level pricing. Classroom favorites such as the Code & Go Mouse withstand daily handling and fulfill coding-concept objectives at scale. Yet, humanoid platforms are accelerating at a 23.4% CAGR as schools observe stronger engagement, especially in autism programs. Early adopters report higher attention spans when robots mirror emotions via facial LEDs and compliant joints. The educational robot market size for humanoids is therefore forecast to close part of the gap as falling part costs narrow the price delta.
Large-language-model integration lets humanoids deliver unscripted dialogue and dynamic feedback. A 2025 pilot using the Duet system linked proficiency scores to facial-recognition-derived engagement metrics, enabling teachers to intervene only when needed. Suppliers now ship humanoids with plug-in curricula for language, social-emotional learning, and special-needs therapy. Although capital costs remain higher, financing schemes such as Robots-as-a-Service lower adoption barriers, positioning humanoids for rapid share gains in niche, high-impact settings.
Hardware accounted for 74% of 2024 revenue due to the tangible nature of robots-chassis, sensors, processors and power systems remain indispensable. Component innovation centers on compact AI accelerators and low-cost servos that reduce bill-of-materials outlays. Simultaneously, the services segment is growing at 25% CAGR as schools pivot to subscription bundles covering maintenance, software updates and teacher training. Vendors highlight predictable budgeting and continual feature refreshes to justify monthly fees.
Software, while a smaller slice, is the value engine: adaptive-learning algorithms, cloud analytics and compliance modules now decide procurement. As a result, hardware margins compress, and firms bundle lifetime software licences or pivot entirely to service contracts. This shift realigns incentives-manufacturers invest in iterative AI improvements because renewals, not one-off sales, drive revenue. For districts, the pay-as-you-go model frees capex and ensures that classroom fleets stay current.
Educational Robots Market Report is Segmented by Type (Humanoid, Non-Humanoid), Component (Hardware, Software and Services), Education Level (Primary Education, Secondary Education, Higher Education and More), Learning Mode / Application (Coding and STEM, Language Learning, Special-Needs Therapy and More), End User (Schools, Universities and Colleges, and More), Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific led with 38% revenue in 2024, anchored by China, Japan and South Korea. Beijing's 14th Five-Year Plan earmarks USD 45.2 million for robotics innovation, while Tokyo's New Robot Strategy deploys USD 440 million to sustain its domestic industry. High robot density-1,012 units per 10,000 workers in Korea-creates a skilled labor pool and a receptive education sector. Shenzhen-based suppliers export low-cost component kits, compressing global bill-of-materials and elevating Asia's manufacturing influence on the educational robot market.
The Middle East records the fastest CAGR at 22% to 2030. Saudi Arabia's Future Intelligence Program intends to train 30,000 students in AI, and the SAMAI initiative targets 1 million citizens. Corporate CSR budgets underwrite robotics labs in public schools, sidestepping procurement bottlenecks. The UAE deepens alliances with US and Asian chipmakers, seeking supply-chain independence and positioning Dubai and Abu Dhabi as testing grounds for multilingual educational robots optimized for Arabic curricula.
North America remains a mature yet expanding arena. The White House's 2024 CoSTEM report confirms USD 70 million in NSF robotics grants and over 1,300 Department of Defense-backed FIRST teams. University-industry consortia accelerate prototype-to-classroom cycles, and telepresence robots address teacher shortages in rural districts. GDPR-free data regimes allow cloud-centric analytics, shortening deployment times relative to Europe.
Europe's mandatory robotics curricula sustain steady demand, but GDPR compliance raises integration costs. Horizon Europe assigns USD 183.5 million to robotics R&D, and Germany's High-Tech Strategy channels USD 369.2 million into educational applications. Vendors embed on-device processing to satisfy data-sovereignty requirements. Nordic countries pilot explainable-AI modules that log decision trees for every robot-student interaction, setting a benchmark others may follow.
- SoftBank Robotics Corp.
- UBTECH Robotics Inc.
- Hanson Robotics Ltd.
- Lego Education (The Lego Group)
- Wonder Workshop Inc.
- Robotis Co., Ltd.
- VEX Robotics Inc.
- Makeblock Co., Ltd.
- Sphero Inc.
- Modular Robotics (Cubelets)
- Blue Frog Robotics
- Aisoy Robotics
- Sanbot Innovation (Qihan)
- PAL Robotics
- Probotics America
- Robobuilder Co., Ltd.
- Dash Robotics (Kamigami)
- RobotLAB Inc.
- DJI RoboMaster
- Ozobot and Evollve Inc.
- Fischertechnik GmbH
- RoboTerra Inc.
- Roborisen (e-Bo)
- RoboSense (Edu)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Adoption of AI-enabled Social Robots for Early-Childhood Language Tutoring in East Asia
- 4.2.2 Mandatory Robotics Curriculum in K-12 Schools across Europe
- 4.2.3 Government-funded STEM Initiatives (e.g., US NSF DRK-12) Fueling University Procurement
- 4.2.4 Falling ASP of Education-grade Servo Motors and Sensors in China
- 4.2.5 Surge of Remote/Hybrid Learning Driving Telepresence Teaching Robots in North America
- 4.2.6 Corporate CSR Budgets Sponsoring Robotics Labs in Middle-East Public Schools
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Failure Rates of Battery Packs in Continuous Classroom Use (Tropical Regions)
- 4.3.2 Limited Multilingual Content Libraries for Humanoid Robots in Non-Latin Script Nations
- 4.3.3 GDPR-Driven Data-privacy Compliance Costs for Cloud-connected Robots in EU
- 4.3.4 Shortage of Certified Robotics Instructors in Rural Africa
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory and Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 Investment Analysis (Funding, MandA, VC Trends)
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Humanoid
- 5.1.2 Non-humanoid
- 5.2 By Component
- 5.2.1 Hardware
- 5.2.2 Software
- 5.2.3 Services
- 5.3 By Education Level
- 5.3.1 Pre-primary (Kindergarten)
- 5.3.2 Primary Education
- 5.3.3 Secondary Education
- 5.3.4 Higher Education
- 5.3.5 Special Education
- 5.4 By Learning Mode / Application
- 5.4.1 Coding and STEM
- 5.4.2 Language Learning
- 5.4.3 AI and Robotics Research
- 5.4.4 Special-needs Therapy
- 5.4.5 Telepresence and Remote Instruction
- 5.5 By End User
- 5.5.1 Schools
- 5.5.2 Universities and Colleges
- 5.5.3 Vocational Institutes
- 5.5.4 Ed-Tech Companies
- 5.5.5 Special-education Centers
- 5.5.6 Maker Spaces and Robotics Clubs
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.2 Germany
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Nordics
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Middle East
- 5.6.4.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.4.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.4.3 Turkey
- 5.6.4.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5 Africa
- 5.6.5.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2 Egypt
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.6 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.6.1 China
- 5.6.6.2 Japan
- 5.6.6.3 South Korea
- 5.6.6.4 India
- 5.6.6.5 Southeast Asia
- 5.6.6.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (Partnerships, Curriculum Alliances, CSR Labs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 SoftBank Robotics Corp.
- 6.4.2 UBTECH Robotics Inc.
- 6.4.3 Hanson Robotics Ltd.
- 6.4.4 Lego Education (The Lego Group)
- 6.4.5 Wonder Workshop Inc.
- 6.4.6 Robotis Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.7 VEX Robotics Inc.
- 6.4.8 Makeblock Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Sphero Inc.
- 6.4.10 Modular Robotics (Cubelets)
- 6.4.11 Blue Frog Robotics
- 6.4.12 Aisoy Robotics
- 6.4.13 Sanbot Innovation (Qihan)
- 6.4.14 PAL Robotics
- 6.4.15 Probotics America
- 6.4.16 Robobuilder Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Dash Robotics (Kamigami)
- 6.4.18 RobotLAB Inc.
- 6.4.19 DJI RoboMaster
- 6.4.20 Ozobot and Evollve Inc.
- 6.4.21 Fischertechnik GmbH
- 6.4.22 RoboTerra Inc.
- 6.4.23 Roborisen (e-Bo)
- 6.4.24 RoboSense (Edu)
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet Need Analysis










