 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851157
杀幼虫剂:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Larvicides - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
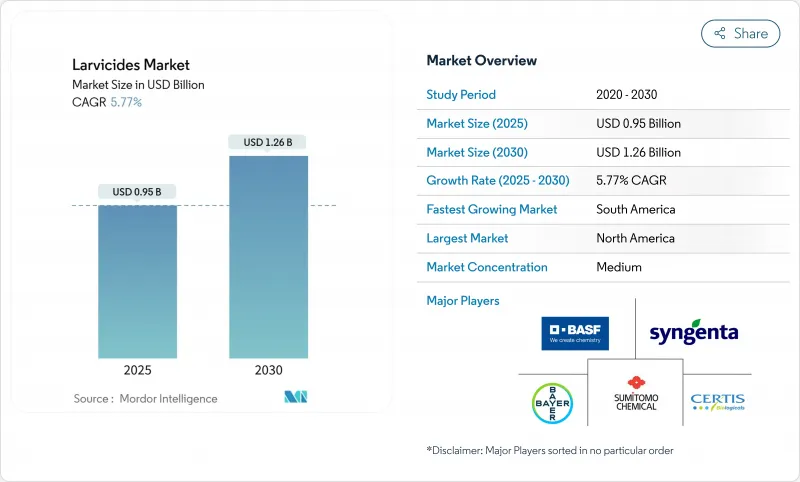
预计到 2025 年,杀幼虫剂市场规模将达到 9.5 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 12.6 亿美元,预测期内复合年增长率为 5.77%。
市场成长的驱动因素包括:由于成蚊杀虫剂效果下降,人们越来越需要针对蚊子幼虫阶段进行防治;美洲地区医疗保健预算不断增长;以及环境友善生物製剂的持续研发。其他成长因素还包括:温带地区蚊子繁殖季节延长;热带都市区登革热持续流行;以及稻鱼共作系统的日益普及,这些系统需要适用于水产养殖的安全型杀幼剂。市场面临的挑战包括:生物製药生产成本上升;农村地区应用方法不一致;以及需要基于地理资讯系统(GIS)的监测系统来提高防治效率。
全球杀幼虫剂市场趋势与洞察
成蚊对杀虫剂产生抗药性的迅速增加,加速了幼虫期干预措施的实施。
蚊子透过标靶不敏感性和代谢解毒作用产生对杀虫剂的抗药性。按蚊和伊蚊透过基因适应、行为改变和代谢抗性来逃避化学处理。目前,病媒控制计画着重于控制早期蚊群,透过消灭孪生地(例如静水体和都市区水库)中的幼虫来实现。这种方法可以阻止蚊子发育为成虫,从而阻断疾病传播循环。害虫防治计画也越来越多地采用整合策略,轮换使用不同的活性成分,以降低单一药剂的选择压力。这种转变在一些地区尤其明显,因为拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂的失效已经危及紧急喷洒预算,促使市政当局投资建设季节性幼虫杀灭网,以在成虫大量出现之前保护蓄洪池和雨水排水沟。
登革热和基孔肯雅热预防计划
拉丁美洲各大城市正加强登革热和基孔肯雅热的防治工作,以应对不断上升的感染率和都市区蚊虫数量。世界卫生组织(世卫组织)报告称,感染病例显着增加,尤其是在玻利维亚和巴拉圭。防治策略包括控制库蚊数量、进行公众宣传活动,以及结合卫生、城市规划和教育的综合方法。泛美卫生组织(泛美卫生组织)正在指导区域各国政府实施社区层面的措施,以减少疾病传播。为因应2024年巴西可能爆发的登革热疫情,世界蚊子计画(WMP)已与Fiocruz基金会合作,共同应对巴西境内的蚊媒疾病。 WMP正在扩大向家养蚊子体内引入天然细菌的规模,以预防登革热、兹卡和屈公热的传播。
严格的水生毒性阈值
2026 年农药通用许可证要求施药者在处理地表水时记录施药量、地点和非目标物种监测。对包括特灭磷在内的有机磷酸酯类法律规范,减少了可用于洪氾湿地和城市流域的製剂选择。合规成本的增加促使各县从高风险化学品转向生物替代品,儘管生物替代品价格更高。虽然提供全面毒理学数据和数位化施药记录的供应商保持着市场优势,但准入障碍影响着小型经营者,并限制了该地区化学杀幼剂的分销。
细分市场分析
到2024年,合成杀幼剂将占据杀幼剂市场45%的份额。其市场领先地位归功于成本优势和已建立的采购合约。生物製剂正以8.4%的年复合成长率高速成长,这得益于政府推广综合病媒控制方法的措施。苏云苏力菌以色列亚种(Bti)对蚊幼虫、丽蝇和蕈蚋具有特异性毒性。 2023年,加德满都大都会市政府(KMC)实施了一项针对蚊幼虫的生物杀虫剂计划,以预防登革热疫情的爆发。这种有机溶液透过破坏蚊幼虫的消化道来杀死它们,而不会伤害其他生物。
目前处于后期试验阶段的RNAi酵母杀幼虫剂市场开发,可在不影响非目标物种的情况下实现基因特异性控制,预示市场可能转变。製造商正在改进微胶囊化技术,以提高产品的保质期和易用性。 2024年的一项研究表明,植物性杀幼虫剂,特别是万寿菊萃取物,在作物保护方面具有显着效果。班加罗尔PES大学的研究表明,万寿菊(Tagetes erecta)和捲叶万寿菊(Tagetes patula)含有硫酚,对斜纹夜蛾(Spodoptera litura)和黄粉虫(Corcyra cephalonica)等作物害虫具有显着的杀幼虫活性。这些技术进步,加上政府对环境永续产品的奖励,使得生物杀幼虫剂能够获得更多市政合约。
昆虫生长调节剂(IGRs)已成为一种有效的幼虫防治方法,尤其是在传统杀虫剂抗药性日益增强的情况下。 IGRs透过抑制蚊虫蜕皮、繁殖和变态发育来抑制其生长,从而阻止幼虫发育为成虫。化学接触性杀虫剂预计在2024年将占销售额的55%,但田间研究表明,由于抗药性的发展,其有效性正在下降。主要的IGR化合物-METHOPRENE,在浓度低于10 ppb时即可有效,且在水中的迁移性极低。
由于蚊虫对拟除虫菊酯类和有机磷酸盐杀虫剂普遍存在代谢和行为抗性,害虫防治计画越来越多地采用基于昆虫生长调节剂(IGR)的解决方案,例如PYRIPROXYFEN和METHOPRENE。昆虫生长调节剂具有残留活性长、环境影响小、抗药性风险低等优点,使其成为永续蚊虫控制计画的重要组成部分。
区域分析
累计到2024年,北美将成为蚊媒控制领域最大的区域,这主要得益于完善的病媒管理框架以及人们对西尼罗河病毒和东部马脑炎日益增长的担忧。美国是北美蚊子和幼虫防治中杀幼剂使用量最大的国家。美国疾病管制与预防中心(CDC)和地方蚊虫控制区在全国范围内实施病媒控制计画。这些计画将杀幼剂纳入综合蚊虫管理(IMM)策略,以预防西尼罗河病毒和兹卡等蚊媒疾病。
美国环保署 (EPA) 推荐几种针对蚊子幼虫早期阶段的杀幼虫方法:抑制幼虫消化的细菌杀虫剂(如苏云金芽孢桿菌以色列亚种和球形芽孢桿菌);抑制昆虫生长发育的昆虫生长抑製剂,例如METHOPRENE;以及可淹死幼虫的表面油膜。出于环境方面的考虑,某些控制方法已被停止使用,特别是有机磷杀虫剂。所有控制方法都必须符合旨在保护弱势群体的法规。 EPA 于 2026 年发布的《农药通用许可证》对农药在地表水体的应用制定了严格的要求,并对北美地区的农药产品开发产生了深远的影响。
在亚洲,中国和印度正透过喷洒杀虫剂来确保产量,而东南亚市场则利用补贴政策强制在稻米和鱼类养殖系统中使用生物杀幼剂。同时,家猫对有机磷酸酯类和拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂的抗药性迫使印尼议会轮调使用昆虫生长调节剂(IGR)和苏云金芽孢桿菌(Bti)的组合,这支撑了杀幼剂销售量的成长。儘管亚洲杀幼剂的市占率将逐年成长,但由于部分国家对价格较为敏感,利润率仍可能受到挤压。
受登革热和基孔肯雅热疫情引发的公共卫生危机影响,南美洲的成长速度最快。巴西2024年登革热病例达725万例,是2023年的两倍。城市卫生部门正将源头控制倡议与每週喷洒杀幼虫剂结合,以确保稳定的产品需求,从而维持经销商的存量基准。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 抗杀虫剂成蚊数量迅速增加
- 登革热和基孔肯雅热预防方案的製定
- 气候变迁导致蚊子繁殖季节延长
- 美国政府对综合性水产养殖的补贴
- 关于杀幼虫剂的监管政策
- 无人机空中喷洒杀幼虫剂的应用迅速扩展。
- 市场限制
- 严格的水生毒性基准值限制了化学配方的使用。
- GIS繁殖地测绘技术应用率低,阻碍了商业性销售。
- 芽孢桿菌发酵培养基的供应链变异性
- 公众对合成病媒控制化合物的需求压力
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特的五力模型
- 新进入者的威胁
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 依产品类型
- 合成杀幼剂
- 生物杀幼虫剂
- 透过控制方法
- 化学品
- 生物防治剂
- 昆虫生长调节剂(IGRs)
- 目标昆虫
- 蚊子
- 苍蝇
- 甲虫
- 蚂蚁
- 透过使用
- 农业
- 非农业
- 按剂型
- 颗粒
- 液体和悬浮液
- 颗粒剂和片剂
- 粉剂和可湿性粉尘
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 欧洲
- 英国
- 德国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 其他欧洲地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亚
- 埃及
- 其他非洲地区
- 中东
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 卡达
- 其他中东地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 亚太其他地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Syngenta AG
- Sumitomo Chemical Co.
- Clarke Mosquito Control Products Inc.
- Central Life Sciences
- Certis Biologicals
- UPL Ltd.
- FMC Corporation
- Russell IPM
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Larvicides Market size is estimated at USD 0.95 billion in 2025, and is projected to reach USD 1.26 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.77% during the forecast period.

The market growth is driven by several factors, like the increasing necessity to target mosquitoes in their larval stage due to reduced effectiveness of adult mosquito control methods, expanded healthcare budgets in the Americas, and continuous development of environmentally compatible bio-rational formulations. Additional growth drivers include extended mosquito breeding periods in temperate regions, persistent dengue outbreaks in tropical urban areas, and increased adoption of integrated rice-fish farming systems requiring aquaculture-safe larvicides. The market faces challenges including higher production costs for biological products, inconsistent application methods in rural areas, and requirements for GIS-based monitoring systems to enhance treatment efficiency.
Global Larvicides Market Trends and Insights
Surge in Insecticide-Resistant Adult Mosquitoes Accelerating Larval-Stage Intervention
Mosquitoes develop resistance to insecticides through target-site insensitivity and metabolic detoxification. Anopheles and Aedes mosquitoes avoid chemical treatments through genetic adaptations, behavioral changes, and metabolic resistance. Vector control programs now focus on early-stage population control by targeting larvae in breeding sites, including stagnant water bodies and urban reservoirs. This approach prevents mosquitoes from reaching adulthood and interrupts disease transmission cycles. Vector control programs increasingly implement integrated strategies that rotate different active ingredients to reduce selective pressure on individual chemical classes. This shift is most visible where pyrethroid failure jeopardized emergency spraying budgets, encouraging municipalities to invest in season-long larvicide grids that protect floodwater pools and storm drains before adult swarms emerge.
Roll-out of Dengue and Chikungunya Prevention Programs
Latin American megacities are strengthening their dengue and chikungunya prevention programs in response to increased infection rates and urban mosquito populations. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports a significant increase in cases, particularly in Bolivia and Paraguay. Prevention strategies include Aedes aegypti mosquito control, public awareness initiatives, and integrated approaches combining sanitation, urban planning, and education. The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) guides regional governments on implementing community-based measures to reduce disease transmission. In response to the 2024 dengue outbreak in Brazil, the World Mosquito Program (WMP) has partnered with Fiocruz to address mosquito-borne diseases across the country. The WMP is expanding its Wolbachia method, which introduces a natural bacterium into Aedes aegypti mosquitoes to prevent the transmission of dengue, Zika, and chikungunya.
Stringent Aquatic-Toxicity Thresholds
The 2026 Pesticide General Permit requires applicators to document the dosage, location, and non-target species monitoring when treating surface waters. Regulatory oversight of organophosphates, including temephos, has reduced available formulation options for floodwater marshes and urban catch basins. The increased compliance costs have led counties to shift from high-risk chemicals to biorational alternatives, despite their higher prices. While suppliers providing comprehensive toxicological data and digital application records maintain market advantages, the entry barriers affect small operators and limit local chemical larvicide distribution.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Climate-Induced Expansion of Mosquito Breeding Seasons in Temperate Regions
- Government Subsidies for Integrated Rice-Fish Farming
- Low Adoption of GIS Breeding-Site Mapping
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Synthetic larvicides account for 45% of the larvicides market share in 2024. Their market leadership stems from cost advantages and established procurement contracts. Biological products are growing at a higher rate of 8.4% CAGR, supported by government initiatives promoting integrated vector management approaches. Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti) demonstrates specific toxicity to mosquito larvae, blackflies, and fungus gnats. In 2023, the Kathmandu Metropolitan City (KMC) implemented bio-larvicide programs to control dengue outbreaks by targeting mosquito larvae. This organic solution eliminates mosquito larvae by disrupting their digestive systems while preserving other organisms.
The development of RNAi yeast larvicides in late-stage testing indicates potential market shifts, offering gene-specific control without affecting non-target species. Manufacturers are improving microencapsulation techniques to enhance product longevity and ease of use. Research in 2024 demonstrated the efficacy of botanical larvicides in crop protection, specifically marigold extracts. A study conducted by PES University in Bangalore revealed that Tagetes erecta and Tagetes patula contain thiophenes, which demonstrate significant larvicidal effects against crop pests Spodoptera litura and Corcyra cephalonica. These technological improvements, coupled with government incentives for environmentally sustainable products, enable biological larvicides to secure more municipal contracts.
Insect Growth Regulators (IGRs) have emerged as an effective larvicide control method, particularly in response to increasing resistance against conventional insecticides. IGRs disrupt mosquito development by inhibiting molting, reproduction, and metamorphosis, preventing larvae from reaching adulthood. While chemical contact poisons generated 55% of revenue in 2024, field studies indicate reduced effectiveness due to resistance development. Methoprene, a primary IGR compound, demonstrates effectiveness at concentrations of <= 10 ppb with minimal aquatic mobility.
Vector control programs are increasingly adopting IGR-based solutions, including pyriproxyfen and methoprene, due to widespread metabolic and behavioral resistance to pyrethroids and organophosphates. IGRs provide extended residual activity, reduced environmental impact, and lower resistance development risk, positioning them as integral components of sustainable mosquito control programs.
The Larvicides Market Report is Segmented by Control Method (Biocontrol Agents, Chemical Agents, and More), by Product Type (Synthetic Larvicides, and Biological Larvicides), by Application (Agricultural and Non-Agricultural), by Target Insects (Mosquitoes and More), by Formulation (Granules, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America generated the largest regional revenue in 2024, supported by structured vector-management frameworks and rising concern over West Nile and Eastern equine encephalitis. The United States is the primary user of larvicides for mosquito and larva control in North America. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and local mosquito control districts implement vector control programs across the country. These programs incorporate larvicides within integrated mosquito management (IMM) strategies to prevent diseases such as West Nile virus, Zika, and other mosquito-borne illnesses.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) endorses multiple larval mosquito control methods that target immature mosquitoes in their early stages. These methods include:- Bacterial insecticides (Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis and Bacillus sphaericus) that disrupt larval digestion - Insect growth inhibitors like methoprene that prevent development - Surface oils and films that cause larvae to drown. Environmental concerns have resulted in the discontinuation of certain control methods, particularly organophosphate insecticides. All control methods must comply with regulations to protect vulnerable populations. The EPA's 2026 Pesticide General Permit has established strict requirements for pesticide applications to surface waters, which shape product development throughout North America.
Asia presents a diverse mix; China and India anchor volume through agricultural applications, while Southeast Asian markets leverage subsidies that mandate biological larvicides in rice-fish systems. Simultaneously, Aedes aegypti resistance to organophosphates and pyrethroids forces councils in Indonesia to rotate IGRs and Bti combinations, underpinning incremental unit growth. The larvicide market share attributable to Asia will expand each year of the outlook, yet margins may stay compressed given price sensitivity in several economies.
South America demonstrates the highest growth rate, driven by public health crises related to dengue and chikungunya outbreaks. Brazil reported 7.25 million dengue cases in 2024, exceeding twice the number recorded in 2023, prompting increased Bti investments across federal, state, and municipal governments. Urban sanitation departments combine source reduction initiatives with weekly larvicide applications, ensuring consistent product demand that maintains distributor inventory levels.
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Syngenta AG
- Sumitomo Chemical Co.
- Clarke Mosquito Control Products Inc.
- Central Life Sciences
- Certis Biologicals
- UPL Ltd.
- FMC Corporation
- Russell IPM
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in insecticide-resistant adult mosquitoes
- 4.2.2 Roll-out of dengue and chikungunya prevention programs
- 4.2.3 Climate-induced expansion of mosquito breeding seasons
- 4.2.4 Government subsidies for integrated rice-fish farming
- 4.2.5 Regulatory Policies on Larvicides
- 4.2.6 Rapid scale-up of drone-based aerial application of larvicides
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Stringent aquatic-toxicity thresholds limiting chemical formulations
- 4.3.2 Low adoption of GIS breeding-site mapping curbing commercial sales
- 4.3.3 Supply-chain volatility for Bacillus fermentation media
- 4.3.4 Public pressure against synthetic vector-control compounds
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porters Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Synthetic Larvicides
- 5.1.2 Biological Larvicides
- 5.2 By Control Method
- 5.2.1 Chemical Agents
- 5.2.2 Biocontrol Agents
- 5.2.3 Insect Growth Regulators (IGR)
- 5.3 By Target Insect
- 5.3.1 Mosquitoes
- 5.3.2 Flies
- 5.3.3 Beetles
- 5.3.4 Ants
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Agriculture
- 5.4.2 Non Agriculture
- 5.5 By Formulation
- 5.5.1 Granules
- 5.5.2 Liquids and Suspensions
- 5.5.3 Pellets and Tablets
- 5.5.4 Powders and Wettable Dusts
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.2 Germany
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Spain
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Africa
- 5.6.4.1 South Africa
- 5.6.4.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.4.3 Egypt
- 5.6.4.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.5 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.3 Qatar
- 5.6.5.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.6 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.6.1 China
- 5.6.6.2 India
- 5.6.6.3 Japan
- 5.6.6.4 Australia
- 5.6.6.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.3.1 BASF SE
- 6.3.2 Bayer AG
- 6.3.3 Syngenta AG
- 6.3.4 Sumitomo Chemical Co.
- 6.3.5 Clarke Mosquito Control Products Inc.
- 6.3.6 Central Life Sciences
- 6.3.7 Certis Biologicals
- 6.3.8 UPL Ltd.
- 6.3.9 FMC Corporation
- 6.3.10 Russell IPM






