 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851558
石油和天然气资本支出:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Oil And Gas CAPEX - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
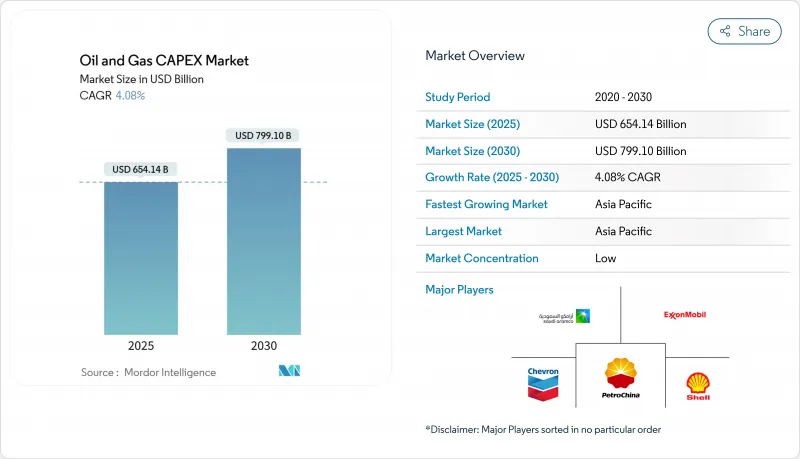
预计到 2025 年,石油和天然气资本支出市场规模将达到 6,541.4 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将达到 7,991.1 亿美元,在预测期(2025-2030 年)内复合年增长率为 4.08%。
营运商正在调整投资组合,以应对长达数十年的能源转型,同时将资金投入到能够确保在价格週期中实现稳定现金流的高回报计划中。深水计画、液化天然气计画和棕地脱碳计画占据了大部分支出,因为它们兼具经济竞争力和战略意义。严格追求全週期损益平衡正在推动最终投资决策(FID)的快速出台,并促使企业从前沿勘探转向开发钻井。大型综合石油公司和国家石油公司(NOC)之间的整合释放了规模效益,而数位化技术则减少了计划超支并降低了营运成本。随着与环境、社会和治理(ESG)相关的契约收紧了债务融资管道并提高了专案审批门槛,策略融资仍然是关注的焦点。
全球油气资本支出市场趋势及洞察
增加液化天然气相容型天然气基础设施的建设
长期承购协议和结构性天然气供需平衡是推动液化天然气大型企划发展的催化剂,例如伍德赛德公司投资175亿美元的路易斯安那州液化天然气项目和科珀斯克里斯蒂三期扩建项目。市场先驱正将投资范围从液化扩展到加工、管道和储存,从而在整个油气资本支出市场产生倍增效应。在天然气滞留地区抢占先机的企业,例如与沙乌地阿美公司签订的里奥格兰德液化天然气承购协议,预计将在未来几十年锁定自由现金流。
深水勘探发现的增加推动了最终投资决定
海底设备成本的套件和标准化计划模式的推行,已将深水油气盈亏平衡点推低至每桶50美元以下,迫使BP价值50亿美元的Kaskida项目和道达尔能源价值60亿美元的Caminho项目等计划进入审批阶段。因此,油气资本支出市场对专业钻机、海底钻井平台(SURF)和浮式生产储卸油装置(FPSO)承包商的订单强劲,预计到2025年,海上EPC(工程、采购、施工)市场规模将达到540亿美元。
布兰特原油价格波动对长期计划带来不利影响。
2024年布兰特原油价格区间预计在每桶68-93美元之间,但这掩盖了日内价格的剧烈波动,也使得投资回收期为7-10年的计划的净现值计算变得复杂。贷款机构的应对措施包括提高最低利率和收紧压力测试,这实际上筛选掉了边际油气资本支出市场的机会。花旗银行预测,到2025年油价可能会跌至每桶60美元左右,进一步抑制了长期投资的意愿。
细分市场分析
2024年,上游产业将占油气资本支出市场份额的72.92%,预计到2030年将以4.20%的复合年增长率增长,这主要得益于运营商加快对高回报深水和传统型计划的最终投资决策。该行业的成长势头反映了其战略重心向短期开发项目的转变,这些项目能够快速适应大宗商品价格波动,同时保持具有竞争力的回报。重要的上游投资项目包括BP投资50亿美元的卡斯基达计划和雪佛龙的腾吉兹未来成长计划,后者已于2025年1月投产,将新增26万桶/日的产能。中游业务的重点是解决关键基础设施瓶颈问题,以促进上游产量的成长,特别是液化天然气加工和管道输送能力的扩张。由于企业优先考虑维护性资本支出而非产能扩张,下游投资仍受到利润率压力和长期需求预测不确定性的限制。
数位转型正透过人工智慧驱动的钻井优化和预测维修系统重塑上游计划执行模式,从而降低营运成本并提高采收率。 SLB公司签署的大型人工智慧驱动深水钻井合约表明,采用技术来提升复杂储存开发领域的竞争力已变得日益迫切。上游资本支出分配越来越侧重于生产优化而非勘探,这反映了过去週期中以勘探为导向的策略收益不足的经验教训。各公司正利用先进的地震成像和油藏建模技术来最大限度地提高现有油田的产量,而不是开展投机性的探勘项目。这种以生产为中心的策略符合投资者对资本纪律和短期现金流的需求,同时也能维持长期蕴藏量替代率。
区域分析
亚太地区是全球最大的油气市场(2024年市场占有率达29%),也是成长最快的区域油气资本支出市场,预计到2030年复合年增长率将达到4.86%。这反映了能源安全的需求,以及各国国家石油公司(NOC)旨在降低进口依赖、抓住国内市场成长机会的大规模投资计画。 PTTEP公司2025年53亿美元的资本支出计画表明,该地区的营运商正优先考虑上游天然气开发和液化天然气(LNG)供应链投资,以满足国内消费和出口需求。经济发展和资料中心扩张带来的电力需求成长推动了该地区的成长势头,雪佛龙等公司在印度设立大型工程中心,以利用成本优势和当地市场机会。中国和印度的国家石油公司正在加速国内勘探和开发计划,同时寻求国际收购以确保长期资源取得。然而,随着国际银行实施与环境、社会和治理(ESG)相关的贷款监管规定,该地区的营运商面临日益严峻的资金筹措挑战。亚太地区的石油和燃气公司96%的收入来自石化燃料业务,而全球同行则更加多元化。
北美和欧洲市场的发展趋势截然不同。北美受益于页岩生产最佳化和液化天然气出口基础设施的建设,而欧洲则日益关注维护性资本支出和脱碳计划。北美营运商,例如德文能源(Devon Energy)和EOG资源公司,展现了卓越的资本纪律。根据investing.com报道,德文能源在2025年第一季创造了10亿美元的自由现金流,同时下调了1亿美元的资本支出预期。儘管各公司仍在继续投资现有业务和碳捕获技术,但欧洲的投资却受到监管压力和可再生能源政策的限制,这些政策限制了新的石化燃料开发。北美页岩气产业可以根据大宗商品价格灵活调整产量,而欧洲营运商则在更严格的政策框架下运作。南美市场继续专注于深水开发和能够满足国内能源安全需求和出口市场机会的计划,但政治稳定性和监管一致性仍然影响着国际营运商的参与程度。
中东和非洲市场的发展动力源自于其丰富的低成本蕴藏量以及鼓励国内外发展的政府扶持政策。该地区受益于通常低于每桶20美元的生产成本和完善的基础设施,与新兴地区相比,开发週期更短,资本支出需求也更低。包括沙乌地阿美在内的区域石油公司正在实施大规模的上游扩张计划,同时投资下游一体化和石化设施,以在整个油气价值链中获得更高的附加价值利润。埃克森美孚计画在奈及利亚投资15亿美元用于深水油气开发,显示儘管面临全球能源转型带来的压力,国际业者仍将该地区列为优先发展区域。该地区资本支出的成长得益于与亚洲买家签订的长期供应协议,以及为应对能源转型期间预期的全球供应趋紧而采取的战略布局。然而,随着可再生能源的加速普及,营运商必须应对不断变化的环境、社会和治理(ESG)预期以及传统出口市场潜在需求下降的问题。
其他好处
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 液化天然气相容天然气基础设施发展进展
- 深水勘探发现的增加推动了最终投资决策
- 中东和亚洲国家石油公司上游投资的復苏
- 棕地脱碳计画「维护资本支出」激增
- 数位双胞胎部署可减少计划超支
- 1兆瓦以下模组化浮式液化天然气装置吸引小型气田建设许可
- 市场限制
- 布兰特原油价格波动剧烈,不利于长期计划开展。
- 经合组织政策转向再生能源
- 一级EPC(工程、采购和施工)劳动力短缺导致成本上升
- 与环境、社会及治理(ESG)相关的债务条款限制石化燃料资本支出
- 供应链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 原油生产与消费展望
- 天然气生产与消费展望
- 管道设置容量分析
- 非传统资源支出展望(緻密油、油砂、深水)
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争的激烈程度
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按行业
- 上游
- 中产阶级
- 下游
- 按地区
- 陆上
- 离岸
- 依资产类型
- 远征
- 开发与生产
- 维护和检修
- 退休
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 欧洲
- 挪威
- 英国
- 俄罗斯
- 荷兰
- 德国
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 东南亚国协
- 澳洲
- 亚太其他地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 哥伦比亚
- 其他南美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 卡达
- 奈及利亚
- 南非
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略性倡议(併购、伙伴关係、购电协议)
- 市场占有率分析(主要企业的市场排名/份额)
- 公司简介
- Saudi Aramco
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- Shell plc
- BP plc
- TotalEnergies SE
- Chevron Corporation
- PetroChina(CNPC)
- CNOOC Ltd
- Equinor ASA
- Petrobras
- ConocoPhillips
- ENI SpA
- Suncor Energy
- Occidental Petroleum
- Woodside Energy
- Lukoil PJSC
- ONGC
- Cairn Oil & Gas(Vedanta)
- QatarEnergy
- SLB(Schlumberger)
- Halliburton
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Oil And Gas CAPEX Market size is estimated at USD 654.14 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 799.11 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.08% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Operators funnel capital toward high-return projects that protect cash flows during volatile price cycles while positioning portfolios for a multi-decade energy transition. Deepwater, LNG, and brownfield decarbonization programs dominate the spending slate because they combine competitive economics with strategic relevance. Tight discipline on full-cycle break-evens prompts faster final investment decisions (FIDs) and a visible shift from frontier exploration to development drilling. Consolidation among integrated majors and national oil companies (NOCs) unlocks scale efficiencies, while digital technologies trim project overruns and lower operating costs. Strategic finance remains a watchpoint as ESG-linked covenants tighten access to debt and raise the hurdle rate for green-light decisions.
Global Oil And Gas CAPEX Market Trends and Insights
Increasing LNG-Ready Gas Infrastructure Build-Out
Long-term offtake contracts and structurally tight gas balances have catalyzed LNG megaprojects such as Woodside's USD 17.5 billion Louisiana facility and the Corpus Christi Stage 3 expansion. Developers are extending spend beyond liquefaction into processing, pipelines, and storage, creating multiplier effects throughout the oil and gas capex market. First-mover positions in regions with stranded gas-illustrated by NextDecade's Rio Grande LNG offtake with Saudi Aramco-are projected to lock in decades of free cash flow.
Rising Deep-Water Discoveries Driving FIDs
Cost deflation in subsea kit and standardized project models has dropped deepwater breakevens below USD 50 per barrel, pushing projects like BP's USD 5 billion Kaskida and TotalEnergies' USD 6 billion Kaminho to sanction. Therefore, the oil and gas capex market sees robust order books for specialized rigs, SURF and FPSO contractors, with 2025 offshore EPC opportunities estimated at USD 54 billion.
Volatility in Dated Brent Discouraging Long-Cycle Projects
Brent's USD 68-93 range in 2024 masked sharp intraday swings that complicate NPV calculations for projects with 7-10 year paybacks. Lenders have responded by raising hurdle rates and tightening stress-test scenarios, effectively screening out marginal oil and gas capex market opportunities. Citi's forecast of prices potentially dropping into the USD 60s by 2025 further discourages long-cycle commitments.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- NOC Upstream Spending Rebound in Middle East & Asia
- Surge in "Maintenance CAPEX" to Decarbonize Brownfields
- Policy Pivots Toward Renewables in OECD
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Upstream activities command 72.92% of the oil and gas capex market share in 2024, benefiting from a 4.20% CAGR forecast through 2030 as operators accelerate final investment decisions on high-return deepwater and unconventional projects. The sector's growth momentum reflects strategic repositioning toward short-cycle developments that adapt quickly to commodity price fluctuations while maintaining competitive returns. Major upstream investments include BP's USD 5 billion Kaskida project and Chevron's Future Growth Project at Tengiz, which commenced production in January 2025 with the capacity to increase output by 260,000 barrels per day. Midstream operations focus on critical infrastructure bottlenecks, particularly LNG processing and pipeline capacity expansions that enable upstream production growth. With companies prioritizing maintenance CAPEX over capacity additions, downstream investments remain constrained by margin pressures and uncertain long-term demand projections.
Digital transformation reshapes upstream project execution through AI-enabled drilling optimization and predictive maintenance systems that reduce operational costs and improve recovery rates. SLB's major AI-enabled deepwater drilling contract demonstrates how technology adoption is becoming essential for competitive positioning in complex reservoir developments. The upstream sector's CAPEX allocation increasingly emphasizes production optimization over exploration, reflecting lessons learned from previous cycles where discovery-focused strategies generated insufficient returns. Companies leverage advanced seismic imaging and reservoir modeling to maximize output from existing fields rather than pursuing speculative exploration programs. This production-centric approach aligns with investor demands for capital discipline and near-term cash flow generation while maintaining long-term reserve replacement ratios.
The Oil and Gas CAPEX Market Report is Segmented by Sector (Upstream, Midstream, and Downstream), Location (Onshore and Offshore), Asset Type (Exploration, Development and Production, Maintenance and Turn-Around, and Decommissioning), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa). The Market Sizes and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific emerges as the largest (29% of the market share in 2024) and the fastest-growing regional oil and gas capex market with 4.86% CAGR through 2030, reflecting energy security imperatives and substantial NOC investment programs designed to reduce import dependence and capture domestic market growth. PTTEP's USD 5.3 billion CAPEX plan for 2025 demonstrates how regional operators prioritize upstream gas development and LNG supply chain investments to serve domestic consumption and export opportunities. The region's growth momentum is supported by rising electricity demand driven by economic development and data center expansion, with companies like Chevron establishing major engineering centers in India to capture cost advantages and local market opportunities. Chinese and Indian NOCs are accelerating domestic exploration and development programs while pursuing international acquisitions that secure long-term resource access. However, regional operators face increasing financing challenges as international banks implement ESG-linked lending restrictions. APAC oil and gas firms generate 96% of revenues from fossil fuel activities compared to more diversified global peers.
North American and European markets are experiencing divergent trends, with North America benefiting from shale production optimization and LNG export infrastructure development while Europe focuses increasingly on maintenance CAPEX and decarbonization projects. North American operators like Devon Energy and EOG Resources demonstrate exceptional capital discipline. Devon generated USD 1 billion in free cash flow during Q1 2025 while reducing CAPEX guidance by USD 100 million, investing.com. Though companies continue to invest in existing operations and carbon capture technologies, European investments are constrained by regulatory pressures and renewable energy policies that discourage new fossil fuel development. The regional divergence reflects different regulatory environments and resource endowments, with North American shale providing flexibility to adjust production levels based on commodity prices while European operators navigate more restrictive policy frameworks. South American markets remain focused on deepwater developments and infrastructure projects that can serve domestic energy security needs and export market opportunities, though political stability and regulatory consistency continue to influence international operator participation levels.
Middle East and Africa market is driven by abundant low-cost reserves and supportive government policies that encourage domestic and international development. The region benefits from production costs often below USD 20 per barrel and established infrastructure networks that reduce development timelines and CAPEX requirements compared to frontier regions. Saudi Aramco and other regional NOCs are implementing substantial upstream expansion programs while investing in downstream integration and petrochemical facilities that capture higher value-added margins throughout the hydrocarbon value chain. ExxonMobil's planned USD 1.5 billion deepwater investment in Nigeria exemplifies how international operators prioritize the region despite global energy transition pressures. The region's CAPEX growth is supported by long-term supply contracts with Asian buyers and strategic positioning for anticipated global supply tightness during the energy transition period. However, operators must navigate evolving ESG expectations and potential demand destruction in traditional export markets as renewable energy adoption accelerates.
- Saudi Aramco
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- Shell plc
- BP plc
- TotalEnergies SE
- Chevron Corporation
- PetroChina (CNPC)
- CNOOC Ltd
- Equinor ASA
- Petrobras
- ConocoPhillips
- ENI SpA
- Suncor Energy
- Occidental Petroleum
- Woodside Energy
- Lukoil PJSC
- ONGC
- Cairn Oil & Gas (Vedanta)
- QatarEnergy
- SLB (Schlumberger)
- Halliburton
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing LNG-ready gas infrastructure build-out
- 4.2.2 Rising deep-water discoveries driving FIDs
- 4.2.3 NOC upstream spending rebound in Middle East & Asia
- 4.2.4 Surge in "maintenance CAPEX" to decarbonise brownfields
- 4.2.5 Digital twin roll-outs cutting project overruns
- 4.2.6 Sub-1 MW modular FLNG attracting small-field sanctioning
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Volatility in Dated Brent discouraging long-cycle projects
- 4.3.2 Policy pivots toward renewables in OECD
- 4.3.3 Scarcity-pricing of Tier-1 EPC labour elevating costs
- 4.3.4 ESG-linked debt covenants capping fossil CAPEX ceilings
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Crude-Oil Production and Consumption Outlook
- 4.8 Natural-Gas Production and Consumption Outlook
- 4.9 Installed Pipeline Capacity Analysis
- 4.10 Unconventional Resources CAPEX Outlook (tight oil, oil sands, deep-water)
- 4.11 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.11.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.11.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.11.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.11.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.11.5 Intensity of Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Sector
- 5.1.1 Upstream
- 5.1.2 Midstream
- 5.1.3 Downstream
- 5.2 By Location
- 5.2.1 Onshore
- 5.2.2 Offshore
- 5.3 By Asset Type
- 5.3.1 Exploration
- 5.3.2 Development and Production
- 5.3.3 Maintenance and Turn-around
- 5.3.4 Decommissioning
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Norway
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 Russia
- 5.4.2.4 Netherlands
- 5.4.2.5 Germany
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 South Korea
- 5.4.3.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.4.3.6 Australia
- 5.4.3.7 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Colombia
- 5.4.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.3 Qatar
- 5.4.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.4.5.5 South Africa
- 5.4.5.6 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Saudi Aramco
- 6.4.2 Exxon Mobil Corporation
- 6.4.3 Shell plc
- 6.4.4 BP plc
- 6.4.5 TotalEnergies SE
- 6.4.6 Chevron Corporation
- 6.4.7 PetroChina (CNPC)
- 6.4.8 CNOOC Ltd
- 6.4.9 Equinor ASA
- 6.4.10 Petrobras
- 6.4.11 ConocoPhillips
- 6.4.12 ENI SpA
- 6.4.13 Suncor Energy
- 6.4.14 Occidental Petroleum
- 6.4.15 Woodside Energy
- 6.4.16 Lukoil PJSC
- 6.4.17 ONGC
- 6.4.18 Cairn Oil & Gas (Vedanta)
- 6.4.19 QatarEnergy
- 6.4.20 SLB (Schlumberger)
- 6.4.21 Halliburton
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment






