 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1910594
电力电子:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Power Electronics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
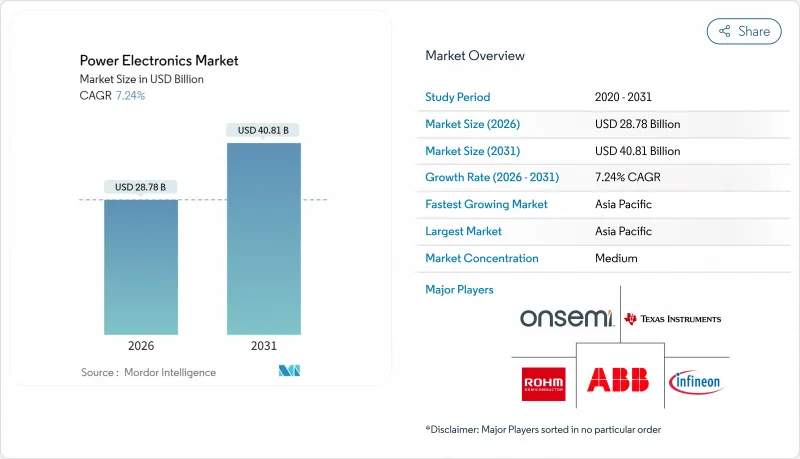
预计电力电子市场规模将从 2025 年的 268.4 亿美元成长到 2026 年的 287.8 亿美元,到 2031 年将达到 408.1 亿美元,2026 年至 2031 年的复合年增长率为 7.24%。
这项进展主要得益于传统硅系统向碳化硅 (SiC) 和氮化镓 (GaN) 解决方案的持续转型,这些转型在关键应用中实现了更高的效率、功率密度和更小的外形规格。随着汽车製造商扩大电动车产量、电力公司更新逆变器以适应可再生能源以及资料中心营运商采用高压直流 (HVDC) 架构,市场需求加速成长。此外,区域政策也促进了国内半导体製造和电动车基础设施建设,从而推动了宽能带隙材料的应用。同时,供应链多元化倡议,尤其是在亚太地区,提高了基板、外延和先进封装的本地化生产能力,缩短了前置作业时间并降低了运输风险。
全球电力电子市场趋势与洞察
加速在电动车快速充电基础设施中采用碳化硅和氮化镓装置
为了达到併网效率目标,欧洲充电网路营运商优先采用800V架构,该架构需要1200V和1700V的碳化硅(SiC)MOSFET。奖励计划支持了SiC功率级标准化的计划,这些项目降低了能量损耗并缩小了冷却子系统的尺寸。系统整合商和半导体供应商之间的合作缩短了设计週期,而与汽车製造商的合作协议则确保了长期的大规模生产。互通性法规进一步为基于宽能带隙装置的模组化、高密度充电器创造了更公平的竞争环境。成功的部署吸引了全球的关注,使欧洲成为下一代快速充电解决方案的标竿市场。
亚洲大型太阳能和风力发电厂逆变器更换
中国、印度和越南的公用事业级太阳能发电厂正在用碳化硅(SiC)组件取代传统的硅逆变器,这些组件能够在高温高湿环境下承受高开关频率。 Wolfspeed 最新推出的公用事业级组件能够满足集中式 3MW 至 5MW 逆变器所需的热循环可靠性。离岸风电开发商也正在采用类似的功率等级,以满足涡轮机机舱的尺寸和重量限制。区域契约製造製造商正在推动本地组装,以避免进口关税,从而加快与传统硅产品的价格竞争。这些升级符合各国政府的可再生能源部署标准,并有助于在新兴经济体中维持具有竞争力的电力价格。
150毫米及以上尺寸碳化硅晶圆的供应链瓶颈
长期的基板短缺限制了产能扩张,导致平均售价居高不下。 Wolfspeed 暂时的融资挑战增加了依赖其 200mm 晶圆蓝图的合作伙伴的风险,最终导致瑞萨电子计划退出 SiC 平台。中国的新参与企业加快了产能扩张,但在获得汽车製造商客户的认证方面面临挑战。晶圆厂宣布投产到量产准备就绪之间存在多年的滞后,这使得装置製造商和系统 OEM 的需求预测变得复杂。因此,一些汽车製造商采取了双重采购策略来确保晶圆配额。
细分市场分析
到2031年,功率模组的复合年增长率将达到8.49%,这主要得益于设计团队选择预封装组件,从而简化了散热布局和电磁屏蔽。 2025年,分立电晶体和二极体的收入占比将达到45.92%,它们在消费性电子产品和低功率工厂设备领域保持了柔软性。 50kW以上的牵引逆变器和可再生能源转换设备对模组的需求激增,其中闸极驱动器、温度感测器和隔离功能的整合缩短了开发週期。整合式冷却基板正进入试生产阶段,这提高了模组的功率密度,并使电动车的逆变器机壳得以缩小。整合功率IC在100W以下快速充电适配器市场占据了更大的份额,它将控制和开关功能整合到单一塑胶封装中,满足了严格的尺寸限制。智慧型手机製造商采用了这些单晶片GaN解决方案,实现了透过紧凑型墙插进行65W充电。随着汽车供应商向800V平台过渡,功率电子模组市场预计将稳定成长。同时,消费性电子产品设计的应用也推动了分立元件的销售成长。
市场上的转注成型封装标准化为在恶劣气候下运作的工业驱动器带来了成本节约和卓越的防潮性能。製造商已利用自动化组装来满足不断增长的生产需求,尤其是在亚太地区。然而,在照明安定器、家用电器和机器人控制设备等应用领域,分立元件仍然占据主导地位,因为在这些应用中,客製化的基板布局和多样化的电压等级比整合化更具优势。在预测期内,碳化硅晶圆供应量的增加将进一步推动模组化,而分立元件的销售量预计将逐步下降,而非急剧下降。
到2025年,MOSFET将占总营收的43.62%,成为规模最大且成长最快的装置类别,复合年增长率(CAGR)为8.98%。这种架构有利于渐进式研发,例如Wolfspeed的第四代平台,该平台在保持传统闸极驱动要求的同时降低了导通电阻。充电适配器和太阳能微型逆变器中的高频谐振拓扑结构越来越倾向于使用GaN增强MOSFET,而SiC平面MOSFET则在100kW以上的车辆驱动级中占据主导地位。 IGBT在铁路推进系统和大型工业驱动装置中仍然至关重要,能够满足超出MOSFET实际应用范围的功率等级需求。闸流体继续用于併网缓衝启动器和高压直流输电线路,但其整体份额有所下降。
装置製造商已推出用于碳化硅 MOSFET 和肖特基二极体的共封装技术,从而缓解反向恢復限制并简化基板布局;与此同时,氮化镓供应商正在改进动态导通电阻 (RDS(on)) 特性,以延长装置在硬开关条件下的使用寿命。电力电子市场持续重视 MOSFET 的创新,因为其外形尺寸与现有驱动系统相容,并降低了系统工程师的设计门槛。未来市占率的波动将取决于宽能带隙晶圆的价格趋势以及新一代 MOSFET 闸极技术的汽车级认证速度。
电力电子市场按组件(分立元件、模组、整合功率 IC)、装置类型(MOSFET、IGBT、闸流体、二极体)、材料(硅、碳化硅、其他)、终端用户产业(家用电子电器、汽车、ICT 和通讯、工业、能源和电力、航太和国防等)以及地区(北美、欧洲、亚太地区、中东、中东和欧洲)进行细分、中东和国防等地区(北美、欧洲、亚洲)。
区域分析
到2025年,亚太地区将占全球营收的53.88%,以10.05%的复合年增长率进一步扩大领先优势。中国、日本和韩国的国家级专案已为晶圆厂、模组组装和电动车供应链提供资金支持,确保基板和先进封装的在地采购。日本政府承诺投入670亿美元扶持国内半导体产业,扶持SONY和三菱电机等公司,同时加强与大学的研究合作。中国当地虽然在最尖端科技方面存在滞后,但已利用材料增长和后端组装的规模经济优势,实现了向区域客户更快的供货速度和更低的到岸成本。
北美仍然是第二大市场,其创新实力与人工智慧伺服器、电动皮卡和可再生能源微电网等充满活力的终端市场相结合。各州政府的奖励措施吸引了新的碳化硅晶圆厂,并促进了向200毫米晶圆过渡的资金投入。国防采购持续资助抗辐射氮化镓(GaN)的研究,后来被应用于商业通讯系统。随着资料中心营运商采用400V直流架构以减少铜用量并提高机架密度,北美电力电子市场规模正在不断扩大。欧洲将资源集中于电动车充电走廊和电网级储能。政策制定者强制要求充电硬体互通性,由于碳化硅在800V电压下的效率,间接推动了其应用。一级汽车供应商与半导体供应商合作,共同开发牵引逆变器,建构整合参考平台并加速型式认证。中东和非洲地区投资建造了大型太阳能发电厂和海水淡化厂,儘管占地面积较小,但这些项目仍需要强大的逆变器等级。在南美洲,巴西和阿根廷的风能走廊以及鼓励在该地区组装功率模组的在地采购政策,正在创造新的机会。这些趋势共同推动电力电子市场在全球各大洲的扩张,儘管不同地区在产业成熟度和政策支持力度方面存在差异。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 欧洲电动车快速充电基础设施中SiC/GaN装置的采用速度加快
- 亚洲大型太阳能和风力发电厂对逆变器更换的需求正在推动高压功率模组市场的发展。
- 在北美部署5G基地台需要高效率的射频功率放大器。
- 东南亚7.5kW以上工业电机驱动装置电气化
- 中国的电网级电池计画推动了对双向功率转换器的需求
- 美国向全电动平台现代化转型推动了强劲的电力电子技术发展。
- 市场限制
- 150毫米及以上尺寸碳化硅晶圆的供应链瓶颈限制了其大规模生产。
- 1.2kV以上模组的封装温度控管限制
- 200mm宽能带隙晶圆厂的高额资本投入阻碍了新进者。
- 供应链分析
- 监理与技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
- 投资与资金筹措分析
- 对影响市场的宏观经济因素进行评估
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按组件
- 离散的
- 模组
- 整合电源IC
- 依设备类型
- MOSFET
- IGBT
- 闸流体
- 二极体
- 材料
- 硅(Si)
- 碳化硅(SiC)
- 氮化镓(GaN)
- 按最终用户行业划分
- 家用电子电器
- 汽车(电动车、充电)
- 资讯与通讯科技(ICT)与电讯
- 工业(驱动装置、自动化)
- 能源与电力(可再生能源、高压直流输电)
- 航太/国防
- 医疗设备
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 日本
- 韩国
- 台湾
- 印度
- 亚太其他地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 中东
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 土耳其
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 其他非洲地区
- 中东
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略性倡议(併购、合资、许可)
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Infineon Technologies AG
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- ON Semiconductor Corporation
- STMicroelectronics NV
- Texas Instruments Inc.
- ROHM Co., Ltd.
- ABB Ltd.
- Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corp.
- Vishay Intertechnology Inc.
- Renesas Electronics Corp.
- Wolfspeed Inc.
- Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- SEMIKRON Danfoss
- Littelfuse Inc.
- GeneSiC Semiconductor
- Navitas Semiconductor Corp.
- GaN Systems Inc.
- Alpha & Omega Semiconductor
- Microchip Technology Inc.
- Diodes Incorporated
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The power electronics market is expected to grow from USD 26.84 billion in 2025 to USD 28.78 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 40.81 billion by 2031 at 7.24% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Continued migration from legacy silicon systems toward silicon-carbide and gallium-nitride solutions underpins this advance, enabling higher efficiency, power density, and smaller form factors in critical applications. Demand accelerated as automakers scaled electric-vehicle production, utilities upgraded renewable-energy inverters, and data-center operators adopted high-voltage direct-current architectures. Wide-bandgap adoption also benefited from regional policy support that encouraged domestic semiconductor manufacturing and electric-mobility infrastructure. Meanwhile, supply-chain diversification initiatives, especially across Asia-Pacific, bolstered localized production of substrates, epitaxy, and advanced packaging, reducing lead times and transportation risk.
Global Power Electronics Market Trends and Insights
Accelerated adoption of SiC and GaN devices in EV fast-charging infrastructure
European charging-network operators prioritized 800 V architectures that require 1,200 V and 1,700 V SiC MOSFETs to meet grid-connection efficiency targets. Projects backed by incentive programs are standardized on SiC power stages that cut energy losses and shrink cooling subsystems. Collaboration between system integrators and semiconductor suppliers shortened design cycles, while alliance agreements with automotive OEMs ensured long-term volume commitments. Interoperability regulations further created a level playing field that favors modular, high-density chargers based on wide-bandgap devices. Successful deployments draw global attention, positioning Europe as the reference market for next-generation fast-charging solutions.
Large-scale solar and wind farm inverter upgrades in Asia
Utility-scale solar farms in China, India, and Vietnam replaced legacy silicon inverters with SiC-based modules that withstand high switching frequencies in hot, humid environments. Wolfspeed's latest utility modules provided the thermal-cycling reliability demanded by centralized 3 MW to 5 MW inverters. Offshore wind developers adopted similar power stages to meet size and weight limits on turbine nacelles. Regional contract manufacturers localized assembly to avoid import duties, accelerating price parity with conventional silicon alternatives. These upgrades align with government renewable portfolio standards, keeping energy tariffs competitive across emerging economies.
Supply-chain bottlenecks for 150 mm and larger SiC wafers
Chronic substrate shortages constrained volume ramps, keeping average selling prices elevated. Wolfspeed's temporary liquidity challenges increased risk exposure for partners that relied on its 200 mm roadmap, leading Renesas to exit its planned SiC platform. Chinese entrants accelerated capacity additions yet faced qualification hurdles with automotive customers. The multiyear lag between announced fabs and production readiness complicated demand-forecast accuracy for both device makers and system OEMs. As a result, several automakers executed dual-sourcing strategies to hedge wafer allocations.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- 5G base-station roll-outs requiring high-efficiency RF power amplifiers
- Electrification of industrial motor drives above 7.5 kW in Southeast Asia
- Packaging thermal-management constraints above 1.2 kV modules
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Power modules delivered 8.49% CAGR through 2031 as design teams opted for pre-packaged assemblies that simplify thermal layout and electromagnetic shielding. In 2025, discrete transistors and diodes still contributed 45.92% of revenue, preserving flexibility in consumer and low-power factory equipment. Demand for modules surged in traction inverters and renewable-energy converters above 50 kW where integrating gate drivers, temperature sensors, and isolation reduced development cycles. Embedded-cooling substrates entered pilot production, pushing module power density upward and enabling smaller inverter housings in electric vehicles. Integrated power ICs gained share in fast-charger adapters below 100 W, combining control and switching in a single plastic package that meets stringent size constraints. Smartphone brands adopted these monolithic GaN solutions to achieve 65 W charging in compact wall plugs. The power electronics market size for modules is forecast to expand steadily as automotive suppliers transition to 800 V platforms, while consumer design wins sustain volume in discrete devices.
Market-wide standardization on transfer-molded packages offered cost reductions and better moisture resistance for industrial drives operating in harsh climates. Manufacturers leveraged automated assembly lines to meet rising output needs, particularly across Asia-Pacific. Discrete devices nevertheless preserved a sizeable presence in lighting ballasts, home appliances, and robotic controllers, where customized board layouts and diverse voltage classes outweighed the integration advantage. Over the forecast span, increased silicon-carbide wafer availability will further tilt the share toward modules, yet discrete volumes will decline gradually rather than collapse.
MOSFETs captured 43.62% of 2025 revenue and their 8.98% CAGR positions them as both the largest and fastest-growing device category. The architecture lends itself to incremental R&D, evident in Wolfspeed's Gen 4 platform that reduced on-state resistance while maintaining familiar gate-drive requirements. High-frequency resonance topologies in charger adapters and solar micro-inverters gravitated to GaN enhancement-mode MOSFETs, whereas SiC planar MOSFETs excelled in vehicle traction stages above 100 kW. IGBTs remained essential in rail propulsion and large industrial drives, sustaining demand in power classes beyond practical MOSFET limits. Thyristors continued serving grid-tied soft-starters and HVDC links, though their overall contribution shrank.
Device-makers introduced co-packaged Schottky diodes with SiC MOSFETs, easing reverse-recovery constraints and simplifying board layouts. Meanwhile, gallium-nitride suppliers improved dynamic-RDS(on) behavior to extend device life in hard-switching conditions. The power electronics market continues to reward MOSFET innovation because the form factor aligns with existing driver ecosystems, lowering design barriers for system engineers. Future share shifts will hinge on wide-bandgap wafer pricing and the speed of automotive qualification for next-generation MOSFET gates.
Power Electronics Market is Segmented by Component (Discrete, Module, and Integrated Power IC), Device Type (MOSFET, IGBT, Thyristor, and Diode), Material (Silicon, Silicon Carbide, and More), End-User Industry (Consumer Electronics, Automotive, ICT and Telecommunication, Industrial, Energy and Power, Aerospace and Defense, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific generated 53.88% of global revenue in 2025 and is widening its lead with a 10.05% CAGR. National programs in China, Japan, and South Korea funded wafer fabs, module assembly, and electric-vehicle supply chains, ensuring local availability of substrates and advanced packaging. Japanese authorities pledged USD 67 billion to support domestic semiconductor fleets, aiding companies such as Sony and Mitsubishi Electric, and reinforcing university research collaborations. Mainland China leveraged economies of scale in material growth and backend assembly to supply regional customers quickly, lowering landed cost despite technology gaps in the leading edge.
North America remained the second-largest region, pairing innovation strengths with thriving end-markets in AI servers, electric pickup trucks, and renewable microgrids. State-level incentives attracted new SiC wafer plants and helped secure capital for 200 mm transitions. Defense procurement continued to fund radiation-tolerant GaN research, which later filtered into commercial telecom systems. The power electronics market size in North America is on an upward trajectory as data-center operators adopt 400 V DC architectures that reduce copper usage and improve rack density. Europe focused resources on e-mobility charging corridors and grid-level storage. Policymakers mandated interoperability of charging hardware, indirectly favoring SiC adoption due to its efficiency at 800 V. Automotive Tier 1 suppliers partnered with semiconductor vendors to co-develop traction inverters, creating integrated reference platforms that accelerate homologation. The Middle East and Africa region, while starting from a smaller base, invested in large photovoltaic plants and desalination facilities that require robust inverter stages. South America's opportunities emerged from wind corridors in Brazil and Argentina and from local content rules that encourage assembly of power modules within the region. Collectively, these dynamics keep the power electronics market expanding on every continent, though rates vary with industrial maturity and policy support.
- Infineon Technologies AG
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- ON Semiconductor Corporation
- STMicroelectronics N.V.
- Texas Instruments Inc.
- ROHM Co., Ltd.
- ABB Ltd.
- Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corp.
- Vishay Intertechnology Inc.
- Renesas Electronics Corp.
- Wolfspeed Inc.
- Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- SEMIKRON Danfoss
- Littelfuse Inc.
- GeneSiC Semiconductor
- Navitas Semiconductor Corp.
- GaN Systems Inc.
- Alpha & Omega Semiconductor
- Microchip Technology Inc.
- Diodes Incorporated
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Accelerated Adoption of SiC/GaN Devices in EV Fast-Charging Infrastructure across Europe
- 4.2.2 Large-Scale Solar and Wind Farm Inverter Upgrades in Asia Driving High-Voltage Power Modules
- 4.2.3 5G Base-Station Roll-outs Requiring High-Efficiency RF Power Amplifiers in North America
- 4.2.4 Electrification of Industrial Motor Drives Exceeding 7.5 kW in South-East Asia
- 4.2.5 Grid-Level Battery Storage Programs in China Boosting Bidirectional Power Converters
- 4.2.6 U.S. DoD Modernization Toward All-Electric Platforms Stimulating Rugged Power Electronics
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Supply-Chain Bottlenecks for 150 mm+ SiC Wafers Limiting Volume Production
- 4.3.2 Packaging Thermal-Management Constraints Above 1.2 kV Modules
- 4.3.3 High CAPEX for 200 mm Wide-Bandgap Fabs Hindering New Entrants
- 4.4 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory and Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 Investment and Funding Analysis
- 4.8 Assessment of macroeconomic factors on the market
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Discrete
- 5.1.2 Module
- 5.1.3 Integrated Power IC
- 5.2 By Device Type
- 5.2.1 MOSFET
- 5.2.2 IGBT
- 5.2.3 Thyristor
- 5.2.4 Diode
- 5.3 By Material
- 5.3.1 Silicon (Si)
- 5.3.2 Silicon Carbide (SiC)
- 5.3.3 Gallium Nitride (GaN)
- 5.4 By End-user Industry
- 5.4.1 Consumer Electronics
- 5.4.2 Automotive (xEV, Charging)
- 5.4.3 ICT and Telecommunication
- 5.4.4 Industrial (Drives, Automation)
- 5.4.5 Energy and Power (Renewables, HVDC)
- 5.4.6 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.4.7 Healthcare Equipment
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 South Korea
- 5.5.3.4 Taiwan
- 5.5.3.5 India
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, JVs, Licensing)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Infineon Technologies AG
- 6.4.2 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 6.4.3 ON Semiconductor Corporation
- 6.4.4 STMicroelectronics N.V.
- 6.4.5 Texas Instruments Inc.
- 6.4.6 ROHM Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.7 ABB Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corp.
- 6.4.9 Vishay Intertechnology Inc.
- 6.4.10 Renesas Electronics Corp.
- 6.4.11 Wolfspeed Inc.
- 6.4.12 Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 SEMIKRON Danfoss
- 6.4.14 Littelfuse Inc.
- 6.4.15 GeneSiC Semiconductor
- 6.4.16 Navitas Semiconductor Corp.
- 6.4.17 GaN Systems Inc.
- 6.4.18 Alpha & Omega Semiconductor
- 6.4.19 Microchip Technology Inc.
- 6.4.20 Diodes Incorporated
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment







