 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1852040
非洲农业拖拉机:市场份额分析、行业趋势与统计、成长预测(2025-2030 年)Africa Agricultural Tractor - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
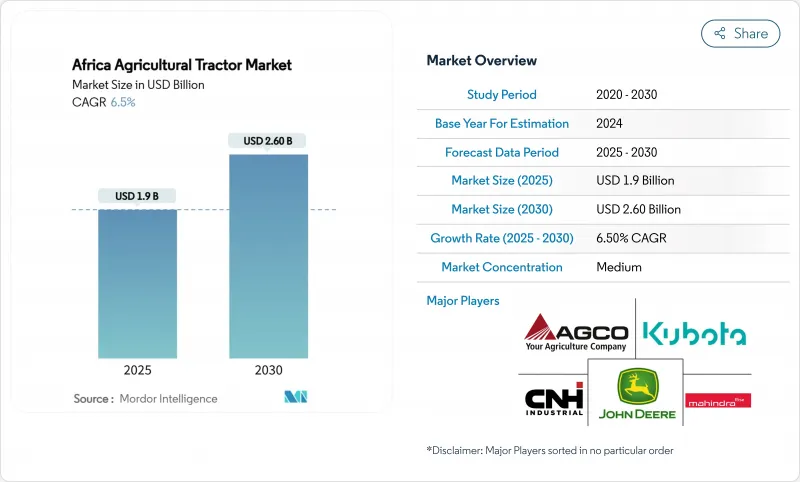
预计到 2025 年,非洲农业拖拉机市场规模将达到 19 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 26 亿美元,年复合成长率为 6.5%。
市场成长主要受机械化程度提高、商业农地扩张和政府扶持计画的推动。创新资金筹措方案的引入降低了农机设备购置门槛,而精准导航和互联技术的进步则鼓励农民升级到更大马力的拖拉机。数位化农机租赁平台透过提高利用率,改善了小农户的农机使用条件。外汇波动和所拥有土地分散制约了市场成长,而熟练操作人员和维修人员的短缺问题仍然是一项关键挑战。
非洲农业拖拉机市场趋势与洞察
扩大农业机械化和精密农业的引进
目前,非洲每1000公顷土地上运作的拖拉机不足两台,这意味着设备普及潜力巨大。尼日利亚透过与Hello Tractor公司官民合作关係,计划在五年内将拖拉机推广到900万公顷新土地上。南非的商业农民正在应用GPS导航和远端资讯处理系统,而凯斯纽荷兰公司(Case IH)则透过免除2024年10月之后购买的设备使用FieldOps应用程式的费用来提高其应用普及率。肯亚的「四大发展议程」(Big 4 Agenda)正在支持将机电一体化和数据驱动型作物管理相结合的自动化试验。这些技术带来的产量提升和废弃物减少将激励非洲农民在农业拖拉机市场投资购买更强大、更先进的机械设备。
政府补贴和机械化计划
政府补贴正在降低农民的前期成本。肯亚国家化肥补贴计画于2022年9月拨款35.5亿肯亚先令(约2,300万美元),用于2023年7月前发放350万袋50公斤的化肥,进而刺激农业机械的需求。尼日利亚正从政府经营的租赁项目转向混合模式,将私人业者和计量型租赁相结合,以提高设备运转率。南非的农业总体规划采用混合融资机制向农民提供信贷,以支持出口收入,预计2024年出口收入将达137亿美元。埃及的气候智慧型策略强调机械化,以因应预计2050产量下降的问题。成功与否取决于能否将财政支持与私人服务提供者和农民培训计划结合。
土地所有权分散限制了拖拉机的使用。
随着家庭农场日益分散,耕地面积持续减少,机械效率也随之降低。肯亚的研究表明,分散地块之间的运输增加了运输成本和设备停机时间。东非和南部非洲的劳动力评估显示,劳动力需求超过供给,凸显的是劳动力获取管道有限,而非缺乏需求。卢安达的土地利用整合计画前景可期,但主要受益者是拥有邻近地块的农民。客製化租赁服务有助于解决土地分散问题,但车队管理成本仍然很高。土地交换和密集种植有可能提高设备利用率,但要广泛实施还需要时间。
细分市场分析
到2024年,35-50马力细分市场将占据35.2%的市场份额,为多元化的小农户提供最佳的性价比。农民可以透过土地准备、播种和运输等融资项目获得这些拖拉机。由于农场整合和出口作物的增加,76-100马力拖拉机细分市场将以8.2%的复合年增长率成长。市场转向高功率机型的转变将使收入成长超过销售成长。
製造商正在开发适用于不同功率等级的模组化平台。 2024年,马恆达在开普敦发布了其OJA系列,该系列包含功率从20马力到70马力的四轮车型,并配备了数位智慧系统,强调其适应性。 35马力以下的拖拉机在果园和小块农田中仍然占有一席之地,但由于租赁车队更倾向于中阶拖拉机,其增长受到限制。 100匹马力以上的拖拉机市场规模虽小,但成长迅速,尤其是在南非的粮食产区,更高的生产力需求推动了相关投资。不同功率范围的需求差异反映了机械化普及率、农场规模和经济能力之间的关联。
到2024年,两轮驱动(2WD)拖拉机将占非洲农业拖拉机市场规模的81.2%。这一主导地位主要归功于该地区平坦的地形和成本优势。随着农民将耕作范围扩展到坡地和未耕地,并推广精密农业,预计四轮驱动(4WD)拖拉机的年复合成长率将达到10.1%。这一成长趋势在南非尤为显着,当地降雨模式的改善为农业扩张提供了支持。
四轮驱动(4WD)拖拉机能够减少土壤压实,并允许使用保护性犁地所需的重型设备。肯亚政府以粮食安全为重点,支持推广多功能四轮驱动拖拉机,这些拖拉机能够胜任整个生长季的多种田间作业。远端资讯处理数据显示,四轮驱动拖拉机的作业效率更高,促使农业承包商投资购买四轮驱动拖拉机,以提高服务可靠性。这种向高性能设备的持续转变预计将逐步降低两轮驱动拖拉机的市场份额。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 扩大农业机械化和精密农业的引进
- 政府补贴和机械化计划
- 商业园艺及种植出口经济作物
- 扩大农业信贷和拖拉机融资计划
- 透过行动平台计量型租赁拖拉机
- 在大面积农田推广低马力自主电动拖拉机
- 市场限制
- 土地所有权分散限制了拖拉机的使用。
- 熟练操作人员和维修技术人员短缺
- 外汇波动和进口关税推高了拖拉机的购买价格。
- 灰色市场零件供应链中断
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模和成长预测(价值和数量)
- 按引擎输出
- 不到35马力
- 35-50 HP
- 51-75 HP
- 76-100 HP
- 100马力或以上
- 透过牵引技术
- 两轮驱动(2WD)
- 四轮驱动(4WD)
- 透过推进力
- 柴油引擎
- 混合动力/电动
- 透过使用
- 农田作物
- 园艺和葡萄栽培
- 人工林和庄园作物
- 透过分销管道
- 授权经销商
- 线上和行动应用程式租赁平台
- 按地区
- 南非
- 肯亚
- 埃及
- 其他非洲地区
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- AGCO Corporation
- CNH Industrial NV
- Deere & Company
- Kubota Corporation
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.
- Argo Tractors SpA
- Tractors and Farm Equipment Limited
- International Tractors Limited
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- SDF SpA(Same Deutz-Fahr Tanzania Limited)
- YTO Group Corporation
- Zetor Tractors as
- JC Bamford Excavators Ltd.
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Captain Tractors Pvt. Ltd.
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Africa agricultural tractor market size is USD 1.9 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 2.6 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 6.5%.

The market growth is driven by increasing mechanization, expansion of commercial farming estates, and government support programs. The introduction of innovative financing options has reduced barriers to equipment ownership, while advancements in precision guidance and connectivity technologies encourage farmers to upgrade to higher-horsepower tractors. Digital platforms for equipment rental have improved access for smallholder farmers by increasing utilization rates. Currency fluctuations and fragmented landholdings constrain market growth, while addressing the shortage of skilled operators and maintenance personnel remains a key challenge.
Africa Agricultural Tractor Market Trends and Insights
Increasing Adoption of Farm Mechanization and Precision Agriculture
Africa currently operates fewer than two tractors per 1,000 hectares, indicating significant potential for equipment adoption. Nigeria aims to deploy tractors across 9 million hectares of new production through a public-private partnership with Hello Tractor over five years. South African commercial farmers are implementing GPS guidance and telematics systems, while Case IH eliminated subscription fees for its FieldOps application on machines purchased after October 2024 to increase usage. Kenya's Big Four Agenda supports automation trials combining mechatronics with data-driven crop management. The improved yields and reduced waste from these technologies encourage farmers to invest in higher horsepower and advanced machinery in the Africa agricultural tractor market.
Government Subsidies and Mechanization Programs
Government subsidies are reducing initial costs for farmers. Kenya's National Fertilizer Subsidy Program allocated 3.55 billion Kenyan shillings (USD 23 million) in September 2022 and distributed 3.5 million 50 kg bags by July 2023, driving demand for agricultural equipment. Nigeria has shifted from government-operated rental programs to mixed models combining private operators and pay-as-you-go leasing, which has improved equipment utilization. South Africa uses blended financing mechanisms in its agricultural master plan to provide credit to farmers, supporting export earnings that reached USD 13.7 billion in 2024. Egypt's climate-smart strategy emphasizes mechanization to address projected yield reductions by 2050. Success depends on combining financial support with private service providers and farmer training programs.
Fragmented Land Holdings Limiting Tractor Utilization Rates
Farm plot sizes continue to decrease as families subdivide their agricultural holdings, reducing equipment efficiency. Studies in Kenya show increased transportation costs and equipment downtime due to movement between scattered land parcels. Labor assessments in Eastern and Southern Africa indicate that demand surpasses supply, emphasizing access limitations rather than lack of need. While Rwanda's Land Use Consolidation program demonstrates promise, it primarily benefits farmers with adjacent plots. Though custom-hire services help address land fragmentation issues, significant fleet management costs remain. Land parcel exchanges and intensive cropping practices may enhance equipment utilization, but broad implementation requires time.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growth in Commercial Horticulture and Export-Oriented Cash Crops
- Expansion of Agricultural Credit and Tractor Financing Facilities
- Shortage of Skilled Operators and Maintenance Technicians
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The 35-50 HP segment holds 35.2% of the Africa agricultural tractor market share in 2024, providing an optimal cost-to-performance ratio for diverse smallholder operations. Farmers access these units through financing programs for land preparation, seeding, and transport activities. The 76-100 HP tractor segment grows at 8.2% CAGR, driven by farm consolidation and expansion of export crops. This market evolution toward higher-powered models increases revenue growth beyond unit sales volumes.
Manufacturers develop modular platforms across power segments. In 2024, Mahindra introduced the OJA series in Cape Town, featuring 20-70 HP four-wheel-drive models with digital intelligence systems, emphasizing adaptability. While below-35 HP tractors remain crucial for orchards and small plots, their growth is limited as rental fleets prefer mid-range machines. Over 100 HP tractors represent a small but growing segment, particularly in South African grain-producing regions where productivity requirements support higher investments. The varying demand across horsepower ranges reflects the correlation between mechanization adoption, farm size, and economic capacity.
Two-wheel drive (2WD) tractors account for 81.2% of the Africa agricultural tractor market size in 2024. The dominance stems from the region's predominantly flat terrain and cost considerations. Four-wheel drive (4WD) tractors are projected to grow at a 10.1% CAGR as farmers expand operations into sloped and uncultivated areas while implementing precision agriculture. This growth trend is particularly evident in South Africa, where improved rainfall patterns support agricultural expansion.
Four-wheel drive (4WD) tractors reduce soil compaction and enable the use of heavier implements required for conservation tillage practices. The Kenyan government's focus on food security supports increased adoption of 4WD tractors, which offer greater versatility for multiple field operations throughout the growing season. Telematics data demonstrating operational efficiency has prompted agricultural contractors to invest in 4WD models to enhance service reliability. This ongoing transition toward performance-focused equipment is anticipated to gradually reduce the two-wheel-drive market share.
The Africa Agricultural Tractor Market Report is Segmented by Engine Power (Less Than 35 HP, and More), by Traction Technology (2-Wheel Drive (2WD), and More), by Propulsion (Diesel, and Hybrid/Electric), by Application (Row-Crop Farming, and More), by Distribution Channel (Authorised Dealerships, and More), and by Geography (South Africa, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- AGCO Corporation
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- Deere & Company
- Kubota Corporation
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.
- Argo Tractors S.p.A.
- Tractors and Farm Equipment Limited
- International Tractors Limited
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- SDF S.p.A (Same Deutz-Fahr Tanzania Limited)
- YTO Group Corporation
- Zetor Tractors a.s.
- J C Bamford Excavators Ltd.
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Captain Tractors Pvt. Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Adoption of Farm Mechanization and Precision Agriculture
- 4.2.2 Government Subsidies and Mechanization Programs
- 4.2.3 Growth in Commercial Horticulture and Export-Oriented Cash Crops
- 4.2.4 Expansion of Agricultural Credit and Tractor Financing Facilities
- 4.2.5 Pay-As-You-Go Tractor Leasing via Mobile Platforms
- 4.2.6 Uptake of Low-Horsepower Autonomous Electric Tractors on Large Estates
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Fragmented Land Holdings Limiting Tractor Utilization Rates
- 4.3.2 Shortage of Skilled Operators and Maintenance Technicians
- 4.3.3 Volatile Foreign-Exchange Rates and Import Duties Inflating Tractor Purchase Prices
- 4.3.4 Grey-Market Spare-Parts Supply-Chain Disruptions
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value and Volume)
- 5.1 By Engine Power
- 5.1.1 Less than 35 HP
- 5.1.2 35 - 50 HP
- 5.1.3 51 - 75 HP
- 5.1.4 76 - 100 HP
- 5.1.5 Above 100 HP
- 5.2 By Traction Technology
- 5.2.1 2-Wheel Drive (2WD)
- 5.2.2 4-Wheel Drive (4WD)
- 5.3 By Propulsion
- 5.3.1 Diesel
- 5.3.2 Hybrid/Electric
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Row-Crop Farming
- 5.4.2 Horticulture and Viticulture
- 5.4.3 Plantation and Estate Crops
- 5.5 By Distribution Channel
- 5.5.1 Authorized Dealerships
- 5.5.2 Online and Mobile-App-Based Rental Platforms
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 South Africa
- 5.6.2 Kenya
- 5.6.3 Egypt
- 5.6.4 Rest of Africa
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 AGCO Corporation
- 6.4.2 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.3 Deere & Company
- 6.4.4 Kubota Corporation
- 6.4.5 Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Argo Tractors S.p.A.
- 6.4.7 Tractors and Farm Equipment Limited
- 6.4.8 International Tractors Limited
- 6.4.9 CLAAS KGaA mbH
- 6.4.10 SDF S.p.A (Same Deutz-Fahr Tanzania Limited)
- 6.4.11 YTO Group Corporation
- 6.4.12 Zetor Tractors a.s.
- 6.4.13 J C Bamford Excavators Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Caterpillar Inc.
- 6.4.15 Captain Tractors Pvt. Ltd.







