 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1852121
电脑辅助製造:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Computer Aided Manufacturing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
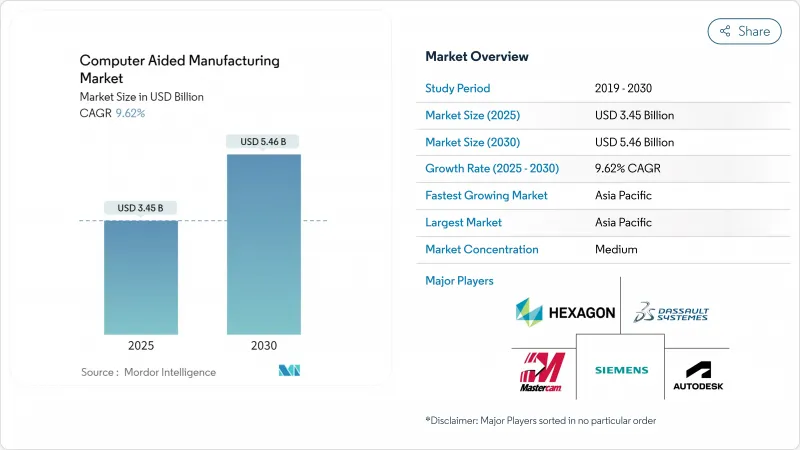
预计到 2025 年,电脑辅助製造市场规模将达到 34.5 亿美元,到 2030 年将扩大到 54.6 亿美元,复合年增长率为 9.62%。
成长的驱动力来自减材-增材混合生产单元的转型、人工智慧与刀具路径生成的融合,以及政府鼓励国产半导体封装和电动车零件的再共享激励措施。能够将云端原生协作与本地安全相结合的供应商,正受益于横跨多个大洲且遵循国防级智慧财产权通讯协定的航太专案。西门子、欧特克和达梭系统正在将即时机器分析整合到其设计到製造的套件中,为用户提供超越纯粹编程速度的预测性维护洞察,并增强平台整合。
全球电脑辅助製造市场趋势与洞察
混合加工中心的兴起改变了生产经济格局
混合系统将雷射或定向能量沉淀和高速精加工整合于同一机壳内,无需二次装夹,并将原料浪费减少高达 40%。西门子 NX 现在可自动执行轮胎边缘沉淀和精加工刀具路径,仅在需要的地方沉淀材料,即可达到航太级表面光洁度,从而将复杂钛零件的整体加工週期缩短 25-30%。该技术的实际应用依赖于经过培训的操作人员,他们能够在微秒级的精度内同步增材和减材加工操作——而这种技能在大多数机械加工车间都非常稀缺。
工业4.0数位线程赋能预测性製造
此闭合迴路平台将CAM编程参数与即时主轴功率、振动和刀具磨损感测器连接起来。 Hexagon的演算法能够提前15到20分钟侦测到即将发生的刀具故障,并自动调整进给速度,从而将表面品质保持在公差范围内,减少易碎航太合金的废品率。这些解决方案需要密集的感测器网路和高吞吐量的分析,因此限制了它们在零件价值足以支撑资本支出的加工车间中的应用。
开放原始码CAM挑战商业定价模式
FreeCAD PathWorkbench 现在可以输出 2.5 轴 G 代码,无需任何许可费用,使其成为学校和小型研讨会可靠的入门级选择。商业供应商透过捆绑功能来展开竞争,这些功能超越了大多数社群计划的运算能力,例如 AI 驱动的最佳化和云端协作,但他们必须防止其基础模组被同质化。
细分市场分析
云端託管套件目前在整个电脑辅助製造市场中所占份额仍然较小,但其到2030年的复合年增长率(CAGR)高达10.9%,显示这一趋势不可逆转。一家在三大洲拥有工厂的航太集团利用基于浏览器的刀具路径编辑技术实现隔夜交付,将前置作业时间缩短了20%至25%。由于ITAR法规要求在现场维护资料主权,国防承包商对全面迁移持抵制态度。因此,将本地后处理器与云端求解器连接的混合堆迭构成了一座桥樑。边缘网关可以改装到没有OPC-UA或MTConnect的旧机器上,从而在不更换控制器的情况下实现加密资料流传输。订阅模式将成本从资本预算转移到营运支出。云端分析还使供应商能够对匿名化的全机主轴利用率进行基准测试,并将其输入到预测性维护仪表板中,从而减少非计划性停机时间。随着零信任架构的成熟,即使是较保守的行业也计划在2027年前进行试点迁移,这表明电脑辅助製造市场将在下一个预算週期内跨越云端采用的心理门槛。
儘管如此,对于采用空气间隙网路或专有合金配方的工厂而言,本地部署基础设施仍然至关重要。供应商透过授权数位线程模组来赢得这些客户,这些模组可以将选定的元资料同步到云端,供远端专家访问,同时仍保留在防火墙内。这种双轨策略既能稳定授权续约,也能随着顾客转向混合分析而增加经常性收入。随着时间的推移,不同部署模式之间的单独定价可能会消失,因为平台订阅层级只需简单地启用或停用云端处理额度即可。网路保险费现在反映了工具机网路的风险敞口,财务长们也正在将安全认证纳入整体拥有成本的考虑范围。因此,电脑辅助製造市场正在从云端和本地部署的二元选择演变为灵活的部署期限模式。
汽车产业是更广泛的电脑辅助製造 (CADM) 市场的核心组成部分,占 2024 年总收入的 36.2%。然而,从内燃机 (ICE) 零件加工到电动车 (EV) 零件加工的转变,对沿用已久的刀具路径库提出了挑战。电池托盘铣削需要采用薄壁加工策略来控制振动,同时保持高硅铝加工效率。同时,航太和国防领域虽然规模较小,但对五轴加工和复合材料加工的高级许可需求也日益增长。医疗设备製造商正在采用人工智慧驱动的参数调整来满足 ISO 13485 可追溯性要求,从而能够在单人操作单元中实现亚 10μm 的公差,而无需手动编辑。电子和半导体封装製程需要采用热感知钻孔定序,以防止在 100,000 rpm 的钻孔过程中出现铜层剥离。医疗设备製造商正在复製航太领域的表面处理流程,而汽车製造商则从电池模组晶圆厂引进清洁通讯协定,这些都扩大了 CADM 的潜在市场。
汽车製造业的多元化同样引人注目。结构件的千兆铸造工艺省去了数十个冲压件,但也引入了铝晶粒件的大规模数控精加工,这要求极高的材料去除率和可靠的刀具寿命模型。投资此类生产单元的供应商要求软体能够自动补偿20小时无人值守轮班期间的刀具磨损漂移。相较之下,一家专注于碳纤维装饰件的小众超级跑车製造商则使用五轴铣床,并在每个生产週期中根据探针更新路径。这种差异意味着单一垂直行业可能需要多个CAM软体授权级别,从而确保即使整车产量趋于稳定,电脑辅助製造市场仍保持强劲成长。
区域分析
亚太地区47.1%的市占率凸显了其製造业的实力,但该地区仍面临数控通讯协定片段化的问题,这使得即插即用的互通性变得复杂。中国的政策鼓励自主研发的CAM演算法和国产控制器,从而催生了一个平行生态系统,全球供应商必须透过双语后处理器和开放API工具库来连接这个生态系统。日本工具机OEM厂商正在将CAM直接整合到控制韧体中,从而缩短刀具路径载入时间,但客户却被锁定在专有软体堆迭中。印度的「生产关联激励计画」(Production Linked Incentive program)透过补贴CAM授权费用来促进劳动力技能提升,这有望帮助供应商在新兴的中端市场站稳脚跟,这些市场到2030年可能足以与传统巨头匹敌。
随着《晶片製造和整合法案》(CHIPS Act)向区域晶圆厂注入520亿美元资金,北美用户在云端技术应用方面处于领先地位。欧洲则更倾向于节能加工,强制要求减少压缩空气消耗和工具重复使用,CAM策略模拟器现在能够以每零件的千瓦时为单位进行建模。资料主权规则虽然造成了一些摩擦,但一级供应商正在接受本地化的资料湖,以换取跨工厂的最佳化演算法。这些区域差异使得电脑辅助製造市场能够保持广泛的多样性,并缓解区域经济衰退的影响。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 混合式(减材+增材)加工中心的兴起
- 工业4.0数位线程的应用日益普及
- 先进包装生产线对超精密零件的需求
- 需要灵活的生产方式来实现电动车平台的本地化
- 转向云端原生CAM以实现多站点协作
- 政府对战略部门的激励措施再分配
- 市场限制
- 开放原始码/低成本CAM替代方案的兴起
- NC程式设计和后处理方面持续存在的技能差距
- 国防企业在采用云端运算时面临智慧财产权安全的担忧。
- 细分的工具机控制器标准
- 产业价值链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 宏观经济因素的影响
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按部署模式
- 本地部署
- 云端基础的
- 按最终用户行业划分
- 航太/国防
- 车
- 医疗设备
- 能源与公共产业
- 电子和半导体
- 工业机械
- 按组件
- 软体
- 服务
- 透过製造工艺
- 铣削
- 转弯
- 挖掘
- 多轴/5轴
- 增材製造
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 日本
- 印度
- 韩国
- 东南亚
- 亚太其他地区
- 中东和非洲
- 中东
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Autodesk Inc.
- Siemens Digital Industries Software(Siemens AG)
- Dassault Systemes SE
- Hexagon AB(Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence)
- CNC Software LLC(Mastercam)
- HCL Technologies Ltd.
- OPEN MIND Technologies AG
- SolidCAM Ltd.
- Cimatron Ltd.
- NTT Data Engineering Systems Corp.
- BobCAD-CAM Inc.
- MecSoft Corporation
- PTC Inc.
- ZWSOFT Co. Ltd.
- SmartCAMcnc Inc.
- GibbsCAM(3D Systems Corp.)
- Hypertherm Inc.
- SprutCAM Tech Ltd.
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Computer Aided Manufacturing market size reached USD 3.45 billion in 2025 and is forecast to expand to USD 5.46 billion by 2030, registering a 9.62% CAGR.

Growth stems from the shift to hybrid subtractive-plus-additive production cells, the fusion of artificial intelligence with tool-path generation, and government re-shoring incentives that favor domestic semiconductor packaging and electric-vehicle components. Vendors able to blend cloud-native collaboration with on-premises security benefit from aerospace programs that span multiple continents while respecting defense-grade intellectual-property protocols. Platform consolidation is intensifying as Siemens, Autodesk, and Dassault Systemes embed real-time machine analytics inside their design-to-manufacturing suites, giving users predictive maintenance insight that trumps pure programming speed.
Global Computer Aided Manufacturing Market Trends and Insights
Rise in Hybrid Machining Centers Transforms Production Economics
Hybrid systems integrate laser or directed-energy deposition with high-speed finishing inside one enclosure, eliminating secondary setups and cutting raw-material waste by up to 40%. Siemens NX now automates bead-on-wall deposition and finishing toolpaths so manufacturers deposit material only where needed before achieving aerospace-grade surface finish, reducing overall cycle time for complex titanium parts by 25-30%. Real-world rollouts still hinge on operators trained to synchronize additive and subtractive motions within microsecond windows, a skill set in short supply across most job shops.
Industry 4.0 Digital Threads Enable Predictive Manufacturing
Closed-loop platforms connect CAM programming parameters to real-time spindle power, vibration, and tool-wear sensors. Hexagon algorithms detect impending tool failure 15-20 minutes in advance and auto-adjust feed rates to hold surface quality within tolerance, mitigating scrap on fragile aerospace alloys. These solutions require dense sensor networks and high-throughput analytics, restricting adoption to plants where part value justifies the capital outlay.
Open-Source CAM Alternatives Challenge Commercial Pricing Models
FreeCAD PathWorkbench now outputs 2.5-axis G-code at no license cost, making it a credible entry-level choice for schools and micro-workshops. Commercial vendors counter by bundling AI-driven optimization and cloud collaboration, features that exceed the computing means of most community projects, yet must guard against basic modules edging toward commoditization.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Ultra-Precision Packaging Lines Drive CAM Innovation
- EV Platform Localization Accelerates Precision Machining Demand
- Skills Gap in CNC Programming Constrains Market Expansion
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Cloud-hosted suites still represent a minority of the overall Computer Aided Manufacturing market, but their 10.9% CAGR through 2030 underscores an irreversible direction. Aerospace groups with plants on three continents rely on browser-based toolpath editing to hand off jobs overnight, trimming lead times by 20-25%. Defense contractors resist full migration because ITAR rules demand onsite data sovereignty; consequently, hybrid stacks local post-processors linked to cloud solvers form the bridge. Edge gateways retrofit older machines lacking OPC-UA or MTConnect, letting them stream encrypted data without controller replacement. Subscription models shift costs from capital budgets to operating expenses, a boon for small shops that previously deferred software upgrades. Cloud analytics also enable vendors to benchmark spindle utilization across an anonymized fleet, feeding predictive-maintenance dashboards that slash unscheduled downtime. As zero-trust architectures mature, even conservative sectors plan pilot migrations by 2027, suggesting the Computer Aided Manufacturing market will cross a psychological cloud-adoption threshold within the next budget cycle.
The on-premises base nevertheless remains indispensable for plants with air-gapped networks and proprietary alloy formulations. Vendors court these accounts by licensing digital-thread modules that reside behind the firewall yet sync selected metadata to a cloud vault for remote experts. This twin-track strategy stabilizes license renewals while boosting recurring revenue as customers graduate to hybrid analytics. Over time, discrete pricing between deployment modes may vanish as platform subscription tiers simply toggle cloud compute credits on or off. With cyber-insurance premiums now reflecting machine-tool network exposure, CFOs increasingly factor security accreditation into total cost of ownership. Consequently, the Computer-Aided Manufacturing market is evolving toward flexible tenancy rather than binary cloud-versus-on-site choices.
Automotive held 36.2% revenue in 2024, making it the anchor segment of the broader Compute Aided Manufacturing market. Yet the shift from internal-combustion machining to electric-vehicle parts challenges long-standing toolpath libraries. Battery tray milling demands thin-wall strategies that manage chatter while sustaining throughput in high-silicon aluminum. Meanwhile, aerospace and defense, though smaller, command premium licenses for 5-axis and composite machining. Medical-device firms adopt AI-assisted parameter tuning to meet ISO 13485 traceability, letting single-operator cells hit sub-10 µm tolerances without manual edits. Electronics and semiconductor packaging operators require thermal-aware drill sequencing to prevent copper delamination during 100,000-rpm via drilling, a niche that the latest CAM modules fulfill through physics solvers. Cross-pollination is rising: medical device shops replicate aerospace surface-finish routines, while automotive tiers import wafer-fab cleanliness protocols for battery modules, expanding the total addressable market of Computer Aided Manufacturing.
Diversification inside automaking is equally profound. Gigacasting of structural components eliminates dozens of stamped parts, but introduces massive CNC finishing of die-cast aluminum, requiring high material-removal rates and robust tool-life models. Suppliers investing in these cells demand software that auto-compensates for tool-wear drift across 20-hour unmanned shifts. In contrast, niche hypercar builders focus on carbon-fiber trim, using 5-axis routers and probe-based path updates each production cycle. Such divergence means one vertical now spans multiple CAM license tiers, ensuring that the Computer Aided Manufacturing market retains depth even if overall car volumes level off.
The Computer Aided Manufacturing Market Report is Segmented by Deployment Model (On-Premises, and Cloud-Based), End-User Industry (Aerospace and Defense, Automotive, Medical Devices, and More), Component (Software, and Services), Manufacturing Process (Milling, Turning, Drilling, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific's 47.1% share underscores its manufacturing heft, yet the region still wrestles with CNC protocol fragmentation that complicates plug-and-play interoperability. Chinese policy favors indigenous CAM algorithms tied to homegrown controllers, spurring parallel ecosystems that global vendors must bridge through dual-language post-processors and open-API tool libraries. Japan's machine OEMs integrate CAM directly into control firmware, shortening toolpath load times but locking customers into proprietary stacks. India's Production Linked Incentive schemes subsidize CAM licenses if tied to workforce upskilling, giving vendors a foothold in an emerging mid-market that could rival traditional giants by 2030.
North American users lead in cloud adoption, partly because the CHIPS Act funnels USD 52 billion into regional fabs that require distributed programming sooner than brick-and-mortar capacity is completed. Europe champions energy-efficient machining, mandating compressed-air reduction and tool reuse targets that CAM strategy simulators now model in kilowatt-hours per part. Data-sovereignty rules add friction, but tier-one suppliers accept localized data lakes in exchange for cross-plant optimization algorithms. These regional nuances ensure the Computer Aided Manufacturing market maintains broad diversification, cushioning it against localized downturns.
- Autodesk Inc.
- Siemens Digital Industries Software (Siemens AG)
- Dassault Systemes SE
- Hexagon AB (Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence)
- CNC Software LLC (Mastercam)
- HCL Technologies Ltd.
- OPEN MIND Technologies AG
- SolidCAM Ltd.
- Cimatron Ltd.
- NTT Data Engineering Systems Corp.
- BobCAD-CAM Inc.
- MecSoft Corporation
- PTC Inc.
- ZWSOFT Co. Ltd.
- SmartCAMcnc Inc.
- GibbsCAM (3D Systems Corp.)
- Hypertherm Inc.
- SprutCAM Tech Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rise in hybrid (subtractive + additive) machining centres
- 4.2.2 Expanding adoption of Industry 4.0-ready digital threads
- 4.2.3 Demand for ultra-precision parts in advanced packaging lines
- 4.2.4 Agile production needs for EV platform localisation
- 4.2.5 Shift toward cloud-native CAM for multi-site collaboration
- 4.2.6 Government re-shoring incentives for strategic sectors
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Proliferation of open-source / low-cost CAM alternatives
- 4.3.2 Persistent skills gap in NC programming and post-processing
- 4.3.3 IP-security concerns with cloud adoption in defence firms
- 4.3.4 Fragmented machine-tool controller standards
- 4.4 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Deployment Model
- 5.1.1 On-Premises
- 5.1.2 Cloud-Based
- 5.2 By End-User Industry
- 5.2.1 Aerospace and Defence
- 5.2.2 Automotive
- 5.2.3 Medical Devices
- 5.2.4 Energy and Utilities
- 5.2.5 Electronics and Semiconductor
- 5.2.6 Industrial Machinery
- 5.3 By Component
- 5.3.1 Software
- 5.3.2 Services
- 5.4 By Manufacturing Process
- 5.4.1 Milling
- 5.4.2 Turning
- 5.4.3 Drilling
- 5.4.4 Multi-Axis / 5-Axis
- 5.4.5 Additive Manufacturing
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Russia
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 Japan
- 5.5.4.3 India
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 South-East Asia
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Egypt
- 5.5.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Autodesk Inc.
- 6.4.2 Siemens Digital Industries Software (Siemens AG)
- 6.4.3 Dassault Systemes SE
- 6.4.4 Hexagon AB (Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence)
- 6.4.5 CNC Software LLC (Mastercam)
- 6.4.6 HCL Technologies Ltd.
- 6.4.7 OPEN MIND Technologies AG
- 6.4.8 SolidCAM Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Cimatron Ltd.
- 6.4.10 NTT Data Engineering Systems Corp.
- 6.4.11 BobCAD-CAM Inc.
- 6.4.12 MecSoft Corporation
- 6.4.13 PTC Inc.
- 6.4.14 ZWSOFT Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.15 SmartCAMcnc Inc.
- 6.4.16 GibbsCAM (3D Systems Corp.)
- 6.4.17 Hypertherm Inc.
- 6.4.18 SprutCAM Tech Ltd.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment












