 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1907287
钼:市占率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Molybdenum - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
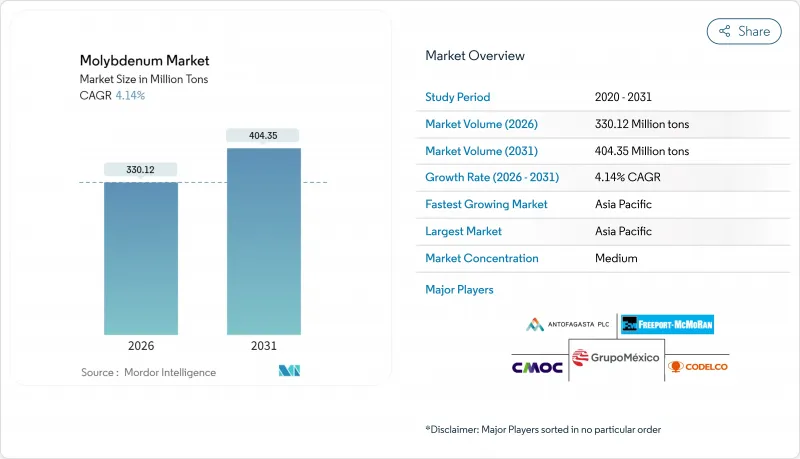
预计到 2025 年,钼市场价值将达到 3.17 亿吨,在预测期(2026-2031 年)内,将以 4.14% 的复合年增长率增长,从 2026 年的 3.3012 亿吨增长到 2031 年的 4.0435 亿吨。
钢铁製造仍然是主要应用领域,高强度低合金钢(HSLA)在建筑、汽车和能源基础设施领域的应用日益广泛。由于对无污染燃料催化剂、排放气体控制和二氧化碳转化等应用的需求不断增长,化学应用也随之扩展。中国于2025年2月宣布对包括钼在内的关键矿产实施出口限制,这项政策转变可能改变全球贸易路线和价格,加剧了地缘政治风险。供应受限的风险正促使钢铁製造商、油气营运商、可再生能源设备製造商和电动车电力电子供应商重新评估其筹资策略,提高回收利用率,并投资研发不可替代的合金设计。
全球钼市场趋势与洞察
高强度低合金钢需求快速成长
快速的基础设施建设和对更轻、更强车辆的需求,正推动高强度低合金钢(HSLA钢)成为钼市场成长的关键驱动力。添加0.5%至1%的钼可使屈服强度提高高达20%,增强低温韧性,并提高抗硫化物应力腐蚀开裂性能。这些优异的机械性质使得桥樑、隧道和高层建筑的上部结构能够采用更薄的钢材厚度,并延长使用寿命。同时,汽车製造商正在采用HSLA钢製造素车零件,以减轻车身重量、提高燃油经济性并延长电动车的续航里程。最新研究证实,(Ti, Mo)C析出物在酸性环境中具有更强的抗裂性能,此特性深受管线业者的青睐。随着世界各国政府大力推动交通基础设施和可再生能源网路的奖励策略,HSLA钢在钢铁生产中的份额不断增长,进一步推动了对钼的潜在需求。
越来越多的可再生能源设施需要钼基合金。
大型风力发电和水力发电设施采用含钼马氏体钢和高温合金来承受盐雾、循环负荷和空化作用。离岸风力发电机塔筒和机舱内部组件必须在其25年的使用寿命内承受潮湿和氯化物侵蚀,而钼合金钢板和铸件正是满足这一需求的。 Mobarcar公司2024年的一项研究表明,经热机械处理的含钼钢即使在长期暴露于海水中后仍能保持高强度和断裂韧性。在电力转换设备中,钼散热器的热膨胀係数与硅相匹配,并为风电场逆变器中使用的绝缘栅双极电晶体(IGBT)模组提供可靠的支撑。政府的清洁能源目标和创纪录的离岸风力发电竞标规模正在对此需求因素施加结构性上行压力。
钼高成本
价格波动扰乱了预算週期,促使企业尽可能地用钨和铌替代钼,并迫使小规模买家支付风险溢价。中国限製造成的供应紧张加剧了这种影响,使小型钢厂、铸造厂和催化剂製造商的原材料成本难以预测,从而衝击钼市场。
细分市场分析
钢铁业占据钼市场的大部分份额,预计到2025年将占全球消费量的70.62%。高温石油、液化天然气和化学工厂需要添加2-4%钼的铁素体和奥氏体不銹钢来抵抗氯化物裂解。酸性气体管道规范通常要求添加高达1%的钼,这样可以减少壁厚并降低焊接成本。
儘管目前化学产业规模较小,但预计它将成为成长最快的需求来源,到2031年复合年增长率将达到4.62%。钴钼/氧化铝基加氢脱硫(HDS)催化剂用于去除柴油和喷射机燃料中的硫,以满足超低硫排放标准;而三氧化钼则被添加到催化剂中,将二氧化碳和可再生原料转化为合成燃料。这种成长动能将使化学产业在预测期后半段逐步蚕食钢铁业的市场份额,从而进一步拓展钼市场。
本钼市场报告按最终产品(钢铁、化工、铸造等)、产品形态(钼精矿、焙烧钼、钼铁等)、最终用途行业(石油天然气、化工及石化、汽车、工业、建筑等)和地区(亚太、北美、欧洲、世界其他地区)进行细分。市场预测以吨为单位。
区域分析
到2025年,亚太地区将占全球钼加工量的53.60%,主要得益于中国、日本、韩国和印度钢铁生产、汽车组装和先进电子製造业的扩张。该地区的复合年增长率(CAGR)为4.71%,主要驱动力来自「一带一路」基础设施、能源管道和造船业。北京于2025年2月实施的钼出口许可证制度将下游买家置于配额监管之下,加速了库存累积。
北美正充分利用美国的资源禀赋,预计2024年开采量将达3.3万吨。 2025年3月的一项总统令旨在加快采矿许可审批,预计将提高北美的自给自足能力。欧洲目前面临供不应求,但德国和义大利的不銹钢厂和电动车零件工厂的需求仍然强劲。
欧盟委员会提出的再生钢配额提案提案到2030年,新车用钢的25%来自废钢,并鼓励从汽车切碎机回收钼。中东炼油厂进口钼用于加氢处理催化剂,非洲斑状铜矿计划则生产钼产品,并以现货形式供应欧洲和亚洲。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 高强度低合金钢(HSLA)需求快速成长
- 由于可再生能源设施的增加,对钼合金的需求不断增长。
- 深水油气钻探活动活性化了对耐腐蚀钼合金的需求
- 用于电动汽车电力电子的高温钼元件
- 金属3D列印中钼粉的应用日益广泛
- 市场限制
- 钼高成本
- 政府对采矿业的监管
- 特种钢中钨和铌的替代品。
- 由于回收基础设施不发达,二次供应有限。
- 价值链分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争程度
- 贸易分析
- 价格趋势
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 最终产品
- 钢
- 化学
- 晶圆代工厂
- 钼金属
- 镍合金
- 按产品形式
- 钼浓缩物
- 焙烧钼(工业氧化钼)
- 钼铁
- 钼金属粉末
- 钼化学品
- 按最终用户行业划分
- 石油和天然气
- 化工和石油化工
- 车
- 产业
- 建筑/施工
- 航太与国防
- 其他产业(能源产出和储存、电子和半导体等)
- 按地区(生产分析)
- 中国
- 美国
- 智利
- 秘鲁
- 墨西哥
- 亚美尼亚
- 其他生产国
- 按地区划分(消费分析)
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 亚太其他地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 义大利
- 法国
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 世界其他地区
- 南美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 亚太地区
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率(%)分析
- 公司简介
- Air Liquide
- Anglo American plc
- Antamina
- Antofagasta plc
- Centerra Gold Inc.
- China Molybdenum Co. Ltd.
- Codelco
- Freeport-McMoRan
- GRUPO MEXICO
- HONGDA GROUP
- Jiangxi Copper Corporation
- JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO.,LTD.
- KAZ Minerals
- KGHM
- Moltun International
- MOLYMET SA
- Multi Metal Development Limited
- Rio Tinto
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Molybdenum Market was valued at 317 million tons in 2025 and estimated to grow from 330.12 million tons in 2026 to reach 404.35 million tons by 2031, at a CAGR of 4.14% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

Steelmaking remained the primary outlet, as high-strength, low-alloy (HSLA) grades spread through construction, automotive, and energy infrastructure. Chemical uses advanced on the back of rising catalyst demand for clean fuels, emissions control, and CO2 conversion. Geopolitical exposure intensified after China's February 2025 export-control notice on critical minerals, including molybdenum, a policy shift that threatens to alter trade routes and price formation worldwide. Tight supply risk is prompting steelmakers, oil-and-gas operators, renewable-energy OEMs, and EV power-electronics suppliers to re-evaluate sourcing strategies, expand recycling, and invest in substitute-proof alloy designs.
Global Molybdenum Market Trends and Insights
Surge in High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel Demand
Rapid infrastructure rollouts and the push for lighter yet stronger vehicles have made HSLA steel a central growth lever for the molybdenum market. Adding 0.5-1% Mo boosts yield strength by up to 20%, enhances low-temperature toughness, and reduces susceptibility to sulfide stress corrosion. These mechanical gains allow thinner gauges and longer service life in bridges, tunnels, and high-rise superstructures. Automakers, meanwhile, use HSLA body-in-white parts to shave vehicle mass and raise fuel economy or EV range. New research on (Ti, Mo)C precipitation confirms improved resistance to cracking in sour environments, a property valued by pipeline operators. As governments channel stimulus into transport and renewable grids, HSLA grades are capturing a growing slice of steel output, magnifying baseline demand for molybdenum.
Increasing Renewable-Energy Installations Requiring Mo-Based Alloys
Utility-scale wind and hydropower assets use Mo-containing martensitic steels and superalloys to survive salt spray, cyclic loading, and cavitation. Offshore turbine towers and nacelle internals must tolerate humidity and chloride attack over 25-year lifecycles, a job handled by Mo-alloyed plate and castings. Mohrbacher's 2024 study showed that thermomechanically processed Mo-bearing steels sustain high strength and fracture toughness even after prolonged exposure to seawater. In power converters, molybdenum heatspreaders match silicon's thermal expansion, serving as reliable bases for insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) modules used in wind farm inverters. Government clean-energy targets and record auction volumes for offshore wind impose a structural uplift on this driver.
High Cost of Molybdenum
Price volatility disturbs budget cycles, prompts substitution with tungsten or niobium where feasible, and forces smaller buyers to pay risk premiums. Supply tightness linked to Chinese controls compounds the effect, keeping feedstock invoices unpredictable for steel minimills, foundries, and catalyst producers, influencing in the molybdenum market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Intensifying Deep-Water Oil and Gas Drilling Boosting Corrosion-Resistant Mo Alloys
- Adoption of High-Temperature Mo Components for Electric-Vehicle Power Electronics
- Government Regulations Concerning Mining
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Steel retained the lion's share of the molybdenum market, accounting for 70.62% of global offtake in 2025. High-temperature petroleum, LNG, and chemical plants demand ferritic and austenitic stainless varieties enriched with 2-4% Mo to resist chloride cracking. Linepipe specifications for sour gas routinely call for up to 1% Mo, allowing thinner walls and lower welding costs.
Chemicals, although smaller at present, represent the fastest-growing outlet at a 4.62% CAGR through 2031. Hydrodesulfurization (HDS) catalysts based on Co-Mo/Al2O3 remove sulfur from diesel and jet fuel to meet ultra-low sulfur directives, while MoO3 screws into catalysts that convert CO2 and renewable feedstock into synthetic fuels. This momentum positions chemicals to chip away share from steel in the latter half of the forecast window, lending depth to the molybdenum market.
The Molybdenum Market Report is Segmented by End Product (Steel, Chemical, Foundry, and More), Product Form (Molybdenum Concentrates, Roasted Molybdenum, Ferromolybdenum, and More), End-Use Industry (Oil & Gas, Chemical & Petrochemical, Automotive, Industrial, Building & Construction, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, Rest of the World). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (Tons).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific held 53.60% of global throughput in 2025 as China, Japan, South Korea, and India escalated steel output, vehicle assembly, and advanced-electronics fabrication. The region's 4.71% CAGR stems from Belt-and-Road infrastructure, energy pipelines, and shipbuilding. Beijing's February 2025 export-license regime for molybdenum puts downstream buyers on allocation watch and accelerates inventory build-ups.
North America is leveraging resource endowment in the United States, which mined 33,000 tons in 2024. A March 2025 executive order now seeks to fast-track mining permits, potentially lifting North American self-reliance. Europe, though supply-short, retains robust demand driven by German and Italian stainless mills and EV-component plants.
The European Commission's recycled-steel quotas propose that 25% of steel in new cars originate from scrap by 2030, stimulating molybdenum recovery from automotive shredders. Middle-East refiners import Mo for hydro-treating catalysts, while African copper porphyry projects contribute by-product molybdenum that feeds spot cargoes into Europe and Asia.
- Air Liquide
- Anglo American plc
- Antamina
- Antofagasta plc
- Centerra Gold Inc.
- China Molybdenum Co. Ltd.
- Codelco
- Freeport-McMoRan
- GRUPO MEXICO
- HONGDA GROUP
- Jiangxi Copper Corporation
- JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO.,LTD.
- KAZ Minerals
- KGHM
- Moltun International
- MOLYMET SA
- Multi Metal Development Limited
- Rio Tinto
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel Demand
- 4.2.2 Increasing Renewable Energy Installations Requiring Mo-based Alloys
- 4.2.3 Intensifying Deep-water Oil and Gas Drilling Boosting Corrosion-Resistant Mo Alloys
- 4.2.4 Adoption of High-Temperature Mo Components for the Electric Vehicle Power Electronics
- 4.2.5 Increasing Usage of Molybdenum Powders for Metal 3-D Printing
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Cost of Molybdenum
- 4.3.2 Government Regulations Concering Mining
- 4.3.3 Substitution by Tungsten and Niobium in Specialty Steels
- 4.3.4 Under-developed Recycling Infrastructure Limiting Secondary Supply
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
- 4.6 Trade Analysis
- 4.7 Price Trends
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By End Product
- 5.1.1 Steel
- 5.1.2 Chemical
- 5.1.3 Foundry
- 5.1.4 Molybdenum Metal
- 5.1.5 Nickel Alloys
- 5.2 By Product Form
- 5.2.1 Molybdenum Concentrates
- 5.2.2 Roasted Molybdenum (Technical Oxide)
- 5.2.3 Ferromolybdenum
- 5.2.4 Molybdenum Metal Powder
- 5.2.5 Molybdenum Chemicals
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 Oil and Gas
- 5.3.2 Chemical and Petrochemical
- 5.3.3 Automotive
- 5.3.4 Industrial
- 5.3.5 Building and Construction
- 5.3.6 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.3.7 Other Industries (Energy Generation and Storage Electronics and Semiconductors, etc.)
- 5.4 By Geography (Production Analysis)
- 5.4.1 China
- 5.4.2 United States
- 5.4.3 Chile
- 5.4.4 Peru
- 5.4.5 Mexico
- 5.4.6 Armenia
- 5.4.7 Other Producer Countries
- 5.5 By Geography (Consumption Analysis)
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 India
- 5.5.1.3 Japan
- 5.5.1.4 South Korea
- 5.5.1.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 North America
- 5.5.2.1 United States
- 5.5.2.2 Canada
- 5.5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 Italy
- 5.5.3.4 France
- 5.5.3.5 Russia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Rest of the World
- 5.5.4.1 South America
- 5.5.4.2 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share(%) Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 Air Liquide
- 6.4.2 Anglo American plc
- 6.4.3 Antamina
- 6.4.4 Antofagasta plc
- 6.4.5 Centerra Gold Inc.
- 6.4.6 China Molybdenum Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Codelco
- 6.4.8 Freeport-McMoRan
- 6.4.9 GRUPO MEXICO
- 6.4.10 HONGDA GROUP
- 6.4.11 Jiangxi Copper Corporation
- 6.4.12 JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO.,LTD.
- 6.4.13 KAZ Minerals
- 6.4.14 KGHM
- 6.4.15 Moltun International
- 6.4.16 MOLYMET SA
- 6.4.17 Multi Metal Development Limited
- 6.4.18 Rio Tinto
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment
- 7.2 Rising Demand for Molybdenum-bearing Chemicals in Clean-fuel Processes









