 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1852177
复合材料:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Composite Material - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
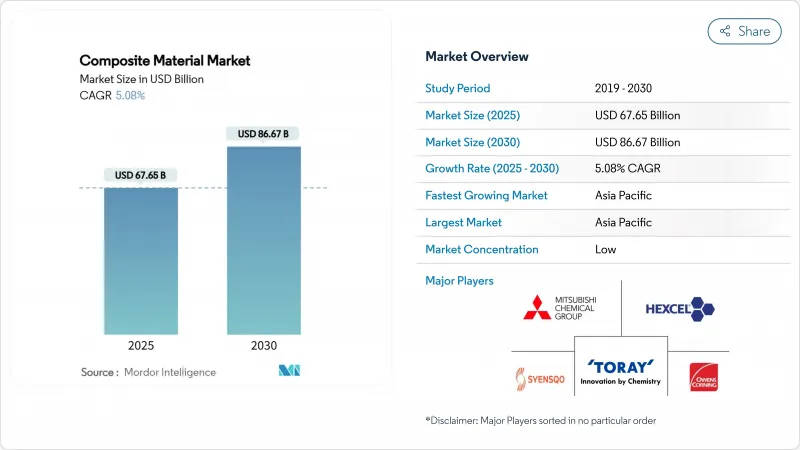
复合材料市场规模预计到 2025 年将达到 676.5 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 866.7 亿美元,预测期(2025-2030 年)复合年增长率为 5.08%。
交通运输、能源、基础设施和电子产业对轻质高性能材料的强劲需求正在拓展其应用范围,而持续的製程自动化则缩短了生产週期并减少了废料。亚太地区预计在2024年将占全球销售额的45.12%,并将继续保持销售成长的中心地位,因为风力发电机的安装、电气化计画和大型基础设施计划将推动区域消费。陶瓷基质技术的快速发展、聚合物基体材料对金属的持续替代以及特种增强材料的供应基础不断完善,都增强了后进企业的竞争壁垒。然而,回收的限制仍为长期循环经济目标蒙上阴影,如果报废处理方案无法跟上安装速度,则可能限制其应用。
全球复合材料市场趋势与洞察
电动化驱动的电动车对碳纤维的需求
电动车大约使用450磅塑胶和聚合物复合材料,比内燃机汽车平台增加了18%。碳纤维增强聚合物与铝相比,可在不牺牲热稳定性的前提下减轻30%的重量。采用玻璃纤维增强热塑性塑胶模製的车身面板可实现具有成本竞争力的轻量化,而内装中使用的天然纤维层压板则进一步提升了永续性。汽车製造商正致力于开发融合碳纤维、玻璃纤维和生物增强材料的多材料架构,以优化车身刚度、碰撞安全性和生命週期排放。供应链正在积极应对,透过在北美、欧洲和东亚地区扩大运输能力和合格的预浸料生产线,以避免在2026-2028年车型上市期间出现瓶颈。
在风力发电机叶片製造领域的应用不断扩展
预计2024年全球风电装置容量将成长17%,2025年将成长35%,推动累积装置容量在2035年达到450吉瓦的里程碑。下一代离岸风力发电的功率将超过15兆瓦,需要长度超过110公尺的叶片,而这只能透复合材料积层法来实现。到本世纪末,叶片製造将每年消耗超过100万吨的玻璃纤维和碳纤维增强材料,这将对玻璃纤维熔炼能力和高模量碳纤维的供应造成越来越大的压力。虽然玻璃纤维增强塑料在单位米成本方面仍然占据主导地位,但选择性碳纤维翼梁帽正变得越来越受欢迎,以限制叶尖挠度和叶片根部质量。欧洲正在试用具有根部焊接功能的热塑性叶片,这有望实现一种无需在水泥窑中进行共处理的回收途径。该行业关于叶片循环利用的新法规已使材料可追溯性和树脂再製造成为原始设备製造商和加工商的当务之急。
复合材料高成本
碳纤维复合材料的单件交付成本通常是钢材的五到十倍,这阻碍了其在对成本敏感的细分市场的渗透。航太预浸料需要高压釜固化、严格的环境控制和广泛的无损检测,这些都会推高单位成本。汽车工程也面临类似的障碍,儘管碳纤维具有优异的重量效益比,但其应用主要限于豪华车。由于纤维纺丝生产线和前驱工厂都是资本密集的,生产规模仍然是关键的限制因素。像美国国家可再生能源实验室的热成型製程这样的突破性技术有望将可回收碳纤维片材的成本降低90%至95%,但商业性应用需要多年的认证宣传活动。许多潜在的采用者可能会推迟大规模替代,直到原材料价格下降或设计工程师发现系统层面的显着成本节约。
细分市场分析
高分子复合材料(PMC)预计将占2024年市场收入的56.21%,巩固其作为兼顾性能和可製造性的理想选择的地位。虽然热固性环氧树脂在航太、船舶和风力涡轮机叶片领域仍占据主导地位,但可回收热塑性塑胶在汽车和消费品领域的市场份额正在稳步下降。目前市售热塑性单向带材的宽度已超过1米,有利于电池托盘和片材结构的高通量压模成型。同时,受航太推进系统和聚光型太阳光电接收器等应用的推动,陶瓷基质材料(CMC)预计将在2025年至2030年间以8.57%的复合年增长率增长。 CMC可承受1600°C以上的高温,可取代镍基高温合金,降低冷却需求,并提供无与伦比的热效率。虽然投资成本较高,但一旦Quiver的生产稳定下来,其生命週期提案将透过减轻重量、降低消费量和减少维护成本来抵消初始投入。金属复合材料的市场份额较小,凭藉其卓越的导热性和耐磨性,在电子基板载体和刹车盘占优势。积层製造和五轴数控加工技术的进步正在拓展设计范围,预示将在本世纪后半叶逐步渗透市场。
区域分析
亚太地区引领复合材料市场,2024年营收成长率达45.12%,预计到2030年将维持7.91%的年增长率,这主要得益于中国离岸风力发电装置容量的扩张、印度地铁网路的扩建以及东南亚电网基础设施的升级改造。韩国晓星集团正将年产量提升至9,000吨,以满足航太和氢气罐的需求。日本的价值链则专注于高精度丝束拉伸和预浸料技术,以服务国内飞机机身专案和出口客户。
北美紧随其后,这主要得益于永续航太交付、联邦政府对可再生能源的投资以及休閒和海洋产业的復苏。美国能源局已累计2,000万美元用于促进风力发电机复合材料的回收,显示政策正朝着循环经济的方向发展。加拿大各省正在资助先进材料丛集,将学术研究与开发和注塑成型试验生产线相结合,旨在保护生物基热塑性塑胶领域的国家智慧财产权。
欧洲先进的设计能力和严格的环境法规正在推动生物基树脂和闭合迴路製程的快速普及。儘管供应链中断和能源成本上涨导致2024年下半年产量下降,但欧盟仍维持全球22%的产量份额。维斯塔斯(Vestas)的圆形叶片和低排放气体塔等倡议表明,欧盟气候政策正引导原始设备製造商(OEM)将整体永续性。东欧国家凭藉其熟练的劳动力和毗邻西方市场的地理优势,正在吸引对拉丝厂和长丝復卷厂的投资。
南美洲和中东及非洲虽然整体规模较小,但由于基础设施现代化和海水淡化计划中复合材料解决方案的广泛应用,这些地区的复合材料市场正呈现显着增长。巴西的风能走廊、沙乌地阿拉伯的海水淡化输水管以及南非的电动公车车身都是值得关注的需求区域。跨国公司的技术转让,加上本地增强材料(剑麻、黄麻)的供应,正在刺激本土创新,并逐步缩小与进口零件的成本差距。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 电动交通领域电气化主导的碳纤维需求
- 风力发电机製造领域的应用不断扩展
- 热塑性复合材料在大规模生产车的应用日益广泛
- 材料科学的技术进步
- 航太和国防工业中复合材料的使用日益增多
- 市场限制
- 复合材料高成本
- 回收的挑战
- 自动化积层法工艺中技术纯熟劳工短缺。
- 价值链分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争程度
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 透过基体材料
- 聚合物基复合材料(PMC)
- 热固性树脂
- 热塑性树脂
- 陶瓷/碳基复合材料(CMC)
- 其他基体(金属基复合材料)
- 聚合物基复合材料(PMC)
- 透过增强纤维
- 玻璃纤维
- 碳纤维
- 酰胺纤维
- 其他纤维(天然纤维/生物纤维)
- 按最终用途行业划分
- 汽车与运输
- 风力发电
- 航太/国防
- 管道和储罐
- 建造
- 电气和电子
- 运动与休閒
- 其他终端用户产业(医疗保健、海运等)
- 按地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 泰国
- 马来西亚
- 印尼
- 越南
- 亚太其他地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 北欧国家
- 土耳其
- 其他欧洲地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 哥伦比亚
- 其他南美洲国家
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 奈及利亚
- 卡达
- 埃及
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 亚太地区
第六章 竞争情势
- 策略趋势
- 市占率(%)/排名分析
- 公司简介
- 3M
- Arkema
- BASF
- CPIC BRASIL Fibras de Vidro Ltda
- DuPont
- Exel Composites
- Gurit Services AG
- Hexcel Corporation
- HS HYOSUNG ADVANCED MATERIALS
- Lanxess
- Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation.
- Nippon Graphite Fiber Co., Ltd.
- Owens Corning
- SGL Carbon
- Syensqo
- Teijin Limited
- Toray Industries Inc.
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Composite Material Market size is estimated at USD 67.65 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 86.67 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.08% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Robust demand for lightweight, high-performance materials in transportation, energy, infrastructure and electronics is widening the application portfolio, while continuous process automation is lowering cycle times and defects. Asia-Pacific, holding 45.12% of global revenue in 2024, remains the epicenter of volume growth as wind-turbine expansion, electrification programs and large-scale infrastructure projects accelerate regional consumption. Rapid progress in ceramic matrix technologies, steady substitution of metals by polymer matrix grades and an improving supply base for specialty reinforcements are strengthening competitive barriers for late entrants. Recycling limitations, however, continue to cloud long-term circularity targets and could restrain adoption if end-of-life solutions do not keep pace with installation rates.
Global Composite Material Market Trends and Insights
Electrification-Driven Carbon-Fiber Demand in E-Mobility
Electric vehicles integrate roughly 450 lb of plastics and polymer composites-an 18% rise compared with internal-combustion platforms-because every 10% curb in curb weight typically stretches driving range by 6-8%. Battery enclosures have become a flagship application, where carbon-fiber reinforced polymers deliver a 30% mass cut versus aluminum without sacrificing thermal stability. Body panels molded from glass-fiber reinforced thermoplastics enable cost-competitive lightweighting, while natural-fiber laminates in interior trim broaden sustainability credentials. Automakers are converging on multi-material architectures that blend carbon, glass and bio reinforcements to optimise stiffness, crashworthiness and lifecycle emissions. Supply chains are responding by expanding tow capacity and qualified prepreg lines across North America, Europe and East Asia to avert bottlenecks during the 2026-2028 model-launch window.
Increasing Usage in the Manufacturing of Wind Turbine Blades
Global wind installations climbed 17% in 2024 and 35% in 2025, pushing cumulative capacity toward the 450 GW mark envisaged for 2035. Next-generation offshore machines now exceed 15 MW, requiring blades longer than 110 m that can only be realised with tailored composite lay-ups. More than 1 million t of glass and carbon reinforcements will be consumed annually for blade manufacture by the end of the decade, intensifying pressure on glass-fiber melt capacity and high-modulus carbon supply. While glass-fiber reinforced plastics continue to dominate on a cost-per-meter basis, selective carbon spar caps are proliferating to curb tip deflection and blade-root mass. Europe is piloting thermoplastic blades for weldable root joints, potentially enabling recycling routes that avoid co-processing in cement kilns. The sector's emerging blade-circularity regulations make material traceability and resin reformulation urgent priorities for OEMs and fabricators.
High Cost of Composite Materials
Carbon-fiber composites typically price at five-to-ten times steel on a delivered-part basis, deterring penetration into cost-sensitive segments. Aerospace-grade prepregs entail autoclave curing, tight environmental controls and extensive non-destructive testing, each inflating unit expense. Automotive programs confront similar hurdles, confining carbon-fiber usage largely to premium marques despite favorable weight-benefit ratios. Production scale remains a pivotal barrier, since fiber-spinning lines and precursor plants run capital-intensive. Breakthroughs such as National Renewable Energy Laboratory's thermoforming route promise 90-95% cost savings for recyclable carbon sheets, yet commercial deployment will require multi-year qualification campaigns. Until raw-material prices drop or design engineers capture superior system-level savings, many potential adopters may defer high-volume substitution.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing Adoption of Thermoplastic Composites in Mass-Production Automotive
- Increasing Use of Composites in the Aerospace and Defense Industry
- Challenges in Recycling Composite Materials
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Polymer matrix composites (PMCs) delivered 56.21% of 2024 revenue, reinforcing the composites market as the preferred option for balanced performance and manufacturability. Thermoset epoxies remain mainstream in aerospace, marine and wind blades, yet recyclable thermoplastics are steadily eroding share in automotive and consumer goods. Commercial thermoplastic UD-tape lines now exceed 1 m wide, favouring high-throughput press forming for battery trays and seat structures. In parallel, the composites market size attributable to ceramic matrix composites is projected to post an 8.57% CAGR between 2025 and 2030, propelled by aerospace propulsion and concentrated solar-power receivers. CMCs withstand more than 1 600 °C, replacing nickel super-alloys and slashing cooling demands, thereby unlocking unrivalled thermal efficiencies. Investment outlays are significant, but once quiver production stabilises, their life-cycle value proposition offsets initial premiums through weight savings, fuel burn reductions and lower maintenance. Metal matrix composites occupy a smaller niche that thrives on extraordinary thermal conductivity and wear resistance for electronic substrate carriers and brake rotors. Additive-manufacturing pathways and five-axis CNC finishing are broadening design envelopes, hinting at incremental penetration in the latter half of the decade.
The Composites Market Report Segments the Industry by Matrix Material (Polymer Matrix Composites (PMC), Ceramic/Carbon Matrix Composites (CMCs), Other Matrices), Reinforcement Fiber (Glass Fiber, Carbon Fiber, and More), End-Use Industry (Automotive and Transportation, Wind Energy, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific anchors the composites market with 45.12% revenue in 2024 and is projected to grow at 7.91% through 2030 as China escalates offshore wind installations, India expands metro rail networks and Southeast Asia upgrades grid infrastructure. The regional composites market size also benefits from escalating carbon-fiber capacity; South Korea's Hyosung is lifting annual output to 9 000 t to meet aerospace and hydrogen-tank demand. Japan's value chain focuses on high-precision tow spreading and prepreg technologies, serving both domestic air-frame programs and export customers.
North America trails closely, propelled by sustained aerospace deliveries, federal investments in renewable energy and a resurgent recreational-marine segment. The United States Department of Energy earmarked USD 20 million to advance wind-turbine composite recycling, signalling policy momentum toward circularity. Canadian provinces sponsor advanced-materials clusters that couple academic R&D with injection over-molding pilot lines, aiming to retain domestic IP around bio-based thermoplastics.
Europe commands sophisticated design capabilities and stringent environmental regulations that foster rapid adoption of bio-resins and closed-loop processes. Although supply-chain disruptions and energy-cost spikes trimmed production in late-2024, the bloc maintains a 22% share of global volumes. Initiatives such as Vestas's circular blades and low-emission towers illustrate how EU climate policy is steering OEM priorities toward holistic sustainability. Eastern European nations, leveraging skilled labor and proximity to Western markets, are courting investment in pultrusion and filament-winding plants.
South America and the Middle East & Africa, while collectively smaller, are registering outsized percentage gains as infrastructure modernization and desalination projects specify composite solutions. Brazilian wind corridors, Saudi desalination brine lines and South African electric-bus bodies are notable demand pockets. Technology transfer from multinational players, combined with local reinforcement supply (sisal, jute), is catalysing indigenous innovation and gradually narrowing cost gaps with imported parts.
- 3M
- Arkema
- BASF
- CPIC BRASIL Fibras de Vidro Ltda
- DuPont
- Exel Composites
- Gurit Services AG
- Hexcel Corporation
- HS HYOSUNG ADVANCED MATERIALS
- Lanxess
- Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation.
- Nippon Graphite Fiber Co., Ltd.
- Owens Corning
- SGL Carbon
- Syensqo
- Teijin Limited
- Toray Industries Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Electrification-Driven Carbon-Fiber Demand in E-Mobility
- 4.2.2 Increasing Usage in the Manufacturing of Wind Turbine
- 4.2.3 Growing Adoption of Thermoplastic Composites in Mass-Production Automotive
- 4.2.4 Technological Advancement in the Field of Material Science
- 4.2.5 Increasing Use of Composites in the Aerospace and Defense Industry
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Cost of Composite Material
- 4.3.2 Challenges in Recycling of these Materials
- 4.3.3 Skilled-Labour Gap in Automated Lay-up Processes
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Matrix Material
- 5.1.1 Polymer Matrix Composites (PMC)
- 5.1.1.1 Thermoset Resins
- 5.1.1.2 Thermoplastic Resins
- 5.1.2 Ceramic/Carbon Matrix Composites (CMCs)
- 5.1.3 Other Matrices (Metal Matrix Composites)
- 5.1.1 Polymer Matrix Composites (PMC)
- 5.2 By Reinforcement Fiber
- 5.2.1 Glass Fiber
- 5.2.2 Carbon Fiber
- 5.2.3 Aramid Fiber
- 5.2.4 Other Fibers (Natural/Bio Fiber)
- 5.3 By End-use Industry
- 5.3.1 Automotive and Transportation
- 5.3.2 Wind Energy
- 5.3.3 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.3.4 Pipes and Tanks
- 5.3.5 Construction
- 5.3.6 Electrical and Electronics
- 5.3.7 Sports and Recreation
- 5.3.8 Other End user Industries (Healthcare, Marine, etc.)
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.1.1 China
- 5.4.1.2 India
- 5.4.1.3 Japan
- 5.4.1.4 South Korea
- 5.4.1.5 Thailand
- 5.4.1.6 Malaysia
- 5.4.1.7 Indonesia
- 5.4.1.8 Vietnam
- 5.4.1.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.2 North America
- 5.4.2.1 United States
- 5.4.2.2 Canada
- 5.4.2.3 Mexico
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Russia
- 5.4.3.7 NORDIC Countries
- 5.4.3.8 Turkey
- 5.4.3.9 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Colombia
- 5.4.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Nigeria
- 5.4.5.4 Qatar
- 5.4.5.5 Egypt
- 5.4.5.6 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.7 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.4.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, Recent Developments)}
- 6.3.1 3M
- 6.3.2 Arkema
- 6.3.3 BASF
- 6.3.4 CPIC BRASIL Fibras de Vidro Ltda
- 6.3.5 DuPont
- 6.3.6 Exel Composites
- 6.3.7 Gurit Services AG
- 6.3.8 Hexcel Corporation
- 6.3.9 HS HYOSUNG ADVANCED MATERIALS
- 6.3.10 Lanxess
- 6.3.11 Mitsubishi Chemical Group Corporation.
- 6.3.12 Nippon Graphite Fiber Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.13 Owens Corning
- 6.3.14 SGL Carbon
- 6.3.15 Syensqo
- 6.3.16 Teijin Limited
- 6.3.17 Toray Industries Inc.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment










