 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1906147
聚酯短纤维(PSF):市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
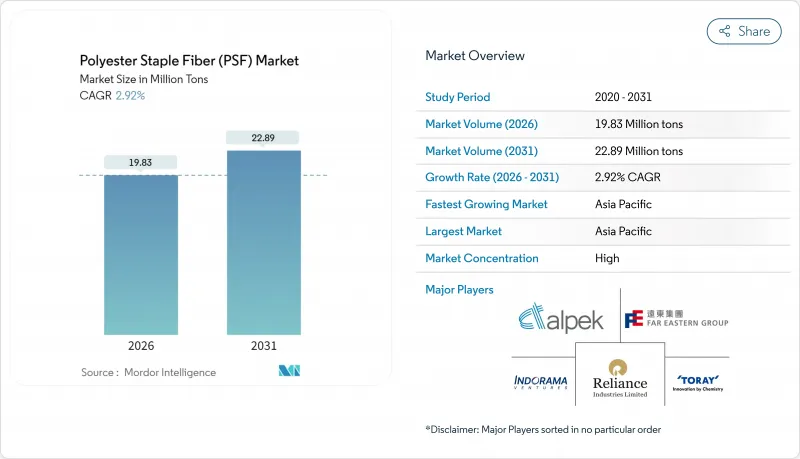
2025年聚酯短纤维(PSF)市值为1,927万吨,预计2031年将达到2,289万吨,高于2026年的1,983万吨。
预计在预测期(2026-2031 年)内,复合年增长率将达到 2.92%。
这种稳定成长反映了该材料在服饰、家居用品、不织布卫生用品、汽车声学零件以及不断扩展的技术应用领域的应用范围日益扩大。对经济实惠的合成纤维的需求不断增长,棉花消费结构逐渐被淘汰,以及对闭合迴路回收的投资,都在增强市场抵御原油价格波动和贸易壁垒带来的衝击。随着全球时尚零售商、汽车製造商和卫生用品生产商将永续性投资转向下游纤维供应协议,对再生纤维的竞争日益激烈。能够将规模、化学创新和可追溯的原料来源结合的生产商,预计在未来十年内提高利润率。
全球聚酯短纤维(PSF)市场趋势与洞察
快时尚品牌对再生聚苯乙烯泡沫塑胶的需求迅速成长
消费者日益严格的监管以及欧洲新推出的数位产品护照计划,正迫使全球零售商用再生纤维取代原生聚酯纤维。 H&M 已向拥有闭环聚合物再生技术的 Syre 公司投资 6 亿美元,标誌着其原料来源永久地从宝特瓶转向其他材料。 Shein 推出了一项专有的解聚工艺,并计划在达到每年 3000 吨的试点产能后,将其授权给合作工厂。各大品牌纷纷签署多年采购协议,导致优质再生短纤维供应紧张,并推动了欧洲和亚洲先进化学回收中心的扩张。随着可追溯性成为一项必要条件,拥有检验的监管链数据的纤维生产商有望获得长期批量合约和价格溢价,从而推动整个聚酯短纤维市场的成长。
价格波动下棉涤混纺的替代。
棉花价格的持续波动促使服装製造商将目光转向合成纤维替代品,因为合成纤维能够确保成本和供应的可预测性。美国农业部 (USDA) 发布的 2024/25 年展望报告显示,儘管全球棉花面积不断增加,但美国工厂棉花消费量仍处于多年来的低位,这凸显了聚酯纤维相对的经济稳定性。纺织加工商透过提供手感类似棉且具有抗缩水性的聚酯纱线,正在丹宁布料混纺、休閒和大众时尚市场中不断扩大份额。这种转变在印度和中国尤为明显,两国布料製造商正在扩大用于针织 T 恤和 Polo 衫的拉伸变形纱线生产线。这种结构性转变正在推动基准需求,并为 2030 年前的聚酯短纤维市场奠定基础。
原物料价格波动与原油价格波动有关
对二甲苯 (PX) 和对苯二甲酸 (PTA) 的价格与布兰特原油价格密切相关,使聚酯产业面临能源市场波动的风险。 2024 年,炼油厂的趋势(被称为「汽油效应」)导致北美 PX 的交易价格高于亚洲,扩大了交付成本差异。儘管中国石油化学公司(中石化)在江苏省的 300 万吨 PTA 工厂有助于缓解供应压力,但价格飙升迫使纤维生产商调整库存管理和避险策略,并常常因利润率收窄而推迟产能扩张。预计这种波动将使聚酯短纤维市场的复合年增长率 (CAGR) 下降约 0.6 个百分点。
细分市场分析
截至2025年,实心纤维占总份额的59.35%,这主要得益于其在服饰、家用纺织品和填充材料等领域的广泛应用。中空纤维占据了剩余的市场份额,预计到2031年将以每年5.62%的速度成长,显着超过聚酯短纤维(PSF)市场的整体成长速度。这一优异表现归功于中空纤维的隔热和吸湿排汗性能,使其成为休閒、睡袋和被子填充物的理想选择。
生产技术的进步有效防止了纤维崩坏,从而实现了轻质高蓬鬆度。汽车内部装潢建材、空气过滤器和卫生面巾等产品均采用双组分中空纤维产品,并辅以亲水整理,以促进流体输送。亚洲中空不织布提供克重从13克/平方公尺到100克/平方公尺的热黏合网,展现出广泛的应用潜力。随着技术客户对轻量化和节能性的日益重视,中空纤维预计将在隔热材料和过滤应用领域占据聚酯短纤维市场越来越大的份额。
区域分析
预计到2025年,亚太地区将引领市场,占据全球整体72.40%的份额,主要得益于中国PTA、MEG和纤维一体化资产以及印度泰米尔纳德邦针织业的扩张。全部区域拉伸变形纱和中空纱生产线的普及率预计将推动亚太地区以5.18%的复合年增长率成长,成为各区域中最快的成长速度。中国石油化学股份有限公司(中石化)的300万吨PTA工厂正在提升上游供应安全,并降低下游纺纱企业的损益平衡点。
印度继续利用绩效激励措施扩大人造纤维出口,同时该国不断加快的都市化也推动了家用纺织品消费的成长。越南、印尼和泰国正在吸引对卫生不织布的投资,这带动了树脂进口,并促使纺粘厂与新的短纤维生产线推出。这些趋势共同为区域聚酯短纤维市场注入了新的活力。
北美和欧洲的产量小规模,但其生产的纤维附加价值很高,主要用于汽车、家具和过滤等领域。这两个地区的反倾销诉讼正在改变贸易格局。拉丁美洲和土耳其正在接收来自亚洲的传输发货,而欧洲生产商则将目标客户锁定在价格敏感度较低的技术型客户。在预测期内,对回收基础设施(例如西班牙、法国和美国东部的化学解聚工厂)的额外投资预计将减缓原生原料的生产成长,同时提高再生材料在聚酯短纤维(PSF)市场的渗透率。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 快时尚品牌对再生聚苯乙烯泡沫塑胶的需求激增
- 扩大东南亚不织布卫生用品的生产能力
- 由于价格波动,棉花被聚酯纤维替代
- 轻量化NVH汽车零件的成长
- 印度和中国的都市化推动了家用纺织品的繁荣。
- 市场限制
- 原物料价格波动与原油价格波动有关
- 美国和欧盟对聚酯短纤维(PSF)征收反倾销税
- 严格的法律和政治规章
- 价值链分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 依产品类型
- 固体的
- 中空的
- 起源
- 处女
- 混合物
- 生殖
- 透过使用
- 纺织品
- 家居布置
- 车
- 过滤
- 建造
- 其他用途
- 按地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 东南亚国协
- 亚太其他地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 其他欧洲地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地区
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 亚太地区
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率(%)/排名分析
- 公司简介
- Alpek Polyester
- Barnet
- Bombay Dyeing
- BoReTech Environmental Engineering Co., Ltd.
- Diyou Fibre(M)Sdn Bhd
- Far Eastern Group
- Hang Zhou Benma Chemfibre and Spinning Co.,Ltd.
- Huvis Corp
- Indorama Ventures Public Company Limited.
- Komal Fibres
- Nirmal Fibres(P)Ltd.
- Reliance Industries Limited
- Sanfame Group
- Shubhalakshmi
- SINOPEC YIZHENG CHEMICAL FIBRE LIMITED
- Thai polyester Co., Ltd.
- Tongkun Holding Group
- TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
- XINDA
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) Market was valued at 19.27 Million tons in 2025 and estimated to grow from 19.83 Million tons in 2026 to reach 22.89 Million tons by 2031, at a CAGR of 2.92% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

This steady rise mirrors the material's expanding footprint in apparel, home furnishings, non-woven hygiene products, automotive noise-control parts, and a growing range of technical uses. Rising demand for cost-effective synthetics, the structural shift away from cotton, and investment in closed-loop recycling are reinforcing the market's resilience even as oil-linked raw-material costs and trade barriers add volatility. Competition is intensifying around recycled grades as global fashion retailers, automakers, and hygiene converters move sustainability spending downstream into fiber supply contracts. Producers able to blend scale, chemistry innovation, and traceable feedstocks are positioned to strengthen margins over the decade.
Global Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) Market Trends and Insights
Surge in Demand for Recycled PSF from Fast-Fashion Brands
Mounting consumer scrutiny and new European Digital Product Passports are compelling global retailers to replace virgin polyester with textile-to-textile recycled alternatives. H&M has committed USD 600 million to Syre for closed-loop polymer regeneration, signalling a permanent shift away from bottle-based feedstock. Shein has introduced a proprietary depolymerisation process and intends to license it to partner mills once pilot output scales to 3,000 tons per year. Brands are also locking multi-year offtake agreements, which is tightening supply of high-quality recycled staple and encouraging expansion of advanced chemical recycling hubs in Europe and Asia. As traceability becomes non-negotiable, fiber producers able to validate chain-of-custody data stand to win long-term volume contracts and price premiums, lifting overall growth in the polyester staple fiber market.
Substitution of Cotton with Polyester amid Price Volatility
Persistent swings in cotton prices have sharpened apparel makers' focus on synthetic alternatives that guarantee predictable cost and supply. USDA's 2024 and 25 outlook shows U.S. mill cotton use at multi-year lows even as global cotton crops rise, underscoring polyester's relative economic security. Fiber converters are capturing share in denim blends, athleisure and mass-market fashion by offering polyester yarns that mimic cotton's hand feel while resisting shrinkage. The shift is most pronounced in India and China where fabric mills are scaling draw-texturised yarn lines dedicated to knitted t-shirt and polo production. This structural migration lifts baseline demand, underpinning the polyester staple fiber market through 2030.
Raw-Material Price Volatility Linked to Crude-Oil Swings
Paraxylene and PTA prices mirror Brent movements, exposing polyester economics to energy market turbulence. In 2024 North American PX traded at premiums to Asia because of refinery dynamics referred to as the "gasoline effect," widening delivered-cost gaps. Although Sinopec's 3 million-ton PTA unit in Jiangsu eases supply pressure, price spikes compel fiber makers to juggle inventory cover and hedging, often deferring capacity upgrades when margins compress. Volatility therefore subtracts an estimated 0.6 percentage points from the polyester staple fiber market CAGR.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Urbanisation-Led Home-Textile Boom in India & China
- Growth of Lightweight NVH Automotive Components
- Anti-Dumping Duties on PSF in United States and European Union
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Solid fibers accounted for 59.35% of volume in 2025, underpinned by broad usage in apparel, home textiles and stuffing materials. In the same year hollow grades captured the remaining share yet are predicted to expand 5.62% annually to 2031-well above the overall polyester staple fiber (PSF) market. Performance stems from the thermal-insulation value of hollow cores and their ability to wick moisture, essential for athleisure, sleeping bags and quilt fillings.
Production advances now prevent fiber collapse, allowing higher loft at lower weight. Automotive interior trims, air filters and hygiene topsheets are specifying bi-component hollow products designed with hydrophilic finishes that speed liquid transport. Thermal-bonded webs between 13-100 gsm supplied by Asian non-woven converters demonstrate the breadth of end-use possibilities. As technical customers prioritize weight savings and energy efficiency, hollow variants are set to capture a larger slice of the polyester staple fiber market size for insulation and filtration sub-segments.
The Polyester Staple Fiber (PSF) Market Report Segments the Industry by Product Type (Solid, Hollow), Origin (Virgin, Blended, Recycled), Application (Textile, Home Furnishing, Automotive, Filtration, Construction, Other Applications), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, Middle-East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (Tons).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific dominated global volume with a 72.40% share in 2025, propelled by China's integrated PTA, MEG and fiber assets and India's expanding knitwear hub in Tamil Nadu. Region-wide adoption of draw-texturised yarns and hollow variant lines positions APAC to grow at a 5.18% CAGR, the fastest regional rate. Sinopec's megascale 3 million-ton PTA plant improves upstream security, lowering break-even costs for downstream spinners.
India continues to leverage the Performance-Linked Incentive scheme to boost man-made fiber exports while domestic urbanisation lifts household textile consumption. Vietnam, Indonesia, and Thailand attract hygiene-non-woven investments, drawing resin imports and sparking new staple lines co-located with spunbond units. Together, these trends inject momentum into the regional polyester staple fiber market.
North America and Europe account for a smaller volume, yet fibre engineered for automotive, furniture, and filtration draws premium margins. Anti-dumping cases in both regions alter trade flows: Latin America and Turkiye receive redirected Asian shipments while European producers target technical customers less sensitive to price. Over the forecast horizon, incremental investments in recycling infrastructure-such as chemical depolymerisation plants in Spain, France and the eastern United States, will taper virgin volume growth but raise recycled penetration within the polyester staple fiber (PSF) market.
- Alpek Polyester
- Barnet
- Bombay Dyeing
- BoReTech Environmental Engineering Co., Ltd.
- Diyou Fibre (M) Sdn Bhd
- Far Eastern Group
- Hang Zhou Benma Chemfibre and Spinning Co.,Ltd.
- Huvis Corp
- Indorama Ventures Public Company Limited.
- Komal Fibres
- Nirmal Fibres (P) Ltd.
- Reliance Industries Limited
- Sanfame Group
- Shubhalakshmi
- SINOPEC YIZHENG CHEMICAL FIBRE LIMITED
- Thai polyester Co., Ltd.
- Tongkun Holding Group
- TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
- XINDA
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in Demand for Recycled PSF from FastFashion Brands
- 4.2.2 Expansion of Nonwoven Hygiene Capacity in Southeast Asia
- 4.2.3 Substitution of Cotton with Polyester amid Price Volatility
- 4.2.4 Growth of Lightweight NVH Automotive Components
- 4.2.5 UrbanisationLed Home Textile Boom in India & China
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 RawMaterial Price Volatility Linked to CrudeOil Swings
- 4.3.2 Anti Dumping Duties on PSF in United States & EU
- 4.3.3 Stringent Legal and Political Regulations
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Solid
- 5.1.2 Hollow
- 5.2 By Origin
- 5.2.1 Virgin
- 5.2.2 Blended
- 5.2.3 Recycled
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Textile
- 5.3.2 Home Furnishing
- 5.3.3 Automotive
- 5.3.4 Filtration
- 5.3.5 Construction
- 5.3.6 Other Applications
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 Asia Pacific
- 5.4.1.1 China
- 5.4.1.2 India
- 5.4.1.3 Japan
- 5.4.1.4 South Korea
- 5.4.1.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.4.1.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.4.2 North America
- 5.4.2.1 United States
- 5.4.2.2 Canada
- 5.4.2.3 Mexico
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Italy
- 5.4.3.5 Spain
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 Asia Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank / Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Alpek Polyester
- 6.4.2 Barnet
- 6.4.3 Bombay Dyeing
- 6.4.4 BoReTech Environmental Engineering Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Diyou Fibre (M) Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.6 Far Eastern Group
- 6.4.7 Hang Zhou Benma Chemfibre and Spinning Co.,Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Huvis Corp
- 6.4.9 Indorama Ventures Public Company Limited.
- 6.4.10 Komal Fibres
- 6.4.11 Nirmal Fibres (P) Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Reliance Industries Limited
- 6.4.13 Sanfame Group
- 6.4.14 Shubhalakshmi
- 6.4.15 SINOPEC YIZHENG CHEMICAL FIBRE LIMITED
- 6.4.16 Thai polyester Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Tongkun Holding Group
- 6.4.18 TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
- 6.4.19 XINDA
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 Whitespace & UnmetNeed Assessment
- 7.2 Growing Awareness Regarding Recycled Polyester Staple Fiber












