 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1906866
颜料:市占率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Pigments - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
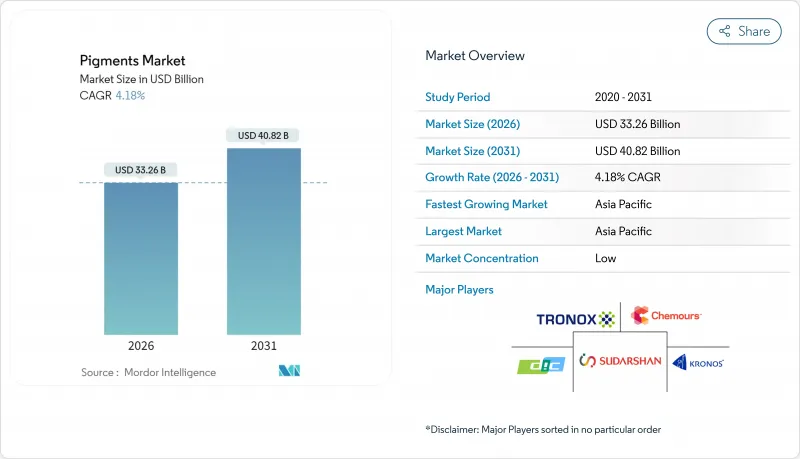
2025年颜料市值为319.3亿美元,预计从2026年的332.6亿美元成长到2031年的408.2亿美元,在预测期(2026-2031年)内复合年增长率为4.18%。
儘管生产商正在应对供应链重组和安全法规日益严格的挑战,但建筑、包装和运输领域的强劲需求仍然支撑着这一扩张。无机颜料在建筑涂料领域保持着成本优势,而有机和特殊化学品则在高性能汽车和电子应用领域占据越来越大的份额。二氧化钛 (TiO2) 来源的地域多角化,以及逐步淘汰 PFAS(全氟不对称合成化合物)和其他受限物质的努力,正在加速颜料市场的产品配方改良。产业整合进一步塑造了竞争格局,例如 Cronos Worldwide 于 2024 年 7 月收购 Louisiana Pigment Company,这使得规模更大的企业能够简化原材料采购流程并加强下游分销网络的扩张。
全球颜料市场趋势与洞察
新兴经济体对油漆和涂料的需求快速成长
印尼、奈及利亚和越南的基础设施发展计画正推动建筑涂料需求的稳定成长,印尼涂料产量在2024年10月突破100万吨便印证了这一点。在撒哈拉以南非洲,受中国援助的9个计划(已于2023年完工)和5个项目(计划于2024年开工)的推动,水泥产能的扩张持续提振着建筑颜料的需求。政府大力推广水性涂料和低VOC配方,迫使供应商提供既能满足更严格排放标准又具有成本竞争力的分散体。这为中型颜料生产商创造了更大的市场基础,使他们能够在主要建筑丛集附近开展配方和物流业务。中期来看,住宅和交通基础设施的持续投入预计将促成多年期供应合约的签订,即使私部门的翻新週期放缓,也能稳定产量。
监管部门推动环保/生物基颜料的发展
世界各地的监管机构正在逐步缩小可接受的颜料化学品范围。加州的AB418法案将于2025年1月起禁止在食品中使用二氧化钛,纽西兰将于2026年12月起禁止在化妆品中使用全氟烷基和多氟烷基物质(PFAS)。欧莱雅等大型配方商已承诺在2030年使用95%的生物基成分,整个产业正向可再生着色剂转型。学术界和工业界正在利用酵素辅助萃取方法和动态空化技术,将海藻衍生的藻胆蛋白和岩藻黄素商业化,从而获得与传统偶氮颜料相当的显色强度。随着现有化学品合规成本的上升,小规模生物基供应商或许能够利用先前大众市场无法企及的价格优势。然而,生物基产品的广泛应用将取决于能否克服新建生物炼製基础设施的资本成本,以及能否满足外墙涂料等高要求终端应用的耐久性要求。
严格的环境和毒理学法规
OEKO-TEX于2024年10月在其限制性物质检测通讯协定中新增了PFAS的碱性水解筛检。加拿大全国范围内的煤焦油禁令将于2025年3月生效,欧盟REACH法规第79条也于同月引入了PFHxA的限制。美国多个州将于2025年1月起禁止在纺织品使用PFAS。每项新法规都要求颜料供应商检验替代化学品,并建立双重库存系统以适应不同司法管辖区的不同阈值。合规需要基于ISO 22716标准的复杂品管体系,而增加的固定成本对于中小型生产者而言难以负担。其直接影响是成熟市场的产能精简,降低了战术性的价格竞争,同时提高了新进入者的策略准入门槛。
细分市场分析
到2025年,无机颜料市场丛集将保持在75.42%,这主要得益于二氧化钛(TiO2)的应用,它在建筑和包装应用中对遮盖力和白度至关重要。在这一类别中,铁基颜料因其成本和耐久性优势,继续在建筑涂料和建材领域占据主导地位。有机颜料虽然目前销量小规模,但预计到2031年将以5.18%的复合年增长率增长,这得益于监管政策为那些需要高饱和度色彩和低重金属含量的应用提供了发展空间。高性能的Quinacridones和Perylenes颜料广泛应用于汽车底涂层,DIKETO-PYRROLO-PYRROLES红色颜料则越来越多地应用于机壳。感温变色颜料和磁性颜料等特殊颜料已在安全印刷和电子元件标记领域获得了高价值合约。
二氧化钛原料成本的上涨导致一些软包装应用中出现了高遮盖力有机颜料的替代,但功能等效性的限制阻碍了完全替代。防晒油化妆品中氧化锌紫外线阻隔剂的引入推动了矿物颜料的增量增长,抵消了传统造纸应用领域需求的下降。炭黑在导电聚合物复合复合材料和墨粉系统中保持稳定的地位。整体而言,随着无机颜料领域的成熟,竞争重点正转向製程效率,而有机颜料供应商则透过分子层面的创新和与终端用户的合作来展开竞争。
本颜料报告按产品类型(无机颜料、有机颜料、特殊颜料及其他产品类型)、应用领域(油漆涂料、纺织品、印刷油墨、塑胶、皮革及其他应用领域)和地区(亚太地区、北美地区、欧洲地区、南美地区以及中东和非洲地区)进行细分。市场预测以美元以金额为准。
区域分析
预计到2025年,亚太地区将占全球营收的45.60%,并在2031年之前维持5.32%的年复合成长率,成为成长最快的地区,巩固其在规模和发展动能方面的主导地位。中国约占该地区颜料产量的一半,并透过二氧化钛(TiO2)产能的波动和能源强度课税持续影响着全球价格。印度已推出与特种化学品生产挂钩的激励措施,促进与日本和欧洲主要颜料生产商的合资企业,并扩大了该地区的产品线。预计到2024年底,印尼的建筑涂料产量将超过100万吨,随着国内市场对品质要求的不断提高,市场也日益成熟。
北美和欧洲正转向高价值的细分市场,这些市场整体产量较低,更注重技术差异化和价值链稳定性。在美国,根据《国防授权法》,联邦政府对特种化学品的拨款已流入国内颜料中间体产业,这在一定程度上保护了买家免受地缘政治动盪的影响。
中东和非洲正崛起为充满成长机会的地区。波湾合作理事会(GCC)成员国正投资氯化钛(TiO2)产业,以实现下游业务多元化;同时,北非的纺织产业丛集正吸引寻求从邻国采购原料的欧洲品牌。南美洲的成长轨迹取决于宏观经济的稳定和大宗商品出口週期,而这些因素又会影响基础建设支出和汽车组装量。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 新兴经济体对油漆和涂料的需求快速成长
- 监管部门推动环保/生物基颜料的发展
- 高性能和特效颜料的广泛应用
- 奈米技术赋能的数位与3D列印应用
- 促进美国和欧盟供应链本地化的措施
- 市场限制
- 严格的环境和毒理学法规
- 原料价格波动(二氧化钛、氧化铁等原料)
- 食品级奈米颗粒禁用(E171,化妆品限制)
- 价值链分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争程度
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 依产品类型
- 无机颜料
- 二氧化钛
- 氧化锌
- 其他产品种类(碳颜料、干土、群青颜料、镉、铬酸铅等)
- 有机颜料
- 特殊颜料和其他产品类型(功能性颜料、磁性颜料等)
- 无机颜料
- 透过使用
- 油漆和涂料
- 纤维
- 印刷油墨
- 塑胶
- 皮革
- 其他用途
- 按地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- ASEAN
- 亚太其他地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 义大利
- 法国
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 亚太地区
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率(%)/排名分析
- 公司简介
- ALTANA
- Cathay Industries
- DIC Corporation
- Heubach GmbH
- Kronos Worldwide, Inc.
- Lanxess
- LB Group
- Shepherd Color
- Sudarshan Chemical Industries Limited(Heubach GmbH)
- The Chemours Company
- Tronox Holdings Plc
- Trust Chem Co., Ltd.
- Venator Materials PLC
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Pigments Market was valued at USD 31.93 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 33.26 billion in 2026 to reach USD 40.82 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 4.18% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

Resilient demand for construction, packaging, and mobility applications underpins this expansion even as producers navigate supply chain realignments and tightening safety rules. Inorganic grades retain cost-based advantages in bulk architectural coatings, while organic and specialty chemistries capture share in high-performance automotive and electronics uses. Regional diversification of titanium dioxide (TiO2) sourcing, coupled with initiatives to phase out PFAS and other restricted substances, is accelerating product reformulation activity across the pigments market. Competitive dynamics are further shaped by consolidation, exemplified by Kronos Worldwide's July 2024 acquisition of Louisiana Pigment Company, which is allowing scale players to streamline raw-material procurement and reinforce downstream distribution reach.
Global Pigments Market Trends and Insights
Surging Paints and Coatings Demand in Emerging Economies
Infrastructure programs in Indonesia, Nigeria, and Vietnam are driving a steady uptick in architectural coatings volumes, evidenced by Indonesia's paint output surpassing 1.00 million tons in October 2024. Growing cement capacity across sub-Saharan Africa-bolstered by nine Chinese-backed projects completed in 2023 and five more slated for 2024-continues to lift demand for construction-grade pigments. Governments' drive toward water-based, low-VOC formulations is forcing suppliers to deliver cost-competitive dispersions compatible with stricter emission limits. The result is a larger addressable base for mid-tier pigment producers able to localize blending and logistics operations near major construction clusters. Over the medium term, recurring housing and transport infrastructure outlays are expected to translate into multi-year offtake contracts that stabilize volumes even when private sector repaint cycles slow.
Regulatory Push Toward Eco-Friendly/Bio-Based Pigments
Global regulators are methodically narrowing the palette of allowable pigment chemistries. California's AB 418 will prohibit TiO2 in foods from January 2025, while New Zealand's cosmetics ban on PFAS enters force in December 2026. Large formulators such as L'Oreal have pledged to source 95% bio-based ingredients by 2030, signaling an industry-wide pivot toward renewable colorants. Academic and industrial programs are commercializing seaweed-derived phycobiliproteins and fucoxanthin using enzyme-assisted extraction and hydrodynamic cavitation, achieving color strength comparable with conventional azo pigments. As compliance costs rise for incumbent chemistries, early-scale bio-based suppliers can exploit a pricing corridor that was previously unavailable in volume markets. Adoption, however, hinges on overcoming the capital cost of new biorefinery infrastructure and meeting the durability expectations of demanding end uses such as outdoor coatings.
Stringent Environmental and Toxicology Regulations
OEKO-TEX updated its restricted-substance testing protocol in October 2024 to include alkaline hydrolysis screening for PFAS, and Canada enacted a nationwide coal-tar ban in March 2025. EU REACH Entry 79 introduced PFHxA controls in the same month, while several U.S. states imposed PFAS prohibitions on textiles from January 2025. Each new rule forces pigment suppliers to validate alternative chemistries and establish dual inventories to serve jurisdictions with divergent thresholds. Compliance requires sophisticated quality-management systems under ISO 22716, raising fixed costs that smaller producers struggle to absorb. The immediate impact is a wave of capacity rationalization in mature markets, reducing tactical price competition but heightening strategic barriers for new entrants.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Adoption of High-Performance and Effect Pigments
- Nano-Enabled Digital and 3-D Printing Applications
- Raw-Material Price Volatility (TiO2, Iron-Oxide Feedstocks)
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The inorganic cluster maintained 75.42% share of the pigments market in 2025, a position anchored by TiO2's indispensability for opacity and whiteness in architectural and packaging formulations. Within this cohort, iron oxides continue to dominate masonry coatings and construction materials thanks to cost and durability advantages. Organic pigments, although smaller in volume, are set to advance at a 5.18% CAGR to 2031, leveraging superior chroma and regulatory headroom in applications that demand low heavy-metal content. High-performance quinacridones and perylenes now populate automotive basecoats, while diketopyrrolo-pyrrole reds are penetrating consumer electronics housings. Specialty sub-segments, such as thermochromic and magnetic pigments, are winning premium contracts in security printing and electronic component marking.
Cost inflation for titania feedstock is tilting certain flexible-packaging jobs toward high-opacity organic alternatives, though functional equivalence still limits broader substitution. The introduction of zinc-oxide UV blockers in sun-care cosmetics is driving incremental growth for mineral pigments, offsetting softer demand in legacy paper applications. Carbon blacks retain a stable foothold in conductive polymer compounds and toner systems. Overall, the inorganic segment's maturity has shifted competitive emphasis toward process efficiency, whereas organic suppliers compete on molecular innovation and end-user collaboration.
The Pigments Report is Segmented by Product Type (Inorganic Pigments, Organic Pigments, and Specialty Pigments and Other Product Types), Application (Paints and Coatings, Textiles, Printing Inks, Plastics, Leather, and Other Applications), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle-East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific held a 45.60% share of global revenue in 2025 and is expected to post the fastest 5.32% CAGR through 2031, cementing its lead in both scale and momentum. China accounts for roughly half of regional pigment output and continues to influence global price discovery through its TiO2 capacity swings and energy-intensity levies. India's production-linked incentives for specialty chemistry are encouraging joint ventures with Japanese and European pigment majors, thereby broadening the region's product breadth. Indonesia's output of architectural coatings exceeded 1.00 million tons in late 2024, signaling a maturing domestic market with rising quality expectations.
North America and Europe, though collectively smaller in volume, are pivoting toward value-add niches that reward technical differentiation and supply-chain security. U.S. federal funding for specialty chemicals under defense authorization acts is channeling capital into domestic pigment intermediates, partially insulating buyers from geopolitical disruptions.
The Middle East and Africa are emerging as opportunistic growth zones. Gulf Cooperation Council countries are investing in chloride-route TiO2 as part of downstream diversification, while North African textile clusters are courting European brands seeking near-shore sourcing. South America's trajectory is tied to macroeconomic stabilization and commodity export cycles that affect infrastructure spending and automotive assembly volumes.
- ALTANA
- Cathay Industries
- DIC Corporation
- Heubach GmbH
- Kronos Worldwide, Inc.
- Lanxess
- LB Group
- Shepherd Color
- Sudarshan Chemical Industries Limited (Heubach GmbH)
- The Chemours Company
- Tronox Holdings Plc
- Trust Chem Co., Ltd.
- Venator Materials PLC
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surging paints and coatings demand in emerging economies
- 4.2.2 Regulatory push toward eco-friendly/bio-based pigments
- 4.2.3 Rising adoption of high-performance and effect pigments
- 4.2.4 Nano-enabled digital and 3-D printing applications
- 4.2.5 Supply-chain localization incentives in US-EU
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Stringent environmental and toxicology regulations
- 4.3.2 Raw-material price volatility (TiO2, iron-oxide feedstocks)
- 4.3.3 Nano-particle food-grade bans (E171, cosmetics limits)
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Inorganic Pigments
- 5.1.1.1 Titanium Dioxide
- 5.1.1.2 Zinc Oxide
- 5.1.1.3 Other Product Types (Carbon Pigments, Dry Earth, Ultramarine Pigments, Cadmium, Lead Chromate, and Others)
- 5.1.2 Organic Pigments
- 5.1.3 Specialty Pigments and Other Product Types (Functional Pigments, Magnetic Pigments, and Others)
- 5.1.1 Inorganic Pigments
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Paints and Coatings
- 5.2.2 Textiles
- 5.2.3 Printing Inks
- 5.2.4 Plastics
- 5.2.5 Leather
- 5.2.6 Other Applications
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.1.1 China
- 5.3.1.2 India
- 5.3.1.3 Japan
- 5.3.1.4 South Korea
- 5.3.1.5 ASEAN
- 5.3.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 North America
- 5.3.2.1 United States
- 5.3.2.2 Canada
- 5.3.2.3 Mexico
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.3 Italy
- 5.3.3.4 France
- 5.3.3.5 Spain
- 5.3.3.6 Russia
- 5.3.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 South Africa
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ALTANA
- 6.4.2 Cathay Industries
- 6.4.3 DIC Corporation
- 6.4.4 Heubach GmbH
- 6.4.5 Kronos Worldwide, Inc.
- 6.4.6 Lanxess
- 6.4.7 LB Group
- 6.4.8 Shepherd Color
- 6.4.9 Sudarshan Chemical Industries Limited (Heubach GmbH)
- 6.4.10 The Chemours Company
- 6.4.11 Tronox Holdings Plc
- 6.4.12 Trust Chem Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Venator Materials PLC
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment








