 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1906950
马来西亚塑胶产业:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Malaysia Plastics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
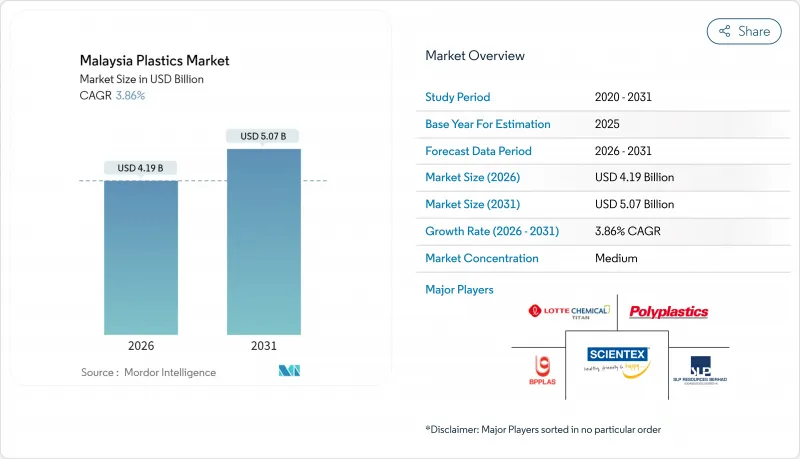
预计到2026年,马来西亚塑胶市场规模将达到41.9亿美元,高于2025年的40.4亿美元。预计到2031年,该市场规模将达到50.7亿美元,2026年至2031年的复合年增长率为3.86%。
马来西亚作为区域石化原料供应中心和下游製造地,为东南亚电子、汽车和包装价值链提供原料,其双重角色支撑着马来西亚石化产业的稳定扩张。马来西亚国家石油公司(Petronas)的综合工厂、雪兰莪州、柔佛州和槟城州的出口导向製造群以及政府对下游石化行业的主导奖励,共同增强了供应安全性和成本竞争力。此外,全球品牌对再生材料和生物基材料的需求、马来西亚的零一次性塑胶蓝图以及为解决技能短缺问题而对自动化加工的投资,都推动了成长动能。同时,环境法规和原材料价格波动限制了利润率,促使企业转向高附加价值应用领域,例如特殊等级产品和精密成型产品,这些产品可以获得更高的溢价。
马来西亚塑胶市场趋势与洞察
食品和饮料包装行业的需求不断增长
食品饮料製造商依赖塑胶阻隔薄膜和多层结构来满足出口市场的高食品安全标准。马来西亚国家石油公司(PETRONAS)决定在其彭朗综合设施内建造生物炼製厂,预示着本地生物基包装树脂供应即将到来。马来西亚出口食品贸易中广泛适用的清真认证法规要求使用特殊包装,以确保产品在长途运输过程中保持完整性。都市区收入水准的提高以及消费者对即食产品的日益偏好,推动了便捷包装需求的成长。因此,为立式袋、杀菌袋和PET饮料瓶提供包装的加工商,能够获得与产品性能和永续性认证相关的高额利润。
不断发展的电子製造生态系统
马来西亚的国家半导体策略正吸引英飞凌等全球企业的新投资,推动后端封装、测试和积体电路设计活动的扩张。用于5G基础设施和电动车的半导体模组越来越多地采用具有高热稳定性和阻燃性的工程塑胶。因此,在槟城峇六拜和居林高科技园区,微米级精准度的射出成型线正快速普及。自动化视觉检测和闭合迴路成型系统使製造商能够在满足严格的缺陷率要求的同时,解决当地精密聚合物加工技术工人短缺的问题。
环境问题和一次性产品的禁令
马来西亚的《2025-2030年零一次性塑胶蓝图》逐步限制一次性塑胶袋、吸管和发泡聚苯乙烯餐具的使用。 2025年7月收紧的塑胶废料进口限制虽然切断了一个低成本的原料来源,但也提高了公众对家庭废弃物的认识。无法转型使用可回收或可堆肥产品的加工商将面临吉隆坡大都会区、新山和乔治市更高的消费税和更严格的执法。同时,拥有可堆肥薄膜生产线和可重复使用餐饮服务模式的公司正抓住机会,转型使用符合规定的替代方案。
细分市场分析
到2025年,聚乙烯和聚丙烯等传统聚合物仍将占据马来西亚塑胶市场78.84%的份额,这主要得益于边佳兰一体化裂解聚合物生产线,该生产线支持低成本生产。同时,受可堆肥包装品牌目标和马来西亚禁止一次性产品的措辞推动,生物分解性塑胶预计将以4.86%的复合年增长率实现最快增长。用于电绝缘材料和汽车发动机舱盖下部件的工程树脂实现了适度的个位数增长,这主要得益于进口半成品化合物经本地重新配製后用于本地加工。
马来西亚塑胶市场的生产商利用现有的从裂解到成膜的物流网络供应大众市场应用,但不断上涨的生产者延伸责任(EPR)附加税正给利润率带来压力。柔佛州一家综合设施计划建设的生物炼製厂将提供化石基PET和PE的替代品,使当地加工商能够在出口竞标中获得高级回收积分。马来西亚塑胶产业的特殊复合材料生产商透过提供阻燃、玻璃纤维增强和无卤等级的产品(特别是用于智慧型装置连接器的产品)而获得溢价。材料科学领域日益增长的技能缺口凸显了技术服务团队的价值,这些团队能够对用于食品接触应用和电子元件认证的新型生物基材料进行鑑定。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 食品和饮料包装行业的需求不断增长
- 不断发展的电子製造生态系统
- 政府对下游石化产业的激励措施
- 全球品牌对循环经济的承诺
- 扩大医疗设备丛集
- 市场限制
- 环境问题和一次性产品的禁令
- 原物料价格波动
- 先进聚合物加工技能短缺
- 价值链分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争程度
- 价格趋势分析
- 进出口
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按类型
- 传统塑料
- 工程塑料
- 生质塑胶
- 透过技术
- 吹塑成型
- 挤出成型
- 射出成型
- 其他技术
- 透过使用
- 包装
- 电气和电子设备
- 建筑/施工
- 汽车/运输设备
- 家居用品
- 家具和床上用品
- 其他用途
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率(%)/排名分析
- 公司简介
- Behn Meyer
- BP Plastics Holding Bhd
- Commercial Plastic Industries Sdn Bhd
- CYL Corporation
- Ee-Lian Enterprise(M)Sdn. Bhd.
- Fu Fong Plastic Industries Sdn Bhd
- Guppy Group
- HICOM-Teck See
- Lam Seng Plastics Industries Sdn Bhd
- LOTTE CHEMICAL TITAN HOLDING BERHAD.
- Malayan Electro-Chemical Industry Co. Sdn Bhd
- Meditop International
- Megafoam Containers Enterprise Sdn Bhd(MEGAFOAM)
- Metro Plastic Manufacturer Sdn. Bhd.
- Polyplastics Co., Ltd.
- Sanko Plastics(M)Sdn Bhd
- Scientex Berhad
- SLP RESOURCES BERHAD
- Teck See Plastic Sdn Bhd(TSP)
- TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Malaysia Plastics Market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 4.19 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 4.04 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 5.07 billion, growing at 3.86% CAGR over 2026-2031.

This steady expansion is anchored by Malaysia's dual role as a regional petrochemical feedstock hub and a downstream manufacturing base that supplies the electronics, automotive, and packaging value chains across Southeast Asia. Stable feedstock from PETRONAS's integrated complexes, export-oriented manufacturing clusters in Selangor, Johor, and Penang, and policy-driven incentives for downstream petro-chemicals together reinforce supply security and cost competitiveness. Momentum is further supported by global brands demanding recycled or bio-based content, Malaysia's zero single-use plastics roadmap, and investments in automated processing that counter skills shortages. Meanwhile, environmental regulation and feedstock price volatility continue to temper margins but also catalyze upgrades into higher-value applications where specialty grades and precision molding command premium pricing.
Malaysia Plastics Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand From Food and Beverage Packaging
Food and beverage manufacturers rely on plastic barrier films and multilayer structures to meet higher food-safety standards in export markets. PETRONAS's decision to embed a biorefinery inside the Pengerang Integrated Complex signals an upcoming local supply of bio-based packaging resins. Halal certification rules, prevalent in Malaysia's export food trade, necessitate specialized packaging that maintains product integrity during long transit times. Rising urban income levels and a preference for ready-to-eat formats amplify the consumption of convenience packaging. As a result, converters supplying stand-up pouches, retort pouches, and PET beverage bottles are securing premium margins tied to performance and sustainability credentials.
Growth of Electronics Manufacturing Ecosystem
Malaysia's National Semiconductor Strategy has attracted fresh investments from global players such as Infineon to expand back-end packaging, testing, and IC design activities. Semiconductor modules for 5G infrastructure and electric vehicles increasingly specify engineering plastics with high thermal stability and flame-retardant performance. Injection molding lines capable of micron-level tolerances are therefore proliferating within Penang's Bayan Lepas and Kulim High-Tech parks. Automated vision inspection and closed-loop molding systems allow manufacturers to meet tight defect-rate requirements while offsetting the local skills gap in precision polymer processing.
Environmental Concerns and Single-Use Bans
Malaysia's 2025-2030 zero single-use plastics roadmap imposes phased restrictions on disposable bags, straws, and EPS foodware. Import controls on plastic scrap, tightened in July 2025, have removed low-cost feedstock streams but improved public perception of domestic waste handling. Converters that cannot pivot to recyclable or compostable formats face higher excise levies and tighter enforcement in Greater Kuala Lumpur, Johor Bahru, and George Town. Conversely, firms with compostable film lines and reusable food-service models are capturing the shift toward regulatory-compliant alternatives.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Incentives for Downstream Petro-Chemicals
- Circular-Economy Commitments by Global Brands
- Feedstock Price Volatility
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Traditional polymers such as polyethylene and polypropylene retained 78.84% Malaysia plastics market share in 2025, buoyed by Pengerang's integrated cracker and polymer lines that anchor low-cost output. Bioplastics, however, are forecast to grow fastest at a 4.86% CAGR, aided by brand targets for compostable packaging and the country's single-use ban trajectory. Engineering resins addressing electrical insulation and under-hood automotive parts achieved mid-single-digit growth, supported by imported semifinished compounds rewired for localized finishing.
Producers associated with the Malaysia plastics market leverage existing cracker-to-film logistics to supply high-volume FMCG applications, yet face mounting EPR levies that narrow margins. The upcoming biorefinery within Johor's complex will enable drop-in replacements for fossil-based PET and PE, positioning local converters to claim advanced recycling credit in export tenders. Specialty compounders catering to the Malaysia plastics industry gain premium prices by offering flame-retardant, glass-fiber, and halogen-free grades, particularly for smart-device connectors. A widening skills gap in materials science underscores the value of technical service teams able to qualify new bio-based grades for food-contact and electronic-component certification.
The Malaysia Plastics Market Report is Segmented by Type (Traditional Plastics, Engineering Plastics, and Bioplastics), Technology (Blow Molding, Extrusion, Injection Molding, and Other Technologies), and Application (Packaging, Electrical and Electronics, Building and Construction, Automotive and Transportation, Houseware, Furniture and Bedding, and Other Applications). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Behn Meyer
- BP Plastics Holding Bhd
- Commercial Plastic Industries Sdn Bhd
- CYL Corporation
- Ee-Lian Enterprise (M) Sdn. Bhd.
- Fu Fong Plastic Industries Sdn Bhd
- Guppy Group
- HICOM-Teck See
- Lam Seng Plastics Industries Sdn Bhd
- LOTTE CHEMICAL TITAN HOLDING BERHAD.
- Malayan Electro-Chemical Industry Co. Sdn Bhd
- Meditop International
- Megafoam Containers Enterprise Sdn Bhd (MEGAFOAM)
- Metro Plastic Manufacturer Sdn. Bhd.
- Polyplastics Co., Ltd.
- Sanko Plastics (M) Sdn Bhd
- Scientex Berhad
- SLP RESOURCES BERHAD
- Teck See Plastic Sdn Bhd (TSP)
- TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising demand from food and beverage packaging
- 4.2.2 Growth of electronics manufacturing ecosystem
- 4.2.3 Government incentives for downstream petro-chemicals
- 4.2.4 Circular-economy commitments by global brands
- 4.2.5 Expansion of medical-device clusters
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Environmental concerns and single-use bans
- 4.3.2 Feed-stock price volatility
- 4.3.3 Skills gap in advanced polymer processing
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
- 4.6 Price Trend Analysis
- 4.7 Imports and Exports
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Traditional Plastics
- 5.1.2 Engineering Plastics
- 5.1.3 Bioplastics
- 5.2 By Technology
- 5.2.1 Blow Molding
- 5.2.2 Extrusion
- 5.2.3 Injection Molding
- 5.2.4 Other Technologies
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Packaging
- 5.3.2 Electrical and Electronics
- 5.3.3 Building and Construction
- 5.3.4 Automotive and Transportation
- 5.3.5 Houseware
- 5.3.6 Furniture and Bedding
- 5.3.7 Other Applications
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Behn Meyer
- 6.4.2 BP Plastics Holding Bhd
- 6.4.3 Commercial Plastic Industries Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.4 CYL Corporation
- 6.4.5 Ee-Lian Enterprise (M) Sdn. Bhd.
- 6.4.6 Fu Fong Plastic Industries Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.7 Guppy Group
- 6.4.8 HICOM-Teck See
- 6.4.9 Lam Seng Plastics Industries Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.10 LOTTE CHEMICAL TITAN HOLDING BERHAD.
- 6.4.11 Malayan Electro-Chemical Industry Co. Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.12 Meditop International
- 6.4.13 Megafoam Containers Enterprise Sdn Bhd (MEGAFOAM)
- 6.4.14 Metro Plastic Manufacturer Sdn. Bhd.
- 6.4.15 Polyplastics Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Sanko Plastics (M) Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.17 Scientex Berhad
- 6.4.18 SLP RESOURCES BERHAD
- 6.4.19 Teck See Plastic Sdn Bhd (TSP)
- 6.4.20 TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment










