 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1911428
纺织机械:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Textile Machinery - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
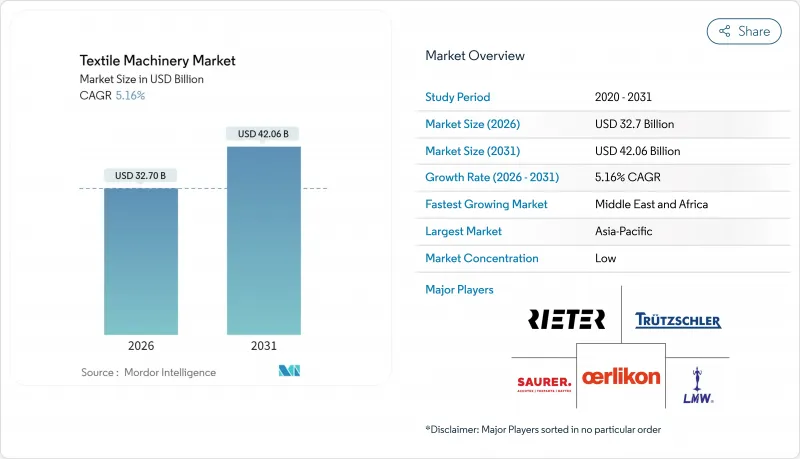
2025年全球纺织机械市场价值为311亿美元,预计从2026年的327亿美元成长到2031年的420.6亿美元,在预测期(2026-2031年)内复合年增长率为5.16%。
工厂投资正日益围绕工业4.0工具展开,以应对技术纯熟劳工短缺并提高产能运转率。智慧感测器、云端分析和人工智慧驱动的缺陷检测技术正在推动设备升级,而回收的强制性要求则带动了对自动化分类和纤维对纤维系统的订单。医疗、防护和体育用品行业对技术纺织品的需求持续超过传统服装,开启了新的收入来源。经济高效的合成纤维和生物基替代品都在促进机械销售,而关税引发的美洲近岸外包则刺激了对灵活的小批量生产线的订单。
全球纺织机械市场趋势与洞察
工业4.0的推广推动了对自动化的需求。
根据製造业采购负责人指数(PMI),纺织厂在2025年4月扩大了生产活动,机器人和人工智慧技术正被用来弥补长期的劳动力短缺问题。美国製造商实施了智慧针织软体,以优化图案复杂性并减少废弃物。物联网平台使管理人员能够即时追踪湿度和能源消耗,巴基斯坦的工厂试点计画证明了这一点。基于卷积模型的人工智慧视觉系统将缺陷检测准确率提高到90%以上,从而减少了返工。产量提高和废弃物减少的累积效应使得自动化生产线成为策略性投资,而非可选项。
新兴经济体服饰消费不断成长
受中国需求復苏和国内零售扩张的推动,印度棉纱製造商预计2025财年营收将成长7-9%。有利的纱线价差和棉花供应的改善正在推动工厂升级。东协和非洲地区的人口结构变化带来了纺纱和针织生产线的新增产能需求。关税正在扰乱传统的供应链,而新兴市场品牌仍需要规模化生产,这促使企业在成本效益高且现代化的机械设备方面进行均衡投资。灵活的资金筹措和模组化升级仍然是吸引供应商的关键卖点。
高额资本投入及投资回收期不明确
一套完整的纺纱织造生产线造价可能超过1000万美元,这对中型纺织厂来说是一个不小的障碍。由于技术更新换代速度加快,即使是大型供应商也谨慎地计算投资报酬率。即使是最先进的环锭纺纱机,也可能在折旧期间被淘汰。 2023年,受宏观经济不确定性预算冻结的义大利原始设备製造商(OEM)订单下降了16%。在南亚和非洲,外汇波动进一步推高了进口设备的价格。供应商正以旧换新计画、融资方案和模组化附加元件分摊成本,避免技术锁定。
细分市场分析
至2025年,纺纱设备将占纺织机械市场份额的44.02%,巩固其在纱线生产中的核心地位。全球短纤维锭的装机量将达到2.32亿锭,纺纱厂对更高纺纱速度和更低断纱率的需求强劲,推动了新锭的更新换代。立达(Rieter)的专利併条机和托尔茨勒(Torzschler)的12头精梳机(生产效率提升50%)便是原始设备製造商(OEM)透过创新保障利润率的典范。织造和针织机械也是核心领域,但与再生纤维切碎机、数位印花机和生物纤维挤出机相比,其成长速度有所放缓。
其他机械类别虽然规模较小,但预计到2031年将以6.66%的复合年增长率成长。投资者关注的焦点是棉涤混纺回收生产线以及用于化学分解混纺织物的技术。此外,用于织造汽车复合材料用玄武岩和酰胺纤维的专用织布机需求也在成长。随着服装生产週期的缩短,直接在服装上印製独一无二的图案的直喷印花机正在为纺织和数位领域的机械供应商创造新的收入来源。设备种类的多样化使供应商能够追求多元化的现金流,而不仅仅依赖大宗纱线系统。
到2025年,半自动化平台将占纺织机械市场规模的43.05%,这反映了人事费用和自动化成本之间的平衡。这些生产线仍然需要操作人员进行拆线和品质检验,但整合了用于张力和速度控制的感测器。实现完全自动化的路径已经很清晰,数据连接和人工智慧视觉技术将显着提高运作,同时最大限度地降低额外的硬体成本。
预计到2031年,全自动化、工业4.0系统将以6.78%的复合年增长率成长。工厂表示,在决定转向无人化生产车间时,技术人员短缺而非资金问题才是更大的限制阻碍因素。透过物联网仪錶板进行预测性维护可以显着减少非计划性停机时间。虽然在低工资地区仍然存在手动机械,但随着工资上涨缩小成本差距,其份额正在持续下降。供应商提供模组化升级方案,例如机器人拆卸装置,从而实现逐步过渡,而无需报废整条生产线。
区域分析
到2025年,亚太地区将占全球纺织机械市场需求的55.10%,这主要得益于中国庞大的装机量以及印度总额达5.35亿美元的七区「总理纺织机械製造商和贸易促进局」(PM MITRA)计划。中国二线城市的工厂持续现代化改造,以降低对劳动力的依赖;而印度工业园区的丛集效应和公用设施共用,则推动了从纺纱到后整理的整套设备的应用。中国沿海地区工资水准的上涨,促使企业向内陆地区转移,延长而非缩短了中国的产业升级週期。
预计中东和非洲地区将实现最快成长,到2031年复合年增长率将达到6.31%。贸易多元化预计将推动对埃及、摩洛哥和衣索比亚的订单增加。海湾地区的投资者正在投资建造以低成本能源为驱动的综合性聚酯工厂,这将带动对下游加捻和经编生产线的需求。非洲工厂正利用《非洲成长与机会法案》(AGOA)和欧盟的贸易优惠政策,将原本受关税影响的亚洲地区的服装合约转移到非洲。设备供应商正与当地大学合作进行技能培训项目,以缓解可能阻碍技术普及的操作人员短缺问题。
在北美,美国墨加协定(USMCA)的规定保护了墨西哥和加拿大的纱线和布料,推动了美国边境附近新的环锭纺纱和喷气织布机计划。品牌商估计,考虑到关税、运输成本和库存风险,10天的供应链前置作业时间足以抵销与亚洲的成本差异。欧洲则专注于高附加价值领域——技术面料、再生材料和优质羊毛——这些领域采用自动化技术来降低能源和人事费用。土耳其和德国正向邻近地区出口高性能织机,并透过改造这些织布机使其符合欧盟生态设计法规来获得业务收益。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 工业4.0带来的自动化需求
- 扩大技术纺织品生产
- 新兴国家服饰消费量不断成长
- 近岸外包和关税主导的产能转移
- 循环经济:投资回收机器
- 生物基纺织品加工专用设备
- 市场限制
- 高额资本投入与不确定的投资回收期
- 原物料成本波动会影响预算
- 先进机械设备熟练操作人员短缺
- 精密运动部件的出口限制
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 产业吸引力—五力分析
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模及成长预测(价值,单位:十亿美元)
- 按模型
- 纺纱机械
- 织布机
- 针织机
- 纹理机
- 其他机器类型
- 按自动化类型
- 手动的
- 半自动
- 全自动化(智慧/工业4.0整合系统)
- 透过使用
- 服饰和服饰
- 家用及家用纺织品
- 技术纺织品(医疗、防护、运动等)
- 按原料
- 棉布
- 合成纤维(聚酯纤维、尼龙、腈纶)
- 羊毛
- 丝绸
- 其他纤维(韧皮纤维、生物基纤维等)
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 秘鲁
- 南美洲其他地区
- 欧洲
- 英国
- 德国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 比荷卢经济联盟(比利时、荷兰、卢森堡)
- 北欧国家(丹麦、芬兰、冰岛、挪威、瑞典)
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韩国
- 东协(印尼、泰国、菲律宾、马来西亚、越南)
- 亚太其他地区
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 卡达
- 科威特
- 土耳其
- 埃及
- 南非
- 奈及利亚
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Rieter Holding AG
- Trutzschler Group SE
- Saurer Intelligent Technology AG
- OC Oerlikon
- Lakshmi Machine Works Ltd
- Murata Machinery Ltd
- Savio Macchine Tessili SpA
- Santoni SpA
- Mayer & Cie. GmbH & Co. KG
- Picanol NV
- Toyota Industries Corporation
- Itema SpA
- Tsudakoma Corporation
- Karl Mayer Holding GmbH & Co. KG
- Shima Seiki Mfg., Ltd.
- TMT Machinery, Inc.
- Hangzhou Jingwei Textile Machinery Co., Ltd.
- Jiangsu Cixing Co., Ltd.
- Vardhman Textile Machinery
- Zhejiang Rifa Textile Machinery Co., Ltd.
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Global Textile Machinery Market was valued at USD 31.10 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 32.7 billion in 2026 to reach USD 42.06 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 5.16% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

Factory investments increasingly revolve around Industry 4.0 tools that counter skilled-labor shortages and raise uptime. Smart sensors, cloud analytics, and AI-driven defect detection push equipment upgrades, while recycling mandates spur orders for automated sorting and fiber-to-fiber systems. Technical-textile demand in medical, protective, and sporting goods continues to outpace traditional apparel, opening fresh profit pools. Cost-efficient synthetic fibers and bio-based alternatives both lift machinery sales, and tariff-induced near-shoring in the Americas accelerates orders for flexible, low-lot production lines.
Global Textile Machinery Market Trends and Insights
Industry 4.0-driven Automation Demand
Manufacturing PMI readings showed textile mills expanding in April 2025, and operators now use robotics and AI to offset chronic labor gaps. U.S. producers adopted intelligent knitting software that optimizes pattern complexity and cuts scrap. IoT platforms let managers track humidity and energy in real time, as documented in Pakistan's mill trials. AI vision systems based on convolutional models push defect-detection accuracy into the high-90% range, reducing rework. The cumulative gains in throughput and waste reduction make automated lines a strategic rather than an optional investment.
Rising Apparel Consumption in Emerging Economies
India's cotton-yarn producers expect 7-9% revenue growth in fiscal 2025 as Chinese demand rebounds and local retail expands. Favorable yarn spreads and improved cotton availability underpin mill upgrades. Demographic tailwinds across ASEAN and Africa add fresh capacity requirements for spinning and knitting lines. While tariffs unsettle traditional supply chains, developing-market brands still need scale, prompting balanced investments in cost-efficient yet modern machinery. For suppliers, flexible financing and modular upgrades remain critical selling points.
High CAPEX & Uncertain Payback Periods
Complete spinning or weaving lines can exceed USD 10 million, a hurdle for mid-size mills. Even large suppliers carefully model ROI because technology cycles shorten; a state-of-the-art ring-spinning frame today risks obsolescence before amortization. Italian OEMs saw orders dip 16% in 2023 when macro uncertainty froze budgets. Currency swings further inflate imported equipment in South Asia and Africa. Vendors respond with trade-in programs, financing packages, and modular add-ons that spread costs and limit technological lock-in.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Near-shoring & Tariff-driven Capacity Relocation
- Expansion of Technical-Textile Production
- Raw Material Cost Volatility Affecting Budgets
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Spinning equipment accounted for 44.02% of the textile machinery market share in 2025, underscoring its central role in yarn conversion. Global installed short-staple spindle capacity hit 232 million units, and replacement demand remains steady as mills chase higher speed and lower breakage. Rieter's draw-frame patent win and Trutzschler's 12-head comber that lifts output 50% illustrate how OEMs defend margins through innovation. Weaving and knitting machines follow as core pillars but face slower growth relative to recycling shredders, digital printers, and bio-fiber extruders.
Other machine categories, while smaller, are set to post a 6.66% CAGR to 2031. Investors favor recycling lines that separate cotton and polyester streams or dissolve blended fabrics chemically. Specialty looms that weave basalt or aramid for automotive composites also gain traction. As apparel cycles compress, direct-to-garment printers that deliver one-off designs create new revenue for machinery vendors willing to straddle textile and digital domains. The broadening equipment menu positions suppliers to chase diverse cash flows rather than rely solely on commodity yarn systems.
Semi-automatic platforms led with 43.05% of the textile machinery market size in 2025, reflecting the balance between labor costs and automation pricing. These lines still need operators for doffing and quality checks, but integrate sensors for tension and speed control. The pathway to fully automatic operations is clear; data connectivity and AI vision add only incremental hardware but deliver exponential uptime gains.
Fully automatic, Industry 4.0-ready systems are forecast to grow at a 6.78% CAGR through 2031. Mills cite the inability to recruit technicians as a bigger constraint than loan financing, tipping decisions toward lights-out production floors. IoT dashboards allow predictive maintenance that slashes unplanned downtime. Manual machines persist in low-wage clusters yet continuously lose share as wage inflation erodes the cost gap. Vendors market modular upgrades such as robotic doffers that let owners transition stepwise without scrapping entire lines.
The Textile Machinery Market Report is Segmented by Machine Type (Spinning Machines, Weaving Machines, and More), by Automation Type (Manual, Semi-Automatic and Fully Automatic), by Application (Garments & Apparels, Household and Home Textiles, and More), by Raw Material (Cotton, Synthetic Fibers, and More), and by Geography (North America, South America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific retained 55.10% of 2025 demand for the textile machinery market, anchored by China's large installed base and India's seven-park PM MITRA scheme worth USD 535 million. Tier-2 Chinese mills still modernize to cut labor dependence, while Indian parks promise cluster synergies and shared utilities that spur equipment packages covering spinning to finishing. Rising wages in coastal China drive inland relocation, lengthening the domestic upgrade cycle rather than shrinking it.
The Middle East and Africa are projected to log the fastest 6.31% CAGR through 2031 as trade diversification sends orders to Egypt, Morocco, and Ethiopia. Gulf investors bankroll integrated polyester plants tied to low-cost energy, requiring downstream texturizing and warp-knitting lines. African mills leverage AGOA and EU trade preferences to secure apparel contracts shifted from tariff-hit Asia. Equipment suppliers partner with local universities on skill programs, mitigating operator shortages that could blunt adoption.
North America benefits from USMCA rules that shield Mexican and Canadian yarn and fabric, fueling new ring-spinning and air-jet weaving projects near the U.S. border. Brands calculate that a 10-day supply-chain lead beats the cost delta with Asia once tariffs, freight, and inventory risks are considered. Europe focuses on value-added segments technical fabrics, recycling, and luxury wool, underpinned by automation that offsets energy and labor costs. Turkey and Germany export high-spec looms to neighboring regions and capture service revenue from retrofits complying with EU eco-design regulations.
- Rieter Holding AG
- Trutzschler Group SE
- Saurer Intelligent Technology AG
- OC Oerlikon
- Lakshmi Machine Works Ltd
- Murata Machinery Ltd
- Savio Macchine Tessili S.p.A
- Santoni S.p.A.
- Mayer & Cie. GmbH & Co. KG
- Picanol NV
- Toyota Industries Corporation
- Itema S.p.A.
- Tsudakoma Corporation
- Karl Mayer Holding GmbH & Co. KG
- Shima Seiki Mfg., Ltd.
- TMT Machinery, Inc.
- Hangzhou Jingwei Textile Machinery Co., Ltd.
- Jiangsu Cixing Co., Ltd.
- Vardhman Textile Machinery
- Zhejiang Rifa Textile Machinery Co., Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Industry 4.0-driven automation demand
- 4.2.2 Expansion of technical-textile production
- 4.2.3 Rising apparel consumption in emerging economies
- 4.2.4 Near-shoring & tariff-driven capacity relocation
- 4.2.5 Circular-economy recycling machinery investments
- 4.2.6 Specialty equipment for bio-based fiber processing
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High CAPEX & uncertain payback periods
- 4.3.2 Raw-material cost volatility impacting budgets
- 4.3.3 Skilled-operator shortage for advanced machinery
- 4.3.4 Export controls on precision motion components
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts(Values, In USD Billion)
- 5.1 By Machine Type
- 5.1.1 Spinning Machines
- 5.1.2 Weaving Machines
- 5.1.3 Knitting Machines
- 5.1.4 Texturing Machines
- 5.1.5 Other Machine Types
- 5.2 By Automation Type
- 5.2.1 Manual
- 5.2.2 Semi-Automatic
- 5.2.3 Fully Automatic(Smart / Industry 4.0 Integrated Systems)
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Garments & Apparels
- 5.3.2 Household and Home Textiles
- 5.3.3 Technical Textiles (Medical, Protective, Sports, etc.)
- 5.4 By Raw Material
- 5.4.1 Cotton
- 5.4.2 Synthetic Fibers (Polyester, Nylon, Acrylic)
- 5.4.3 Wool
- 5.4.4 Silk
- 5.4.5 Other Fibers (Bast, Bio-based, etc.)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Peru
- 5.5.2.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.2 Germany
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 BENELUX (Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg)
- 5.5.3.7 NORDICS (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden)
- 5.5.3.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 Australia
- 5.5.4.5 South Korea
- 5.5.4.6 ASEAN (Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam)
- 5.5.4.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.3 Qatar
- 5.5.5.4 Kuwait
- 5.5.5.5 Turkey
- 5.5.5.6 Egypt
- 5.5.5.7 South Africa
- 5.5.5.8 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.9 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Products & Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Rieter Holding AG
- 6.4.2 Trutzschler Group SE
- 6.4.3 Saurer Intelligent Technology AG
- 6.4.4 OC Oerlikon
- 6.4.5 Lakshmi Machine Works Ltd
- 6.4.6 Murata Machinery Ltd
- 6.4.7 Savio Macchine Tessili S.p.A
- 6.4.8 Santoni S.p.A.
- 6.4.9 Mayer & Cie. GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.10 Picanol NV
- 6.4.11 Toyota Industries Corporation
- 6.4.12 Itema S.p.A.
- 6.4.13 Tsudakoma Corporation
- 6.4.14 Karl Mayer Holding GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.15 Shima Seiki Mfg., Ltd.
- 6.4.16 TMT Machinery, Inc.
- 6.4.17 Hangzhou Jingwei Textile Machinery Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Jiangsu Cixing Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.19 Vardhman Textile Machinery
- 6.4.20 Zhejiang Rifa Textile Machinery Co., Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment










