 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1132080
华为重振努力:云上成功固然重要,但确保芯片独立性和建立强大的供应炼是关键Huawei's Quest for Resurgence: Cloud Success is Vital, but Attaining Chip Independence and Grooming a Robust Supply Chain Holds Key |
||||||
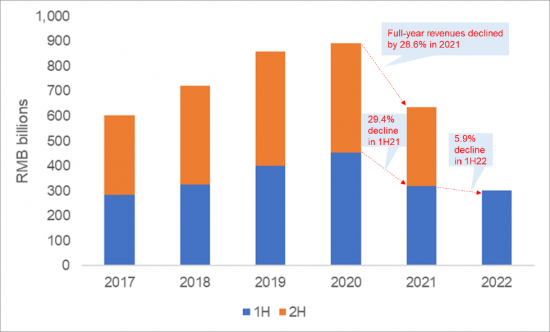
2018 年和 2020 年的美国製裁继续困扰着华为。该公司被迫出售多个业务线,包括其低端智能手机部门荣耀和 x86 服务器业务,这对其“黄金宝石”电信设备业务的全球地位造成了影响。这些挫折让华为陷入了动盪,2021年的年收入降幅最大,达到28.6%。 2022年上半年销量下滑趋势将持续,但下滑速度明显放缓。然而,由于美国技术限制带来的恶劣经济环境,客户需求下降了一半以上,这不足以遏制这一时期的净收入下降。
图表示例
受当前动荡的影响,华为在云计算和供应链独立性上押注很大,以进一步降低风险。对云的关注源于实体清单裁决对服务和软件缺乏直接影响。该公司已经在云领域取得了长足的进步,成为仅次于阿里巴巴的中国第二大云提供商。考虑到华为在与中国省级政府和国有企业打交道的经验,强大的政府部门云产品组合是一大优势。另一个优势是我们在不受美国製裁直接影响的市场中的海外云数据中心的记录。在中国宏伟的“一带一路”倡议(BRI)下,华为也是全球数字扩张计划——数字丝绸之路(DSR)的重要参与者。
为了重建供应链,华为致力于端到端的自主创新,以加强硬件和云相关业务。公司旗下芯片子公司海思为数据中心服务器处理器和设备以及电信网络设备设计芯片,同时也生产自己的芯片,与国内晶圆厂合作,投资国内芯片初创企业。我们的主要战略。
华为的复兴有两个方面:
- 云服务业务:基于硬件的消费行业受到了重创,因此您的工作是弥补一些差距。
- 获得可以在竞争中脱颖而出的先进芯片
华为能够提出独特的建议,例如云服务与电信设备业务之间的协同效应,通过其最近发布的电信运营商云解决方案以及与电信运营商的灵活合作模式,方面似乎是可以实现的。
但第二点可能是华为的绊脚石。这是因为国产芯片製造所取得的技术能力落后于英特尔、台积电、三星很多年。在找到解决先进製造短板的方法之前,华为将继续依赖能力较弱的国内晶圆厂,并在未来三到四年内处于生存模式。此外,华为目前严重依赖 ARM 在其华为云产品中心的数据中心设计服务器芯片。美国还可以找到限制 ARM 与华为合作的方法,迫使中国供应商诉诸 RISC-V 替代方案。
在这份报告中,我们调查了华为近期的业绩趋势和主要问题,以及克服困难的措施——推进云业务、加强供应炼等——以及需要解决的问题。我们来了。
分析范围
本报告分析的公司和组织:
|
|
内容
- 概览
- 制裁动摇了华为的全球地位
- 华为全力以赴保护云和足够的芯片
- 华为要找回失去的魔力还有很长的路要走
The US sanctions imposed way back in 2018, and then again in 2020, continue to haunt Huawei. The company was forced to divest some business lines- including its mid- to low-end smartphone unit, Honor, and x86 server business - and its global standing in its "crown jewel" telecom equipment business has taken a hit. These setbacks have sent Huawei into a tizzy as it reported its biggest ever annual revenue drop of 28.6% in 2021. Though the revenue downtrend continued into 1H22, the pace of drop slowed down drastically. But that wasn't enough to contain net profit decline during the period, which more than halved as a difficult economy reduced demand from customers, intensifying woes brought by the US technology curbs.
VISUALS

Hard-pressed by the current turmoil, Huawei is betting big on cloud and supply chain independence to alleviate any further risks. The cloud focus emerges from the fact that there is no direct impact from the Entity List ruling on services and software. The company is already making notable strides in the cloud space, with its emergence as the second-biggest cloud provider after Alibaba in China. Its strong cloud portfolio for the government sector is a big advantage, considering Huawei's experience working with provincial governments and state-owned enterprises in China. The other advantage is its overseas cloud data center footprint, which are in markets less directly impacted by US sanctions. Huawei is also an essential player engaged in China's global digital expansion initiative, "Digital Silk Road" (DSR), under its grand Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
To rebuild its supply chain, Huawei is aspiring to end-to-end home-grown innovation to power both its hardware- and cloud-related businesses. While its chip subsidiary, HiSilicon, designs data center server processors and chips for devices and telecom network equipment, it is seeking to ramp up production capabilities through a three-pronged strategy: build in-house chips, partner with domestic fabs, and invest in domestic chip startups.
Huawei's efforts to stage a comeback will depend on two aspects:
- Cloud services business, which will be tasked to somewhat address the gap left by the severely hit hardware-based consumer division
- Access to advanced chips that can take on the competition
The first aspect looks achievable as Huawei will be able to offer distinctive propositions such as synergies between its cloud offering and telecom equipment business, through its recently launched telco cloud solutions, coupled with a flexible collaboration model with the telcos.
The second aspect, though, could prove to be a stumbling block for Huawei, as technological capabilities achieved through homegrown chip manufacturing are years behind the capabilities possessed by Intel, TSMC, and Samsung. Until a solution to its advanced manufacturing shortcoming is figured out, Huawei will continue to rely on less-capable domestic fabs, which will put the company in survival mode for the next 3-4 years. Further, Huawei is currently relying heavily on ARM for design of its data center server chips, which are central to the Huawei Cloud offering. There is some chance that the US will find a way to restrict ARM from working with Huawei, forcing the Chinese vendor to lean on RISC-V alternatives.
Coverage:
Companies and organizations mentioned in this report include:
|
|
Table of Contents
- Summary
- Sanctions roil Huawei's global standing
- Huawei goes full throttle on cloud, and chip sufficiency
- Huawei's journey to regain its lost mojo will be a long one
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Huawei's annualized share of telco network infrastructure market
- Figure 2: Huawei total revenues: Half-yearly basis, 2017-22
- Figure 3: Huawei's R&D and R&D/revenues: 2017-21













