|
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1688514
迈向更绿色的网路-营运商提升流量效率:2023 年营运商每 PB 的能耗将比 2022 年降低 15.4%,同时排放量和再生能源采用率仍将维持在较低水平Greener Networks - Telcos Power Up Traffic Efficiency: Telcos Consumed 15.4% Less Energy in 2023 per Petabyte of Traffic Carried than 2022, Emissions and Renewables Adoption Remain Dismal |
|||||||
2023 年末,MTN Consulting 发布了第一份关于电信营运商网路中流量成长与能源消耗之间关係的评论。此次审查涵盖了 16 家营运商的数据,重点关注 2020-22 年的数据。在此次更新版本中,目标电信业者数量扩大至30家,并增加了2019年、2023年两年的数据。我们的分析目前涵盖 2019-23 年的时间范围。
视觉
本次分析涵盖的 30 个营运商集团按收入计算约占全球市场的 55%。到 2023 年,电信业者每 100 万美元收入将平均承载 2.06PB 的流量,比 2019 年每 100 万美元 1.00PB 的流量增加一倍以上。这是因为营运商不断进行改进,旨在降低流量承载成本。能源是成本的很大一部分。那么,网路在单位能耗方面的传输流量效率是否变得更高了?
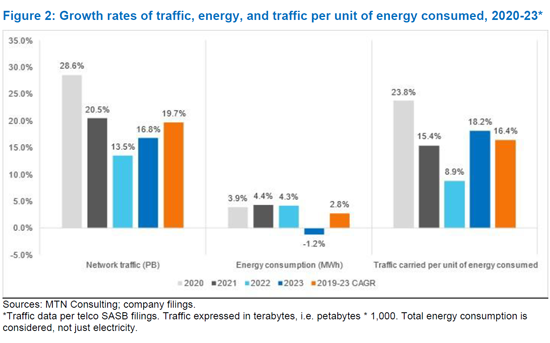
从 2019 年到 2023 年,30 家电信业者的网路流量将以 19.7% 的复合年增长率成长,而其总能源消耗将以 2.8% 的复合年增长率增长。因此,电信业者的能源消耗将在 2023 年平均为 90.0 MWh/PB,低于 2019 年的 165.5 MWh/PB。这意味着每 PB 兆瓦时的复合年增长率为 14.1%。这意味着,营运商平均每年所需的能源比前一年减少 14.1% 即可承载相同的流量负荷。这些改进符合营运商及其供应商长期提高网路能源效率的目标。自 2019 年以来,MWh/PB 指标进步最大的是 BT、Entel、Rogers、Tele2 和 Veon。
目标范围
刊载组织
|
|
目录
- 摘要
- 提高通讯网路的能源效率:年度14%
- 资料集:概要
- 收益和流量的难题:依然持续的
- 每消费能源单位的流量
- 供应商担挑着改善在持续的上中心性的作用
- 总论
- 附录
In late 2023, MTN Consulting published an initial review of the relationship between traffic growth and energy consumption in telco networks. That review included data for 16 telcos, and focused on 2020-22 data. This updated analysis extends coverage to 30 telcos, and adds two years (2019 and 2023) of data. Our analysis now addresses the 2019-23 timeframe.
VISUALS

The group of 30 telcos included in this analysis represent about 55% of the global market, based on revenues. Our data verify the well-known revenue-traffic conundrum, where traffic rises faster than revenues: in 2023, the average telco carried 2.06 Petabytes of traffic per US$1M in revenue, over double the 1.00 Petabytes per $M carried in 2019. This is possible because telcos make constant improvements aimed at carrying traffic more cheaply. Energy is a big part of the cost story. So, are networks getting more efficient in their carriage of traffic per unit of energy consumed? In the 2019-23 timeframe, our group of 30 telcos increased network traffic at an average annual rate (CAGR) of 19.7%, while their total energy consumption grew at a CAGR of 2.8%. As a result, in 2023 the average telco consumed 90.0 MWh of energy per Petabyte of traffic, down from 165.5 MWh/PB in 2019. That works out to an annual average (CAGR) improvement in MWh per Petabyte of 14.1%. Meaning, on average, telcos need 14.1% less energy per year to carry the same traffic load as the prior year. This improvement is in line with the stated goal of both telcos and their vendors: to improve the network's energy efficiency over time. The biggest improvements in the MWh/Petabyte metric since 2019 are BT, Entel, Rogers, Tele2, and Veon. The worst result came from Saudi Telecom (STC), which used 104 MWh/PB in 2023, from 90 in 2019. The poorest result in 2023 alone was reported by Vodafone, which improved (lowered) its MWh/PB ratio by just 3.8% YoY.
For climate change watchers, an important metric is greenhouse gas emissions (GHG), as measured in CO2 equivalent metric tons. We don't address emissions in this report, but we did in a December 2024 report. That report found that telco emissions in 2023 were about the same level (per unit of revenue) as in 2019, and that renewables accounted for only about 20% of energy used in 2023. Both findings were disappointing. So, this current report's conclusion is a welcome bit of good news.
Telco sustainability reports emphasize the importance of adopting energy efficient technologies and network designs. Vendors consider the energy efficiency of their solutions a crucial differentiator. As telcos attempt to lower energy costs and reduce their carbon footprints, vendors have an opportunity to support further improvements.
Coverage
Organizations mentioned:
|
|
Table of Contents
- Summary
- Telco network energy efficiency rising 14% per year
- Overview of the dataset
- The revenue-traffic conundrum persists
- Traffic carried per unit of energy consumed
- Vendors have a central role in sustaining improvements
- Conclusion
- Appendix
List of Tables and Figures
- Table 1: Summary metrics for the "Group of 30" telcos
- Figure 1: Petabytes of traffic on network per US$M in revenue, 2019-23*
- Figure 2: Growth rates of traffic, energy, and traffic per unit of energy consumed, 2020-23*
- Figure 3: Terabytes of traffic per MWh of energy consumed*







