 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1250812
智能汽车座舱驾驶集成分析(2023)Intelligent Vehicle Cockpit-Driving Integration Research Report, 2023 |
||||||
汽车的电子和电气架构正在朝着域集成和中央计算的方向发展。 座舱技术与智能驾驶技术在成熟度和需求上存在差异,但座舱驾驶融合正在逐步推进。
本报告探讨了智能汽车的座舱驾驶集成,并提供了全面的信息,包括产品和解决方案、趋势和挑战。
内容
第1章E/E架构与座舱驾驶集成
- 驾驶舱驾驶集成背景
- E/E 架构和驾驶舱驾驶集成
- 跨域集成架构和驾驶舱驾驶集成
- 区域 EEA 和驾驶舱驾驶集成
- 驾驶舱驾驶集成的演变
- 驾驶/停车/一体化的发展形式
- 驾驶舱停车一体化研发
- 驾驶舱驾驶集成的关键技术
- 主要 OEM 的座舱驾驶集成解决方案和计划
- 来自主要一级供应商的驾驶舱驾驶集成产品和解决方案
- 来自芯片和软件公司的驾驶舱驾驶集成产品和解决方案
第2章OEM座舱驾驶集成产品及解决方案
- 特斯拉
- E/E 架构
- Model 3 架构
- 智能驾驶和智能座舱系统的迭代
- 自动驾驶仪 HW4
- 新一代模型
- 大众汽车
- E/E 架构计划
- 与高通合作
- 吉利
- GEEA 3.0
- 基于 SOA 的操作系统
- 广汽永恆
- X-灵魂架构
- X-Soul架构升级
- 基于 X-Soul 架构的模型
- 长城汽车
- 咖啡情报
- E/E 架构
- GEEP 4.0
- GEEP 5.0
- 智能驾驶规划
- 智能驾驶舱规划
- 驾驶舱驾驶集成预测
- 红旗
- FEEA
- FME 智能超架构
- 座舱驾驶集成芯片
- 小鹏
- E/E 架构
- E/E 架构:SOA
- E/E 架构:硬件和软件集成
- 新一代驾驶舱系统
- 新一代智能驾驶系统
- 典型型号:G9
- 理想汽车
- E/E 架构迭代
- 新一代架构:中央计算平台
- 新一代架构:区域控制器
- 新一代架构:软件规划
- 蔚来
- E/E 架构迭代
- 与科博达合作
- 极度汽车
- 简介
- 开发成果
- 机器人
- 机械师
- 内塔
- 新一代 E/E 架构
- 中央计算平台
- IM 电机
- 新一代智能数字架构
第 3 章主要一级供应商的座舱驾驶集成产品和解决方案
- 博世
- 大陆航空
- 安波福
- 采埃孚
- 德赛西威
- 航盛电子
- 无限人工智能
- 技术
- 百度
- 华为
- Z-One
- ECARX
- 联想
第4章芯片和软件公司的座舱驱动集成产品和解决方案
- 高通
- 英伟达
- 地平线机器人
- 半驱动
- 东软睿驰
- 迅达软件
- 享受移动技术
- 诚迈科技
第 5 章驾驶舱驾驶集成的趋势和问题
- 驾驶舱驾驶集成解决的问题
- 如何实现座舱驾驶一体化
- 驾驶舱驾驶集成的技术挑战
- 硬件
- 软件
- 沟通
- 安全
- 座舱驾驶一体化发展模式挑战
- Cockpit Driving Integration 组织结构问题
- 驾驶舱驾驶集成公司的方向
Cockpit-Driving Integration Research: many companies are making layout and may implement it during 2024-2025.
1. What is the real cockpit-driving integration?
At present, automotive electronic and electrical architectures are evolving towards domain integration and central computing. Some functional domains (intelligent driving domain, cockpit domain, chassis domain, body domain, power domain, etc.) are being integrated, for example, body and chassis domain integration, and cockpit and intelligent driving domain integration.
Cockpit-driving integration refers to the integration of cockpit and intelligent driving domains into a high-performance computing unit that supports both intelligent driving and intelligent cockpit functions. It is an effective solution to reducing development cycle and vehicle cost.
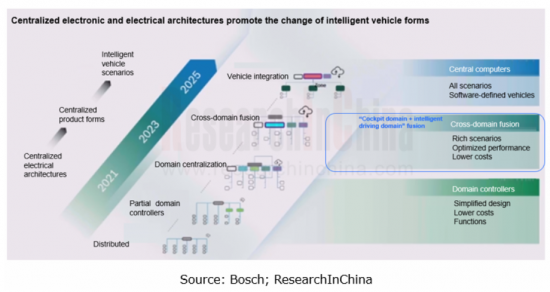
Cockpit-driving integration falls into two types: multi-SoC integration, that is, cockpit and intelligent driving functions are deployed on different boards; single SoC integration, that is, the software and algorithms of cockpit and intelligent driving are all deployed on one board.
Based on a single SoC and with a hypervisor running on the chip, the real cockpit-driving integration divides different functional modules through the hypervisor to enable different security levels of secure cockpit and driving functions. Yet limited by architecture solutions, software and hardware technologies, supply chain and other factors, the cockpit-driving integration based on a single SoC is hard to come true in a short time.
2. How to facilitate cockpit-driving integration?
Given varying maturity and requirements of cockpit and intelligent driving technologies, cockpit-driving integration is iterating and being promoted in a gradual manner.
Zhao Jianhong, the vice president of product at EnjoyMove Technology, said that the company will prioritize cockpit-driving integrated solutions because of the demand from OEMs. At present, for parking solutions are relatively mature, and cockpit domain controllers offer sufficient computing power, integrating parking into cockpit domain controllers brings a cost advantage. Cockpit-parking integration signifies the first step of cockpit-driving integration, that is, cockpit-driving integration will be considered after the cockpit-parking integration technology matures.
Bosch Group also plans to achieve cockpit-driving integration around 2024 after the implementation of the Cockpit-Parking Integration 1.0 (based on Qualcomm 8155) and Cockpit-Parking Integration 2.0 (based on Qualcomm 8295).
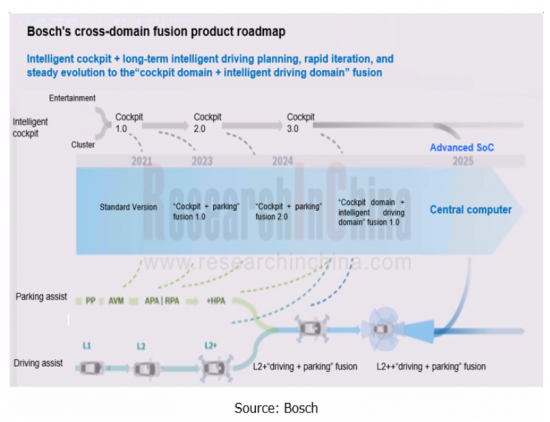
In the future, both the driving-parking integration (launched in 2022 on large scale) around intelligent driving, and the cockpit-parking integration (expected to be mass-produced in 2023) centering on the cockpit will eventually head towards the cockpit-driving integration expected to be spawned around 2025.

3. How companies deploy cockpit-driving integration?
Since 2022, cockpit-driving integration has become the focus of the industry, attracting entrants like Z-ONE, Neta Auto, Tesla, Desay SV, ThunderSoft and Continental.
Z-ONE: the Galaxy Full-stack Solution 3.0 for smart cars was released in November 2022. It adopts central computing and zonal control, and is equipped with ZXD, a cockpit-driving integrated computing platform. It is scheduled to be mass-produced in 2025.
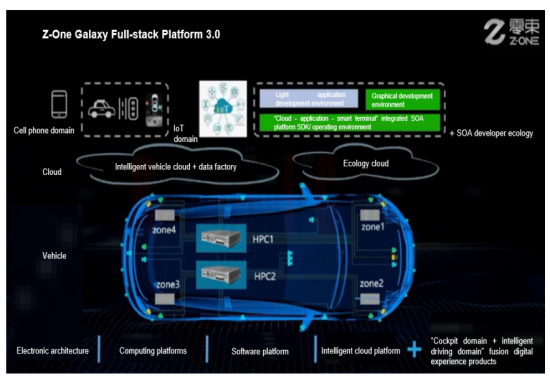
Features of ZXD:
- The conventional domain framework is broke up for the layered design of "cloud platform + central brain + zone + intelligent sensing and execution" so as to realize software and hardware decoupling, and cross-domain integration.
- Based on Chinese homemade chips, the AI compute up to 1,000 TOPS supports continuously simultaneous operation of multi-domain functions (e.g., autonomous driving and in-vehicle infotainment), independent calculation of cockpit and intelligent driving domains, and hard-core information encryption, as well as L4 and above autonomous driving, and high-resolution multi-screen display of intelligent cockpit.
- The pre-installed intelligent vehicle operating system ZOS can realize "software and hardware synergy" with China's local chips, offer standard uniform interfaces for software and hardware decoupling, and provide a unified development platform for cross-domain integration.
Neta Auto: the latest electronic and electrical architecture is a central computing architecture whose core is a supercomputing platform (including Haozhi Supercomputer 1.0 and Haozhi Supercomputer 2.0). With computing power up to 1,000 TOPS, it supports L4 autonomous driving integrated with intelligent driving and cockpit functions.

Haozhi Supercomputer 2.0 uses a "central + zonal" architecture composed of two boards: a cockpit-driving integration domain unit and an intelligent control unit. It will be applied to Neta S+/Shanhai Platform.
Desay SV: in April 2022, Desay SV unveiled "Aurora", an automotive intelligent computing platform. As a multi-SoC based cockpit-driving integrated solution, it realizes a leap from domain controllers to central computing platform, with the following features:
- Hardware: supports mainstream heterogeneous SoCs with high computing power, such as NVIDIA Orin, Qualcomm SA8295, and Black Sesame Huashan A1000, and deliver total computing power of over 2,000 TOPS.
- Function: integrate core functional domains such as intelligent cockpit domain, intelligent driving domain and connectivity services, to achieve cross-domain integration.
- Structure: adopt a plug-in structure, and offer flexibly configured computing power to meet the requirements of models at varying prices.
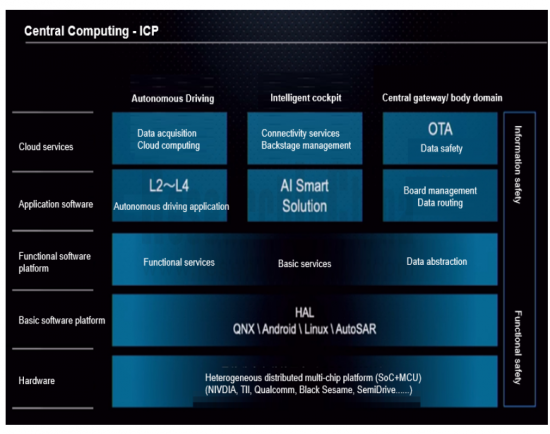
Most of the cockpit-driving integrated solutions of OEMs and Tier1 suppliers in China are based on multiple SoCs from Qualcomm, Nvidia and SemiDrive. The single SoC based solutions are still under development.
It is worth noting that NVIDIA and Qualcomm have successively released high-compute cockpit-driving integrated chips since 2022, providing strong support for application of single SoC solutions.
Nvidia: Nvidia announced DRIVE Thor, a superchip of epic proportions, in September 2022. With computing power of 2,000 TOPS, it is compatible with Linux, QNX and Android-based IVI systems, and supports cockpit-driving integration. Nvidia plans to put DRIVE Thor into production in 2024.

Nvidia DRIVE Thor will be installed in ZEEKR's next-generation smart cars to be produced in early 2025. The latest news in March showed that Lenovo will also adopt Nvidia DRIVE Thor. According to Lenovo's plan, its cockpit-driving integrated controller will be launched during 2024-2025, with computing power of 1,000/2,000 TOPS.
OEMs can integrate all the functions of intelligent vehicles on a single SoC by virtue of DRIVE Thor.
Qualcomm: in January 2023, Qualcomm launched the Snapdragon Ride Flex, the automotive industry's first scalable family of SoCs to simultaneously support digital cockpits and ADAS. The expected start of production will begin in 2024.
The Snapdragon Ride Flex has three levels: Mid, High, and Premium. The AI compute of the single Premium SoC is above 600 TOPS. Combined with AI accelerators (probably NPUs or MAC arrays), it can support performance of up to 2,000 TOPS.
It is known that Volkswagen will adopt the Snapdragon Ride Flex to support single-chip multi-domain computing (covering driving assistance and intelligent cockpit). The Snapdragon Ride Flex will first land on the new-generation PPE-based Porsche Macan that will be launched in 2024.

Generally speaking, cockpit-driving integration is still in the exploration stage, facing quite a few problems and challenges in organizational structure, technology development and industrial chain coordination, for example: integration of high-compute chips; SOA-based software layered design, and cross-domain integration of operating systems and middleware; application of high-bandwidth, low-latency automotive Ethernet communication technology.
Table of Contents
1. E/E Architecture and Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 1.1 Background of Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 1.2 E/E Architecture and Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 1.2.1 Cross-domain Integrated Architecture and Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 1.2.2 Zonal EEA and Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 1.3 Evolution of Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 1.3.1 Development Form of Driving-Parking Integration
- 1.3.2 Development and Exploration of Cockpit-Parking Integration
- 1.4 Key Technologies of Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 1.5 Cockpit-Driving Integrated Solutions and Planning of Major OEMs
- 1.6 Cockpit-Driving Integrated Products and Solutions of Major Tier1 Suppliers
- 1.7 Cockpit-Driving Integrated Products and Solutions of Chip and Software Companies
2. Cockpit-Driving Integrated Products and Solutions of OEMs
- 2.1 Tesla
- 2.1.1 E/E Architecture
- 2.1.2 Model 3 Architecture
- 2.1.3 Iteration of Intelligent Driving & Intelligent Cockpit System
- 2.1.4 Autopilot HW4
- 2.1.5 New-generation Models
- 2.2 Volkswagen
- 2.2.1 E/E Architecture Planning
- 2.2.2 Cooperation with Qualcomm
- 2.3 Geely
- 2.3.1 GEEA 3.0
- 2.3.2 SOA-based Operating System
- 2.4 GAC Aion
- 2.4.1 X-Soul Architecture
- 2.4.2 X-Soul Architecture Upgrade
- 2.4.3 Models Based on X-Soul Architecture
- 2.5 Great Wall Motor
- 2.5.1 Coffee Intelligence
- 2.5.2 E/E Architecture
- 2.5.3 GEEP 4.0
- 2.5.4 GEEP 5.0
- 2.5.5 Intelligent Driving Planning
- 2.5.6 Intelligent Cockpit Planning
- 2.5.7 Prediction on Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 2.6 Hongqi
- 2.6.1 FEEA
- 2.6.2 FMEs Intelligent Hyper Architecture
- 2.6.3 Cockpit-Driving Integrated Chips
- 2.7 Xpeng
- 2.7.1 E/E Architecture
- 2.7.2 E/E Architecture: SOA
- 2.7.3 E/E Architecture: Hardware and Software Integration
- 2.7.4 New-generation Cockpit System
- 2.7.5 New-generation Intelligent Driving System
- 2.7.6 Typical Model: G9
- 2.8 Li Auto
- 2.8.1 E/E Architecture Iteration
- 2.8.2 New-generation Architecture: Central Computing Platform
- 2.8.3 New-generation Architecture: Zonal Controllers
- 2.8.4 New-generation Architecture: Software Planning
- 2.9 NIO
- 2.9.1 E/E Architecture Iteration
- 2.9.2 Cooperation with KEBODA
- 2.10 Jidu Auto
- 2.10.1 Profile
- 2.10.2 Development History
- 2.10.3 Robot
- 2.10.4 Dynamics
- 2.11 Neta
- 2.11.1 New-generation E/E Architecture
- 2.11.2 Central Computing Platform
- 2.12 IM Motors
- 2.12.1 New-generation Intelligent Digital Architecture
3. Cockpit-Driving Integrated Products and Solutions of Major Tier1 Suppliers
- 3.1 Bosch
- 3.1.1 Profile of XC China
- 3.1.2 Development Route of Cockpit-Driving Integrated Products
- 3.1.3 New-generation Cockpit Domain Controllers
- 3.1.4 Cockpit-Driving Integrated Solutions
- 3.1.5 Design of Cockpit-Driving Integrated Solutions
- 3.2 Continental
- 3.2.1 HPC
- 3.2.2 Continental Automotive Edge (CAEdge) Framework
- 3.3 Aptiv
- 3.3.1 Full Stack Solutions
- 3.3.2 Smart Vehicle Architecture (SVA) Planning
- 3.3.3 Central Computing Platform of SVA
- 3.4 ZF
- 3.4.1 Profile
- 3.4.2 Pro AI
- 3.5 Desay SV
- 3.5.1 Profile
- 3.5.2 Autonomous Driving Domain Controllers
- 3.5.3 First-generation ICP Products
- 3.6 Hangsheng Electronics
- 3.6.1 Profile
- 3.6.2 Core Capabilities of New-generation Cockpit
- 3.6.3 Critical Design of New-generation Cockpit
- 3.7 UnlimitedAI
- 3.7.1 Product Series
- 3.7.2 "Wukong II"
- 3.7.3 "Wukong III"
- 3.7.4 Cooperation Mode
- 3.8 Technomous
- 3.8.1 Profile
- 3.8.2 Domain Controllers & Planning
- 3.9 Baidu
- 3.9.1 Cockpit-Driving Integration Layout
- 3.9.2 Cockpit-Driving Integration Planning
- 3.10 Huawei
- 3.10.1 Intelligent Vehicle Solutions
- 3.10.2 Intelligent Vehicle E/E Architecture
- 3.10.3 CCA + VehicleStack
- 3.11 Z-One
- 3.11.1 Profile
- 3.11.2 Full Stack Technology Solutions
- 3.11.3 Electronic Architecture
- 3.11.4 Intelligent Driving Computing Platform
- 3.11.5 Intelligent Cockpit Computing Platform
- 3.11.6 Cockpit-Driving Integrated Computing Platform
- 3.11.7 Software Platform
- 3.11.8 Intelligent Cloud Platform
- 3.11.9 Cockpit-Driving Integrated Digital Experience Products
- 3.11.10 Key Technologies and Cooperative Ecology
- 3.11.11 Application Cases
- 3.11.12 Dynamics
- 3.12 ECARX
- 3.12.1 Profile
- 3.12.2 Computing Platform
- 3.12.3 Cooperation with SiEngine Technology and FAW
- 3.13 Lenovo
- 3.13.1 Automotive Business Layout
- 3.13.2 Investment and Cooperation in Automotive Industry
4. Cockpit-Driving Integrated Products and Solutions of Chip and Software Enterprises
- 4.1 Qualcomm
- 4.1.1 Automotive Solutions
- 4.1.2 ADAS Chip Iteration
- 4.1.3 ADAS Chip Solutions
- 4.1.4 Cockpit Chip Iteration
- 4.1.5 Cockpit-Driving Integrated Chips
- 4.1.6 Dynamics in Cooperation
- 4.2 NVIDIA
- 4.2.1 Autonomous Driving Chip Iteration
- 4.2.2 Cockpit-Driving Integrated Chips
- 4.3 Horizon Robotics
- 4.3.1 Chips and Planning
- 4.3.2 Vehicle Intelligent Development Platform
- 4.3.3 Major Customers
- 4.4 SemiDrive
- 4.4.1 Profile
- 4.4.2 Central Computer Architecture
- 4.4.3 Chip Planning
- 4.5 Neusoft Reach
- 4.5.1 NeuSAR Platform
- 4.5.2 NeuSAR 4.0
- 4.5.3 NeuSAR "Software First" Development Model
- 4.6 Thundersoft
- 4.6.1 Cockpit-Driving Integration Planning
- 4.6.2 ThunderX (Subsidiary) and Main Products
- 4.6.3 Domain Controller Middleware of ThunderX
- 4.7 Enjoy Move Technology
- 4.7.1 Profile
- 4.7.2 EMOS Software Platform
- 4.7.3 XCG Gen1
- 4.8 ArcherMind
- 4.8.1 Profile
- 4.8.2 Cross-domain Fusion Vehicle Software Computing Platform
- 4.8.3 Fusion3.0 Software Platform
- 4.8.4 Software Technology
5. Trends of and Challenges for Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 5.1 What Problems Does Cockpit-Driving Integration Solve?
- 5.2 How to Realize Cockpit-Driving Integration?
- 5.3 Technical Challenges for Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 5.3.1 Hardware
- 5.3.2 Software
- 5.3.3 Communication
- 5.3.4 Security
- 5.4 Development Mode Challenges for Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 5.5 Organizational Structure Challenges for Cockpit-Driving Integration
- 5.6 What Is the Direction of Cockpit-Driving Integration Companies?








