 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1443437
锂离子电池硅负极技术现况及展望(至2035年)<2024> LIB Si-Anode Technology Status and Outlook (~2035) |
||||||
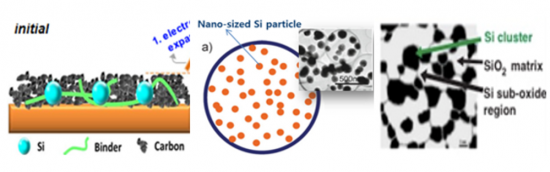
迄今为止,碳基材料已成为锂离子电池负极材料的主流。最初广泛使用的是无定形碳材料,但现在天然石墨和人造石墨是主要选择。近年来,为了克服石墨材料的理论容量限制,开发具有优异电化学反应活性和长寿命的材料,新型负极材料,特别是硅(Si)正在积极研究。对高容量负极材料的需求不断增加,特别是在电动车和储能係统中使用的大型电池市场。传统上,碳基负极材料和石墨基负极材料一直是主流,但作为金属复合材料的硅基负极材料越来越受到业界的关注。随着对高容量负极的需求增加,获取这些材料的竞争正在加剧。在这种情况下,研发和製造硅基负极材料的新公司数量正在稳步增加。
截至2020年初,只有10至20家公司在开发硅基高容量材料。不过,从目前的情况来看,已有60多家企业正积极致力于硅基材料的研发并准备量产。硅基材料对于开发高容量电池至关重要,这些电池可解决电动车续航里程限制并满足快速充电能力的需求。电动车原始设备製造商和电池公司预计,到 2035 年,硅阳极材料的年增长率将达到 30%。硅负极材料在整个负极材料市场中的市占率预计将从2019年的1%扩大到2030年的7%,到2035年进一步扩大到10%。
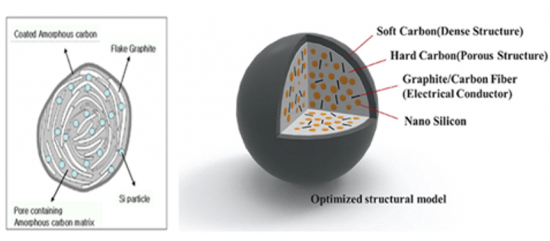
除碳基和石墨基材料外,Si-C复合材料、Si合金和SiOx是典型的锂离子电池高容量负极材料。其中,SiOx和Si合金是最接近实用化的材料,一些电池製造商正在积极开发含有SiOx和Si合金的高容量电池。然而,寿命和体积膨胀(膨胀)等问题仍然存在,人们正在努力解决这些问题。在硅(Si)基负极领域,业界和学术界均就相关技术的最新趋势进行了演讲。
本报告对xEV(电动车)、ESS(储能係统)和IT应用中使用的锂离子电池负极材料市场进行了调查和分析,提供了高容量负极材料的最新发展状况。 Si-C复合材料)在工业界和学术界都有应用。
目录
报告概述
第一章 LIB概述
- LIB 的业绩记录
- LIB类型及特点
- 锂离子电池原理
- 锂离子电池组件
- 锂离子电池的应用领域
- 负极材料技术现况及发展趋势
第二章 锂离子电池负极材料的种类及特点
- LIB负极材料所需的性能和类型
- 碳基负极材料的特性
- 金属负极材料的特性
- 复合负极材料特性
第三章锂离子电池高容量硅基负极材料技术发展现状
- 高容量锂离子电池的发展历史与方向
- 高容量硅基负极材料的基本特性
- 合金基负极材料存在的问题及解决方案
- 高容量硅负极材料技术发展趋势
第四章 高功率硅基负极材料技术发展现状
- 高功率负极材料概述
- 高功率快充负极材料
- 从负极角度快速充电
第5章 锂离子电池负极材料市场趋势与展望
- LIB负极材料市场现状
- 负极材料需求:依国家划分
- 负极材料需求:依材料分类
- 市场状况:依供应商分类
- 负极材料需求:LIB公司
- 锂离子电池负极材料供应展望
- 负极材料产能展望
- 负极材料出货现况及展望
- 负极材料供应展望
- 锂离子电池负极材料价格展望
- 负极材料价格结构
- NG/AG/Si型
- 负极材料价格走势
- NG/AG/Si型
- 各种石墨价格现状
- 针状焦及沥青价格状况
- 价格展望:以负极材料供应商划分
- 负极材料价格结构
第六章 锂离子电池负极材料厂商现状
- LIB负极材料公司概况
- LIB负极材料厂商现状
石墨/碳负极材料生产商
- 1. BTR
- 2. Shanshan
- 3. Zichen
- 4. Shinzoom (Changsha Xingcheng)
- 5. Kaijin
- 6. XFH (XiangFengHua)
- 7. Hitachi Chemical (Resonac)
- 8. Mitsubishi Chemical
- 9. JFE Chemical
- 10. POSCO FutureM
- 11. Aekyung Chemical
硅基负极材料製造商(韩国/亚洲)
- 12. Daejoo Electronic Materials
- 13. Shin-Etsu
- 14. MK Electronics
- 15. Il-jin Electric
- 16. EG
- 17. Hansol Chemical
- 18. Innox Eco Chemical
- 19. FIC Advanced Materials
- 20. LPN
- 21. Osaka Titan
- 22. POSCO Silicon Solution
- 23. TCK ((TOKAI CARBON KOREA)
- 24. NM Tech (Acquired by Truewin)
- 25. KBG
- 26. Neo Battery Materials
- 27. Korea Metal Silicon
- 28. EN PLUS
- 29. Lotte Energy Materials
- 30. Dong-jin Semichem
- 31. SJ Advanced Materials
- 32. IEL Science
- 33. S Materials
- 34. HNS
- 35. Y-Fine Tech
- 36. Hana Materials
硅基负极材料製造商(中国)
- 37. Haoxin Tech
- 38. Longtime Tech
- 39. Gotion
- 40. Shinghwa
- 41. Tianmulake
- 42. Chengdu Guibao
- 43. Jereh
- 44. Huawei
- 45. Xinan
- 46. Kingi
硅基负极材料製造商(北美、欧洲)
- 47. Group14 (With SK Materials)
- 48. NEXEON (With SKC)
- 49. Sila Nano Technologies
- 50. Enovix
- 51. Enervate
- 52. EO Cell
- 53. Amprius Technologies
- 54. Nanotek' Instrument
- 55. One D
- 56. Nanograf
- 57. LeydenJar
- 58. ADVANO
- 59. Targray
- 60. StoreDot
- 61. Trion Battery
- 62. Black Diamond Structures
- 63. Nanospan
第7章 参考资料
The anode material for lithium-ion batteries has predominantly been carbon-based to date. In the early stages, amorphous carbon materials were widely used, but presently, natural and synthetic graphite are the primary choices. Recently, there has been active consideration of new anode materials, particularly those centered around silicon (Si), to overcome the theoretical capacity limits of graphite materials and develop materials with excellent electrochemical reaction potential and extended lifespan. The demand for high-capacity anode materials has been increasing, particularly in the market for large-scale batteries used in electric vehicles and energy storage systems. While carbon and graphite-based anode materials were traditionally prevalent, there is a growing focus, especially within the industry, on silicon-based anode materials, which are metal composites. The competition to secure these materials has intensified as the need for high-capacity anode rises. In this context, there is a continual increase in new entrants developing and manufacturing silicon-based anode materials.
As of early 2020, silicon-based high-capacity materials were primarily developed by only 10-20 companies. However, the current landscape shows that over 60 companies are actively engaged in the development and preparation for mass production of silicon-based materials. Silicon-based materials are essential for the development of high-capacity batteries to address the range limitations of electric vehicles and meet the demand for fast-charging capabilities. Electric vehicle OEMs and battery companies anticipate a projected annual growth rate of 30% for silicon anode materials until 2035. The market share of silicon anode materials in the overall anode material market is expected to expand from 1% in 2019 to 7% in 2030 and further to 10% by 2035.
In addition to carbon-based and graphite-based materials, Si-C composite, Si-alloy, and SiOx are representative high-capacity anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Among these, SiOx and Si-alloy are the closest to commercialization, with some battery manufacturers actively developing high-capacity batteries by incorporating them. However, challenges such as lifespan and volume expansion (swelling) persist, prompting ongoing efforts to address these issues. In the realm of silicon (Si)-based anodes, recent announcements of related technological developments have been made by both industry and academia. Anode material companies are also concentrating on new technology development, fostering expectations for imminent commercialization.
This report serves as a technical document focusing on recent developments in the anode material market for lithium-ion batteries used in xEV (electric vehicles), ESS (energy storage systems), and IT applications. Specifically, it delves into the technological advancements and performance enhancements in Si-based anode development for high-capacity batteries. The report provides an overview of the latest developments in Si-based high-capacity anode materials (Si-alloy, SiOx, Si-C composite) by both industry and academia. It also examines the current status and challenges associated with batteries incorporating these materials, aiming to offer insights and potential solutions for future developments in high-capacity/high-output battery technologies.


Strong Point of this report:
- 1. Overall market share and technological status of anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. (including graphite-based and silicon-based materials.)
- 2. Technical issues and key technological factors related to high-capacity silicon-based anode materials.
- 3. Recent technological developments in silicon-based anode materials by battery manufacturers.
- 4. Applications and commercialization prospects for future silicon-based anode materials.
- 5. Technological trends and product introductions from over 70 global silicon-based anode material companies.
Table of Contents
Report Overview
Chapter I. Overview of LIBs
- 1.1. History of LIBs
- 1.2. Types and Characteristics of LIBs
- 1.3. Principle of LIBs
- 1.3.1. Charging / Discharging Reactions
- 1.3.2. Voltage
- 1.3.3. Movement of Charge and Ions
- 1.3.4. Theoretical Capacity
- 1.4. Components of LIBs
- 1.4.1. Cathode active materials
- 1.4.2. Anode active materials
- 1.4.3. Seperator
- 1.4.4. Electrolyte
- 1.5. Application areas of LIBs
- 1.6. Technology Status and Development Trend of Anode Materials
Chapter II. Types and Characteristics of LIB Anode Materials
- 2.1. Required Characteristics and Types of LIB Anode Materials
- 2.2. Characteristics of Carbon-based Anode Materials
- 2.2.1. Graphite-based Anode Materials
- 2.2.2. Amorphous Carbon-based Anode Materials
- 2.2.3. Carbon-based Anode Materials / Electrolyte Interfacial Reaction
- 2.3. Characteristics of Metal-based Anode Materials
- 2.3.1. Lithium Metal Anode Materials
- 2.3.2. Alloy-based Anode Materials
- 2.4. Characteristics of Compound-Based Anode Materials
- 2.4.1. Oxide-Based Anode Materials
- 2.4.2. Nitride-Based Anode Materials
Chapter III. Current Status of Technological Development for High-Capacity Si-Based Anode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries
- 3.1. Development History and Direction of High-Capacity Lithium-ion Batteries
- 3.2. Basic Characteristics of High-Capacity Si-based Anode Materials
- 3.2.1. Lithium Insertion/Extraction Reactions of Si-based Anode Materials
- 3.2.2. Issues of Si-based Anode Materials and Degradation Mechanisms
- 3.2.3. Volume Expansion Control of Si-based Anode Materials
- 3.3. Problems and Solutions for Alloy-based Anode Materials
- 3.3.1. Representative Problems
- 3.3.2. Metal Composite-based Anode Materials
- 3.3.3. Metal-Carbon Composite-based Anode Materials
- 3.3. Trends in the Technological Development of High-Capacity Si Anode Materials
- 3.3.1. SiOx Anode Materials
- Structural Characteristics
- Electrochemical Properties
- Manufacturing Methods
- Application of Prelithiation Process
- 3.3.2. Si-C Composite Anode Materials
- 3.3.3. Si-M Alloy Anode Materials
- 3.3.4. Practical Application Research of Si Anode Materials
- Differences of Electrochemical Behavior
- Si Single Electrode and Si/Graphite Hybrid Electrode
- 3.3.5. Various Nanostructures of Si-based Anode Materials
- Si nanostructure
- Porous Si structure
- Nano-Si/C structure
- Nano-Si/metal or polymer structure
- 3.3.6. Binders for Si-based Anode Materials
- 3.3.7. Current Collectors for Si-based Anode Materials
- 3.3.8. Comprehensive Review of Research Trends in Si-based Anodes and Future Research Directions
- 3.3.9. Examples of Si-based Anode Material Developments in Academic/Industries
- 3.3.10. Key Technology Roadmap for Si-Based Anode Materials
- 3.3.1. SiOx Anode Materials
Chapter IV. Current Status of High-Output Si-Based Anode Material Technology Development
- 4.1. Overview of High-Output Anode Materials
- 4.2. Anode Materials for High-Output Fast Charging
- 4.2.1. Intercalation Materials
- 4.2.2. Alloy-based Materials / Transition Materials
- 4.2.3. Nano-Structured Micro-Sized Particles (Nano-structured micro-sized particles)
- 4.2.4. Si-Graphite Hybrid Materials (SEAG)
- 4.2.5. Graphene-SiO2 Materials (Graphene Ball)
- 4.3. Fast Charging from Anode Perspective
- 4.3.1. Factors Influencing Anode Materials (Active Materials)
- 4.3.2. Factors Influencing Electrodes
- 4.3.3. Design of Fast Charging Technology by Major Battery Companies
- 4.4.4. Summary and Future Outlook
Chapter V. Trends and Outlook in the LIB Anode Material Market
- 5.1. Current Status of LIB Anode Material Market
- 5.1.1. Demand for Anode Materials by Country
- 5.1.2. Demand for Anode Materials by Material Type
- 5.1.3. Market Status by Supplier
- 5.1.4. Demand for Anode Materials by LIB Companies
- SDI/LGES/SKon/Panasonic/CATL/ATL/BYD/Lishen/Guoxuan/AESC/CALB
- 5.2. Supply Outlook for LIB Anode Materials
- 5.2.1. Outlook of Anode Material Production Capacity
- 5.2.2. Status and Outlook of Anode Material Shipments
- 5.2.3. Supply Outlook for Anode Materials
- 5.3. Price Outlook for LIB Anode Materials
- 5.3.1. Anode Material Price Structure
- NG/AG/Si-based
- 5.3.2. Anode Material Price Trends
- NG/AG/Si-based
- 5.3.3. Price Status of Different Types of Graphite
- 5.3.4. Price Status of Needle Coke and Pitch
- 5.3.5. Price Outlook by Anode Material Suppliers
- 5.3.1. Anode Material Price Structure
Chapter VI. Current Status of LIB Anode Material Manufacturers
- 6.1. Summary of LIB Anode Material Companies
- 6.2. Current Status of LIB Anode Material Manufacturers
Graphite/Carbon-Based Anode Material Manufacturers
- 1. BTR
- 2. Shanshan
- 3. Zichen
- 4. Shinzoom(Changsha Xingcheng)
- 5. Kaijin
- 6. XFH(XiangFengHua)
- 7. Hitachi Chemical(Resonac)
- 8. Mitsubishi Chemical
- 9. JFE Chemical
- 10. POSCO FutureM
- 11. Aekyung Chemical
Si-based Anode Material Manufacturers (Korean/Asian)
- 12. Daejoo Electronic Materials
- 13. Shin-Etsu
- 14. MK Electronics
- 15. Il-jin Electric
- 16. EG
- 17. Hansol Chemical
- 18. Innox Eco Chemical
- 19. FIC Advanced Materials
- 20. LPN
- 21. Osaka Titan
- 22. POSCO Silicon Solution
- 23. TCK((TOKAI CARBON KOREA)
- 24. NM Tech(Acquired by Truewin)
- 25. KBG
- 26. Neo Battery Materials
- 27. Korea Metal Silicon
- 28. EN PLUS
- 29. Lotte Energy Materials
- 30. Dong-jin Semichem
- 31. SJ Advanced Materials
- 32. IEL Science
- 33. S Materials
- 34. HNS
- 35. Y-Fine Tech
- 36. Hana Materials
Si-Based Anode Material Manufacturers (Chinese)
- 37. Haoxin Tech
- 38. Longtime Tech
- 39. Gotion
- 40. Shinghwa
- 41. Tianmulake
- 42. Chengdu Guibao
- 43. Jereh
- 44. Huawei
- 45. Xinan
- 46. Kingi
Si-based Anode Material Manufacturers (North America, Europe)
- 47. Group14 (With SK Materials)
- 48. NEXEON (With SKC)
- 49. Sila Nano Technologies
- 50. Enovix
- 51. Enervate
- 52. EO Cell
- 53. Amprius Technologies
- 54. Nanotek' Instrument
- 55. One D
- 56. Nanograf
- 57. LeydenJar
- 58. ADVANO
- 59. Targray
- 60. StoreDot
- 61. Trion Battery
- 62. Black Diamond Structures
- 63. Nanospan










