 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1516953
全球鱼雷市场(2024-2034)Global Torpedo Market 2024-2034 |
||||||
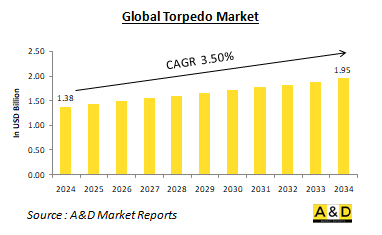
预计到2024 年,全球鱼雷市场将达到13.8 亿美元,在预测期内(2024-2034 年)将以3.50% 的复合年增长率(CAGR) 扩大,到2034 年将达到19.5 亿美元。
鱼雷市场概况
鱼雷是一种自行式水下武器,旨在瞄准并摧毁敌方船隻和潜艇。它的发展可以追溯到19世纪初,并且在过去的几十年中取得了巨大的进步。第一艘实用鱼雷是Robert Fulton于1813年製造的,但现代自行式鱼雷是由Giovanni Luppis开发的,并于1866年由奥地利工程师Robert Whitehead进一步改进。世纪下半叶才出现。这项创新是海战的关键时刻,实现了隐密而有效的新攻击方法。现代鱼雷配备了各种技术,使其能够自主操作并高精度捕获目标。鱼雷通常由一个装有爆炸弹头的圆柱体、推进系统、导引系统和控制面组成。鱼雷可以从水面舰艇、潜水艇和飞机上发射,使其成为世界各地海军武库中的多功能武器。
科技对鱼雷市场的影响
鱼雷技术的发展受到声学、流体力学和电子学等多个领域进步的影响。现代鱼雷利用先进的导引系统,并经常使用声纳技术来定位目标。这些系统大致分为两种:主动寻的和被动寻的。主动寻的涉及鱼雷发射声纳讯号来侦测目标,而被动寻的涉及侦测敌舰发出的声音。鱼雷推进系统也有了显着的发展。早期的鱼雷使用蒸汽或压缩空气,但现代设计通常使用电力推进系统,该系统提供更安静的操作和更远的射程。先进材料和工程技术的整合提高了鱼雷的水动力效率,使其能够游得更快更远,同时保持稳定性和机动性。
此外, "智慧" 鱼雷的引入彻底改变了海战。这些鱼雷可以适应不断变化的条件并利用即时数据来提高瞄准精度。例如, "Spearfish" 和MU90/Impact采用了先进的导引系统和弹头技术,使其成为现代海战中的强大武器。
鱼雷市场的关键驱动因素
鱼雷技术的发展和现代化是由多种因素所推动的。
随着各国寻求加强海军能力以应对地区威胁,地缘政治紧张局势是关键驱动因素。对先进鱼雷的需求不断增加,各国正投资研发以生产更有效、更可靠的鱼雷。技术进步在鱼雷发展中也扮演重要角色。材料科学、电子学和推进系统的不断改进使得鱼雷设计更加复杂。人工智慧和机器学习的融合开始进一步提高鱼雷性能,并实现更智慧、更具适应性的武器系统。
海军战略和条令对鱼雷技术有重大影响。潜水艇和水面舰艇在海战中的战略重要性促使人们重新关注鱼雷的发展。随着海军理论的发展,对能够有效应对新出现威胁的武器的需求不断增加,从而推动了鱼雷技术的进一步创新。国防预算也是重要因素。国防开支的增加正在推动海军舰队的现代化,包括购买先进的鱼雷。这种趋势在拥有巨大海洋利益的国家尤其明显,维持最先进的海军力量是这些国家的首要任务。
国际合作也正在加速鱼雷技术的进步。国家之间的联合开发项目和合作能够共享专业知识和资源,从而快速开发新系统以满足现代战争的需求。这种协作方式可确保技术创新快速融入营运能力。
鱼雷市场的区域趋势
鱼雷的开发和部署因地区而异,并受到地区地缘政治动态和海军能力的影响。
在北美,美国海军大力投资先进鱼雷系统,例如专为潜水艇设计的 Mark 48 鱼雷。美国继续专注于增强现有系统的能力,同时开发整合先进导引和推进技术的下一代鱼雷。欧洲国家,尤其是英国、法国等拥有庞大海军力量的国家,也在鱼雷技术方面取得长足进展。例如,英国的 "Spearfish" 鱼雷正在不断更新以提高其效能。北约内部的合作计画也在成员国之间分享鱼雷技术的进步。在亚太地区,中国和印度等国家正迅速增强鱼雷能力。中国在先进鱼雷製造方面取得了重大进展,反映了其广泛的军事现代化努力。印度透过国防研究与发展组织(DRDO)专注于鱼雷的本土开发,以增强其海军应对区域威胁的能力。
在中东,各国越来越认识到海军力量的重要性,进而促使对鱼雷系统的投资。以色列等国家正在为潜艇开发先进鱼雷,这凸显了在安全课题不断变化的地区需要有效的水下作战能力。
鱼雷主程序
澳洲皇家海军 (RAN) MU90 轻型鱼雷由Thales Australia根据与澳洲国防部的合约进行维护。Thales Australia基于1,450 万美元(2,000 万澳元)的合同,继续在西澳大利亚维护澳洲皇家海军最先进的反潜鱼雷。这是MU90轻型鱼雷的维护合约。Whitehead Alenia Sistemi Subacquei(义大利,Finmeccanica 子公司)、DCNS International 和Thales(法国)合作开发了 MU90 轻型鱼雷。自 2013 年起,RAN 开始使用 MU90 轻型鱼雷。自 2013 年起,RAN 开始使用 MU90 轻型鱼雷。此后,Thales一直为MU90提供支援和服务。
F21鱼雷也将安装在巴西海军新型Scorpene级潜舰的武库中。由氧化银和铝 (AgO-Al) 製成的海水原电池为 F21 提供动力。原电池的 AgO-Al 海水活性电化学堆迭有助于在较宽的范围内最大限度地提高速度。它还为船舶的电子控制和导航系统提供燃料。
Atlas Elektronik 为德国海军生产的最新重型鱼雷是 DM2A4 Seehecht。DM2A3 后续型号配备了用于鱼雷导引和通讯的光缆,并且还配备了更新的电力推进系统。这些功能,加上任务逻辑和先进的讯号处理,使得鱼雷通常不受对抗措施的影响。第一个由光纤线引导的鱼雷是 DM2A4/SeaHake mod 4。DM2A4/SeaHake mod 4 凭藉全数位系统设计、更大的范围和速度、具有更宽全景感测器角度的新型共形阵列声纳以及附加的轨迹原点感测器性能也得到了显着改善。这种鱼雷被德国海军的212型潜水艇使用。
目录
鱼雷市场:报告定义
鱼雷市场区隔
- 按地区
- 按发射平台
- 按类型
鱼雷市场分析(未来10年)
鱼雷市场的市场技术
全球鱼雷市场预测
鱼雷市场:按地区划分的趋势和预测
- 北美
- 促进/抑制因素和课题
- PEST分析
- 市场预测与情境分析
- 大公司
- 供应商层级状况
- 企业标竿管理
- 欧洲
- 中东
- 亚太地区
- 南美洲
鱼雷市场:国家分析
- 美国
- 防御计划
- 最新趋势
- 专利
- 该市场目前的技术成熟度水平
- 市场预测与情境分析
- 加拿大
- 义大利
- 法国
- 德国
- 荷兰
- 比利时
- 西班牙
- 瑞典
- 希腊
- 澳大利亚
- 南非
- 印度
- 中国
- 俄罗斯
- 韩国
- 日本
- 马来西亚
- 新加坡
- 巴西
鱼雷市场:市场机会矩阵
鱼雷市场:专家对研究的看法
结论
关于Aviation and Defense Market Reports
The global Torpedo market is estimated at USD 1.38 billion in 2024, projected to grow to USD 1.95 billion by 2034 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 3.50% over the forecast period 2024-2034.

Introduction to Torpedoes Market:
Torpedoes are self-propelled underwater weapons designed to target and destroy enemy ships and submarines. Their development dates back to the early 19th century, with significant advancements occurring over the decades. The first practical torpedo was created by Robert Fulton in 1813, but it was not until the late 19th century that the modern self-propelled torpedo was developed by Giovanni Luppis and further refined by the Austrian engineer, Robert Whitehead, in 1866. This innovation marked a pivotal moment in naval warfare, allowing for a new method of attack that was both stealthy and effective. Modern torpedoes are equipped with various technologies, enabling them to operate autonomously and engage targets with high precision. They typically consist of a cylindrical body containing an explosive warhead, propulsion system, guidance system, and control surfaces. The ability to launch torpedoes from surface ships, submarines, and aircraft has made them versatile weapons in naval arsenals worldwide.
Technology Impact on Torpedoes
The evolution of torpedo technology has been influenced by advancements in several fields, including acoustics, hydrodynamics, and electronics. Modern torpedoes utilize sophisticated guidance systems, often employing sonar technology to home in on targets. These systems can be classified into two main categories: active and passive homing. Active homing involves the torpedo emitting sonar signals to detect targets, while passive homing relies on detecting sounds emitted by enemy vessels. The propulsion systems of torpedoes have also evolved significantly. Early torpedoes used steam or compressed air, while contemporary designs often utilize electric propulsion systems, which offer quieter operation and extended range. The integration of advanced materials and engineering techniques has improved the hydrodynamic efficiency of torpedoes, allowing them to travel faster and further while maintaining stability and maneuverability.
Moreover, the advent of "smart" torpedoes has transformed naval warfare. These torpedoes can adapt to changing conditions and utilize real-time data to improve targeting accuracy. Examples include the Spearfish and the MU90/Impact, which incorporate advanced guidance systems and warhead technologies, making them formidable weapons in modern naval engagements.
Key Drivers in Torpedo Market:
Several factors drive the ongoing development and modernization of torpedo technology.
Geopolitical tensions are a significant driver, as nations seek to enhance their naval capabilities in response to regional threats. The demand for advanced torpedoes has increased, prompting countries to invest in research and development to produce more effective and reliable torpedoes. Technological advancements also play a crucial role in torpedo development. Continuous improvements in materials science, electronics, and propulsion systems have enabled the design of more sophisticated torpedoes. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning is beginning to enhance torpedo performance further, allowing for smarter and more adaptive weapon systems.
Naval strategy and doctrine significantly influence torpedo technology. The strategic importance of submarines and surface vessels in naval warfare has led to a renewed focus on torpedo development. As naval doctrines evolve, the need for weapons that can effectively counter emerging threats grows, driving further innovation in torpedo technology. Defense budgets are another critical factor. Increased defense spending by various nations has facilitated the modernization of naval fleets, including the acquisition of advanced torpedoes. This trend is particularly evident in countries with significant maritime interests, where maintaining a cutting-edge naval force is a priority.
International collaboration has also accelerated advancements in torpedo technology. Joint development projects and collaborations between nations allow for the sharing of expertise and resources, leading to the rapid development of new systems that can meet the demands of modern warfare. This collaborative approach ensures that technological innovations are quickly integrated into operational capabilities.
Regional Trends in Torpedo Market:
The development and deployment of torpedoes vary significantly across different regions, influenced by local geopolitical dynamics and naval capabilities.
In North America, the United States Navy has heavily invested in advanced torpedo systems, such as the Mark 48 torpedo, which is specifically designed for use by submarines. The U.S. continues to focus on enhancing the capabilities of existing systems while developing next-generation torpedoes that integrate advanced guidance and propulsion technologies. European nations, particularly those with significant naval forces like the United Kingdom and France, are also making strides in torpedo technology. The UK's Spearfish torpedo, for instance, has undergone continuous upgrades to improve its effectiveness. Additionally, collaborative projects within NATO have led to shared advancements in torpedo technology among member states. In the Asia-Pacific region, countries such as China and India are rapidly advancing their torpedo capabilities. China has made significant progress in producing advanced torpedoes, reflecting its broader military modernization efforts. India, through its Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), is focusing on indigenous torpedo development to enhance its naval capabilities in response to regional threats.
In the Middle East, nations are increasingly recognizing the importance of naval power, leading to investments in torpedo systems. Countries like Israel have developed advanced torpedoes for their submarines, emphasizing the need for effective underwater warfare capabilities in a region with evolving security challenges.
Key Torpedo Program:
The Royal Australian Navy's (RAN) MU90 lightweight torpedo will be maintained by Thales Australia under a contract with the Australian Department of Defence. Thales Australia will continue to maintain the RAN's cutting-edge anti-submarine torpedoes in Western Australia under the $14.5 million (A$20 million) contract (WA). The contract to maintain the MU90 lightweight torpedo. Whitehead Alenia Sistemi Subacquei (Italy, a Finmeccanica firm), DCNS International, and Thales collaborated to create the MU90 lightweight torpedo (France).Since 2013, the RAN has begun utilising the MU90 lightweight torpedo. Since that time, Thales has been working on support contracts with MU90 to offer services.
The F21 torpedo will also be included in the arsenal of the Brazilian Navy's new Scorpene-class submarines. A seawater primary battery made of silver oxide and aluminium (AgO-Al) powers the F21. Two counterrotating propellers are also incorporated into the electric propulsion system.The primary AgO-Al seawater activated electrochemical stack contributes to maximising speed over a wide range. Additionally, it fuels the electronic control and navigation system on board.
The newest heavyweight torpedo created by Atlas Elektronik for the German Navy is the DM2A4 Seehecht. The DM2A3's successor has a fibre optic cable for torpedo guidance and communication as well as an upgraded electrical propulsion system. These features, along with mission logic and advanced signals processing, make the torpedo generally impervious to countermeasures. The first torpedo ever to be guided by a fibre optic wire is the DM2A4/SeaHake mod 4. The DM2A4/SeaHake mod 4 offers much improved performance over its predecessor thanks to its entirely digital system design, greater range and speed, new conformal array sonar with a very wide panoramic sensor angle, and the added wake homing sensor. The torpedo is used by Type 212 submarines of the German Navy.
Table of Contents
Torpedo Market Report Definition
Torpedo Market Segmentation
By Region
By Launch Platform
By Type
Torpedo Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year torpedo market analysis would give a detailed overview of torpedo market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Torpedo Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Torpedo Market Forecast
The 10-year torpedo market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Torpedo Market Trends & Forecast
The regional torpedo market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Torpedo Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Torpedo Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Torpedo Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2024-2034
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2024-2034
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Launch Platform, 2024-2034
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Type, 2024-2034
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2024-2034
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Launch Platform, 2024-2034
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Type, 2024-2034
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Torpedo Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 2: Global Torpedo Market Forecast, By Region, 2024-2034
- Figure 3: Global Torpedo Market Forecast, By Launch Platform, 2024-2034
- Figure 4: Global Torpedo Market Forecast, By Type, 2024-2034
- Figure 5: North America, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 6: Europe, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 7: Middle East, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 8: APAC, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 9: South America, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 10: United States, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 11: United States, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 12: Canada, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 13: Canada, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 14: Italy, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 15: Italy, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 16: France, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 17: France, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 18: Germany, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 19: Germany, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 22: Belgium, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 23: Belgium, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 24: Spain, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 25: Spain, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 26: Sweden, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 27: Sweden, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 28: Brazil, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 29: Brazil, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 30: Australia, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 31: Australia, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 32: India, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 33: India, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 34: China, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 35: China, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 38: South Korea, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 39: South Korea, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 40: Japan, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 41: Japan, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 44: Singapore, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 45: Singapore, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Torpedo Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Torpedo Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Torpedo Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2024-2034
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Torpedo Market, By Region (CAGR), 2024-2034
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Torpedo Market, By Launch Platform (Cumulative Market), 2024-2034
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Torpedo Market, By Launch Platform (CAGR), 2024-2034
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Torpedo Market, By Type (Cumulative Market), 2024-2034
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Torpedo Market, By Type (CAGR), 2024-2034
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Torpedo Market, Cumulative Market, 2024-2034
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Torpedo Market, Global Market, 2024-2034
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Torpedo Market, Total Market, 2024-2034
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Torpedo Market, By Region, 2024-2034
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Torpedo Market, By Launch Platform, 2024-2034
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Torpedo Market, By Type, 2024-2034
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Torpedo Market, Total Market, 2024-2034
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Torpedo Market, By Region, 2024-2034
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Torpedo Market, By Launch Platform, 2024-2034
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Torpedo Market, By Type, 2024-2034
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Torpedo Market, 2024-2034










