 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1339032
印度尼西亚服装製造业:2023-2032Indonesia Garment Manufacturing Industry Research Report, 2023-2032 |
||||||
印度尼西亚是东南亚最大的经济强国,劳动力丰富,劳动力成本低廉。 到2022年底,印度尼西亚人口将约为2.75亿,成为世界第四大人口大国,约70%的人口年龄在15岁至64岁之间,劳动人口约1.4亿。力量和消费市场。 据CRI分析,该国的年轻人口预计将在未来10至15年推动印尼消费市场的增长。
印度尼西亚是世界十大纺织品生产国之一。 纺织及纺织製品业是印尼经济最重要的产业之一,为超过370万印尼人提供了就业机会。 印尼纺织品和服装总产量的70%用于出口,其中美国是最大的出口国。
据CRI分析,2018年至2022年,印尼纺织品服装出口额呈现先降后升的变化趋势,2018年至2022年復合年增长率为4.16%。 2020年,受COVID-19影响,印尼纺织品服装出口额达58.57亿美元。 2021年,印尼政府放鬆监管措施,2021年和2022年出口额快速恢復,分别达到69.09亿美元和79.92亿美元,比上年增长17.98%和15.6%。
纺织业现已成为印尼的战略目标产业。 印尼纺织业的前景为投资者提供了巨大的机会,特别是在精密机械和生产设备的供应以及能力建设方面。 由于公民购买力的增强和电子商务平台的激增,其营商环境变得更加有利。
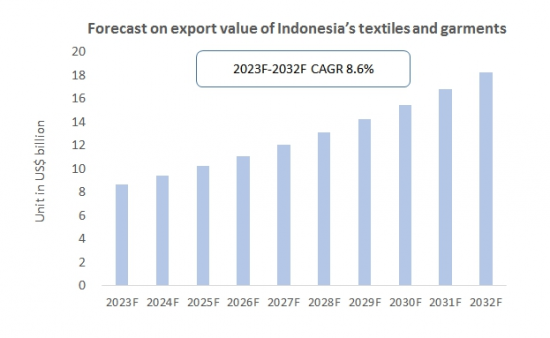
由于其低成本优势,印度尼西亚纺织品服装出口预计将持续增长数年。 预计2032年印尼纺织品服装出口额将达到182亿美元,2023年至2032年復合年增长率约为8.6%。
本报告对印度尼西亚服装製造业进行了调查,包括印度尼西亚服装製造业的发展历史、服装製造业概况、竞争状况、製造成本和价格分析以及服装的需求和供应情况。服装製造。我们整理了主要製造商的概况,包括预测。
目录
第一章印尼服装业:发展概况
- 定义/分类
- 主要产品分析
- COVID-19 对印度尼西亚服装製造业的影响
第二章印尼服装製造业概况
- 印尼服装行业发展环境
- 印尼服装供应分析
- 印尼市场服装需求分析
第三章印尼纺织服装业:进出口分析
- 导入
- 导出
第四章印尼服装製造业竞争状况
- 进入服装行业的壁垒
- 服装製造业的竞争结构
第 5 章印度尼西亚服装製造:成本和价格分析
- 製造成本分析
- 服装价格分析
第六章印尼主要服装製造企业概况
- PT INDONESIA TORAY SYNTHETICS
- PT ACRYL TEXTILE MILLS
- PT CENTURY TEXTILE INDUSTRY TBK
- PT PETNESIA RESINDO
- PT JABATO INTERNATIONAL
- PT INDONESIA SYNTHETICS TEXTILE MILLS
- PT EASTERNTEX
- PT OST FIBRE INDUSTRIES
第七章印尼服装製造业展望
- 影响服装製造业发展的因素
- 服装製造业竞争形势预测
- 服装製造的供应预测
- 服装製造市场需求预测
Indonesia is the largest economy in Southeast Asia, and Indonesia has an abundant labor force with low labor costs. By the end of 2022, the population of Indonesia will be about 275 million, which is the fourth largest population in the world, with about 70% of the population aged 15-64, and the working population will be about 140 million, which is a plentiful labor force and consumer market. According to CRI's analysis, the young population structure will bring 10 to 15 years of growth to the Indonesian consumer market.
SAMPLE VIEW

Indonesia is one of the world's top ten textile producers, and the textile and textile products industry is one of the most important industries in the Indonesian economy, providing employment for more than 3.7 million Indonesians. The majority of Indonesia's total textile and clothing production is used to supply international demand, of which 70% is exported, with the United States of America being the largest exporter of Indonesian clothing and textiles.
As apparel companies continue to shift production out of China, Indonesia has become an attractive alternative. China's position as a global cotton importer is declining, and most cotton exports are being shifted to competing countries, including Indonesia. The USDA forecasts that China's cotton imports will increase by only 3.5 million bales over the 2021-2030 period, compared to an estimated 8.1 million bales for the major competing apparel countries Indonesia, Vietnam, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Turkey combined. By 2030, China is expected to account for 24% of total global imports, while competing countries combined are expected to account for 47%.
Indonesia's garment industry is concentrated in West Java, Central Java, East Java and Banten, which together account for more than 85 percent of all garment, textile and footwear employment. The garment industry is labor-intensive and easy to relocate, and employers have been relocating factories to areas with lower minimum wages.
From 2018 to 2022, according to CRI analysis, Indonesia's textile and apparel export value shows a trend of change firstly decreasing and then increasing, with a CAGR of 4.16% from 2018 to 2022.In 2020, affected by the COVID-19 epidemic, Indonesia's apparel manufacturing industry contracted, and Indonesia's textile and apparel export value was 5.857 billion U.S. dollars, which was a year-on-year decline of 17.19%.In 2021 The Indonesian government relaxed the control measures, and the export of Indonesia's textile and apparel industry recovered rapidly in 2021 and 2022, and the export value of Indonesia's textile and apparel in 2021 and 2022 was US$6.909 billion and US$7.992 billion, respectively, an increase of 17.98% and 15.6% year-on-year, respectively.
The textile industry is now a strategic target industry for Indonesia. The prospects of Indonesia's textile industry offer golden opportunities for investors, especially in the supply of sophisticated machinery and production equipment and capacity building. Its business environment has become more lucrative due to the increased purchasing power of the population and the proliferation of e-commerce platforms. This aggressive consumer behavior following lifestyle trends will fuel high demand for functional textiles for apparel, automotive, fitness, sports and military applications. The recently established Industrial Services and Solutions Centre (ISSC) facility at the Centre for Standardization and Textile Industry Services (BBSPJIT) is in its prime. It provides information services, testing, calibration, product and quality system certification, technical training and consultancy, develops standards for the textile industry and provides inclusive professional assistance to the textile industry. This integrated infrastructure will not only help meet domestic demand, but also increase the competitiveness of the textile industry in the global market, especially in the EU - one of Indonesia's major export destinations. Indonesia is in the process of negotiating with the EU for an Indonesia-EU Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (IEU-CEPA), and Indonesia is looking towards Vietnam and Bangladesh.
At the same time, the Indonesian Government was constantly striving to build a productive, connected and sustainable textile ecosystem. By 2030, the country is expected to become one of the top five global textile manufacturers and one of the world's top 10 economies in the Industry 4.0 era.
In the coming years, Indonesia's textile and apparel exports will continue to grow due to its low-cost advantage. CRI expects the export value of Indonesia's textiles and garments to reach US$ 18.2 billion in 2032, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 8.6% from 2023-2032.
Topics covered:
- Overview of the Garment Industry in Indonesia
- Economic and policy environment of Indonesia's apparel industry
- What is the impact of COVID-19 on the Indonesian garment industry?
- Indonesia Clothing Industry Market Size 2018-2022
- Analysis of major Indonesian apparel companies
- Key Drivers and Market Opportunities in Indonesia's Apparel Industry
- What are the key drivers, challenges and opportunities for the Indonesian apparel industry during the forecast period 2023-2032?
- Which are the key players in the Indonesia Garment Industry market and what are their competitive advantages?
- What is the expected revenue of Indonesia Garment Industry market during the forecast period of 2023-2032?
- What strategies have been adopted by the key players in the market to increase their market share in the industry?
- Which segment of the Indonesia apparel industry market is expected to dominate the market by 2032?
- What are the major unfavorable factors facing the Indonesian apparel industry?
Table of Contents
1. Overview of the Development of the Apparel Industry in Indonesia
- 1.1 Definitions and Classifications
- 1.2 Analysis of Major Products
- 1.3 Impact of COVID-19 on the Garment Manufacturing Industry in Indonesia
2. Overview of Indonesia's Garment Manufacturing Industry
- 2.1 Development Environment of Indonesia's Apparel Industry
- 2.1.1 Economic Environment
- 2.1.2 Policy Environment
- 2.1.3 Social Environment
- 2.2 Indonesia Apparel Supply Analysis 2018-2022
- 2.2.1 Indonesia Garment Manufacturing Industry Major Foreign Investment Source Countries Analysis
- 2.2.2 Clothing Production
- 2.3 Indonesia Market Demand Analysis for Apparel
- 2.3.1 Major Consumer Groups of Clothing
- 2.3.2 Size of Indonesia's Domestic Apparel Market
3. Indonesia Textile and Clothing Industry Import and Export Analysis
- 3.1 Imports
- 3.1.1 Import of Raw Materials
- 3.1.2 Main Sources of Imports
- 3.2 Exports
- 3.2.1 Indonesia Garment Industry Export Analysis
- 3.2.2 Main Export Destinations
4. Competition in Indonesia's Garment Manufacturing Industry
- 4.1 Barriers to Entry in Indonesia's Clothing Industry
- 4.1.1 Government Policies
- 4.1.2 Sales Channels
- 4.1.3 Brand Barriers
- 4.2 Competitive Structure of Indonesia's Garment Manufacturing Industry
- 4.2.1 Bargaining Power of Raw Material Suppliers
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.2.3 Competition within the Apparel Industry
- 4.2.4 Potential Entrants
- 4.2.5 Alternatives
5. Cost and Price Analysis of Garment Manufacturing in Indonesia
- 5.1 Indonesia Garment Manufacturing Cost Analysis 2018-2022
- 5.1.1 Cost of Raw Materials
- 5.1.2 Indonesia Garment Manufacturing Labor Cost Analysis
- 5.2 Indonesia Clothing Price Analysis
6. Profile of Major Garment Manufacturing Companies in Indonesia
- 6.1 PT INDONESIA TORAY SYNTHETICS
- 6.1.1 Business Profile
- 6.1.2 Main Products
- 6.1.3 Modes of Operation
- 6.2 PT ACRYL TEXTILE MILLS
- 6.2.1 Business Profile
- 6.2.2 Main Products
- 6.2.3 Modes of Operation
- 6.3 PT CENTURY TEXTILE INDUSTRY TBK
- 6.3.1 Business Profile
- 6.3.2 Main Products
- 6.3.3 Modes of Operation
- 6.4 PT PETNESIA RESINDO
- 6.4.1 Business Profile
- 6.4.2 Main Products
- 6.4.3 Modes of Operation
- 6.5 PT JABATO INTERNATIONAL
- 6.5.1 Business Profile
- 6.5.2 Main Products
- 6.5.3 Modes of Operation
- 6.6 PT INDONESIA SYNTHETICS TEXTILE MILLS
- 6.7 PT EASTERNTEX
- 6.8 PT OST FIBRE INDUSTRIES
7. Indonesia Garment Manufacturing Outlook, 2023-2032
- 7.1 Factors Influencing the Development of Indonesia's Garment Manufacturing Industry
- 7.1.1 Drivers and Market Opportunities in Indonesia Clothing Manufacturing Industry
- 7.1.2 Threats and Challenges Facing Clothing Manufacturing Industry in Indonesia
- 7.1.3 Industry Prospects and Market Opportunities
- 7.2 Competitive Landscape Forecast for Indonesia Clothing Manufacturing Industry
- 7.3 Supply Forecast of Garment Manufacturing in Indonesia, 2023-2032
- 7.3.1 Indonesia Garment Manufacturing Raw Material Import Forecast 2023-2032
- 7.3.2 Indonesia Garment Export Forecast 2023-2032
- 7.4 Indonesia Garment Manufacturing Market Demand Forecast 2023-2032
- 7.4.1 Overall Market Demand Forecast for Garment Manufacturing in Indonesia, 2023-2032
- 7.4.2 Demand Forecast for Indonesia Garment Manufacturing Segment, 2023-2032






