 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1750503
船舶市场机会、成长动力、产业趋势分析及 2025 - 2034 年预测Marine Vessels Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
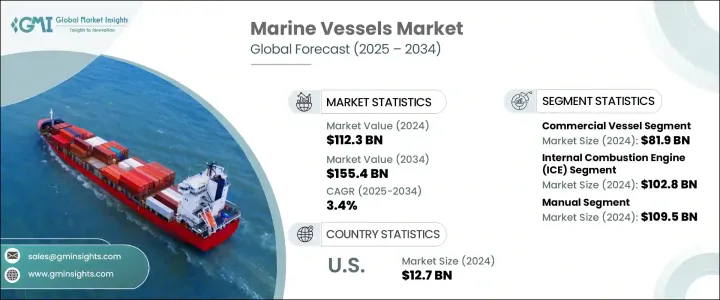
2024年,全球船舶市场规模达1123亿美元,预计到2034年将以3.4%的复合年增长率增长,达到1554亿美元,这得益于全球海上贸易规模的扩大以及各国政府对海军舰队现代化建设的不断投入。随着贸易路线的拓展和地缘政治紧张局势的持续,各国正在加强海军能力建设并推进舰队现代化,从而对商用和军用船舶的需求持续稳定。海上贸易对物流效率的需求,加上不断变化的海上安全要求,将继续影响全球对先进船舶的需求。
近年来,美国对钢铁和铝等主要进口材料征收关税,对整个船舶产业产生了巨大的连锁反应。这些政策提高了国内造船厂的製造成本,使得美国製造的船舶在价格和交货週期方面不如国际同行具有竞争力。原材料成本的上涨导致船舶建造进度放缓,商业和国防合约的预算紧张。此外,其他国家实施的报復性贸易措施限制了美国製造船舶的出口潜力,加剧了国内船厂的营运和财务挑战。这些政策带来的不确定性扰乱了供应链,延误了项目,并促使一些造船厂重新评估采购和生产策略,以维持生存。
| 市场范围 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 预测年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 1123亿美元 |
| 预测值 | 1554亿美元 |
| 复合年增长率 | 3.4% |
2024年,商用船舶市场价值达819亿美元。全球航运活动的不断增长和港口基础设施的升级,推动了对更多油轮、货柜船和散装船的需求。此外,邮轮旅行的復苏和高容量渡轮系统的引入也推动了该市场的成长。一些国家加大了对港口和海上物流网络的投资,这进一步扩大了沿海和内陆水道对专用船舶和支线船舶的需求。
就推进系统而言,2024年内燃机 (ICE) 市场价值为 1,028 亿美元。这类引擎在业界享有盛誉,具有成本效益、动力可靠性和更长的续航里程,对于长途货物运输和远洋作业尤其重要。对于许多航运公司和海上作业而言,内燃机驱动的船舶仍然是最实用的解决方案,尤其是在加油基础设施有限的情况下。这种推进系统也因其能够支援重型船舶执行海上钻井和物流任务而被广泛采用。
受多个强劲需求驱动因素的推动,美国船舶市场规模在2024年达到127亿美元。专业服务和船员转运船的需求不断增长,尤其是在大型海上能源专案中,这推动了新船采购。这些船舶在离岸风电场和能源平台的建设和维护中发挥关键作用。此外,旨在振兴内陆水路运输(尤其是跨河流运输)的投资,也推动了老旧船队的现代化升级,从而提高了整个区域物流的效率和可持续性。
全球船舶产业的主要参与者包括通用动力 NASSCO、Vard、HII、住友重工船舶与工程公司、达门造船集团、迈尔造船厂、三菱重工、巴布科克国际集团、奥斯塔尔、SHI-MCI、芬坎蒂尼、迈耶图尔库、Navantia、Lurssen、日本海洋建筑公司、现代重工、联合造船厂、建筑加工、建筑工工、建筑工厂重建筑工厂。
为了保持市场竞争力并拓展全球业务,领先的船舶製造商专注于下一代船舶设计、混合动力推进系统整合以及先进的自动化技术。企业透过投资绿色造船、液化天然气推进系统和人工智慧驱动的维护解决方案,使其策略与脱碳目标保持一致。与港务局、海军和物流供应商建立策略合作伙伴关係,增强了营运覆盖范围,同时积极的研发和数位转型持续使市场领导者从竞争对手中脱颖而出。
目录
第一章:方法论与范围
第二章:执行摘要
第三章:行业洞察
- 产业生态系统分析
- 川普政府关税
- 对贸易的影响
- 贸易量中断
- 报復措施
- 对产业的影响
- 供给侧影响
- 关键零件价格波动
- 供应链重组
- 生产成本影响
- 需求面影响(售价)
- 价格传导至终端市场
- 市占率动态
- 消费者反应模式
- 供给侧影响
- 受影响的主要公司
- 策略产业反应
- 供应链重组
- 定价和产品策略
- 政策参与
- 展望与未来考虑
- 对贸易的影响
- 产业衝击力
- 成长动力
- 全球贸易快速扩张
- 海军扩张与现代化
- 客运和旅游活动激增
- 本土製造和政府倡议
- 更大、更有效率船舶的需求不断增加
- 产业陷阱与挑战
- 地缘政治紧张与安全风险
- 经济不确定性和通货膨胀
- 成长动力
- 成长潜力分析
- 监管格局
- 技术格局
- 未来市场趋势
- 差距分析
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL分析
第四章:竞争格局
- 介绍
- 公司市占率分析
- 主要市场参与者的竞争分析
- 竞争定位矩阵
- 策略仪表板
第五章:市场估计与预测:按船舶类型,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 商用船舶
- 货柜船
- 油轮
- 散货船
- 游轮
- 其他的
- 海军和防御舰艇
- 驱逐舰
- 潜水艇
- 航空母舰
- 巡逻舰
- 其他的
第六章:市场估计与预测:按推进类型,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 内燃机(ICE)
- 电的
- 混合动力(电动+内燃机)
第七章:市场估计与预测:按控制机制,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 手动的
- 自主
- 半自主
- 完全自主
第八章:市场估计与预测:按地区,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 西班牙
- 义大利
- 荷兰
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韩国
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 阿联酋
第九章:公司简介
- Austal
- Babcock International Group
- China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation
- Cochin Shipyard
- Damen Shipyards Group
- Fincantieri
- Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers
- General Dynamics NASSCO
- HII
- Hyundai Heavy Industries
- Japan Marine United Corporation
- Lurssen
- Meyer Turku
- Meyer Werft
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Navantia
- SHI-MCI
- Sumitomo Heavy Industries Marine and Engineering
- Tsuneishi Shipbuilding
- Vard
The Global Marine Vessels Market was valued at USD 112.3 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 3.4% to reach USD 155.4 billion by 2034, driven by the rising scale of global maritime trade and increasing government investments in naval fleet modernization. As trade routes expand and geopolitical tensions persist, countries are strengthening naval capabilities and modernizing their fleets, creating a stable demand for both commercial and military vessels. The need for logistical efficiency in seaborne trade, coupled with evolving maritime security requirements, continues to shape the global demand for advanced marine vessels.

The imposition of tariffs on key imported materials such as steel and aluminum in recent years created significant ripple effects across the marine vessels industry. These policies raised manufacturing costs for domestic shipbuilders, making U.S.-built vessels less competitive in pricing and lead times than their international counterparts. The increase in raw material expenses led to slower progress on vessel construction and strained budgets for commercial and defense contracts. Furthermore, retaliatory trade measures imposed by other nations restricted the export potential of American-built vessels, compounding the operational and financial challenges for domestic yards. The uncertainty introduced by such policies disrupted supply chains, delayed projects, and prompted some shipbuilders to reevaluate sourcing and production strategies to remain viable.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $112.3 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $155.4 Billion |
| CAGR | 3.4% |
The commercial vessels segment was valued at USD 81.9 billion in 2024. Expanding global shipping activities and infrastructure upgrades across ports fuel the need for more tankers, container ships, and bulk carriers. Additionally, the resurgence of cruise travel and the introduction of high-capacity ferry systems are helping drive segment growth. Several nations have stepped up investments in port and maritime logistics networks, which further amplifies the demand for specialized and feeder vessels across coastal and inland waterways.
On the basis of propulsion, the internal combustion engines (ICE) segment was valued at USD 102.8 billion in 2024. These engines are well-established in the industry, offering cost efficiency, power reliability, and extended range, especially crucial for long-haul cargo transport and deep-sea operations. For many shipping companies and offshore operations, ICE-powered ships remain the most practical solution, particularly where fueling infrastructure is limited. This propulsion type is also widely adopted for its ability to support heavy-duty vessels in offshore drilling and logistics missions.
United States Marine Vessels Market reached USD 12.7 billion in 2024, supported by several robust demand drivers. The expanding need for specialized service and crew transfer vessels, particularly for large-scale offshore energy projects, is fueling new vessel procurement. These vessels play a critical role in enabling the construction and maintenance of offshore wind farms and energy platforms. Additionally, investments aimed at revitalizing inland waterway transportation, especially across river systems, encourage the modernization of older fleets, improving efficiency and sustainability across regional logistics.
Key players in the Global Marine Vessels Industry include General Dynamics NASSCO, Vard, HII, Sumitomo Heavy Industries Marine and Engineering, Damen Shipyards Group, Meyer Werft, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Babcock International Group, Austal, SHI-MCI, Fincantieri, Meyer Turku, Navantia, Lurssen, Japan Marine United Corporation, Hyundai Heavy Industries, Tsuneishi Shipbuilding, Cochin Shipyard, Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers, and China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation.
To maintain market relevance and expand globally, leading marine vessel manufacturers focus on next-generation ship designs, integration of hybrid propulsion systems, and advanced automation technologies. Companies align their strategies with decarbonization goals by investing in green shipbuilding, LNG propulsion, and AI-driven maintenance solutions. Strategic partnerships with port authorities, naval forces, and logistics providers enhance operational reach, while aggressive R&D and digital transformation continue to differentiate market leaders from competitors.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology and Scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definitions
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.3.1 Base year calculation
- 1.3.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.4 Forecast model
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.5.2 Data mining sources
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 3600 synopsis
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.2 Trump administration tariffs
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.2.1.1 Trade volume disruptions
- 3.2.1.2 Retaliatory measures
- 3.2.2 Impact on the industry
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact
- 3.2.2.1.1 Price volatility in key components
- 3.2.2.1.2 Supply chain restructuring
- 3.2.2.1.3 Production cost implications
- 3.2.2.2 Demand-side impact (selling price)
- 3.2.2.2.1 Price transmission to end markets
- 3.2.2.2.2 Market share dynamics
- 3.2.2.2.3 Consumer response patterns
- 3.2.2.1 Supply-side impact
- 3.2.3 Key companies impacted
- 3.2.4 Strategic industry responses
- 3.2.4.1 Supply chain reconfiguration
- 3.2.4.2 Pricing and product strategies
- 3.2.4.3 Policy engagement
- 3.2.5 Outlook and future considerations
- 3.2.1 Impact on trade
- 3.3 Industry impact forces
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3.1.1 Rapid expansion of global trade
- 3.3.1.2 Military navy expansion and modernization
- 3.3.1.3 Surge in passenger and tourism activities
- 3.3.1.4 Indigenous manufacturing and government initiatives
- 3.3.1.5 Increasing demand for larger and more efficient vessels
- 3.3.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.3.2.1 Geopolitical tensions and security risks
- 3.3.2.2 Economic uncertainty and inflation
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.4 Growth potential analysis
- 3.5 Regulatory landscape
- 3.6 Technology landscape
- 3.7 Future market trends
- 3.8 Gap analysis
- 3.9 Porter's analysis
- 3.10 PESTEL analysis
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategy dashboard
Chapter 5 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Vessel Type, 2021 - 2034 (USD Billion and Units)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Commercial vessels
- 5.2.1 Containerships
- 5.2.2 Tankers
- 5.2.3 Bulk carriers
- 5.2.4 Cruise ships
- 5.2.5 Others
- 5.3 Naval & defense vessels
- 5.3.1 Destroyers
- 5.3.2 Submarines
- 5.3.3 Aircraft carriers
- 5.3.4 Patrol ships
- 5.3.5 Others
Chapter 6 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Propulsion Type, 2021 - 2034 (USD Billion and Units)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Internal combustion engine (ICE)
- 6.3 Electric
- 6.4 Hybrid (Electric + ICE)
Chapter 7 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Control Mechanism, 2021 - 2034 (USD Billion and Units)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Manual
- 7.3 Autonomous
- 7.4 Semi-autonomous
- 7.5 Fully autonomous
Chapter 8 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 (USD Billion and Units)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 North America
- 8.2.1 U.S.
- 8.2.2 Canada
- 8.3 Europe
- 8.3.1 Germany
- 8.3.2 UK
- 8.3.3 France
- 8.3.4 Spain
- 8.3.5 Italy
- 8.3.6 Netherlands
- 8.4 Asia Pacific
- 8.4.1 China
- 8.4.2 India
- 8.4.3 Japan
- 8.4.4 Australia
- 8.4.5 South Korea
- 8.5 Latin America
- 8.5.1 Brazil
- 8.5.2 Mexico
- 8.5.3 Argentina
- 8.6 Middle East and Africa
- 8.6.1 Saudi Arabia
- 8.6.2 South Africa
- 8.6.3 UAE
Chapter 9 Company Profiles
- 9.1 Austal
- 9.2 Babcock International Group
- 9.3 China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation
- 9.4 Cochin Shipyard
- 9.5 Damen Shipyards Group
- 9.6 Fincantieri
- 9.7 Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers
- 9.8 General Dynamics NASSCO
- 9.9 HII
- 9.10 Hyundai Heavy Industries
- 9.11 Japan Marine United Corporation
- 9.12 Lurssen
- 9.13 Meyer Turku
- 9.14 Meyer Werft
- 9.15 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- 9.16 Navantia
- 9.17 SHI-MCI
- 9.18 Sumitomo Heavy Industries Marine and Engineering
- 9.19 Tsuneishi Shipbuilding
- 9.20 Vard










